Stream流
stream可以对数组和集合的元素以流的形式进行操作,可以让我们更方便的操作数组、集合元素。
1 快速入门
先做案例数据准备。
依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Author
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode // 用于后期去重使用
public class Author {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String info;
private List<Book> books;
}
Book
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode // 用于后期去重使用
public class Book {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String category;
private String intro;
private Integer score;
}
demo方法。
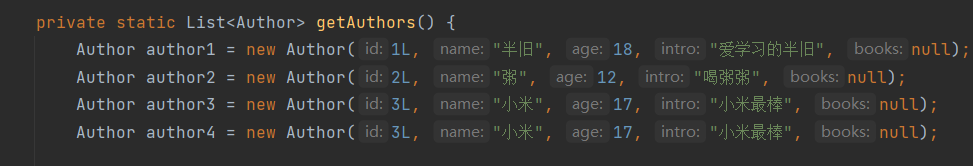
private static List<Author> getAuthors() {
Author author1 = new Author(1L, "半旧", 12, "爱学习的半旧", null);
Author author2 = new Author(2L, "粥粥", 19, "喝粥粥", null);
Author author3 = new Author(3L, "小米", 17, "小米最棒", null);
Author author4 = new Author(3L, "小米", 17, "小米最棒", null);
List<Book> books1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Book> books2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Book> books3 = new ArrayList<>();
books1.add(new Book(1L, "追风筝的人", "小说","温馨治愈的人物小说", 9 ));
books1.add(new Book(2L, "疯狂java讲义", "互联网","java入门枕边书", 7 ));
books2.add(new Book(3L, "中国哲学简史", "哲学, 历史","儒释道", 9 ));
books2.add(new Book(3L, "中国哲学简史", "哲学, 历史","儒释道", 9 ));
books2.add(new Book(4L, "编码", "互联网","作者是大神,举重若轻", 10 ));
books3.add(new Book(5L, "数学之美", "数学","数学之趣味、美好", 8 ));
books3.add(new Book(6L, "封神演绎", "小说","古典文学", 8 ));
books3.add(new Book(6L, "封神演绎", "小说","古典文学", 8 ));
author1.setBooks(books1);
author2.setBooks(books2);
author3.setBooks(books3);
author4.setBooks(books3);
List<Author> authorList = Arrays.asList(author1, author2, author3, author4);
return authorList;
}
现在需求如下:获取作家,打印所有年龄小于18岁的作家姓名并去重。实现如下。
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream() // 把集合转换成流
.distinct()//去重
.filter(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getAge() < 18;
}
}
.forEach(new Consumer<Author>() {
@Override
public void accept(Author author) {
System.out.println(author.getName());
}
});
使用Lambda优化下。
authors.stream() // 把集合转换成流
.distinct()//去重
.filter(author -> author.getAge() < 18)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
想要知道这个过程中每个方法到底做了什么,可以通过加断点,很清晰的跟踪到各个过程的数据变化情况.
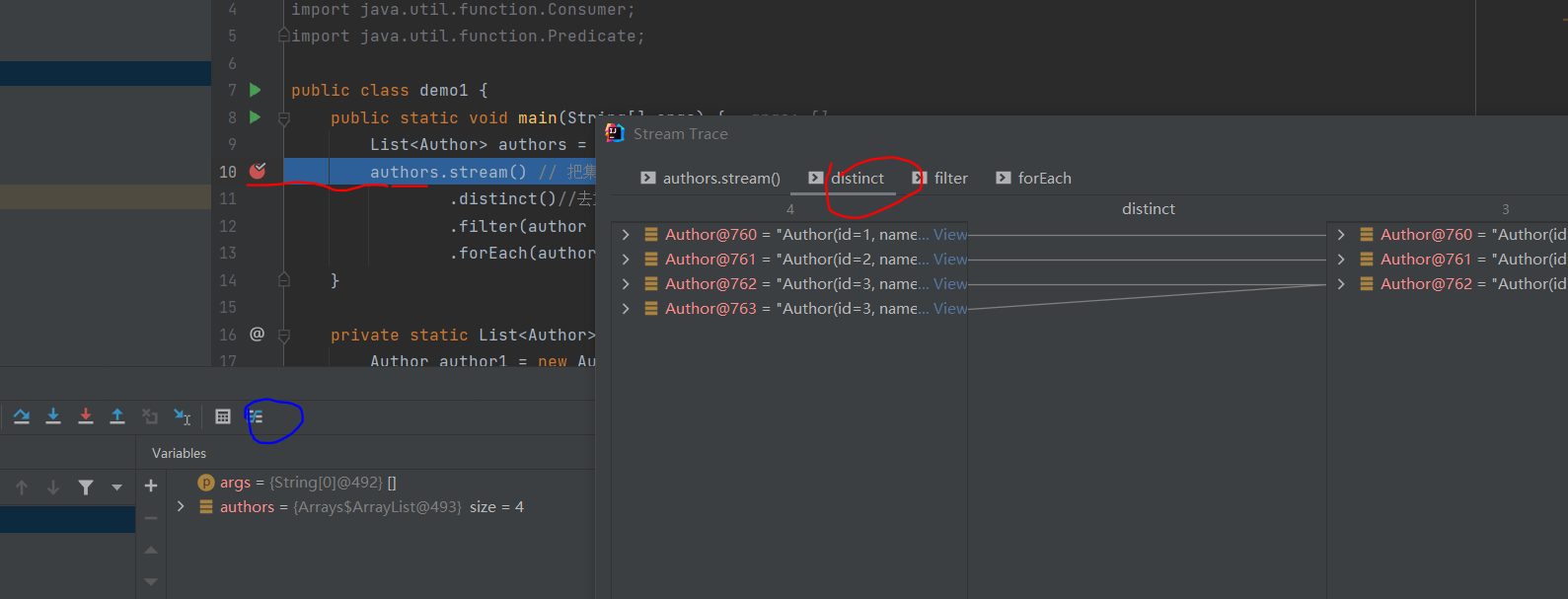
上面的操作简直是太优雅了.如果没有stream流做上面的操作特别繁琐.
2 创建流
流的操作包含三个阶段:创建,中间操作,终结操作.先来介绍流的创建.
(1)单列集合
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream();
(2)数组
private static void test02() {
Integer[] arr = {1, 2, 3 ,4 , 4, 5};
Arrays.stream(arr)
.filter(integer -> integer > 3)
.distinct()
.forEach(integer -> System.out.println(integer));
}
也可以使用Stream的of()方法.
Stream.of(arr);
(3)双列集合
先转成单列集合再转为流.
private static void test03() {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("火影忍者", 18);
map.put("忍者神龟", 16);
map.put("小黄人", 15);
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> mapEntry = map.entrySet().stream();
mapEntry.filter(stringIntegerEntry -> stringIntegerEntry.getValue() < 18)
.forEach(stringIntegerEntry -> System.out.println(stringIntegerEntry.getKey() + "==" + stringIntegerEntry.getValue()));
}
3 中间操作
3.1 filter
条件过滤
private static void test04() {
getAuthors().stream()
.filter(author -> author.getName().length() > 1)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
顺带一提,终结操作必须加上。后续会解释原因。
3.2 map
把流中的元素进行计算或者数据类型的转换。
需求: 打印所有作家的姓名
法1:
getAuthors().stream()
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
法2:
getAuthors().stream()
.map(new Function<Author, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Author author) {
return author.getName();
}
})
.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
简化下。
getAuthors().stream()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
这里我们就清楚map()的作用了,原来它可以映射集合元素,把它的元素替换成其它类型,比如这里就全部替换成了author的姓名,后续操作的就都是name属性了。
map()还可以对流中元素进行计算,也就是进行一些加工处理,参考如下例子。
getAuthors().stream()
.map(author -> author.getName() + ",")
.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s));
3.3 distinct
去重。判断元素重复的依据是Object的equals()方法,如果是自定义的数据类型要重写equals()方法。
实际上,我们之前加再实体类上的注解@EqualsAndHashCode就相当于重写了equals()与hashcode()方法:当所有元素的值相同时判断对象为同一个。它的作用与如下代码等同。
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Author author = (Author) o;
return Objects.equals(id, author.id) && Objects.equals(name, author.name) && Objects.equals(age, author.age) && Objects.equals(intro, author.intro) && Objects.equals(books, author.books);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, age, intro, books);
}
demo如下。
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream() // 把集合转换成流
.distinct()//去重
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
3.4 sorted
对流中的元素进行排序。下面对author进行年龄降序排序,并去重输出。
getAuthors().stream()
.sorted(new Comparator<Author>() {
@Override
public int compare(Author o1, Author o2) {
return o2.getAge() - o1.getAge();
}
})
.distinct()
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName() + " is " + author.getAge()));
简化如下。
private static void test06() {
getAuthors().stream()
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge())
.distinct()
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName() + " is " + author.getAge()));
}
sorted()还有空参的重载方法,当author实现了Comparable()接口并且重写了抽象方法时,可以使用空参版本。
3.5 limit
可以对流的长度进行限制,超出的部分将被抛弃。
对author进行年龄降序排序,去重,输出年龄最大的两位作家。
private static void test07() {
getAuthors().stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge())
.limit(2)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName() + " is " + author.getAge()));
}
3.6 skip
跳过流中前n个元素。实际上应用中常见的有去掉最低分、最高分求平均分等操作可以使用到。这里我们仅实现一个demo需求演示。
对author进行年龄降序排序,去重,输出年龄最大的作家外的其它作家。
private static void test08() {
getAuthors().stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge())
.skip(1)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName() + " is " + author.getAge()));
}
3.7 flatMap
现有需求:打印所有书籍的名字。聪明的你可能会这么做。
private static void test09() {
getAuthors().stream()
.map(author -> author.getBooks())
.forEach(new Consumer<List<Book>>() {
@Override
public void accept(List<Book> books) {
for(Book book : books) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
});
}
不过你发现,打印出来的book似乎有重复的元素,如何对他们去重似乎成了难题,而且代码一点都不优雅。flatMap提供了另外的解决方案。
private static void test10() {
getAuthors().stream()
.flatMap(new Function<Author, Stream<Book>>() {
@Override
public Stream<Book> apply(Author author) {
return author.getBooks().stream();
}
})
.distinct()
.forEach(new Consumer<Book>() {
@Override
public void accept(Book book) {
System.out.println(book);
}
});
}
优化。
private static void test10() {
getAuthors().stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.forEach(book -> System.out.println(book));
}
下面再举一例加深印像。
打印所有书籍分类,并且去重,不要出现类似哲学,爱情这样的格式。
private static void test12() {
getAuthors().stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.flatMap(book -> Arrays.stream(book.getCategory().split(",")))
.distinct()
.forEach(category -> System.out.println(category));
}
4 终结操作
Stream流一定要有终结操作,因为如果没有终结操作,stream流的代码都不会被执行。
4.1 foreach
例:打印所有作家名字。
getAuthors().stream()
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
4.2 count
获取流中元素个数。
例:获取书籍数量,去重。
private static void test14() {
long count = getAuthors().stream()
.distinct()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
4.3 max&min
求流的最值。
例:输出书籍的最高分、最低分,打印。
private static void test15() {
Optional<Integer> max = getAuthors().stream()
.distinct()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.map(book -> book.getScore())
.max((a, b) -> a - b);
System.out.println(max.get());
}
最低分略。
4.4 collect
将流中的元素转换为集合。
例:获取存放所有作者名字的List集合。
private static void test16() {
List<String> authorNames =getAuthors().stream()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (String authorName : authorNames) {
System.out.println(authorName);
}
}
collect的传参我们并没有使用匿名内部类来实现,因为这样会比较复杂(读者可以自己尝试下),而是使用java.util.stream.Collectors工具类的方法。
例:获取所有书名的Set集合。
private static void test17() {
Set bookNames = getAuthors().stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getName())
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(bookNames);
}
例:获取一个map集合,key为作者名,value为List.
private static void test18() {
Map<String, List<Book>> authorAndBooks = getAuthors().stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
new Function<Author, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Author author) {
return author.getName();
}
},
new Function<Author, List<Book>>() {
@Override
public List<Book> apply(Author author) {
return author.getBooks();
}
}
));
System.out.println(authorAndBooks);
}
上面的toMap()有两个参数,分别对应key和value.改良下。
private static void test18() {
Map<String, List<Book>> authorAndBooks = getAuthors().stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
author -> author.getName(),
author -> author.getBooks()
));
System.out.println(authorAndBooks);
}
4.5 anyMatch
例:判断是否有年龄小于14岁的作家。
private static void test19() {
boolean isSmallAuthorExits = getAuthors().stream()
.anyMatch(author -> author.getAge() < 14);
System.out.println(isSmallAuthorExits);
}
4.6 allMatch
例:判断是否所有作家都是未成年人。
private static void test20() {
boolean flag = getAuthors().stream()
.allMatch(author -> author.getAge() < 18);
System.out.println(flag);
}
4.7 noneMatch
判断作家中是否没有成年人。
private static void test21() {
boolean flag = getAuthors().stream()
.noneMatch(author -> author.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println(flag);
}
4.8 findAny&findFirst
如果存在,获取任意一个未成年作家的名字。
private static void test21() {
Optional<Author> authorOptional = getAuthors().stream()
.filter(author1 -> author1.getAge() > 1)
.findAny();
authorOptional.ifPresent(author ->System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
笔者这里测试的结果是固定,并且debug在filter前就只有一个数据了,如果有大佬能够解释下万分感谢。
findFirst会查找第一个元素,略。