许多人初学python可能都会选择sublime text,因为这个软件没有采用那些大的外壳,是个轻量级的软件,如果不需要可视化的编程,它是我非常推荐的一款编辑器,可以编辑c c++ java ,当然python肯定是被支持的。
一、创造虚拟环境
后面的最后一个参数为虚拟环境的名称
python -m venv kivy_venv
建立成功后可以进入虚拟环境
kivy_venv\Scripts\activate
当然,我们打开钱建立的目录 kevy_venv下可以看到activate.bat,我们上面执行的就是这个批处理文件。

或者直接进入到kivy_venv\Scripts目录下执行这个批处理也是一样。
进入后这样

进入以后,我们通过pip freeze查看,发现没有任何第三方库被安装,也就是说kivy没有被安装进来,所以接下来我们需要安装一下kivy。经过查看,发现里面是空的。

二、给虚拟环境安装kivy
可以全版本安装
pip install kivy[full]
也可以简版安装(同时安装了一些例子)
python -m pip install "kivy[base]" kivy_examples --no-binary kivy
安装完成,我们可以查看以下是否安装成功

很显然,都已经安装上去了,运行下面的代码
import kivy
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.label import Label
class MyApp(App):
def build(self):
return Label(text="hello world")
if __name__ == '__main__':
MyApp().run()
现在我们可以运行一个最简单(上一篇博文中就有代码)来看看效果

我们运行成功后会看到这个helloworld的窗口
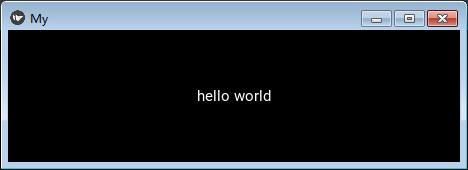
补充说明:
我使用的这个版本已经不需要额外编辑build system来实现编译python,而且可以直接通过ctrl+shift+p调出接口查找框,输入kivy后直接也可以娃不错更kivy是安装,这里不详述了。
编译的快捷键是ctrl+B,也非常方便编译,但不足的就是kivy编译想直接在sublime text中完成和显示出kivy对话框来,目前还是需要自己新建一个build system。这里就不详细说了。
软件和运行库的说明
1、sublime text 4126(build)
2、kivy 2.1
有关build system可以参看官方说明,链接如下
https://www.sublimetext.com/docs/build_systems.html
下面是python的参数,新建build system要用到,可以参考以下
usage: python [option] … [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] …
Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables):
-b : issue warnings about str(bytes_instance), str(bytearray_instance)
and comparing bytes/bytearray with str. (-bb: issue errors)
-B : don’t write .pyc files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : debug output from parser; also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-I : isolate Python from the user’s environment (implies -E and -s)
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : remove assert and debug-dependent statements; add .opt-1 before
.pyc extension; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : do -O changes and also discard docstrings; add .opt-2 before
.pyc extension
-q : don’t print version and copyright messages on interactive startup
-s : don’t add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don’t imply ‘import site’ on initialization
-u : force the stdout and stderr streams to be unbuffered;
this option has no effect on stdin; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
when given twice, print more information about the build
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-X opt : set implementation-specific option
–check-hash-based-pycs always|default|never:
control how Python invalidates hash-based .pyc files
file : program read from script file
-
: program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg …: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
Other environment variables:
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ‘;’-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate directory (or ;<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses \python{major}{minor}.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in ‘import’ statements (Windows).
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONFAULTHANDLER: dump the Python traceback on fatal errors.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to ‘random’, a random value is used
to seed the hashes of str and bytes objects. It can also be set to an
integer in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a
predictable seed.
PYTHONMALLOC: set the Python memory allocators and/or install debug hooks
on Python memory allocators. Use PYTHONMALLOC=debug to install debug
hooks.
PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the locale
coercion behavior. Use PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE=warn to request display of
locale coercion and locale compatibility warnings on stderr.
PYTHONBREAKPOINT: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the default
debugger. It can be set to the callable of your debugger of choice.
PYTHONDEVMODE: enable the development mode.
PYTHONPYCACHEPREFIX: root directory for bytecode cache (pyc) files.
