🚩Java 中操作文件
本节内容中,我们主要涉及文件的元信息、路径的操作,暂时不涉及关于文件中内容的读写操作。
Java 中通过 java.io.File 类来对一个文件(包括目录)进行抽象的描述。注意,有 File 对象,并不
代表真实存在该文件
??File 概述
我们先来看看 File 类中的常见属性、构造方法和方法
属性
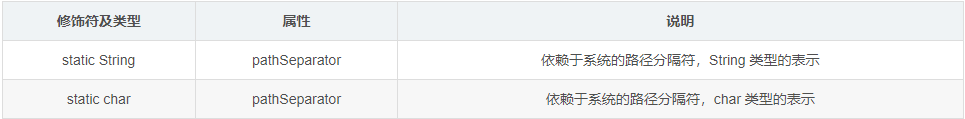
构造方法
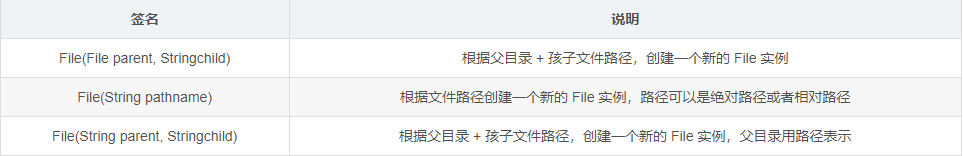
方法

先看看前面五组是如何使用的:
🔴使用方法如下
getParent、getName、getPath、getAbsolutePath、getCanonicalPath
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//绝对路径
File file=new File("d:/test.txt");
System.out.println("创建成功");
System.out.println(file.getParent());// 获取到文件的父目录文件路径
System.out.println(file.getName());// 获取到文件名
System.out.println(file.getPath());// 获取到文件路径(构造 file 的时候指定的路径)
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());// 获取到绝对路径
System.out.println(file.getCanonicalPath());// 获取到绝对路径.[需要处理异常]
System.out.println("====================");
//相对路径
File file1 = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file1.getParent());// 获取到文件的父目录文件路径
System.out.println(file1.getName());// 获取到文件名
System.out.println(file1.getPath());// 获取到文件路径(构造 file 的时候指定的路径)
System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath());// 获取到绝对路径
System.out.println(file1.getCanonicalPath());// 获取到绝对路径.[需要处理异常]
}
}

🔴使用方法如下
exists、isDirectory、isFile
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//绝对路径
File file = new File("d:/test.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());//判断文件是否存在
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//判断文件是否是一个目录
System.out.println(file.isFile());//判断文件是否是一个普通文件
//相对路径
System.out.println("==========");
File file1 = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file1.exists());//判断文件是否真实存在
System.out.println(file1.isDirectory());//判断文件是否是一个目录
System.out.println(file1.isFile());//判断文件是否是一个普通文件
}
}
🔴使用方法如下
createNewFile// 创建文件
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());//判断文件是否存在
file.createNewFile();// 创建文件
System.out.println(file.exists());//判断文件是否存在
}
}
🔴使用方法如下
delete// 删除操作
import java.io.File;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());//存在
file.delete();// 删除操作
System.out.println(file.exists());//不存在
}
}
🔴使用方法如下
mkdir、mkdirs
public class TestDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./bbb"); //在当前项目底下创建一个 bbb 目录
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//不存在
file.mkdir();// mkdir 方法 只能创建一级的目录
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//存在
}
}
🔴使用方法如下
list 、listFiles// // 这个操作就是把 aaa目录里面的内容列举出来
public class TestDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./aaa");
System.out.println(file.list());
// 这个操作就是把bbb目录里面的内容列举出来
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.list()));
}
//listFiles和list差不多,listFiles是打印出来相对路径,list是打印出来简化的路径
}
File 类的用法就先介绍到这里,其实还有很多其他的方法,这里就不一一介绍了。
??文件内容操作
主要操作:
文件内容
1)打开文件
2)读文件
3)写文件
4)关闭文件
针对文件内容的读写,Java标准库提供了一组类~
首先按照文件的内容,分成了两个系列:
1)字节流对象~针对二进制文件,以字节为单位进行读写
2)字符流对象,针对文本文件,是以字符为单位进行读写的
??首先先来看看针对字节流的读方法:


import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream("D:/test.txt") ;
while (true)
{
int b=inputStream.read();
if (b==-1)
{
break;
}
System.out.println(b);
}
inputStream.close();
}
}
大家应该对这个没啥疑问吧,读出来的就是Ascii码值:
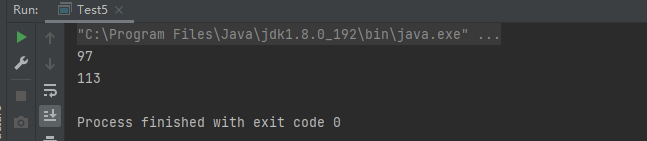
🔴针对字节流的写方法:
和上面的读操作一样,差别不大。
import java.io.*;
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt");
byte[] buffer =new byte[]{97,98,99};
outputStream.write(buffer);
outputStream.close();
}
}

??针对字符流对象进行读写操作
🔴针对字符流的读方法:
import java.io.*;
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Reader reader=new FileReader("D:/test.txt");
while (true)
{
char []buffer= new char[1024];
int len =reader.read(buffer);
if (len==-1)
{
break;
}
for (int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
System.out.println(buffer[i]);
}
}
}
}

🔴针对字符流的写方法:
import java.io.*;
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Writer writer=new FileWriter("D:/test.txt");
writer.write("sas");
writer.close();
}
}



