算法集锦(NO.5)
高频习题
岛屿数量
给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [
[“1”,“1”,“1”,“1”,“0”],
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“1”,“0”],
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”],
[“0”,“0”,“0”,“0”,“0”]
]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:grid = [
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”],
[“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”],
[“0”,“0”,“1”,“0”,“0”],
[“0”,“0”,“0”,“1”,“1”]
]
输出:3
提示:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 300
grid[i][j] 的值为 ‘0’ 或 ‘1’
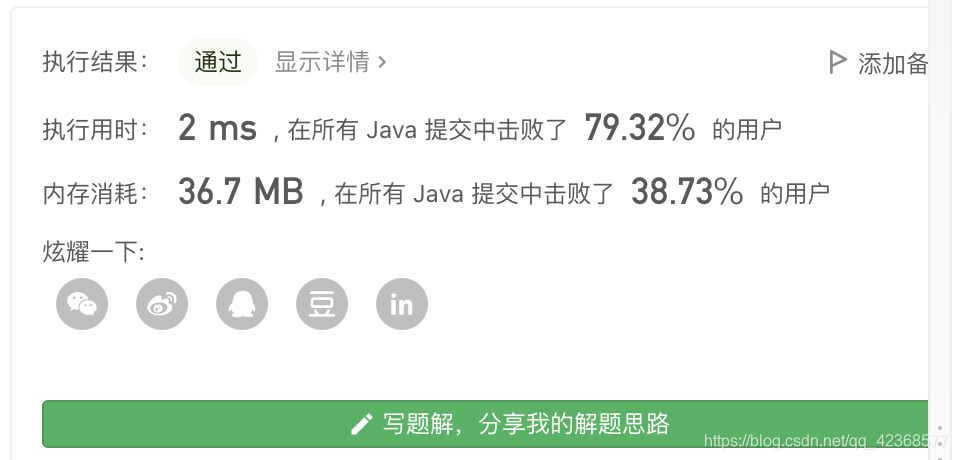
方法一:
递归,使用辅助数组boolean,当遍历原数组时,碰到值为1的时候,就对其周边相连元素的辅助数组变为true。在进行传参遍历时还需要对该点的辅助空间进行判定,即只有当该坐标下的原数组为1,并且其辅助数组为false(未到达)时才可以进行传参,count才能++。
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int m=grid.length;
int n=grid[0].length;
int count=0;
//辅助数组boolean,来判定某个值为1的点是否已经被遍历过
boolean [][]treak=new boolean[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
//当满足该点未遍历并且该点值为1时,才能进行后续遍历
if(!treak[i][j]&&grid[i][j]=='1'){
check(treak,i,j,grid,m,n);
//在遍历完该点相连的符合条件的点后,进行片区count++
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public void check(boolean[][]treak,int h,int l,char[][] grid,int m,int n){
//当满足下标不超过界限,并且点的值为1和未经过该点时,可以进行递归操作
if(h+1<m&&grid[h+1][l]=='1'&&!treak[h+1][l]){
treak[h+1][l]=true;
check(treak,h+1,l,grid,m,n);
}
if(h-1>=0&&grid[h-1][l]=='1'&&!treak[h-1][l]){
treak[h-1][l]=true;
check(treak,h-1,l,grid,m,n);
}
if(l+1<n&&grid[h][l+1]=='1'&&!treak[h][l+1]){
treak[h][l+1]=true;
check(treak,h,l+1,grid,m,n);
}
if(l-1>=0&&grid[h][l-1]=='1'&&!treak[h][l-1]){
treak[h][l-1]=true;
check(treak,h,l-1,grid,m,n);
}
}
}


代码优化:取消了boolean辅助判定栈,在给定数组上进行数值更新。
class Solution {
void dfs(char[][] grid, int r, int c) {
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
//当超过边界,且该点不为1时候,跳出。
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= nr || c >= nc || grid[r][c] == '0') {
return;
}
//将相连板块的1,更新为0
grid[r][c] = '0';
//上下左右的递归遍历
dfs(grid, r - 1, c);
dfs(grid, r + 1, c);
dfs(grid, r, c - 1);
dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
//当grid不存在的时候直接返回0
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
int num_islands = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < nr; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < nc; ++c) {
//当发现某点为1的时候,调用dfs函数,将该点周边的1全部变成0
if (grid[r][c] == '1') {
//片区增加
++num_islands;
dfs(grid, r, c);
}
}
}
return num_islands;
}
}
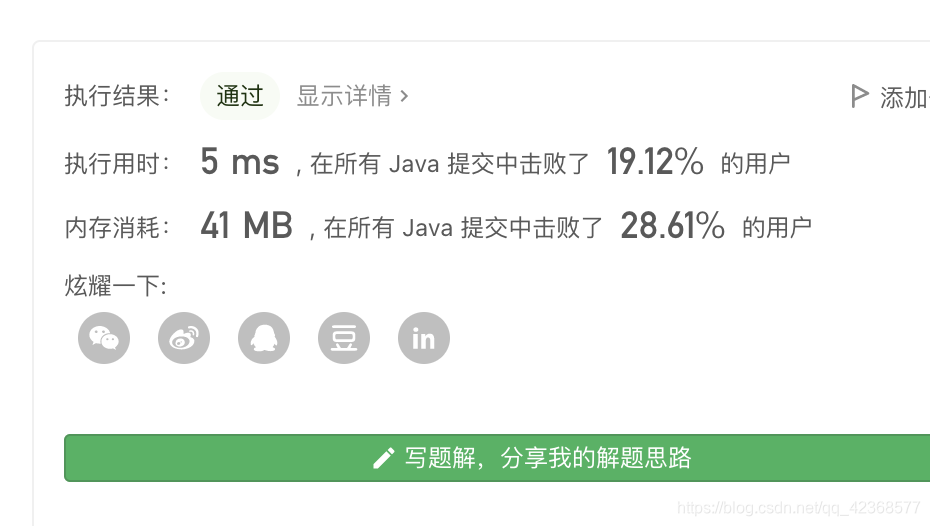
方法二:
广度优先遍历,将搜索到为1的时候,将其加入队列,对队列里的值周边相连的点进行遍历,如果满足值为1的时候,就将其更新为0。
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
int num_islands = 0;
//进行行遍历
for (int r = 0; r < nr; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < nc; ++c) {
//当该点值为1的时候,将其相连附近的值修改为0,并且块数+1
if (grid[r][c] == '1') {
++num_islands;
grid[r][c] = '0';
//使用queue进行每个值为1的点存放
Queue<Integer> neighbors = new LinkedList<>();
//因为该为二维链表,所以需要对其点的下标进行某种加密操作
neighbors.add(r * nc + c);
while (!neighbors.isEmpty()) {
//取出,将下标进行分解
int id = neighbors.remove();
int row = id / nc;
int col = id % nc;
//下面就是在边界范围内,如果该点为1,将其存入queue,并且将点更新为0
if (row - 1 >= 0 && grid[row-1][col] == '1') {
neighbors.add((row-1) * nc + col);
grid[row-1][col] = '0';
}
if (row + 1 < nr && grid[row+1][col] == '1') {
neighbors.add((row+1) * nc + col);
grid[row+1][col] = '0';
}
if (col - 1 >= 0 && grid[row][col-1] == '1') {
neighbors.add(row * nc + col-1);
grid[row][col-1] = '0';
}
if (col + 1 < nc && grid[row][col+1] == '1') {
neighbors.add(row * nc + col+1);
grid[row][col+1] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}
//返回得到的总岛屿板块
return num_islands;
}
}

方法三:
并查集,将相连的板块进行合并
class Solution {
//合并集的编写
class UnionFind {
int count;
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
//将每个1的下标进行存放至parent中,并且值和数组下标相同
public UnionFind(char[][] grid) {
count = 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
parent = new int[m * n];
rank = new int[m * n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
parent[i * n + j] = i * n + j;
//值为1的总数。
++count;
}
//将每个节点的rank都赋为0
rank[i * n + j] = 0;
}
}
}
//当parent的下标不等于值的时候,这说明该点为0,将其值返回0
public int find(int i) {
if (parent[i] != i) parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
return parent[i];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
//rootx为该点为1,rooty为rootx的相连点为1的情况
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
//当这两个点不同时为0时
if (rootx != rooty) {
//遍历完后的点,将其rootx和rooty相连接
if (rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) {
parent[rooty] = rootx;
} else if (rank[rootx] < rank[rooty]) {
parent[rootx] = rooty;
} else {
parent[rooty] = rootx;
rank[rootx] += 1;
}
//相连板块的值,则--
--count;
}
}
//返回总数
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
int num_islands = 0;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(grid);
for (int r = 0; r < nr; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < nc; ++c) {
if (grid[r][c] == '1') {
grid[r][c] = '0';
if (r - 1 >= 0 && grid[r-1][c] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, (r-1) * nc + c);
}
if (r + 1 < nr && grid[r+1][c] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, (r+1) * nc + c);
}
if (c - 1 >= 0 && grid[r][c-1] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, r * nc + c - 1);
}
if (c + 1 < nc && grid[r][c+1] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, r * nc + c + 1);
}
}
}
}
return uf.getCount();
}
}

无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcabcbb”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “abc”,所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = “bbbbb”
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “b”,所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,“pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
示例 4:
输入: s = “”
输出: 0
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
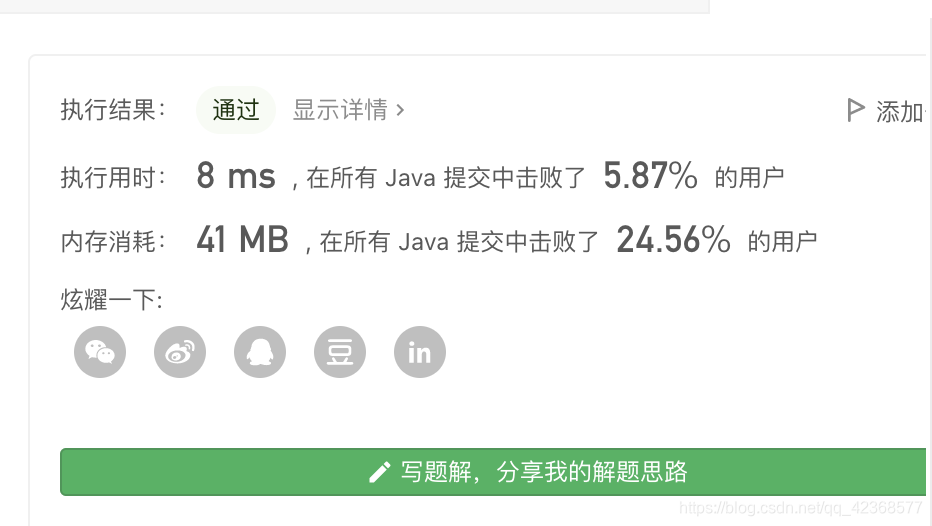
方法:
滑动窗口,设置一个窗口初始节点指针-1,将其向右进行滑动,期间需要有一个hashset进行字符的存储,当遇到set中包含的字符时,进行指针右移动。通过fori的i的遍历节点下标和,滑动窗口左指针下标的相减,即可得到无重复的长度。
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
//set进行字符的存储
Set<Character>occ = new HashSet<>();
//设置滑动窗口的右边界下标,和滑动窗口大小ans初始化
int rk = -1; int ans=0;
//对字符串进行遍历,其中i为滑动窗口的左边界
for(int i =0 ;i<s.length();++i){
if(i!=0){
occ.remove(s.charAt(i-1));
}
//将rk++,此时rk为右边界
while(rk+1<s.length()&&!occ.contains(s.charAt(rk+1))){
occ.add(s.charAt(rk+1));
rk++;
}ans=Math.max(ans,rk-i+1);
}return ans;
}
}
类似方法:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
//使用hashset进行不同字符串的存储
Set<Character>occ = new HashSet<>();
//滑动窗口左边界
int rk = -1; int ans=0;
for(int i =0 ;i<s.length();++i){
//当occ内不存在该字符时,就将其投入,并且更新ans的最大值
if(!occ.contains(s.charAt(i))){
occ.add(s.charAt(i));
ans=Math.max(ans,i-rk);
}else{
//当存在时就将occ内部的重复值抛出,滑动边界左指针收缩。
while(occ.contains(s.charAt(i))){
occ.remove(s.charAt(rk+1));
rk++;
}
occ.add(s.charAt(i));
}
}return ans;
}
}

每日温度
请根据每日 气温 列表,重新生成一个列表。对应位置的输出为:要想观测到更高的气温,至少需要等待的天数。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
例如,给定一个列表 temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73],你的输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。
提示:气温 列表长度的范围是 [1, 30000]。每个气温的值的均为华氏度,都是在 [30, 100] 范围内的整数。
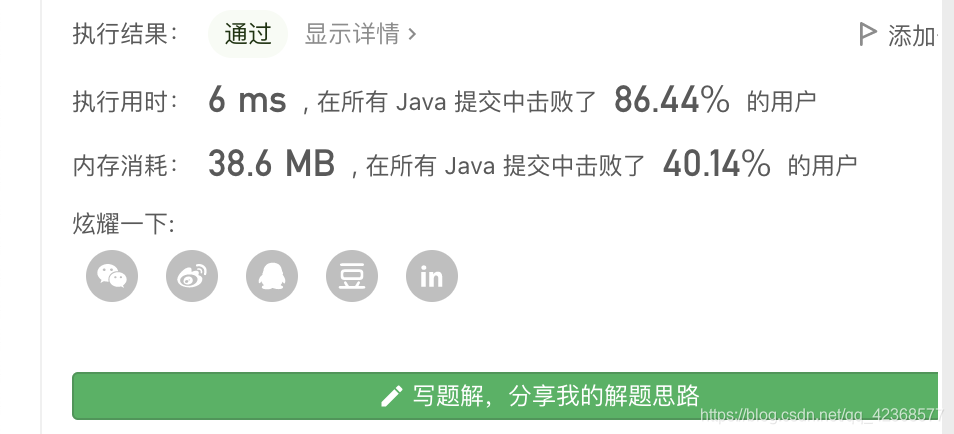
方法:
使用单调递减栈来存储数组下标,遍历数组,如果遇到节点值大于栈顶节点所对应的下标时,就弹出栈顶元素,将其作为下标存到结果数组中,该下标所对应的值为当前遍历的节点序减去栈弹出的节点下标。
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] T) {
int []num = new int [T.length];
Deque<Integer>stack =new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
//当栈为空或者值递减情况下直接存放入栈中
if(stack.isEmpty()||T[stack.peek()]>=T[i]){
stack.push(i);
}else{
//当碰到栈非空并且遍历值大于栈顶元素时,存入辅助数组中
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&T[stack.peek()]<T[i]){
num[stack.peek()]=i-stack.pop();
}
stack.push(i);
}
}
return num;
}
}
方法优化:
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int length = temperatures.length;
int[] ans = new int[length];
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//去除了栈为空和递减栈的判定过程
int temperature = temperatures[i];
while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperature > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
int prevIndex = stack.pop();
ans[prevIndex] = i - prevIndex;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}

森林中的兔子
森林中,每个兔子都有颜色。其中一些兔子(可能是全部)告诉你还有多少其他的兔子和自己有相同的颜色。我们将这些回答放在 answers 数组里。
返回森林中兔子的最少数量。
示例:
输入: answers = [1, 1, 2]
输出: 5
解释:
两只回答了 “1” 的兔子可能有相同的颜色,设为红色。
之后回答了 “2” 的兔子不会是红色,否则他们的回答会相互矛盾。
设回答了 “2” 的兔子为蓝色。
此外,森林中还应有另外 2 只蓝色兔子的回答没有包含在数组中。
因此森林中兔子的最少数量是 5: 3 只回答的和 2 只没有回答的。
输入: answers = [10, 10, 10]
输出: 11
输入: answers = []
输出: 0
说明:
answers 的长度最大为1000。
answers[i] 是在 [0, 999] 范围内的整数。
方法:
使用hashmap进行统计,此时需要考虑3种情况,第一种为0的时候,此时表示该颜色独一无二,此时就count直接加上key==0的时候的value就行。第二种情况,当key+1大于等于对应的value时,此时用贪心思想假设这些兔子所描述的颜色为同一种的情况下。第三种情况,当key+1小于对应的value时,此时也用贪心思想,假设颜色相同且数量达到key+1的兔子都描述了自身的情况,此时就需要对其余值进行考虑,如果无余数则直接加上商就行,如果有余数则商?1。
class Solution {
public int numRabbits(int[] answers) {
Map<Integer,Integer>mapCount = new HashMap<>();
int count=0;
//map进行遍历存储键值对
for(int num:answers){
mapCount.put(num,mapCount.getOrDefault(num, 0)+1);
}
//对map的进行遍历
for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>entry :mapCount.entrySet()){
//当其key为0时直接加上他的value
if(entry.getKey()==0){
count+=entry.getValue();
//当key+1大于等于value时候,表示其为一种颜色,即直接加上key+1
}else if(entry.getKey()+1>=entry.getValue()){
count+=entry.getKey()+1;
}else{
//当key+1<value时候,表示此时需要打包若干颜色相同的兔子对
count+=(entry.getKey()+1)*((entry.getValue()/(entry.getKey()+1))+(entry.getValue()%(entry.getKey()+1)==0?0:1));
}
}
return count;
}
}

最大正方形
在一个由 ‘0’ 和 ‘1’ 组成的二维矩阵内,找到只包含 ‘1’ 的最大正方形,并返回其面积。
示例 1:
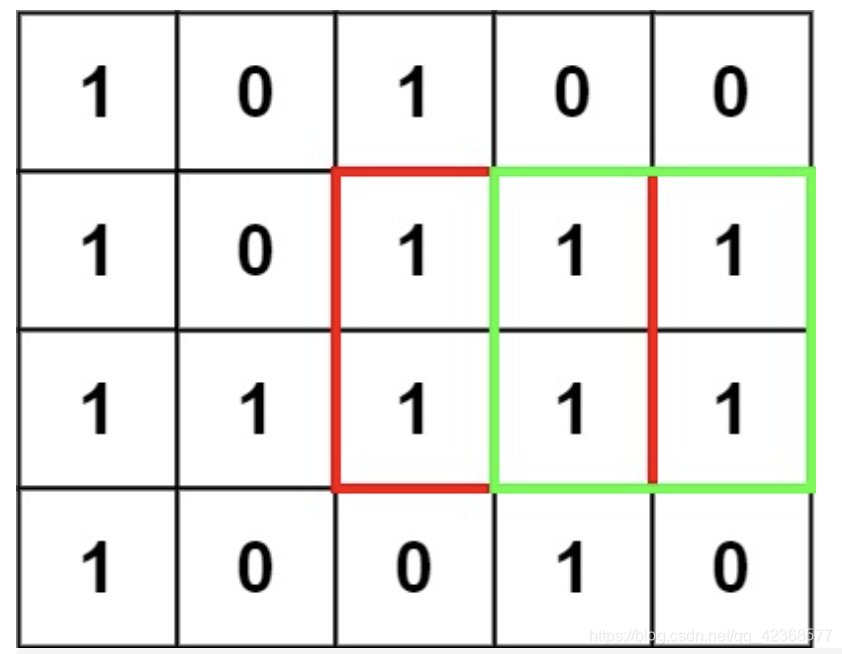
输入:matrix = [[“1”,“0”,“1”,“0”,“0”],[“1”,“0”,“1”,“1”,“1”],[“1”,“1”,“1”,“1”,“1”],[“1”,“0”,“0”,“1”,“0”]]
输出:4
示例 2:
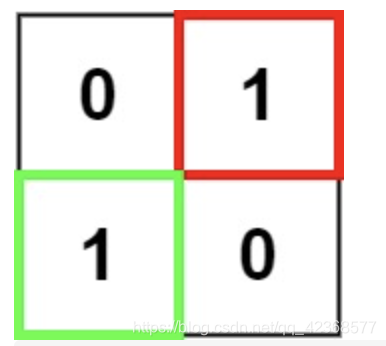
输入:matrix = [[“0”,“1”],[“1”,“0”]]
输出:1
示例 3:
输入:matrix = [[“0”]]
输出:0
提示:
m == matrix.length
n == matrix[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 300
matrix[i][j] 为 ‘0’ 或 ‘1’
方法一:
动态规划
采用对角线相加法则。比如该节点的值为1时候,通过对其左上,上,左这个方向的节点进行值的筛选,选出最小的值?1就是该坐标的值,如果该节点的值为0,则直接将该坐标赋值为0即可。
class Solution {
public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {
//最大正方形边长值
int maxSide = 0;
//当该矩阵为空,并且矩阵的边长为0或者矩阵的列为0时候,直接返回0
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return maxSide;
}
//统计矩阵的长和宽
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
//创建辅助dp矩阵
int[][] dp = new int[rows][columns];
//遍历原有矩阵进行统计其内在值
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
//当节点值为1时
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
//当其为边界点时,不存在前置正方形,直接赋1即可
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
} else {
//考虑到前置正方形,则直接对其左,上,左上三个方向进行取最小值来进行最小正方形的读取
dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
}
//更新最大边
maxSide = Math.max(maxSide, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
//通过最大边来得到最大面积
int maxSquare = maxSide * maxSide;
//输出最大面积
return maxSquare;
}
}

方法二:
暴力法剪枝优化,保存当前最大正方形的边max,当遍历节点的下标行列加上max都超过边界,则不用考虑,直接break。如果在边界内并且该节点值为1,则需要一个辅助函数将该节点,当前最大边界传过去进行验证。
class Solution {
public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {
//得到行列值,初始化最大边
int length = matrix.length;
int width = matrix[0].length;
int max = 0;
//遍历正方形
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
//当遇到该点行+最大边超出边界时,则直接跳出循环
if(i+max>=length){
break;
}
for(int j=0;j<width;j++){
//当遇到该点列+最大边超出边界时,则直接跳出循环
if(j+max>=width){
break;
}
//当该点为1时
if(matrix[i][j]=='1'){
//进行粗略检查
if(matrix[i][j+max]=='0'){
j=j+max;
}else if(i+max<length&&matrix[i+max][j]=='1'){
//考虑到max为0时,考虑到最大正方形左上顶点情况
if(max==0){
max=1;
}
//进行最大边的判定
max = maximalSquareDemo(i,j,matrix,max);
}
}
}
}
return max*max;
}
public int maximalSquareDemo(int i,int j,char[][] matrix,int max){
//通过check去检查是否满足已有的最大边正方形
if(!check(matrix,i,j,max)){
return max;
}
//如果满足则进行正方形的扩张。
int m=matrix.length;
int n=matrix[0].length;
while(i+max<m&&j+max<n){
if(check(matrix,i,j,max+1)){
max++;
}else{
break;
}
}
return max;
}
//检查该最大边是否满足
public boolean check(char[][] matrix,int i,int j,int add){
for(int start=i;start<i+add;start++){
for(int end=j;end<j+add;end++){
if(matrix[start][end]=='0'){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
优化后实际平均时间优于方法一,时间复杂度O(N^ 2),空间复杂度O(N)
单词的压缩编码
单词数组 words 的 有效编码 由任意助记字符串 s 和下标数组 indices 组成,且满足:
words.length == indices.length
助记字符串 s 以 ‘#’ 字符结尾
对于每个下标 indices[i] ,s 的一个从 indices[i] 开始、到下一个 ‘#’ 字符结束(但不包括 ‘#’)的 子字符串 恰好与 words[i] 相等
给你一个单词数组 words ,返回成功对 words 进行编码的最小助记字符串 s 的长度 。
示例 1:
输入:words = [“time”, “me”, “bell”]
输出:10
解释:一组有效编码为 s = “time#bell#” 和 indices = [0, 2, 5] 。
words[0] = “time” ,s 开始于 indices[0] = 0 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
words[1] = “me” ,s 开始于 indices[1] = 2 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
words[2] = “bell” ,s 开始于 indices[2] = 5 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
示例 2:
输入:words = [“t”]
输出:2
解释:一组有效编码为 s = “t#” 和 indices = [0] 。
提示:
1 <= words.length <= 2000
1 <= words[i].length <= 7
words[i] 仅由小写字母组成
方法:
创建一个Set的进行字符串数组的存储,然后对其每个字符串的子字符串进行检查,当某个字符串的子字符串在set内,则将其删除,因为可以通过该字符串,直接得到子字符串,少去冗余操作。
class Solution {
public int minimumLengthEncoding(String[] words) {
//创建存储空间hashset,并且将字符串数组words化成list存入hashset中
Set<String>wordsSet=new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(words));
//设置总数
int count=0;
//对words内部的每个字符进行遍历,如果该字符的子字符串存在于wordSet中,则直接删除。避免冗余操作
for(String str:words){
for(int i=1;i<str.length();i++){
wordsSet.remove(str.substring(i));
}
}
for(String str:wordsSet){
//每个单词后都需要加上#
count+=str.length()+1;
}
return count;
}
}

方法二:
字典树
参考甜姨的算法思想
class Solution {
public int minimumLengthEncoding(String[] words) {
TrieNode trie = new TrieNode();
Map<TrieNode, Integer> nodes = new HashMap<TrieNode, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; ++i) {
String word = words[i];
TrieNode cur = trie;
for (int j = word.length() - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
cur = cur.get(word.charAt(j));
}
nodes.put(cur, i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (TrieNode node: nodes.keySet()) {
if (node.count == 0) {
ans += words[nodes.get(node)].length() + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
class TrieNode {
TrieNode[] children;
int count;
TrieNode() {
children = new TrieNode[26];
count = 0;
}
public TrieNode get(char c) {
if (children[c - 'a'] == null) {
children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
count++;
}
return children[c - 'a'];
}
}


有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
示例 1:
输入:s = “()”
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = “()[]{}”
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = “(]”
输出:false
示例 4:
输入:s = “([)]”
输出:false
示例 5:
输入:s = “{[]}”
输出:true
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s 仅由括号 ‘()[]{}’ 组成
方法:
使用map进行括号的对接。)->(,{->},[->]。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
//先进行字符串的长度奇偶判定,若为奇数则直接判定为错误,因为括号必为偶数
if(s.length()%2!=0)
return false;
//使用map进行括号的对接
Map<Character,Character>map =new HashMap<>();
map.put(')','(');
map.put('}','{');
map.put(']','[');
//使用stack来保存之前未找到右括号的左括号
Deque<Character>stack =new LinkedList<Character>();
char []car =s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
//如果当前为右括号时
if(map.containsKey(car[i])){
//当左括号不为相对应的右括号,或者stack为空的时候,此时不符合题意,直接抛出错误。
if(stack.isEmpty()||stack.peek()!=map.get(car[i])){
return false;
}
//抛出栈顶,表示配对成功
stack.pop();
}else{
//当不存在时,则表示此为左括号,直接存入栈中
stack.push(car[i]);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}