剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
思路:
双指针:让快指针先走k步,这样快慢指针一起走,快指针走到尾部的时候,慢指针刚好走到了n-k处
代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
思路:
先定义一个空节点,将当前节点指向头节点,进入循环体,将当前节点的下一个节点存起来,然后将当前节点的尾部指向空节点,将空节点移向当前节点,然后将存起来的节点给当前节点,最后返回前节点
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
1.判断两个链表是不是为空,其中一个为空则返回另外一个
2.新建一个临时节点,用于添加元素
3.再定义一个指向合并后的尾节点,初始值为新建的头节点
4.合并,最小就给新链表
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null){
return l1;
}
ListNode root = new ListNode();
ListNode pointer = root;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){//都不为空则进行
if(l1.val<l2.val){
pointer.next = l1;//1小于2,所以将尾指针指向1
l1= l1.next;
}else{
pointer.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
pointer = pointer.next;//将指针移动到合并后的链表的末尾
}
if(l1!=null){
pointer.next = l1;//如果第一个链表的元素未处理完,则将尾指针直接指向1
}
if(l2!=null){
pointer.next = l2;
}
return root.next;//最后返回根节点
}
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
采用递归的方法
先序遍历树A中的每个节点(对于issubstructure)
判断树A中的每个节点为根节点的子树是否包含树B(recur)
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
return (A != null && B != null) && (recur(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B));
}
boolean recur(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if(B == null) return true;
if(A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;
return recur(A.left, B.left) && recur(A.right, B.right);
}
}
剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
递归解析:
- 终止条件: 当节点 root为空时(即越过叶节点),则返回 null;
- 递推工作:
初始化节点 tmp ,用于暂存 root 的左子节点;
开启递归 右子节点 mirrorTree(root.right),并将返回值作为 root的 左子节点 。
开启递归 左子节点 mirrorTree(tmp),并将返回值作为 root 的 右子节点 。- 返回值: 返回当前节点 root;
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return null;
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(tmp);
return root;
}
}
剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
和上一题差不多
递归解析:
- 终止条件
- 当 L和 R 同时越过叶节点: 此树从顶至底的节点都对称,因此返回true ;
- 当 L 或 R 中只有一个越过叶节点: 此树不对称,因此返回 false ;
- 当节点 L值 节点 R 值: 此树不对称,因此返回false ;
- 终止工作
- 判断两节点 L.left 和 R.right 是否对称,即 recur(L.left, R.right) ;
判断两节点 L.right和 R.left是否对称,即 recur(L.right, R.left) ;
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root == null?true:recur(root.left,root.right);
}
boolean recur(TreeNode L,TreeNode R){
if(L==null && R==null)
return true;
if(L==null || R == null || L.val!=R.val)
return false;
return recur(L.left,R.right) && recur(L.right,R.left);
}
剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
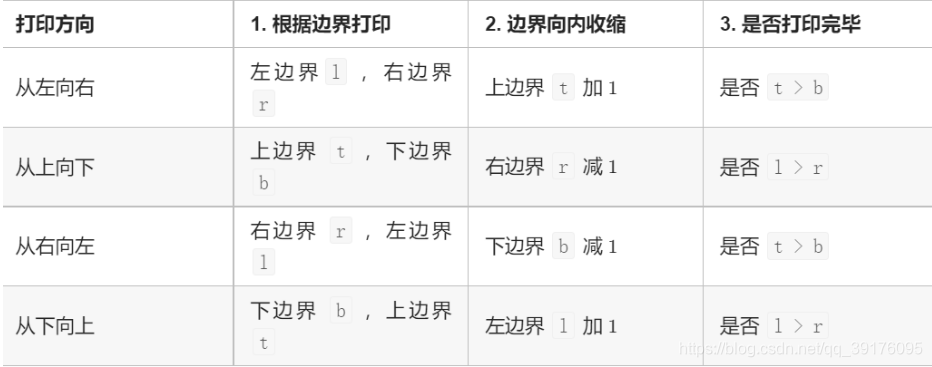
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix.length==0){
return new int[0];
}
int l=0,r=matrix[0].length-1;
int t=0,b=matrix.length-1;
int x=0;
int[] res = new int[(r+1)*(b+1)];
while(true){
for(int i = l;i<=r;i++) res[x++] = matrix[t][i];
if(++t>b) break;
for(int i = t;i<=b;i++) res[x++] = matrix[i][r];
if(--r<l) break;
for(int i = r;i>=l;i--) res[x++] = matrix[b][i];
if(--b<t) break;
for(int i = b;i>=t;i--) res[x++] = matrix[i][l];
if(++l>r) break;
}
return res;
}
剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
辅助栈
数据栈 A: 栈 A用于存储所有元素,保证入栈
push()函数、出栈pop()函数、获取栈顶top()函数的正常逻辑辅助栈 B: 栈 B中存储栈 A 中所有 非严格降序 的元素,则栈 A中的最小元素始终对应栈 B 的栈顶元素,即
min()函数只需返回栈 B 的栈顶元素即可。如果是添加的话,A添加了一个元素,B不为空且这个元素小于B的顶部元素,那么B就要添加
如果是取最小值出来的话,就去取B的顶部元素
class MinStack {
/** initialize your data structure here. */
Stack<Integer> A,B;
public MinStack() {
A = new Stack<>();
B = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
A.add(x);
if(B.empty() || B.peek() >= x)
B.add(x);
}
public void pop() {
if(A.pop().equals(B.peek()))
B.pop();
}
public int top() {
return A.peek();
}
public int min() {
return B.peek();
}
}
剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
辅助栈
初始化:辅助栈,弹出序列的索引
遍历压栈序列:
- 各个元素遍历依次入栈
- 循环出栈,如果栈顶的元素==弹出序列元素,那么执行出栈,此时弹出序列自增
返回值:如果栈为空,那么弹出序列是合法的作出判断
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for(int i = 0,j = 0;i<pushed.length;i++){
stack.push(pushed[i]);
while(stack.size()>0 && stack.peek()==popped[j]){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return stack.size()==0;
}
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
特例处理:当树的根节点为空,则返回空列表
初始化:结果列表、包含根节点的队列
BFS广度优先循环:当队列为空时跳出
- 出队:队首元素出队
- 打印:将值添加到列表尾部
- 添加子节点:如果队首的左右子节点不为空,则将左右子节点加入队列
返回值:打印列表即可
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(root);
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while(!list.isEmpty()){
TreeNode curnode = list.poll();
// System.out.print(curnode.val+" ");
ans.add(curnode.val);
if(curnode.left !=null){
list.add(curnode.left);
}
if(curnode.right != null){
list.add(curnode.right);
}
}
int[] res = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0;i<ans.size();i++){
res[i] = ans.get(i);
}
return res;
}