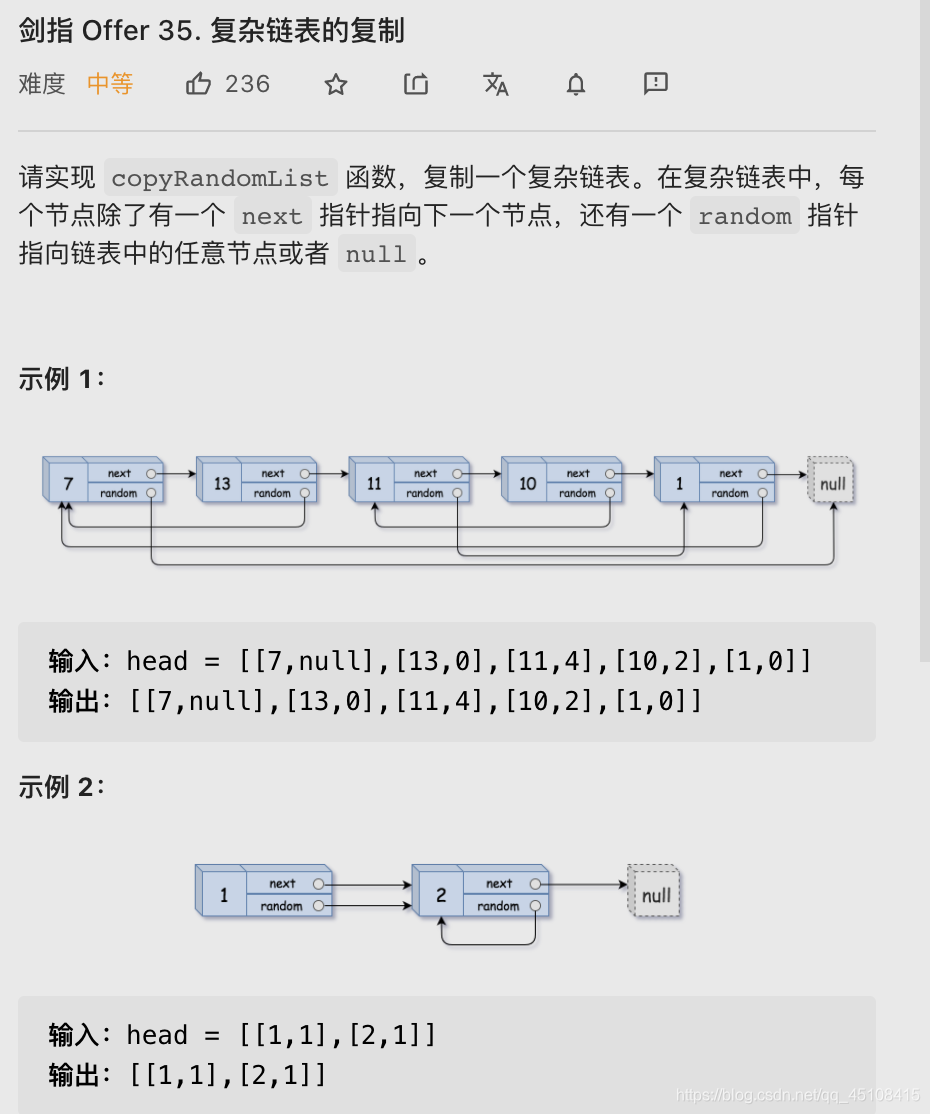
题目描述
- 主要有两个考虑点:
- 不能改变原链表
- 新链表赋予 next、random 时,复制结点不一定存在
思路 && 代码
1. 哈希表法
- O(n)、O(n)
- 参考了dalao的写法,这里哈希表用得非常巧妙~值得学习!
- 思路:在哈希表中建立 Node - CopyNode 的联系,在此基础上进行 next && random 的处理即可。
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Node, Node> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
for(Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next) {
hashmap.put(temp, new Node(temp.val));
}
for(Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next) {
hashmap.get(temp).next = hashmap.get(temp.next);
hashmap.get(temp).random = hashmap.get(temp.random);
}
return hashmap.get(head);
}
}
2. 原地算法
- O(n)、O(1),相对于方法1,此处不需要占用额外空间~
- 注意:原链表的恢复、边界结点的处理
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
for(Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next.next) {
Node copy = new Node(temp.val);
copy.next = temp.next;
temp.next = copy;
}
for(Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next.next) {
if(temp.random != null) {
temp.next.random = temp.random.next;
}
}
Node copyHead = head.next;
for(Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next) {
Node nextNode = temp.next.next;
if(nextNode != null) {
temp.next.next = temp.next.next.next;
}
temp.next = nextNode;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
| 