二叉树的运算
知识点
二叉树生成
广义表表示二叉树结构生成二叉链表
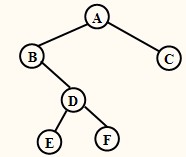
二叉树的广义表表示形式为: (A(B(,D(E,F)),C))。特点:靠近左括号的结点是在左子树上,而逗号右边的结点是在右子树上。
BinTNode *CreateTree(char *str) {
// str为存储广义表的字符串的指针
BinTNode *st[100]; //用指针数组模拟栈
BinTNode *p = NULL;
int top, k, j = 0;
top = -1; //置空栈
char ch = str[j]; //存放广义表的字符串的数组
BinTNode *b = NULL;
while (ch != '\0') //循环读广义表字符串中字符
{
switch (ch) {
case '(':
top++;
st[top] = p;
k = 1;
break; //左括号表示新的子树的开始,所以刚建立的结点指针入栈
case ')':
top--;
break; //右括号表示一个子树的结束,栈顶元素没有子树,出栈
case ',':
k = 2;
break;
default:
p = (BinTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BinTNode)); //读到的是字符
p->data = ch; //填写数据域
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL; //填写指针域
if (b == NULL) //建立第一个结点
b = p;
else {
switch (k) {
case 1:
st[top]->lchild = p;
break; //前一个字符是'(',该结点应该插入到左子树
case 2:
st[top]->rchild = p;
break; //前一个字符是','该结点应该插入到右子树
}
}
}
j++;
ch = str[j]; //读取下一个字符
}
return b; //返回根结点的指针
}
完全二叉树的层次顺序依次输入结点信息建立二叉链表的算法
如下图所示:
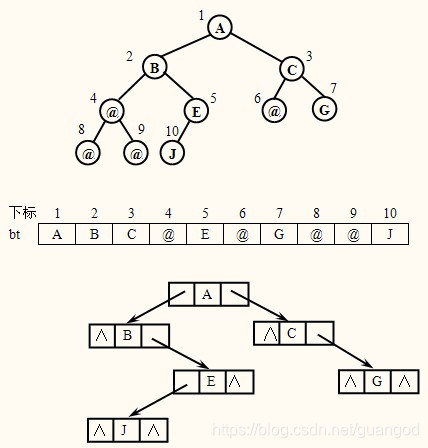
下标从1开始,处理起来更方便些。牺牲下标为0的结点。
算法思想
根据 一维数组读出来的字符,建立下需那个二叉链表。如果读出来不是@,就建立一个新的结点,如果是第一个是那就是根结点,不是,就是左孩子或右孩子链到双亲结点上。
算法实现
BinTree CreateBinTree(BinTree bt) {
// Q[1..n]是一个BinTNode类型的指针数组,front和rear分别是队头和队尾指针
BinTNode *Q[100]; //定义队列
BinTNode *s;
int front,rear;
char ch;
ch = getchar();
bt = NULL; //置空二叉树
front = 1;
rear = 0; //初始化队列
while (ch != '#') //假设结点值为单字符,#为终止符。输入二叉数的字符
{
s = NULL; //先假设读入的为虚结点"@"
if (ch != '@') {
s = (BinTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BinTNode)); //申请新结点
s->data = ch;
s->lchlid = s->rchiId = NULL; //新结点赋值
} // endif_1
rear++; //队尾指针自增
Q[rear] = s; //将新结点地址或虚结点地址(NULL)入队
if (rear == 1) //若rear为1,则说明是根结点,用bt指向它
bt = s;
else {
if (s != NULL && Q[front] != NULL) //当前结点及其双亲结点都不是虚结点
if (rear % 2 == 0) // rear为偶数,新结点应作为左孩子
Q[front]->lchild = s;
else // rear为奇数,新结点应作为右孩子
Q[front]->rchild = s;
if (rear % 2 != 0)
front++; // rear为奇数,说明front所指结点的左右儿子都处理完了,因此front加1指向下一个双亲,完成出队操作。
}
ch = getchar(); //读下一个结点值
} // endwhile
return bt;
}
二叉树遍历,必考
遍历
是指沿着某条搜索路径(线)周游二叉树,依次对树中每个结点访问且仅访问一次。
递归遍历算法
(1)先序遍历DLR(根左右):也叫先根遍历,若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
① 访问根结点; ②遍历左子树;③遍历右子树。
(2)中序遍历LDR(左根右):也叫中根遍历,若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
①遍历左子树; ②访问根结点; ③遍历右子树。
(3)后序遍历LRD(左右根):也叫后根遍历,若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
①遍历左子树; ②遍历右子树; ③访问根结点。
递归算法实现
前根遍历
void Preorder(BinTree bt)
{ //采用二叉链表存储结构,并设结点值为字符型
if(bt!=NULL)
{ printf("%c",bt->data); //访问根结点
Preorder(bt->lchild); //前序遍历左子树
preorder(bt->rchild); //前序遍历右子树
}
}
中根遍历
void Inorder(BinTree bt)
{ if(bt!=NULL)
{ Inorder(bt->lchild); //中序遍历左子树
printf("%c",bt->data); //访问根结点
Inorder(bt->rchild); //中序遍历右子树
}
}
后根遍历
void Postorder(BinTree bt)
{ if(bt!=NULL)
{ Postorder(bt->lchild); //中序遍历左子树
Postorder(bt->rchild); //中序遍历右子树
printf("%c",bt->data); //访问根结点
}
}
非递归算法实现
利用栈的非递归中根遍历算法
void Inorderl(BinTree bt)
{ // 采用二叉链表存储结构
SeqStack S;
BinTNode *P;
InitStack(&S);
Push(&S,bt); //根结点入栈
while (!StackEmpty(&S)) {
while (GetTop(&S)) //读栈顶元素,当栈顶不为空
Push(&S,GetTop(&S)->lchild); //左孩子依次入栈,直到左子树空为止
p = Pop(&S); //最后一个入栈的空指针退栈
if (!StackEmpty(&S)) {
printf("%c",GetTop(&S)->data); //访问根结点
p = Pop(&S);
Push(&S,p->rchild); //右子树进栈
}
}
}
利用指针数组实现中根遍历
实质是用指针数组模拟堆栈
void Inorder2(B1nTree bt)
{ //二叉树非递归中序遍历算法
BinTNode *ST[100]; //用指针数组模拟栈
int top = 0; //初始化数组
ST[top] = bt;
do {
while (ST[top] != NULL) //根结点及其所有的左结点地址装入数组
{
top = top + 1;
ST[top] = ST[top - 1]->lchild;
}
top = top - 1; //最后一个入数组的空指针退"栈"
if (top >= 0) //判数组中地址是否访问完
{
printf("%c", ST[top]->data); //访问结点
ST[top] = ST[top]->rchild; //扫描右子树
}
} while (top != -1);
}
利用栈实现前根遍历
思想:利用栈先将二叉树根结点指针入栈,然后执行出栈,获取栈顶元素值(即结点指针),若不为空值,则访问该结点,再将右、左子树的根结点指针分别入栈,依次重复出栈、入栈,直至栈空为止。
void Preorderl(BinTree bt)
{
SeqStack S;
InitStack(&S); //初始化栈
Push(&S, bt); //根结点指针进栈
while (!StackEmpty(&S))
{
bt = Pop(&S); //出栈
if (bt != NULL)
{
printf("%c", bt->data); //访问结点,假设数据域为字符型
Push(&S, bt->rchild); //右子树入栈 先访问左子树,栈先进后出
Push(&S, bt->lchiid); //左子树入栈
}
}
}
非递归层次遍历
从上到下,从左到右
算法思想:
采用一队列Q,若树不空,先将二叉树根结点输出,并将根结点指针入队,然后出队。然后将左右儿子入队,出队,出队时当左右儿子依次入队,再出队…
void TransLevel(BinTree bt)
{
cirQueue Q; //按层遍历二叉树,从上到下,从左到右
InitQueue(&Q); //初始化队列为空队列
if (bt == NULL)
return;
else {
printf("%c", bt->data); //输出根结点,假设其数据域为字符型
EnQueue(&Q, bt); //根结点指针入队
while (!QueueEmpty(&Q)) {
bt = DeQueue(&Q); //出队列
if (bt->rchild != NULL) {
printf("%c", bt->lchild->data); //输出左子树根结点
EnQueue(&Q, bt->lchild); //左子树入队
}
if (bt->rchild != NULL) {
printf("%c", bt->rchild->data); //输出右子树根结点
EnQueue(&Q, bt->rchild); //右子树入队列
}
} // end of the while
} // end of the if
}
由遍历恢复二叉树,必考
-
已知二叉树的前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列,可以唯一地恢复该二叉树。
原则是:在前序序列中确定根结点(最前面那个结点一定是根结点),然后根据根结点在中序序列中的位置分出根结点的左、右子树(根结点前面的那些结点为根结点的左子树上的结点,根结点后面的那些结点为根结点的右子树上的结点)。恢复该二叉树的任何一棵子树的过程仍然遵循这个原则 -
同理,已知二叉树的中序遍历序列和后序遍历序列,也可以唯一地恢复该二叉树
只是在后序序列中去确定根结点(最后面那个结点一定是根结点),而在中序序列中分出左右子树的过程与上述过程没有区别。 -
已知二叉树的前序遍历序列和后序遍历序列,无法唯一地恢复该二叉树,因为无法确定左右子树。
真题
已知二叉树的链式存储结构,求二叉树的深度。
分析:若一棵二叉树为空,则它的深度为0,否则它的深度等于其左右子树中的最大深度加l。设depl和depr分别表示左右子树的深度,则二叉树的深度为:
max(depl,depr)+1
int BinTreeDepth(BinTree bt)
{
int depl, depr;
if (bt == NULL)
return 0; //对于空树,返回0值,结束递归
else {
depl = BinTreeDepth(bt->lchild); //计算左子树的深度
depr = BinTreeDepth(bt->rchild); //计算右子树的深度
if (depl > depr)
return depl + 1;
else
return depr + 1;
}
}
以二叉链表为存储结构,试编写p所指结点在树中层数的算法。
分析:设h为返回P所指结点的所在层数,初值为0;树为空时返回0。lh指示二叉树bt的层数(即高度),调用时置初值为为l。
int Level(BinTree bt, BinTNode* P, int lh)
{ //求一结点在二叉树中的层次
static int h = 0; // h设置为静态遍历
if (bt == NULL)
h = 0;
else if (bt == p)
h = lh;
else {
Level(bt->lchild, p, lh + 1); //左子树中查找p
if (h == 0) //表示左子树已查完
Level(bt->rchild, p, lh + 1); //右子树中查找p
}
return h;
}
ic int h = 0; // h设置为静态遍历
if (bt == NULL)
h = 0;
else if (bt == p)
h = lh;
else {
Level(bt->lchild, p, lh + 1); //左子树中查找p
if (h == 0) //表示左子树已查完
Level(bt->rchild, p, lh + 1); //右子树中查找p
}
return h;
}