A. Dense Array
思路:
找到不满足条件的数对,小数取两倍与大数比较,统计可插入次数。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define M 1000000000
typedef long long ll;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define For(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i<yyy;i++)
#define fOR(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i>yyy;i--)
#define mst(v,xxx) memset(v,xxx,sizeof(v))
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF //无穷大
int main() {
IOS;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
int ans = 0;
cin >> n;
int a[51] = { 0 };
cin >> a[0];
int last = a[0];
For(i, 1, n) {
cin >> a[i];
double x = min(a[i], last);
double y = max(a[i], last);
if (y/x > 2) {
double z = x;
while (z < y) {
z *= 2;
ans++;
}
ans--;
}
last = a[i];
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B. Balanced Remainders
思路:
三个计数器,统计每种余数的个数。考虑到,加1操作后余数的改变是有规律的。(以八为例:8%3=2, (8+1)%3=0,余数 2——>0,其他,0——>1,1——>2)所以,将计数器放入循环,让这个规律在计数过程中可操作。
接下来,只要在遍历过程中,每次找到大于平均值的数,修改,当前以及下一个余数的计数个数;重复操作,最多两次遍历,就能够完成。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define M 1000000000
typedef long long ll;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define For(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i<yyy;i++)
#define fOR(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i>yyy;i--)
#define mst(v,xxx) memset(v,xxx,sizeof(v))
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF //无穷大
int main() {
IOS;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
int xx = 0;
int m = n / 3;
int c[3] = { 0 };
int ans = 0;
For(i, 0, n) {
cin >> xx;
if (xx % 3 == 0) c[0]++;
else if (xx % 3 == 1) c[1]++;
else c[2]++;
}
int i = 0;
for(;;){
if (c[0] == c[1]&&c[1] == c[2]) {
break;
}
int h = (i + 1) % 3;
if (c[i] > m) {
c[h] += c[i] - m;
ans += c[i] - m;
c[i] = m;
}
i = h;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C. Sum of Cubes
思路:
打表得到1到10000 的三次方,枚举a的三次,与x 相减得到b三次,判断,在不在三次方表中。
注意:判断过程中,用数组进行记录,遍历查找会超时。用map< , > mp; 进行标记,直接记录每一个三次方数,mp[三次方数]=1。由于默认mp[n]=0,mp[非三次方数]=0;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define M 10004
typedef long long ll;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define For(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i<yyy;i++)
#define fOR(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i>yyy;i--)
#define mst(v,xxx) memset(v,xxx,sizeof(v))
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF //无穷大
map<ll, int> mp;
void sheet() {
for (ll i = 1; i < 10001; i++) {
ll x = i * i * i;
mp[x] = 1; //表示存在这个数;
}
//打表
}
int main() {
IOS;
int t;
cin >> t;
sheet();
while (t--) {
ll x;
cin >> x;
if (x == 1) {
cout << "NO" << endl;
continue;
}
int flag = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i < 10001; i++){
ll b = x - i*i*i;
if (mp[b]) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!flag) {
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
D. Permutation Transformation
思路:
二叉树中序遍历。特点:每段序列的根结点左边区间的数字属于它的左子树,右边区间的数字属于它的右子树。
题中,每个子树区间中最大的数字就是它的根节点。
由于是计算层数,每次找到子树的根,将其他非根数字都计数加一,也就是向下移一层。最后得到每个结点的深度。
简单递归就能解决。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define M 102
typedef long long ll;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define For(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i<yyy;i++)
#define fOR(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i>yyy;i--)
//#define int long long
#define mst(v,xxx) memset(v,xxx,sizeof(v))
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF //无穷大
int a[102];
map <int, int> mp;
void f(int x,int y) {
if (x >= y) return;
int max = 0;
int index = 0;
For(i, x, y) {
if (a[i] > max) {
max = a[i];
index = i;
}
}
if (0<= x &&x < index) {
For(i, x, index) mp[a[i]]++;
f(x, index);
}
if (index + 1 < y) {
For(i, index + 1, y) mp[a[i]]++;
f(index + 1, y);
}
}
void main() {
IOS;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
int index = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
if (a[i] == n) {
index = i;
}
mp[a[i]] = 0;
}
For(i, x, index) {
mp[a[i]]++;
}
f(x,index);
For(i, index + 1, y) {
mp[a[i]]++;
}
f(index+1,y);
For(i, 0, n) {
cout << mp[a[i]] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
E. Accidental Victory
思路:
题目要找到可能获胜的人的序号,按升序排列。可以发现规律,当某些人的token之和(农民工们的总资产)比某个人的(地主的总资产)小的时候,那么无论 “农民们” 如何争抢,最后都归 “地主” 所有。
先记录每个人的编号;对tokens 进行升序排列,计算前面段的代数和,找到 某个位置,前面代数和小于这个位置的数字,也必然小于后面的数字。所有,其后的所有数字,都满足。重新排序输出就好。
为了省略一些相等数字产生的特殊情况,不做从前往后的代数和计算,而是从后往前找,由总和依次减去当前数,向前寻找满足前缀和小于当前数的位置。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define M 200002
typedef long long ll;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define For(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i<yyy;i++)
#define fOR(i,xxx,yyy) for(int i=xxx;i>yyy;i--)
#define mst(v,xxx) memset(v,xxx,sizeof(v))
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF //无穷大
struct node {
ll num;
int n;
};
node a[M];
int b[M];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.num < b.num;
}
int main() {
IOS;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
int x;
cin >> n;
ll sum = 0;
For(i, 0, n) {
cin >> a[i].num;
a[i].n = i+1;
sum += a[i].num;
}
sort(a, a + n, cmp);
int j = 0;
fOR(i, n - 1, -1) {
sum -= a[i].num;
if (sum < a[i].num) {
cout << n - i << endl;
j = i;
break;
}
}
int y = 0;
For(i, j, n) {
b[y++] = a[i].n;
}
sort(b, b + y);
For(i, 0, y) {
cout << b[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
F. Equalize the Array
思路:
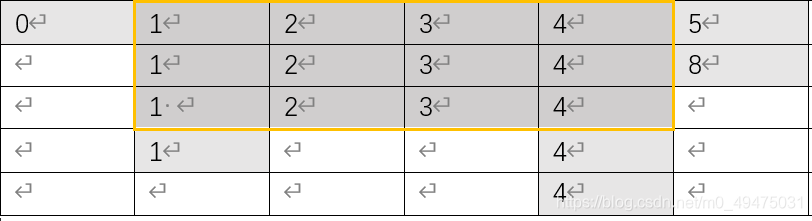
一序列:0 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 8 1 4 4 共18个数;
(顺序不论,所有序列都可列成如图所示的样子)
橙色框内为满足条件的数字,其余部分的总共6个,也就得到结果。
我们的目的是使橙色方框面积最大,得到它的边角料。
首先,要得到每个数字有多少个( 0:1 ,1:4,2:3,3:3,4:5,5:1,8:1);(先升序排列数组a[];遍历a[ ], 如果,与上一个数字相同,则数组b 当前位置计数加一,不同,则数组b 加一个新元素1,即,记录新元素有一个);
然后,升序排列数组b ( 1 1 1 3 3 4 5 共 7个数字);
再者,从第一个数字开始枚举并计算橙色方框的数字个数;
1 * (7-0) = 7;
1 * (7-1) = 6 ;
1 * (7-2)= 5;
3 * (7-3) = 12;
3 * (7-4) = 9;
4 * (7-5) = 8;
5* (7-6) = 5;
显然,方框面积最大为12;所以,答案就是,18 - 12 = 6;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define M 200002
typedef long long ll;
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define For(i,xxx,yyy) for(ll i=xxx;i<yyy;i++)
#define fOR(i,xxx,yyy) for(ll i=xxx;i>yyy;i--)
#define mst(v,xxx) memset(v,xxx,sizeof(v))
#define INFINITE 0xFFFFFFFF //无穷大
ll a[M] ;
ll b[M] ;
int main() {
IOS;
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
ll n;
cin >> n;
b[0] = 1;
For(i, 0, n) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n);
ll last = a[0];
ll j = 0;
For(i, 1, n) {
if (a[i] == last) {
b[j]++;
}
else {
b[++j] = 1;
}
last = a[i];
}
sort(b, b + j + 1);
ll x = 0;
ll ans = 0;
for (; x <= j;x++) {
ll m = b[x] * (j - x+1);
if (ans < m) {
ans = m;
}
}
cout << n-ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}