1、插入排序
与数组插入排序不同,每次从头开始找插入位置。
class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// 从前往后的插入排序
ListNode dummpy = new ListNode(0);
dummpy.next = head;
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = dummpy.next;
ListNode tempPre = dummpy;
while (temp.val < cur.val) {
tempPre = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp != cur) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
tempPre.next = cur;
cur = pre.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummpy.next;
}
}
2、归并排序
递归版的归并和快排,方法都是返回头节点:ListNode mergeSort(head) / quickSort(head, end)
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
return mergeSort(head);
}
private ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head){
if(head == null) return null;
if(head.next == null) return head;
//快慢指针找中点
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
if(pre != null){
pre.next = null;
}
ListNode left = mergeSort(head);
ListNode right = mergeSort(slow);
return merge(left, right);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode first, ListNode second){
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(first != null && second != null){
if(first.val < second.val){
cur.next = first;
cur = cur.next;
first = first.next;
} else {
cur.next = second;
cur = cur.next;
second = second.next;
}
}
if(first != null){
cur.next = first;
}
if(second != null){
cur.next = second;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
2、归并排序2
O(1)空间的归并,非递归。
初始时subLen=1,将链表以subLen切分再两两合并(最后一个可以<subLen),完成后subLen *= 2,直到subLen > len。
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
int length = 0;
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
length++;
node = node.next;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength *= 2) {
ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode head1 = curr;
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr.next != null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode head2 = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode next = null;
if (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2);
prev.next = merged;
while (prev.next != null) {
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = next;
curr = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) {
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 != null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
3、快排
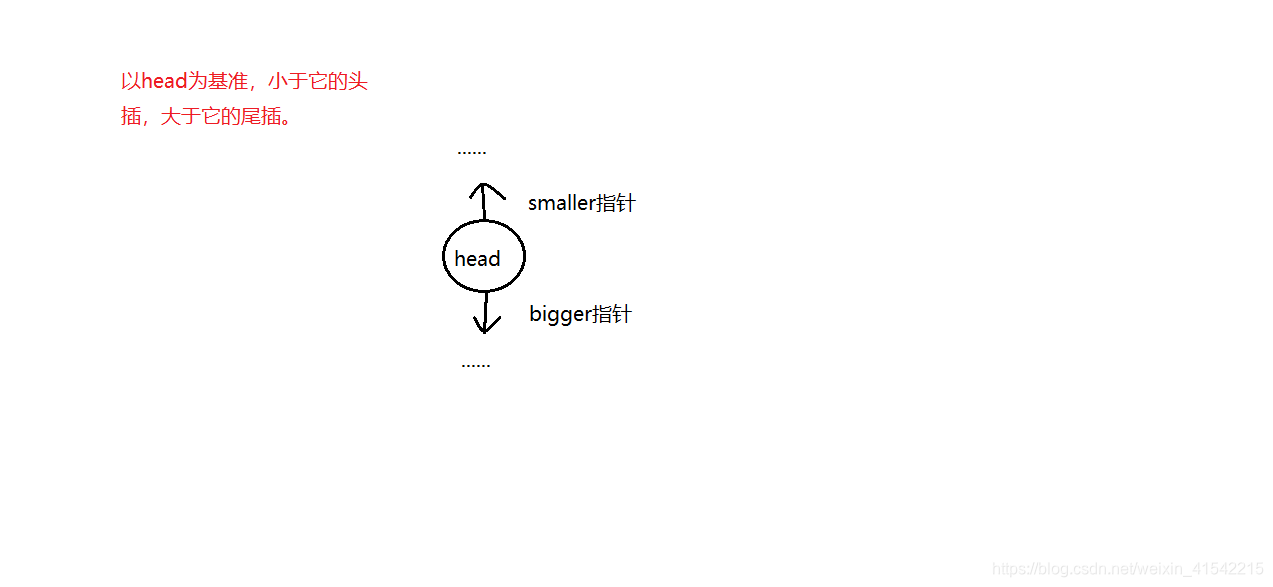
class Solution {
public static ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return quickSort(head ,null);
}
public static ListNode quickSort(ListNode head ,ListNode end){
if(head == end) return head;
ListNode smaller = head ,bigger = head ,cur = head.next;
while (cur != end){
ListNode next = cur.next;
if(cur.val < head.val){//头插
cur.next = smaller;
smaller = cur;
}
else { //尾插
bigger.next = cur;
bigger = cur;
}
cur = next;
}
// 这三句很重要,记住!!!
bigger.next = end;
ListNode node = quickSort(smaller, head);
head.next = quickSort(head.next, end);
return node;
}
}