1.简介
LPA*算法(全称Lifelong Planning A*算法)是由Koenig和Likhachev在2004年提出的,是一种参考人工智能的增量搜索进行改进的A*算法。它被用来处理动态环境下从给定起始点到给定目标点的最短路径问题.
A*算法在此不再赘述.
2. 算法描述
网上有不少博客详细的介绍了论文中的符号和基本算法逻辑, 如:
终身规划A*算法(LPA*):Lifelong Planning A*
在此就不重复介绍论文中的内容, 只强调几个可能困惑的点:
1) 父节点和子节点
子节点 (successors): 节点s的后续节点集合,代表s可以到达的点.
父节点 (predecessors):节点s的前代节点,代表可以到达s的点.
在论文举例中, 由于是无向图, 所以都指向相邻节点.
2) 论文举例中的h (heuristic) 计算
论文中没有明确列出h值的计算, 从例子中可以看出移动时可以走斜线, 所以相邻点为八个方向:
[(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (1, 1), (1, -1), (-1, 1), (-1, -1)]
h值的计算应该取x, y 差值的最大值
h = max(abs(a[0]-b[0]), abs(a[1]-b[1]))3. 伪代码

4. Python代码实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import OrderedDict
class PriorityQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = OrderedDict()
def insert(self, vertex, key):
self.queue[vertex] = key
self.queue = OrderedDict(sorted(self.queue.items(), key=lambda kv: (kv[1][0], kv[1][1])))
def popvertex(self):
first_item = self.queue.popitem(last=False)
return first_item[0]
def topkey(self):
if self.queue:
item = next(iter(self.queue.items()))
return item[1]
else:
return np.inf, np.inf
def remove(self, k):
if k in self.queue:
print('(%s, %s) to remove from priority queue' % (k[0], k[1]))
del self.queue[k]
g = dict()
rhs = dict()
h = dict()
U = PriorityQueue()
# Eight Directions
neighbor_direction = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (1, 1), (1, -1), (-1, 1), (-1, -1)]
def heuristic(a, b):
return max(abs(a[0]-b[0]), abs(a[1]-b[1]))
# # Four Directions
# neighbor_direction = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
# def heuristic(a, b):
# return abs(a[0]-b[0]) + abs(a[1]-b[1])
def get_neighbor(current):
neighbors = list()
for i, j in neighbor_direction:
neighbor = current[0] + i, current[1] + j
if 0 <= neighbor[0] < S.shape[0]:
if 0 <= neighbor[1] < S.shape[1]:
if S[neighbor[0]][neighbor[1]] == 1:
# print('neighbor %s hit wall' % str(neighbor))
continue
else:
# array bound y walls
# print('neighbor %s hit y walls' % str(neighbor))
continue
else:
# array bound x walls
# print('neighbor %s hit x walls' % str(neighbor))
continue
neighbors.append(neighbor)
return neighbors
def update_vertex(s):
print('---update_vertex for (%s, %s)' % (s[0], s[1]))
if s != start:
neighbors = get_neighbor(s)
print('(%s, %s) get neighbors:' % (s[0], s[1]))
print(neighbors)
neighbor_g_c_s = list()
for nb in neighbors:
g_c = g[nb] + heuristic(nb, s)
neighbor_g_c_s.append(g_c)
rhs[s] = min(neighbor_g_c_s)
print('neighbor g_c: %s' % neighbor_g_c_s)
print(rhs[s])
U.remove(s)
if g[s] != rhs[s]:
U.insert(s, calculate_key(s))
def initialize():
print('start initialize...')
for i in range(S.shape[0]):
for j in range(S.shape[1]):
if S[(i, j)] != 1:
g[(i, j)] = np.inf
rhs[(i, j)] = np.inf
rhs[start] = 0
init_h()
U.insert(start, (h[start], 0))
print('Initial U:')
print(U.queue)
print('finish initialize...')
def init_h():
S_shape = S.shape
for i in range(S_shape[0]):
for j in range(S_shape[1]):
if S[(i, j)] != 1:
node = (i, j)
h_calc = heuristic(node, goal)
h[node] = h_calc
def calculate_key(s):
return min(g[s], rhs[s]) + h[s], min(g[s], rhs[s])
def computer_shortest_path():
computer_iteration = 1
while U.topkey() < calculate_key(goal) or rhs[goal] != g[goal]:
print('----------------Iteration #%d----------------' % computer_iteration)
u = U.popvertex()
print('top_vertex (%s, %s)' % (u[0], u[1]))
if g[u] > rhs[u]:
print('overconsistent as (%s, %s) g_value %s > rhs_value %s' % (u[0], u[1], g[u], rhs[u]))
g[u] = rhs[u]
print('set (%s, %s) g_value %s same as rhs_value %s' % (u[0], u[1], g[u], rhs[u]))
neighbors = get_neighbor(u)
for nb in neighbors:
update_vertex(nb)
else:
g[u] = np.inf
neighbors = get_neighbor(u)
for nb in neighbors:
update_vertex(nb)
update_vertex(u)
print(U.queue)
computer_iteration += 1
print('---exit computer shortest path as reach terminate condition---')
def get_path_node():
path_node = list()
path_node.append(goal)
current = goal
while current != start:
nbs = get_neighbor(current)
nbs_rhs_dict = OrderedDict()
for nb in nbs:
nbs_rhs_dict[nb] = rhs[nb]
sorted_nbs_rhs_dict = OrderedDict(sorted(nbs_rhs_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
trace_back_node_rhs = sorted_nbs_rhs_dict.popitem(last=False)
trace_back_node = trace_back_node_rhs[0]
path_node.append(trace_back_node)
current = trace_back_node
return path_node
if __name__ == '__main__':
S = np.array([
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
])
start = (7, 3)
goal = (7, 17)
# S[(7, 12)] = 1
# S[(7, 13)] = 1
# S[(7, 16)] = 1
# S = np.array([
# [0, 0, 0, 0],
# [1, 0, 1, 0],
# [1, 0, 1, 0],
# [1, 0, 1, 0],
# [1, 0, 1, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 0],
# ])
# start = (0, 3)
# goal = (5, 0)
# # # test if there is no route
# # S[(4, 1)] = 1
# # S[(5, 1)] = 1
# # --------------------------------------------
# # this section to test if the environment change
# print()
# print()
# print('--------after update:')
#
# # change_point = (3, 1)
# change_point = (7, 12)
# S[change_point] = 1
# g[change_point] = np.inf
# update_vertex(change_point)
#
# print(U.queue)
# computer_shortest_path()
# # ----------------------------------------------
if rhs[goal] == np.inf:
path_exist = False
else:
path_exist = True
if path_exist:
print()
route = get_path_node()
print('route:')
print(route)
plot_map_and_path = True
if plot_map_and_path:
# plot map and path
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(20, 20))
ax.imshow(S, cmap=plt.cm.Dark2)
ax.scatter(start[1], start[0], marker="o", color="red", s=200)
ax.scatter(goal[1], goal[0], marker="*", color="green", s=200)
if path_exist:
# extract x and y coordinates from route list
x_coords = []
y_coords = []
for k in (range(0, len(route))):
x = route[k][0]
y = route[k][1]
x_coords.append(x)
y_coords.append(y)
ax.plot(y_coords, x_coords, color="black")
ax.xaxis.set_ticks(np.arange(0, S.shape[1], 1))
ax.yaxis.set_ticks(np.arange(0, S.shape[0], 1))
ax.xaxis.tick_top()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
5. 运算结果
以下大约进行大约40多次的迭代
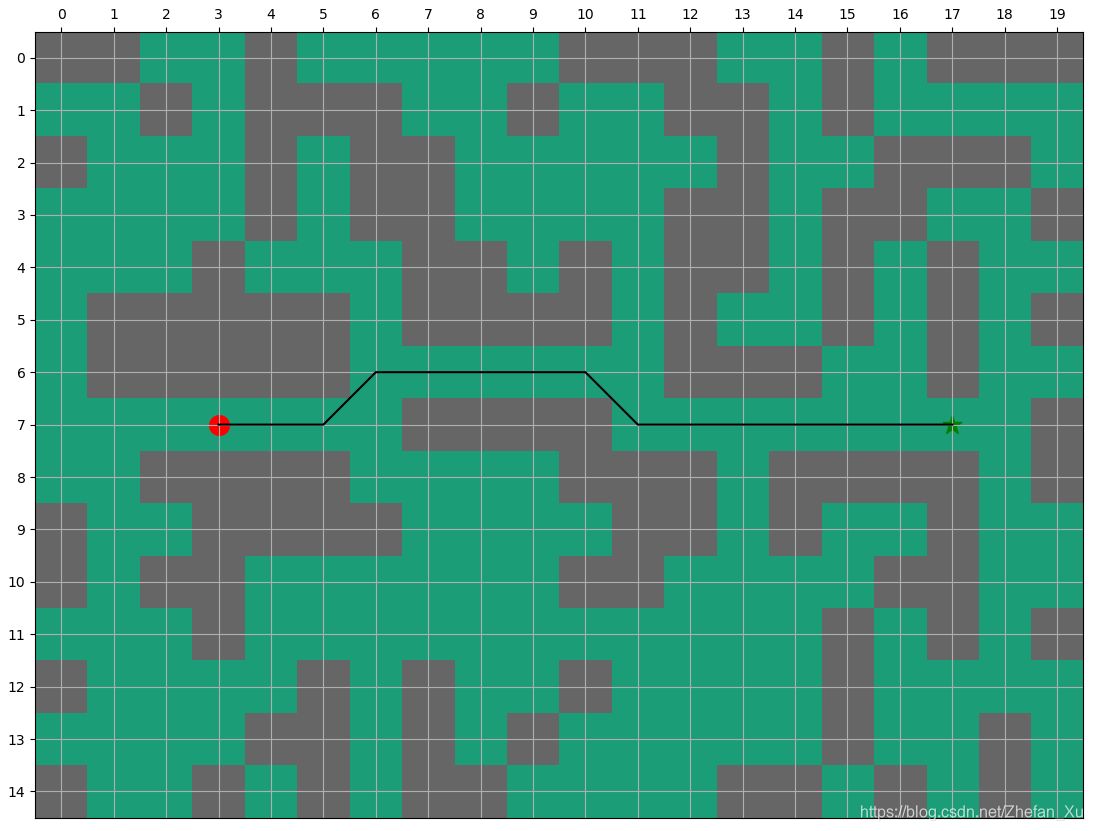
当如论文中所描述环境发生变化, 点(7, 12)有障碍, 如果重新计算大约需要53次迭代.
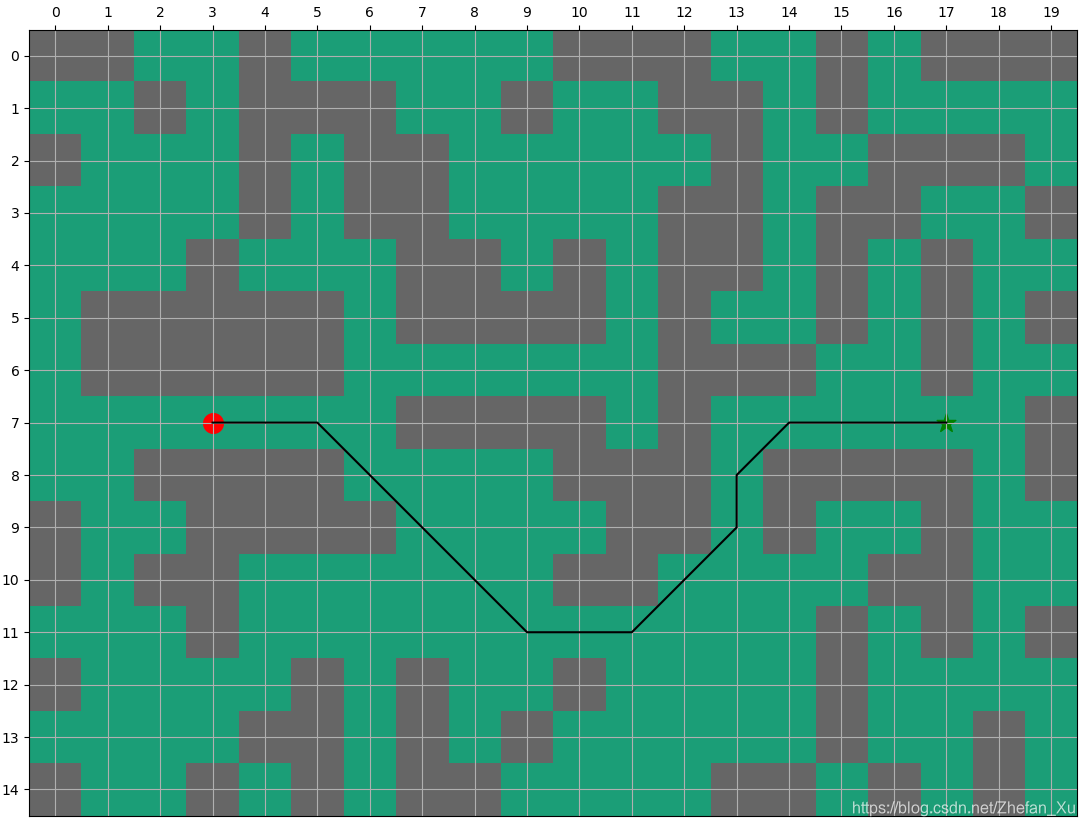
如果已经计算出环境改变之前的路径, 在此基础上继续计算改变的环境, 则需要大约28次迭代, 可以看出要比重新计算所需要的迭代次数更少.
代码中还包含另一个例子, 读者只需要comment掉上图的代码S矩阵, uncomment另一个S矩阵.
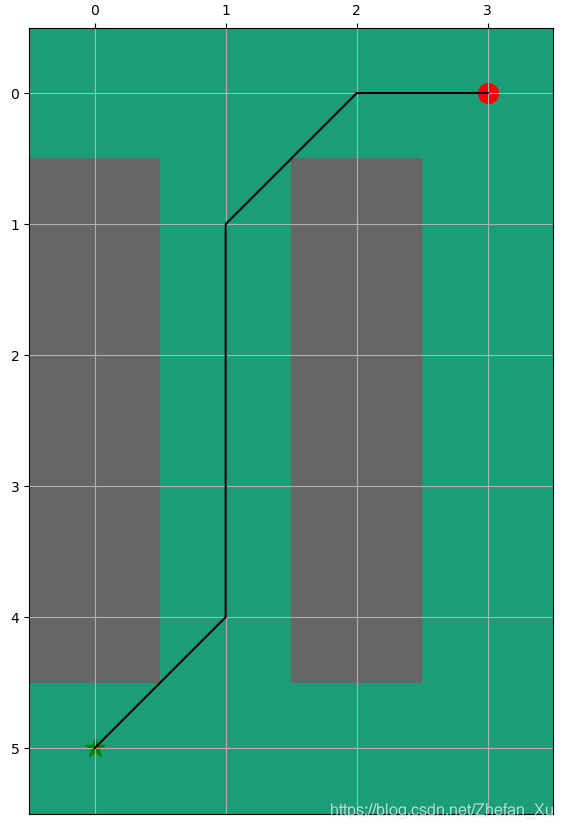
?同时代码提供了如果只允许向四个方向移动, 不允许斜线的相邻矩阵和h值计算.
6. 算法总结
LPA*算法提供了一种解决动态环境下的最短路径搜索方法,但是它针对的是起始点和目标点固定的情况,相比A*算法, 主要保留了能判断环境变化的rhs值.