一.题目描述
给你一个字符串表达式 s ,请你实现一个基本计算器来计算并返回它的值。
整数除法仅保留整数部分。
示例 1:
输入:s = “3+2*2”
输出:7
示例 2:
输入:s = " 3/2 "
输出:1
示例 3:
输入:s = " 3+5 / 2 "
输出:5
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105
s 由整数和算符 (’+’, ‘-’, ‘*’, ‘/’) 组成,中间由一些空格隔开
s 表示一个 有效表达式
表达式中的所有整数都是非负整数,且在范围 [0, 231 - 1] 内
题目数据保证答案是一个 32-bit 整数
二.题目解析
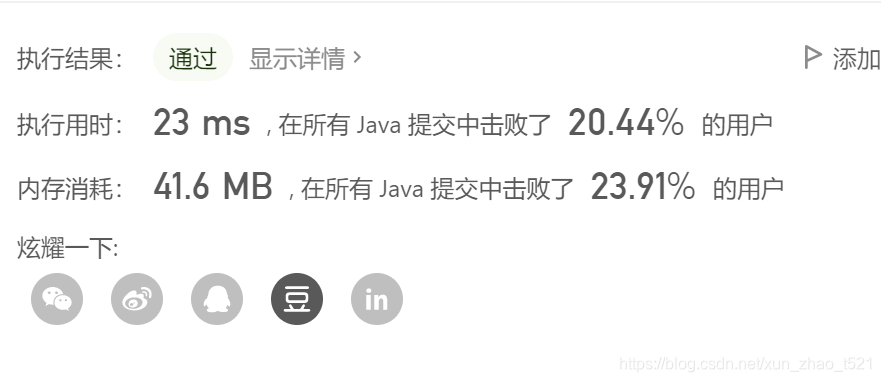
1.双栈法
public static int calculate(String s) {
/*时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
* */
if(s == null || s.length() == 0){
return -1;
}
//!作为终止符,方便读取表达式中的最后一个数
s = s.trim() + "!";
//利用两个栈,一个操作数栈,一个操作符栈
Stack<Integer> operand = new Stack<>();
Stack<Character> operator = new Stack<>();
char cur;
Integer number;
int previous = -1;
int left,right;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
cur = s.charAt(i);
if(cur == ' '){
continue;
}
//每次读到运算符号,获取到这个运算符前面的那个数字,入操作数栈
if(cur == '+' || cur == '-' || cur == '*' || cur == '/' || cur == '!'){
//截取到的字符串可能含有前后空格,需要trim一下
number = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(previous + 1,i).trim());
operand.push(number);
//操作符栈若存在优先级高的运算符,就弹出两个操作数先运算,把结果存入操作数栈
if(!operator.isEmpty() && operator.peek() == '*'){
right = operand.pop();
left = operand.pop();
operand.push(left * right);
operator.pop();
}
if(!operator.isEmpty() && operator.peek() == '/'){
right = operand.pop();
left = operand.pop();
operand.push(left / right);
operator.pop();
}
//无论要不要先运算,当前操作数必须入栈
operator.push(cur);
previous = i;
}
}
int res = 0,rest = 0;
//此时操作符栈中只剩下+-运算符,依次弹出与运算数做运算即可
while (!operand.isEmpty()){
if(operator.isEmpty()){
res += operand.pop();
}else if(operator.peek() == '+'){
operator.pop();
res += operand.pop();
}else if(operator.peek() == '-'){
operator.pop();
res -= operand.pop();
}else{
operator.pop();
}
}
if(operand.isEmpty() && operator.isEmpty()){
return res;
}
return -1;
}
2.单栈法
public static int calculate2(String s) {
/*单栈法,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
* */
if(s == null || s.length() == 0){
return -1;
}
//op表示乘除符号
char op = '#',cur;
//sign表示加减符号
int sign = 1;
int res = 0,number;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] array = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
cur = array[i];
if(cur == ' '){
continue;
}
if(cur >= '0' && cur <= '9'){
number = cur - '0';
int j = i + 1;
//如果当前是数字就一直往下找(数字可能为多位)
while (j <= array.length - 1 && array[j] >= '0' && array[j] <= '9'){
number = number * 10 + (array[j] - '0');
j++;
}
//如果这个数字之前有*或者/那么就弹出一个元素和当前找到的数字先运算
if(op == '*'){
number = stack.pop() * number;
//重置OP
op = '#';
}else if(op == '/'){
number = stack.pop() / number;
op = '#';
}
//将结果进栈
stack.push(number);
//当前j位置即为下次要开始判断的位置,由于for循环后i++,所以置i = j - 1
i = j - 1;
}else if (cur == '+' || cur == '-'){
//遇到+-符号就可计算res了,且当前符号重新赋值sign
res = res + sign * stack.pop();
sign = (cur == '+') ? 1 : -1;
}else if (cur == '*' || cur == '/'){
//遇到乘除符号更新op
op = cur;
}
}
//最后一个数必须单独计算一次
res = res + sign * stack.pop();
return res;
}

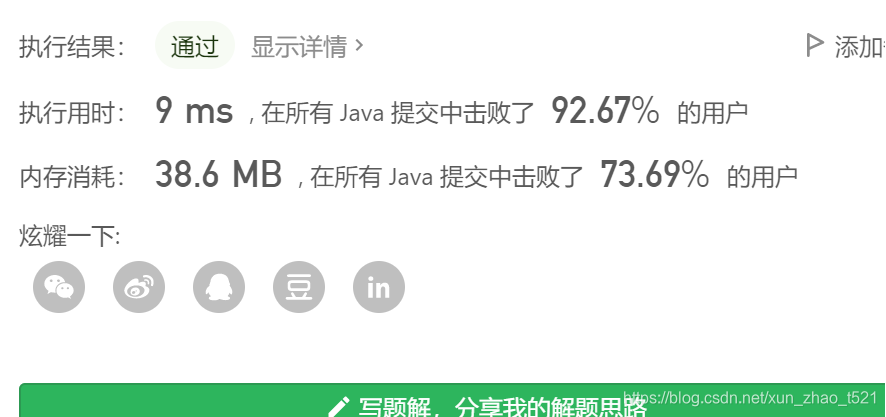
单栈法更简洁的写法:
public int calculate(String s) {
// 保存上一个符号,初始为 +
char sign = '+';
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack<>();
// 保存当前数字,如:12是两个字符,需要进位累加
int num = 0;
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
char cur = s.charAt(i);
if(cur >= '0'){
// 记录当前数字。先减,防溢出
num = num*10 - '0' + cur;
}
//加减乘除空格的ASCII码都小于'0'
//这里|| i == s.length()-1,就不需要再单独计算最后一个数字了
if((cur < '0' && cur !=' ' )|| i == s.length()-1){
// 判断上一个符号是什么
switch(sign){
// 当前符号前的数字直接压栈
case '+': numStack.push(num);break;
// 当前符号前的数字取反压栈
case '-': numStack.push(-num);break;
// 数字栈栈顶数字出栈,与当前符号前的数字相乘,结果值压栈
case '*': numStack.push(numStack.pop()*num);break;
// 数字栈栈顶数字出栈,除于当前符号前的数字,结果值压栈
case '/': numStack.push(numStack.pop()/num);break;
}
// 记录当前符号
sign = cur;
// 数字清零
num = 0;
}
}
// 将栈内剩余数字累加,即为结果
while(!numStack.isEmpty()){
result += numStack.pop();
}
return result;
}
【参考文章】
双栈解决通用表达式问题:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/basic-calculator-ii/solution/shi-yong-shuang-zhan-jie-jue-jiu-ji-biao-c65k/