栈的一个实际需求
请输入一个表达式
计算式:[722-5+1-5+3-3] 点击计算【如下图】
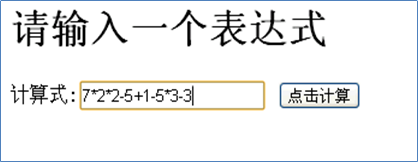
请问: 计算机底层是如何运算得到结果的? 注意不是简单的把算式列出运算,因为我们看这个算式 7 * 2 * 2 - 5, 但是计算机怎么理解这个算式的(对计算机而言,它接收到的就是一个字符串),我们讨论的是这个问题。-> 栈
一、栈的介绍
-
栈的英文为(stack)
-
栈是一个先入后出(FILO-First In Last Out)的有序列表。
-
栈(stack)是限制线性表中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行的一种特殊线性表。允许插入和删除的一端,为变化的一端,称为栈顶(Top),另一端为固定的一端,称为栈底(Bottom)。
-
根据栈的定义可知,最先放入栈中元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶,而删除元素刚好相反,最后放入的元素最先删除,最先放入的元素最后删除
-
出栈(pop)和入栈(push)的概念(如图所示)
- 入栈:
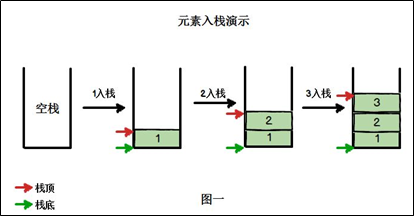
-
出栈:
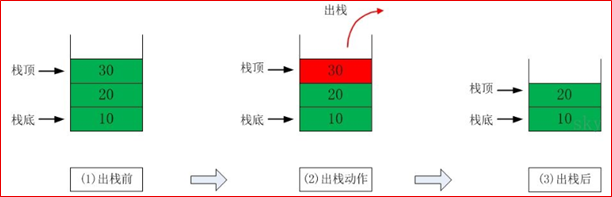
二、栈的应用场景
- 子程序的调用:在跳往子程序前,会先将下个指令的地址存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再将地址取出,以 回到原来的程序中。
- 处理递归调用:和子程序的调用类似,只是除了储存下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆 栈中。
- 表达式的转换[中缀表达式转后缀表达式]与求值(实际解决)。
- 二叉树的遍历。
- 图形的深度优先(depth 一 first)搜索法。
三、栈的快速入门
-
用数组模拟栈的使用,由于栈是一种有序列表,当然可以使用数组的结构来储存栈的数据内容, 下面我们就用数组模拟栈的出栈,入栈等操作。
-
实现思路分析
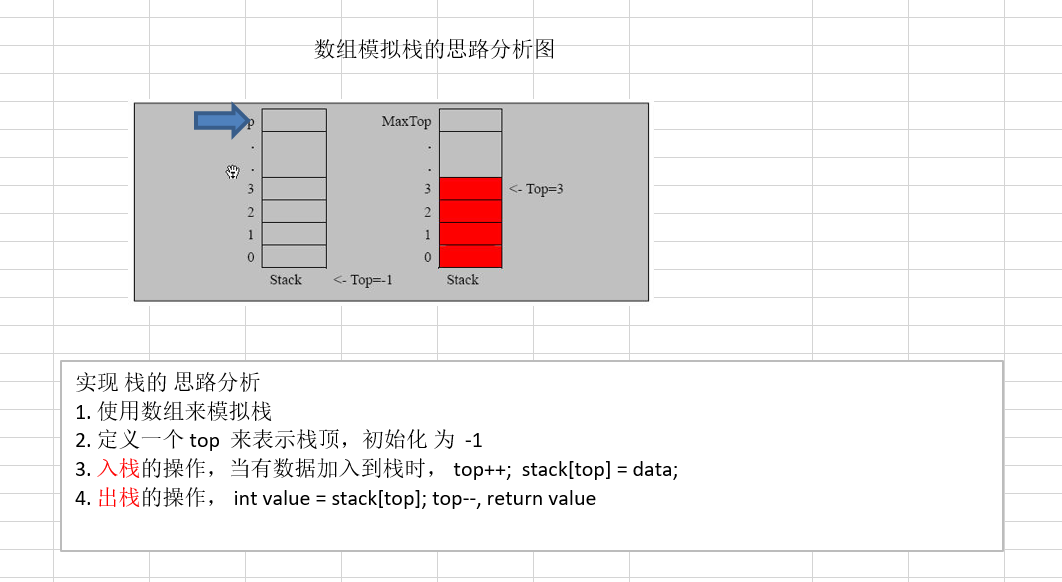
代码实现:
public class ArrayStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一下 ArrayStack 是否正确
//先创建一个 ArrayStack 对象->表示栈
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);
String key = "";
boolean loop = true; //控制是否退出菜单
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(loop) {
System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈");
System.out.println("exit: 退出程序");
System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)");
System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "show":
stack.list();
break;
case "push":
System.out.println("请输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
break;
case "pop":
try {
int res = stack.pop();
System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~~");
}
}
//定义一个 ArrayStack 表示栈
class ArrayStack {
private int maxSize; // 栈的大小
private int[] stack; // 数组,数组模拟栈,数据就放在该数组
private int top = -1;// top 表示栈顶,初始化为-1
//构造器
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
//栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
//栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//入栈-push
public void push(int value) {
//先判断栈是否满
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
//出栈-pop, 将栈顶的数据返回
public int pop() {
//先判断栈是否空
if(isEmpty()) {
//抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据~");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
//显示栈的情况[遍历栈], 遍历时,需要从栈顶开始显示数据
public void list() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据~~");
return;
}
//需要从栈顶开始显示数据
for(int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
关于栈的一个小练习:
课堂练习,将程序改成使用链表来模拟栈
代码实现:
public class LinkedStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedStack stack = new LinkedStack();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
String s;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("输入 s:遍历展示栈");
System.out.println("输入 pop:取出数据");
System.out.println("输入 push:添加数据");
System.out.println("输入 e:退出程序");
s = scanner.next();
switch (s) {
case "s":
stack.showList();
break;
case "pop":
Integer pop = stack.pop();
System.out.println(pop);
break;
case "push":
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
break;
case "e":
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("退出程序!!!");
}
}
class LinkedStack {
private Node node;
public LinkedStack() {
node = new Node();
}
// 是否是空的栈
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.node.getNext() == null;
}
// 入栈
public void push(int value) {
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.setValue(value);
newNode.setNext(this.node.getNext());
this.node.setNext(newNode);
}
// 出栈
public Integer pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空了!!!");
return null;
}
Node next = this.node.getNext();
this.node.setNext(next.getNext());
return next.getValue();
}
// 遍历展示栈
public void showList() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空了!!!");
return;
}
Node temp = this.node.getNext();
while (temp != null) {
System.out.println(temp.getValue());
temp = temp.getNext();
}
}
}
class Node {
// 值
private int value;
// 下一个节点
private Node next;
public Node() {
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}