线性表及实现
**在学习浙江大学的数据结构慕课时,发现了一些问题,在本文章中记录并分享给大家。
在多重链表的表示中有这样一个问题:
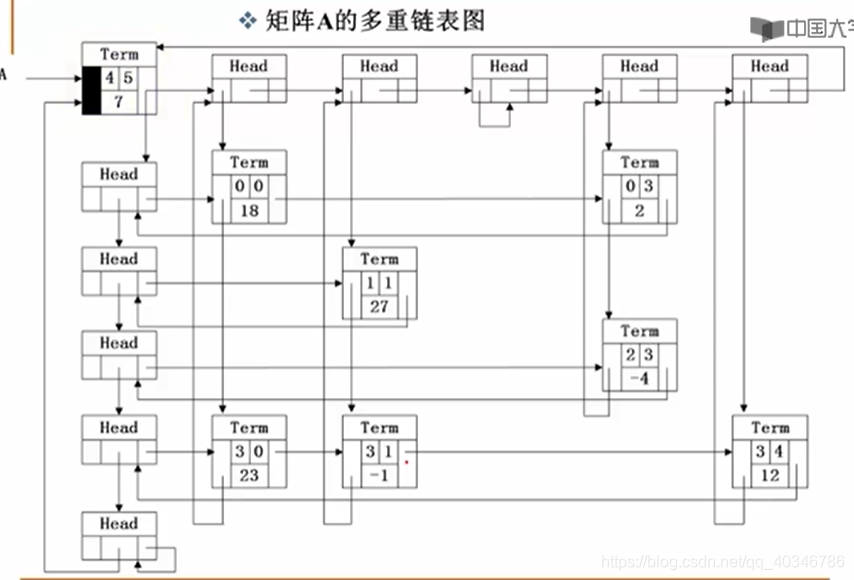

从图中看见表有一个总的头结点存储矩阵的大小和非零元素的个数,同时指向着每行每列的第一个头结点。但实际上第i行第i列的头结点是同一个头结点。第i行第i列的head存储着下i+1行/列的结点指针,也同时存储着第i行的第一个非零元素和第i列的第一个非零元素。因此上面4X5的矩阵一个有5个头结点。
堆栈
在用单向链表实现堆栈时,必须从头结点指针指向top位置,L->next即top位置,可以自由的增删,而不能从尾部,因为尾部无法进行插入操作。
课后习题中有一个堆栈的问题如下:
原题:
Given a stack which can keep M numbers at most. Push N numbers in the order of 1, 2, 3, …, N and pop randomly. You are supposed to tell if a given sequence of numbers is a possible pop sequence of the stack. For example, if M is 5 and N is 7, we can obtain 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 from the stack, but not 3, 2, 1, 7, 5, 6, 4.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 3 numbers (all no more than 1000): M (the maximum capacity of the stack), N (the length of push sequence), and K (the number of pop sequences to be checked). Then K lines follow, each contains a pop sequence of N numbers. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each pop sequence, print in one line “YES” if it is indeed a possible pop sequence of the stack, or “NO” if not.
思考了许久没有什么头绪,只想到是否能用数之间的大小关系来判断,如756这样的顺序是肯定不行的,但又无法解决栈空间不够的问题。在网上搜索发现有一位博主的思路很好,链接如下:
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gxtyx/article/details/105327934
手动用数组实现栈来模拟上面的问题,手动出栈入栈,很方便的解决栈空间的问题,对于顺序的判断也很简单快速。
首先需要将1~N的输入存储起来作为栈输入,然后对顺序输出也需要存储来判断出栈的时机,还需要一个数组模拟栈。代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
/* 02-线性结构4 Pop Sequence (25分) */
#define MAX 1000
int main(void)
{
int arr[MAX], stack[MAX], input[MAX];
int m, n, k, ai = 0, si = 0, ii = 0; /* ai, si, ii分别是数组arr, stack, input的下标 */
scanf("%d %d %d", &m, &n, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) /* 按题目要求生成一个入栈顺序数组1到N */
arr[i-1] = i;
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
ai = 0;
si = -1; /* 这里stack下标初始化为-1是因为在下方进入while循环中会先+1 */
ii = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &input[i]);
while(ai < n)
{
si++;
stack[si] = arr[ai++];
if (si > m - 1) /* 判断是否栈满 */
break;
while(stack[si] == input[ii] && si >= 0) /* 出栈 */
{
si--;
ii++;
}
}
if (si > m - 1 || ii != n)
printf("NO\n");
else
printf("YES\n");
}
return 0;
}
大致思路是,先收集输入和输出,再去push输入直到遇见输出,这时就出栈,在这样的循环下运行直到栈满或者输入以及完全入栈结束。如果是栈满且还在入栈返回NO,如果输入以及完全入栈但输出还没输出完全说明输出序列顺序是错误的,也返回NO。这样就模拟了一个数组的出栈入栈功能,完成了题目的要求。