集合:
Collection(I) + Map(I)
Collection(I)
?? ?| - List(I)
?? ??? ?| - ArrayList(C) - 数组
?? ??? ?| - LinkedList(C) - 双向链表
?? ??? ?| - Vector(C) - 数组
?? ??? ??? ?|- Stack - 作为栈实现
?? ?| - Set(I)
?? ??? ?| - HashSet(C) - 散列表
?? ??? ?| - SortedSet(I)
?? ??? ??? ?| - TreeSet(C) - 二叉树
?? ?| - Queue(I) - 队列
?? ??? ?| - Deque(I) - 双端队列(栈)
?? ??? ??? ?| - LinkedList(C)
Map(I)
? ?? ? ?|- HashMap(C)
? ?? ? ??? ?|- LinkedHashMap(C)
? ?? ? ?|- HashTable(C)
? ?? ? ?|- ConcurrentHashMap(C)
? ?? ? ?|- SortedMap(I)
? ?? ? ??? ?|- TreeMap(C)
Collection
(1)List(I):
? 1)特点:
? ?? ?a.List是有顺序的接口,所以是有序列表,并且可以使用index定位
? ?? ?b.List允许有重复值
? ?? ?c.List中允许有null
? 2)常用API(只要带有index,都是List新增的方法):
? ?? ?void add(int index, E element)
? ?? ?boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
? ?? ?E get(int index)?
? ?? ?int lastIndexOf(Object o)?
? ?? ?E remove(int index)?
? ?? ?E set(int index, E element)?
? ?? ?List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) - 截取子集合
? 3)常见实现类:
? ?? ?(1)ArrayList(C):
? ?? ? ?a.底层数据结构:顺序结构
? ?? ? ?b.底层实现:数组
? ?? ? ?c.特点:
? ?? ? ??? ?①.按照顺序排列,每个元素都带有标号
? ?? ??? ?②.除了有标号是连续的,内存中的物理空间也是连续的
? ?? ? ?d.优缺点:
? ?? ? ??? ?优点: 查询速度快(因为有连续的下标,可以根据下标进行查询)
? ?? ??? ?缺点:?
? ?? ??? ? ?a.插入/删除速度慢(插入/删除都是要移动元素的,所以元素一多就会执行效率慢)
? ?? ??? ? ?b.内存的物理空间是连续的,利用不到碎片空间
用list实现斗地主洗牌和发牌:
ArrayList<String> porkes=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> colors=new ArrayList();
colors.add("黑桃");
colors.add("红心");
colors.add("红桃");
colors.add("梅花");
ArrayList<String> numbers=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 2; i <=10; i++) {
numbers.add(i+"");
}
numbers.add("J");
numbers.add("Q");
numbers.add("K");
numbers.add("A");
for (String color:colors) {
for (String number:numbers) {
String card=color+number;
porkes.add(card);
}
}
porkes.add("大王");
porkes.add("小王");
Collections.shuffle(porkes);
ArrayList<String> player1=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> player2=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> player3=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> dipai=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < porkes.size(); i++) {
String card = porkes.get(i);
if (i >= 51) {
dipai.add(card);
} else {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
player1.add(card);
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
player2.add(card);
} else {
player3.add(card);
}
}
}
System.out.println(player1);
System.out.println(player2);
System.out.println(player3);
System.out.println(dipai);?(2)Vector(C)
? ? ? a.底层数据结构:顺序结构
? ? ? b.底层实现:数组
? ? ? c.特点:
? ? ? ?? ?①.全部和ArrayList一样
? ? ? ?? ?②.Vector上带有线程同步锁(synchronized),所以是线程安全的,效率低
? ? ? d.优缺点:
? ? ? ?? ?全部和ArrayList一样
(3)LinkedList(C)
? ? ? a.底层数据结构:链式结构
? ? ? b.底层实现:Node节点(data[数据] + next[下一个节点的引用])
? ? ? c.特点:
? ? ? ?? ?①.LinkedList是双向链表
? ? ? ?? ?①.链表是内存中固定顺序,但是他的物理空间不连续
?? ? ??? ?②.没有下标
?? ? ??? ?③.所有节点的访问,都必须通过头节点(next)/尾节点(pre)
?? ? ??? ?④.head(头节点): 只存next,不存data
?? ? ??? ? ?last(尾节点): 只存pre,不存data
?? ? ??? ?⑤.head.next = null -> 空链表
?? ? ??? ? ?last.pre = null -> 空链表
?? ? ?d.优缺点:
?? ? ??? ?优点:?
? ?? ??? ? ?a.插入/删除效率高
? ?? ??? ? ?b.不需要连续的内存物理空间,所以空间利用率高
? ?? ??? ?缺点:
? ?? ??? ?查询效率低,只能从头节点出发开始查询
? ?? ? ?e.LinkedList独有的API:
? ? ? ? ? ?
Set(I) - 和Collection中的API完全一致
?1.特点:
??? ?a.Set集合截取Map(映射表)
??? ?b.Set集合的物理空间是不连续的,添加没有顺序(不是随机)
??? ?c.Set集合不允许有重复值,值是唯一的
??? ?d.使用equals()判断元素是否重复
?2.实现类
??? ?1).HashSet(C)
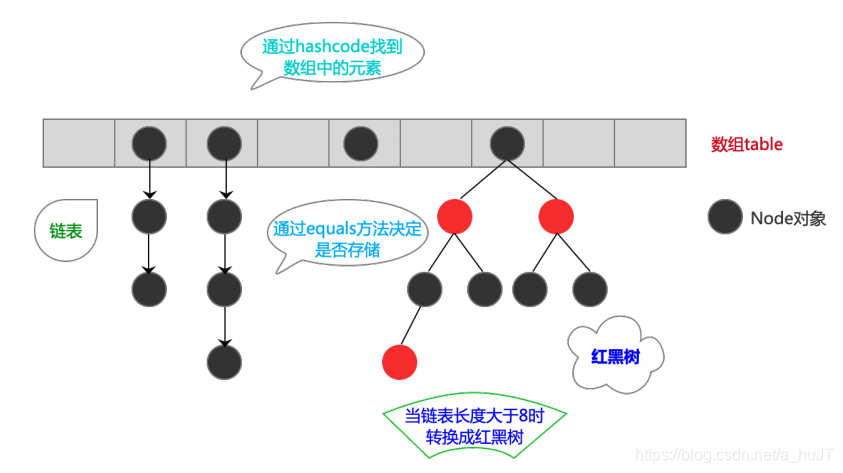
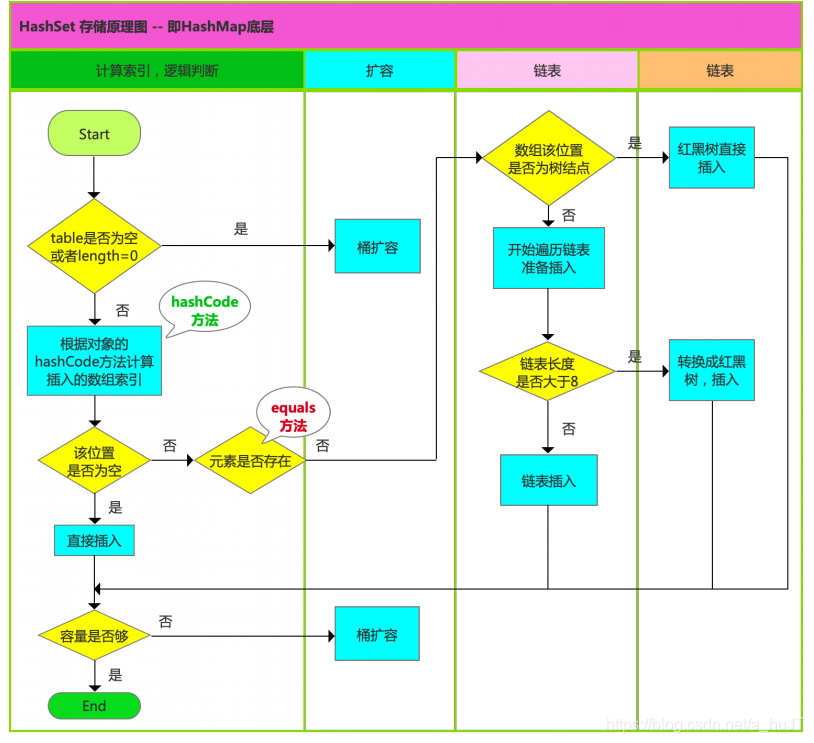
??? ? ?(1).存储过程?
??? ? ??? ?a.调用自身的hashCode()计算存储位置
??? ? ??? ?b.如果该位置上没有元素,则直接存入
??? ? ??? ?c.如果该位置上有元素,则调用equals()和该位置上所有元素进行比较
??? ? ??? ?d.如果相同,则不存入
??? ? ??? ?e.如果不相同,则存入该链表的末尾
JDK1.8之后
?
??? ? ?(2)结论:
??? ? ??? ?a. hashCode() 和 equals() 必须一起重写
??? ? ??? ?b. equals() 判断两个相同的对象,hashCode()必须一致
??? ? ??? ?c. equals判断两个不相等的对象, hashCode值尽量不等
??? ? ??? ?d. 在同一个类中,基本可以忽略hashCode值尽量不等的情况.
?
Queue(I) - 队列
? 1.底层实现:基于数组或者链表实现
? 2.特点:
? ?? ?a.先进先出(后进后出)
? ?? ?b.队列也是线性结构,有顺序的,但是本身没有标号
? 3.常用API:
? ?? ?offer() - 向队列尾部追加元素
? ?? ?poll() - 向队列头部取出元素(出队列)
? ?? ?peek() - 向队列头部获取元素(队列不变)
? 4.Deque(I) - 可以作为双端队列/栈
? ?? ?1).底层实现:基于数组或者链表实现
? ?? ?2).特点:
? ?? ??? ?a.作为双端队列 - 先进先出
? ?? ??? ? ?作为栈 - 先进后出
? ?? ??? ?b.只能通过方法区分是队列/栈
? ?? ?3).常用API:
? ?? ??? ?作为双端队列:
? ?? ??? ? ? 带有First()/Last()的方法
? ?? ??? ?作为栈:
? ?? ??? ??? ?push() - 压栈
? ?? ??? ??? ?pop() - 弹栈