二叉树的遍历
1. “144. 二叉树的前序遍历”

递归解法:
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
ans.add(root.val);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
迭代解法:
我们先看一下前序遍历。
前序遍历是中左右,每次先处理的是中间节点,那么先将跟节点放入栈中,然后将右孩子加入栈,再加入左孩子。
为什么要先加入 右孩子,再加入左孩子呢? 因为这样出栈的时候才是中左右的顺序。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
ans.add(cur.val);
if (cur.right != null) {
stack.push(cur.right);
}
if (cur.left != null) {
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
2. “145. 二叉树的后序遍历”
递归解法:
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
ans.add(root.val);
}
}
迭代解法:
先序遍历是中左右,后续遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
ans.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
stack.push(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
stack.push(cur.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(ans);
return ans;
}
}
3. “94. 二叉树的中序遍历”
递归解法:
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
ans.add(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
迭代解法:
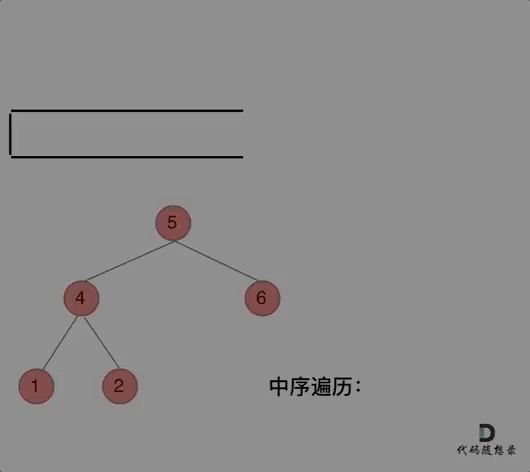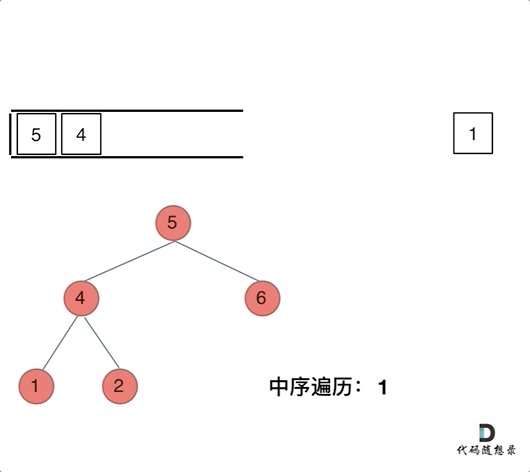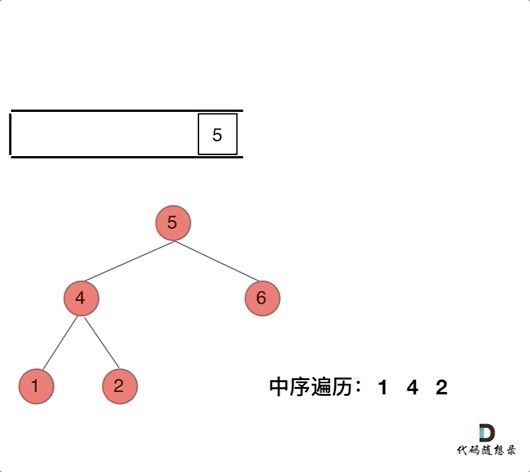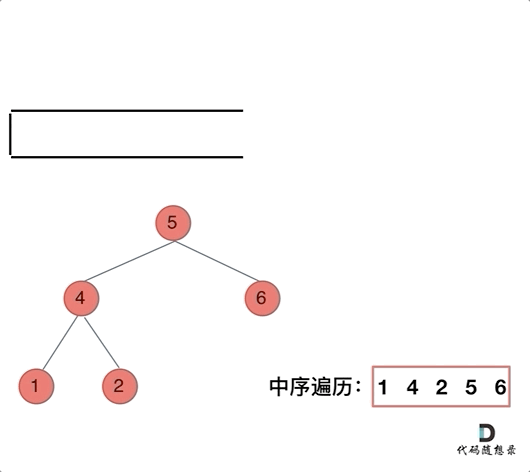
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
} else {
root = stack.pop();
ans.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
4. “102. 二叉树的层序遍历”
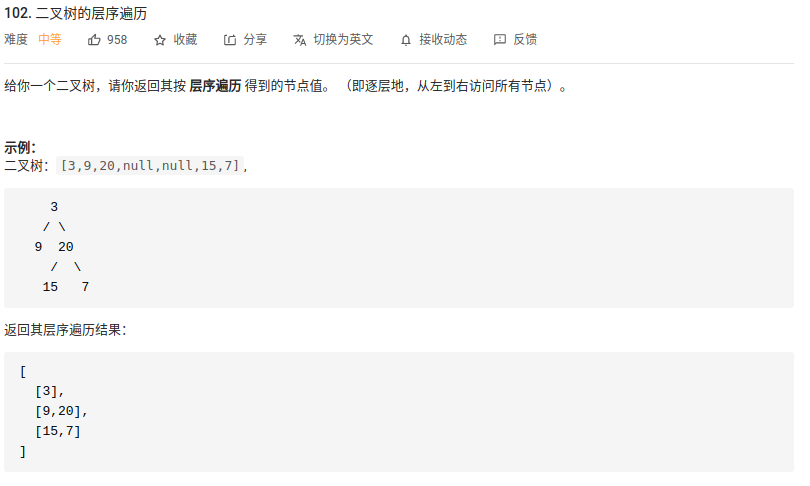
层序遍历思路大概是现将节点放入队列中,再将这些节点取出,再将这些节点的儿子节点放入队列中
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
int n = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
level.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
ans.add(level);
}
return ans;
}
}