一、集合框架的组成
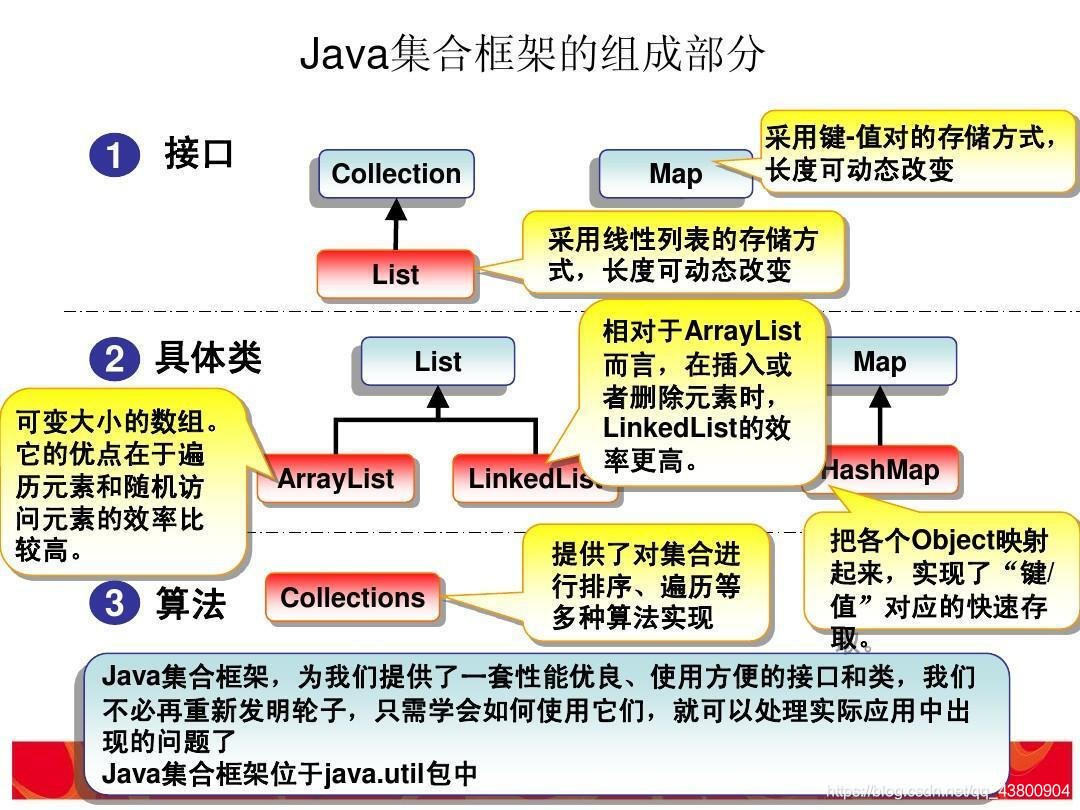
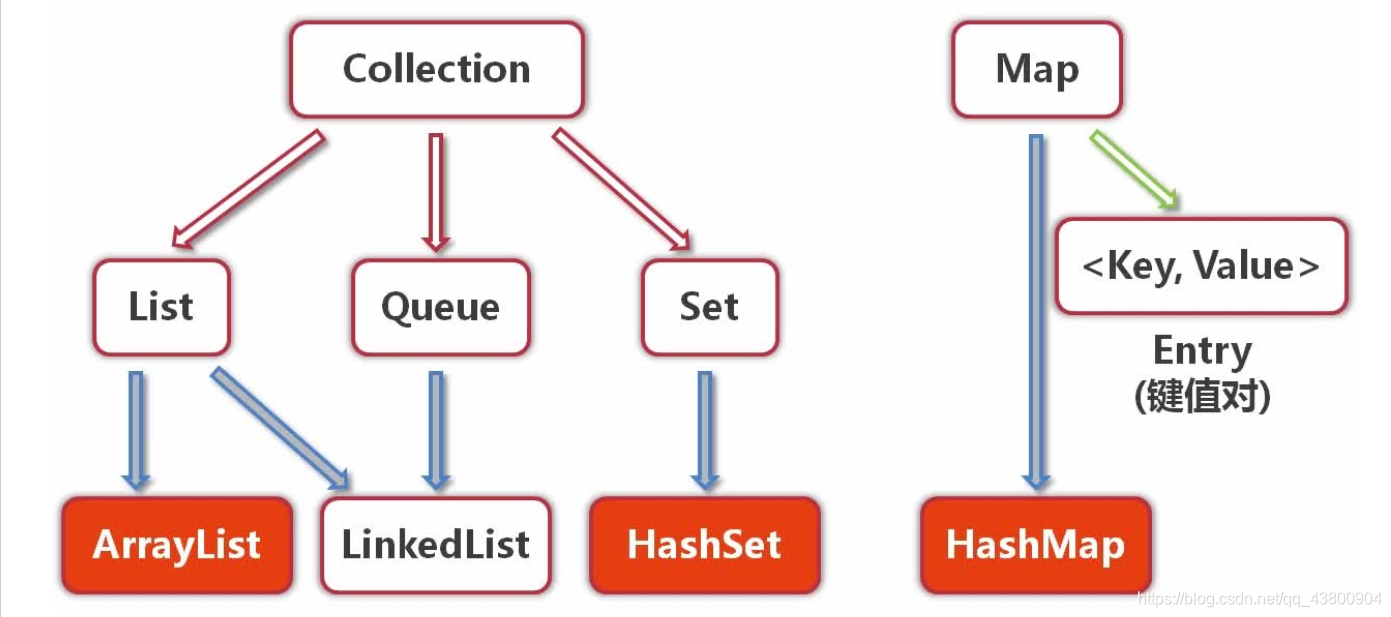
1.接口也可以继承接口
collection、list、map等都是接口 且都能被继承
2.ArrayList和LinkedList
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于链表的数据结构。
2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
ArrayList:ArrayList内部是使用可増长数组实现的,所以是用get和set方法是花费常数时间的,但是如果插入元素和删除元素,除非插入和删除的位置都在表末尾,否则代码开销会很大,因为里面需要数组的移动。
LinkedList:LinkedList是使用双链表实现的,所以get会非常消耗资源,除非位置离头部很近。但是插入和删除元素花费常数时间。
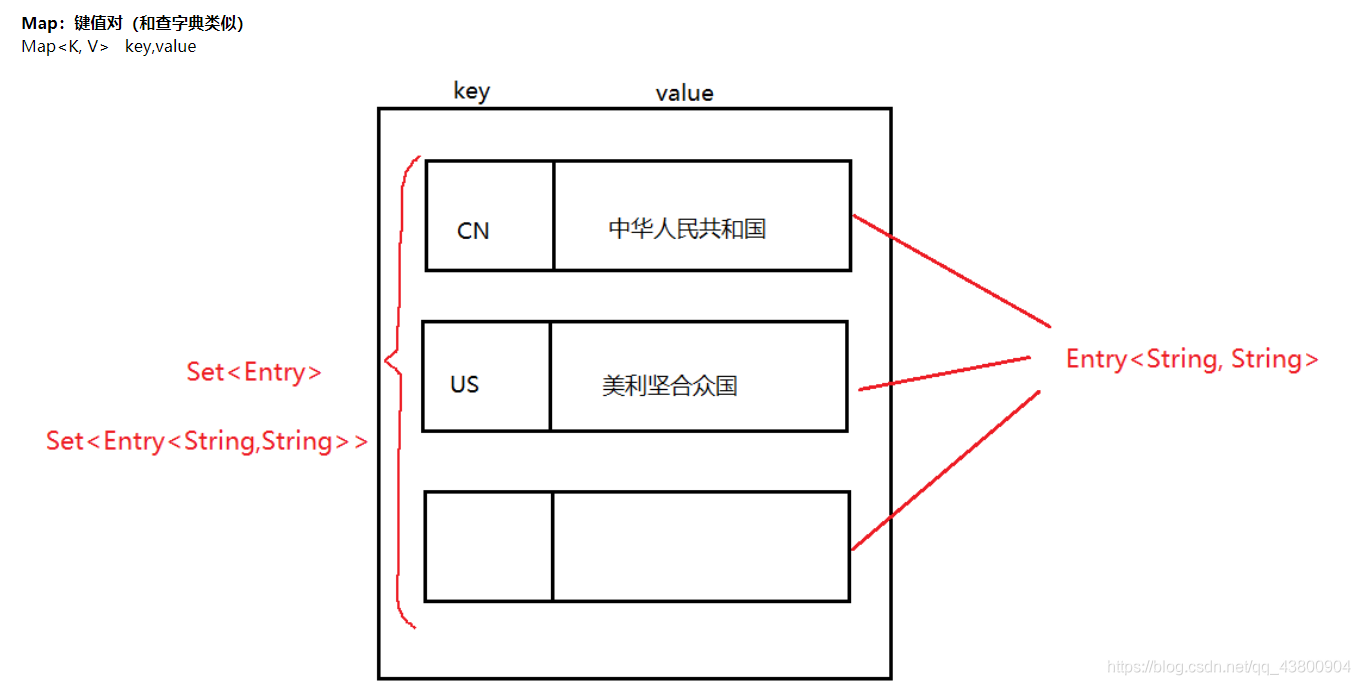
3.MAP
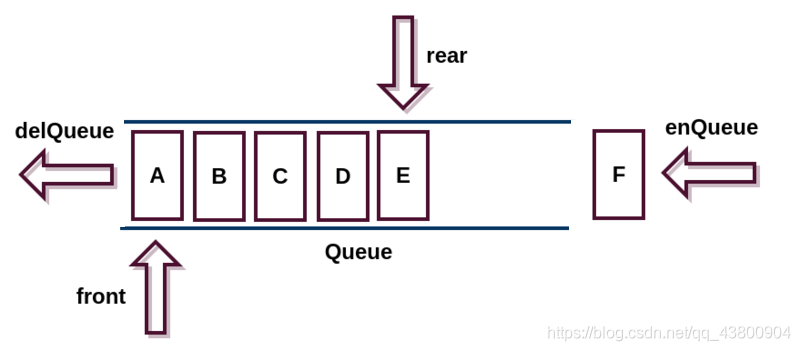
4.队列
队列:Queue先进先出 FIFO Firt In First Out
例如:客服电话、12306排队买票、滴滴打车
二、使用
1.ArrayList HashSet HashMap
ArrayList:
@Test
public void test2(){
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();// ArrayList后面不加< >,表示可以加任意类型的
list.add(12323);
list.add("sadasd");
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(12313123);
list.add(23);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list1);
}
ArrayList HashSet HashMap:
@Test
public void test3(){
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList();
Student student1 = new Student(1, "zhansgan1", 23, "男",12313.0);
Student student2 = new Student(2, "zhansgan1", 23, "男",12313.0);
Student student3 = new Student(3, "zhansgan1", 23, "男",12313.0);
arrayList.add(student1);
arrayList.add(student2);
arrayList.add(student3);
arrayList.add(student1);
arrayList.add(student1);
for (Student student : arrayList) {
System.out.println(student);
}
//ArrayList
//Hashset 和ArrayList差不多 但是 Hashset不能有重复的数据
System.out.println("--------------");
HashSet<Student> set = new HashSet<Student>();
set.add(student1);
set.add(student2);
set.add(student1);
set.add(student3);
set.add(student3);
for (Student student : set) {
System.out.println(student);
}
Hashset 和ArrayList差不多 但是 Hashset不能有重复的数据
ArrayList和LinkedList的大致区别如下:
ArrayList: 有序(放进去顺序和拿出来顺序一致),可重复
HashSet: 无序(放进去顺序和拿出来顺序不一定一致),不可重复
2.MAP
entry :条目 封装成一个类
// Entry:条目,是对key-value封装
// Map.Entry<String, String> entry;
entrySet()
//Map
@Test
public void test6(){
Map<String,String> map =new HashMap();
map.put("cn","中国");
map.put("us","阿美");
map.put("uk","小英");
// Entry:条目,是对key-value封装
// Map.Entry<String, String> entry;
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> set = map.entrySet();//entrySet 是entry组成的一个set集合
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("--------------------");
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> set1 = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : set1) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//可以直接便利Key值
Set<String> strings = map.keySet();
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string+" "+map.get(string));
}
}