总结:二叉树的前中后序遍历递归实现属于easy题,非递归实现属于midium或hard题,后续遍历非递归比较难懂,题解看不懂,就找视频看不懂的点,然后自己演算一遍,就比较好懂
递归实现:
前序遍历? ?根左右
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static void preOrderRecur(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
}中序遍历? ? ? ?左根右
class Solution {
public static void preOrderRecur(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
preOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
}后序遍历? ? ? ?左右根
class Solution {
public static void preOrderRecur(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
}非递归实现(迭代解法)
前序遍历:本质上是在模拟递归,因为递归也是调用了系统栈
思路:后进先出,先压入右节点,再压入左节点
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)
return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
stack.add(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.right!=null)
stack.push(node.right);
if(node.left!=null)
stack.push(node.left);
}
return list;
}
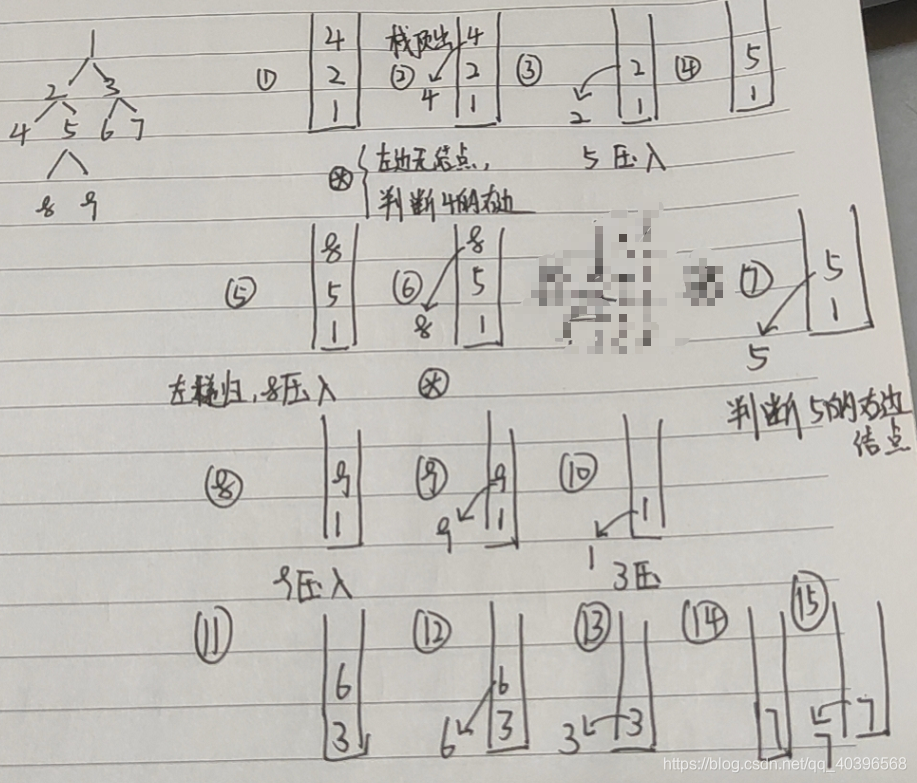
}中序遍历:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(root!=null || !stack.isEmpty())
{
while(root!=null)//根节点左边递归压入
{
if(root!=null)
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}
//左边到底,取出根节点,判断其右节点,对右节点进行左递归压入,最外层while的由来
//循环条件 节点存在但未压入,节点不存在,但栈中仍有节点
root=stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
root=root.right;
}
return list;
}
}什么是二叉树的中序遍历?遍历从左孩子节点开始,依次是左中右,如果左孩子还有孩子节点,则进行递归遍历,遍历顺序依然是左、中、右
先想清楚,或者草稿纸演算出整个过程,再写代码?
?后序遍历【比较正经的遍历方式】

class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode preNode=null;
while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
{
while(root!=null)
{
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}
root=stack.pop();
if(root.right==null || root.right==preNode)
{
list.add(root.val);
preNode=root;
root=null;
}
else
{
stack.push(root);
root=root.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}不正经的后序遍历方式,通过改变前序遍历的方式? 使其为根右左,再将集合翻转即为左右根
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)
return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
{
root=stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
if(root.left!=null)
stack.push(root.left);
if(root.right!=null)
stack.push(root.right);
}
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
}