在map中,有个重要的方法,就是put。 多线程环境中,put值的时候,也是最容易出现线程安全的问题。接下来就看看concurrentHashMap中的put方法。
1.put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
2.接下来主要看看putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent)方法
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
2.1) 多线程环境下.在进入该方法中,初始化阶段, k和v 不能为null
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
2.2)初始化 binCount; binCount 为0 时,node可以直接放着;当为2时,表示当前桶位可能转为红黑树
int binCount = 0;
2.3) 接下来就是for循环的自旋 table 引用map对象的table
在这里,有几个初始化变量
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
这几个变量的分别作用和含义表示
f:表示桶位的头结点
n: 表示散列表数组的长度
i: 表示key通过寻址计算后,得到的桶位下标
fn: 表示桶位结点的hash值
在这个for循环里面,有4种逻辑作用:
CASE 1: 该条件成立,表示 当前map的table未初始化
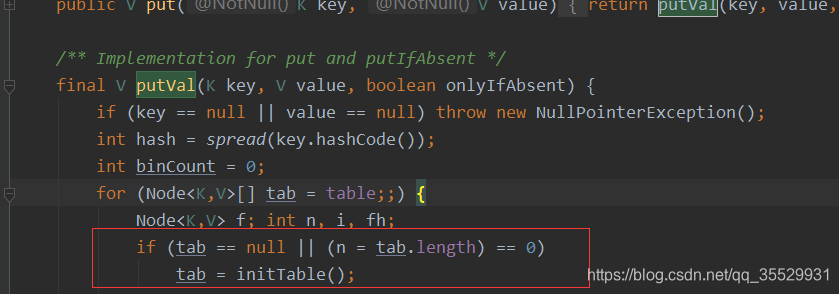
CASE 2: 表示key使用路由寻址算法得到key对应 table数组的下标位置,tableAt获取指定桶位的头结点,头结点是 null

CASE 3:头结点一定不是null, 它的成立条件,表示当前桶位的头结点为FWD节点,表示当前节点正在扩容中。

CASE 4: 当前桶位可能是链表,可能是红黑树
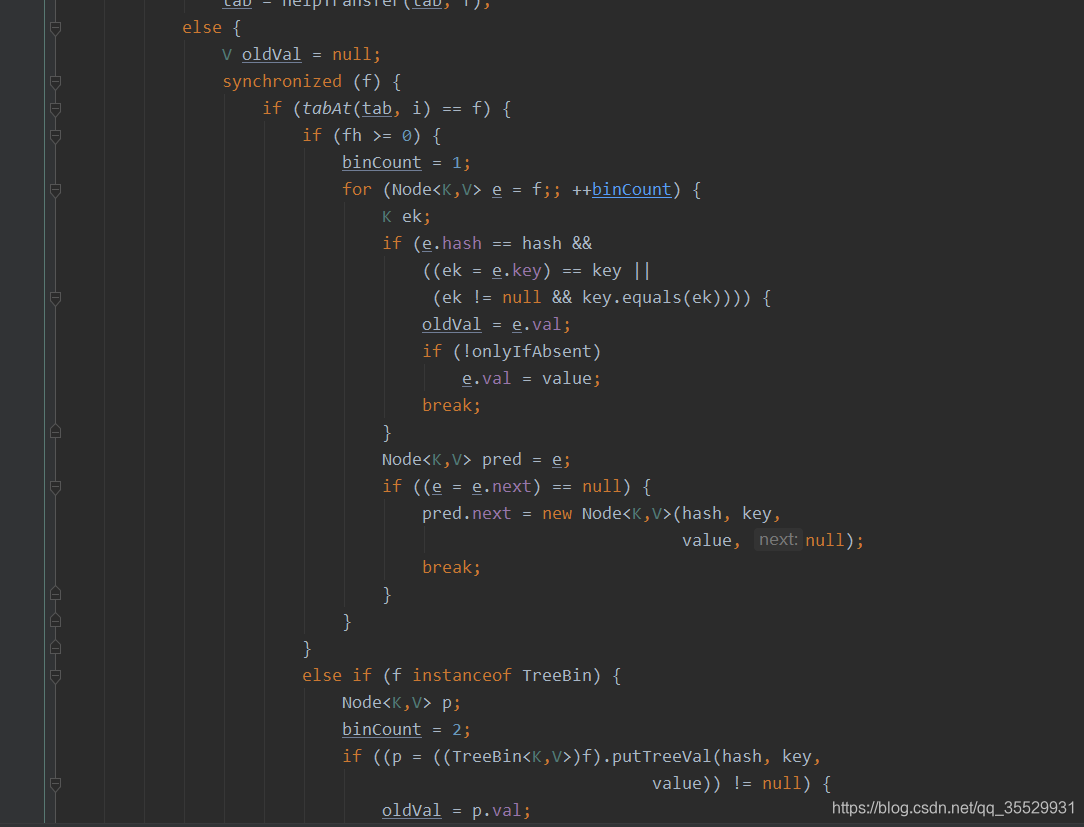
先通过 synchronized 给该条件的进行加锁。
加锁后,又进行 一次对比。避免其他线程将该桶位的头结点修改掉。
在达到满足条件后,又进行了一次for循环的处理, e是每次循环处理的节点。
1.当循环的节点和当前插入节点的key一致时,发生了冲突, 就会进行替换,并跳出该次循环。
2.当前元素和插入元素key不一致时,就会继续走这段程序。
如果满足以下条件,表面是进行红黑树转换的操作

当该次synchronized结束后,会对binCount 不为0的进行一次处理。 将链表的结构转为红黑树。

最后通过addCount()方法,进行统计当前table一共有多少数据,及判断是否达到扩容阈值标准,触发扩容。 具体的该方法,下次再详细描述。
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// 初始化阶段,控制k和v 不能为 null
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 通过spread方法,可以让高位也参与进寻址算法
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
// binCount 表示当前k-v 封装成为Node后插入到指定桶位后,再桶位中的所属链表的下标位置
// 0表示当前桶位为 null , node可以直接放着
// 2 表示当前桶位已经树化为了红黑树
int binCount = 0;
// 自旋 tab 引用map对象的 table
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
// f 表示桶位的头结点
// n 表示散列表数组的长度
// i 表示key通过寻址计算后,得到的桶位下标
// fh 表示桶位结点的hash值
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// CASE 1: 成立,当前map中的table未初始化...
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// CASE2: 表示key使用路由寻址算法得到key对应 table数组的下标位置
// tableAt 获取指定桶位的头结点, f
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// 进入到 CASE 2代码块,前置条件: 当前table数组的i桶位 一定是 null时
// 通过使用CAS方式,设置指定i桶位为 new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null), 且期望值为null
//CAS操作成功,返回oK,直接break; 如果失败,表示在当前线程之前已经有其他线程先进入了 向i桶位设置值了。
// 当前线程只能再次自旋,去走其他逻辑
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// CASE 3: 前置条件: 头结点一定不是 null
// 条件成立,表示当前桶位的头结点为 FWD结点,表示目前 map 正处于扩容中
// 先赋值,再判断
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
// 看到fw结点后,当前节点有义务帮助当前map对象完成迁移数据的工作
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
// CASE 4: 当前桶位 可能是 链表 也可能是红黑树 代理结点 TreeBin
else {
// 当插入 key 存在时,会将旧值赋值给 oldVal,返回给put方法调用处......
V oldVal = null;
// 先加锁, 通过使用sync 加锁"头结点",理论上是"头结点"
synchronized (f) {
// 对比了下,是否是加锁的头结点
// 为什么又要对比一下,当前桶位的头结点是否为之前获取的头结点?
// 为了避免其他线程将该桶位的头结点修改掉,调至从当前线程从sync 加锁就有问题。
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 条件成立,说明加锁的对象 是OK的。
// 当fh > 0 条件成立,说明当前桶位就是普通链表
if (fh >= 0) {
// 1.当前插入key 与链表当中所有的元素的key 都不一致时,当前的插入操作时追加到链表的末尾,binCount 表示链表长度
// 2.当前插入的key 与链表当中的某个key一时,当前插入操作可能是替换了, binCount表示冲突位置(binCount -1)
binCount = 1;
// 迭代循环当前桶位链表,e是每次循环处理节点。
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
// 当前循环节点 key
K ek;
// 条件一: e.hash = hash 成立,表示循环的当前元素hash值与插入节点的hash值一致,需要进一步判断
// 条件二: ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
// 成立:说明循环的节点和当前插入的节点的key 一致,发生了冲突
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
// 将当前循环的元素的值 赋值给 oldVal
oldVal = e.val;
//
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
// 进行替换,跳出循环
e.val = value;
break;
}
// 当前元素 与 插入的元素的key 不一致,会走下面的程序
// 1. 更新循环 节点 为当前节点的下一个节点
// 2. 判断下一个节点是否为null ,如果是 null,说明当前节已经是队尾了,插入数据需要追加到队尾节点的后面
// 如果 e.next 不为空,则继续循环走,直到找到最后一个。
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 前置条件: 该桶位一定不是链表了
// 如果条件成立,当前桶位是红黑树的代理操作节点
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
// p 表示红黑树中如果与你插入的节点 key 有冲突的话, 则 putTreeVal 方法会返回冲突节点的引用
Node<K,V> p;
// 强制设置 binCount 为 2, 因为 binCount <= 1时,有其他含义,在addCount要用到。
binCount = 2;
// 往红黑树中插入一个节点的方法,如果插入成功,返回 null。
// 条件一,成立。说明当前插入的节点key 与红黑树的某个节点key一致,冲突了
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
// 将冲突的节点 赋值给 oldVal
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 说明当前桶位不为null, 可能是红黑树,也可能是链表
if (binCount != 0) {
// 如果binCount >= 8 ,表示处理的桶位一定是链表
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
// 调用转换链表 为红黑树的方法
treeifyBin(tab, i);
// 说明当前线程插入的数据key ,与原有的k-v发生了冲突,需要将元数据v返回给调用者
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 1.统计当前 table 一共有多少数据
// 2.判断是否达到扩容阈值标准,触发扩容。
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}