前言
在半年之前写过一篇关于无向图的构建以及相关常用算法的实现 → 图的构建以及BFS(广度优先搜索)、DFS(深度优先搜索)、普里姆最小生成树算法、并查集与kruskal算法
,近日对这些算法进行了一个回顾,并且对其中的代码进行了全面的优化。
无向图构建
还是以之前的无向城市图为例:
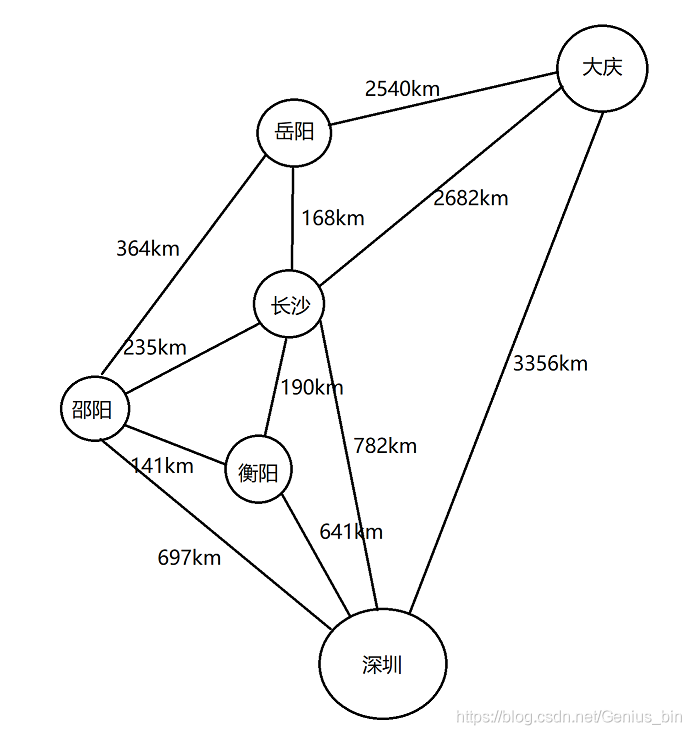
上图列出了城市间的连通关系以及城市间的距离信息,下面的算法将围绕这张图进行展开。
使用临接矩阵表示无向图
在计算机中可以通过使用一些比较精妙的方式例如临界表或者临接矩阵来表示图中各节点的连接关系。笔者更加偏向于使用 临接矩阵。
体现代码中是通过我们手动传入一个装有城市间信息的数组,然后将这些信息体现到矩阵中。
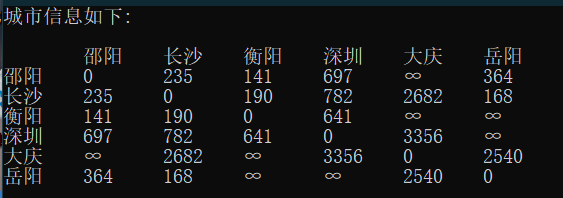
| Relation of Citys | 邵阳 | 长沙 | 衡阳 | 深圳 | 大庆 | 岳阳 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 邵阳 | 0 | 235 | 141 | 697 | INF | 364 |
| 长沙 | 235 | 0 | 190 | 782 | 2682 | 168 |
| 衡阳 | 141 | 190 | 0 | 641 | INF | INF |
| 深圳 | 697 | 190 | 641 | 0 | 3356 | INF |
| 大庆 | INF | 2682 | INF | 3356 | 0 | 2540 |
| 岳阳 | 364 | 168 | INF | INF | 2540 | 0 |
注: 数字表示城市间的距离,单位km;INF 为 infinite 的缩写,表示城市间并不直接相连。
class Graph {
public:
int cityNum;
vector<string> cityName;//存储所有的城市名
unordered_map<string, int> cityIndex;//kv: 城市名对应的编号
vector<vector<int>> cityInf;//城市间关系矩阵
};
以上为创建图会使用到的变量以及容器。
cityNum : 记录城市数量
cityName : 存储所有的城市名
cityIndex : 通过城市名查找对应的城市索引
cityInf : 临接矩阵
void Graph::createGraph(vector<string>& citys, vector<cityRel*>& cityRelation) {
cityNum = citys.size();
for (auto& city : citys)//数组拷贝
cityName.push_back(city);
/*将cityInf空间设置为 cityNum行,列同行*/
cityInf.resize(cityNum);
for (auto& city : cityInf)
city.resize(cityNum, INFINITE);//默认设置为不可到达
//对每一个城市进行编号,存储到哈希表中
int index = 0;
for (string& city : citys) {
cityIndex[city] = index;
++index;
}
//城市间的信息转换到临界矩阵中
for (auto& city : cityRelation) {
//起始城市索引
int startIndex = cityIndex[city->startCity];
//终止城市索引
int endIndex = cityIndex[city->endCity];
//两城市距离
int distance = city->distance;
//由于是无向图,所以两个方向都需要添加上
cityInf[startIndex][endIndex] = distance;
cityInf[endIndex][startIndex] = distance;
}
//到自身的距离设置为 0
for (int i = 0; i < cityInf.size(); ++i)
cityInf[i][i] = 0;
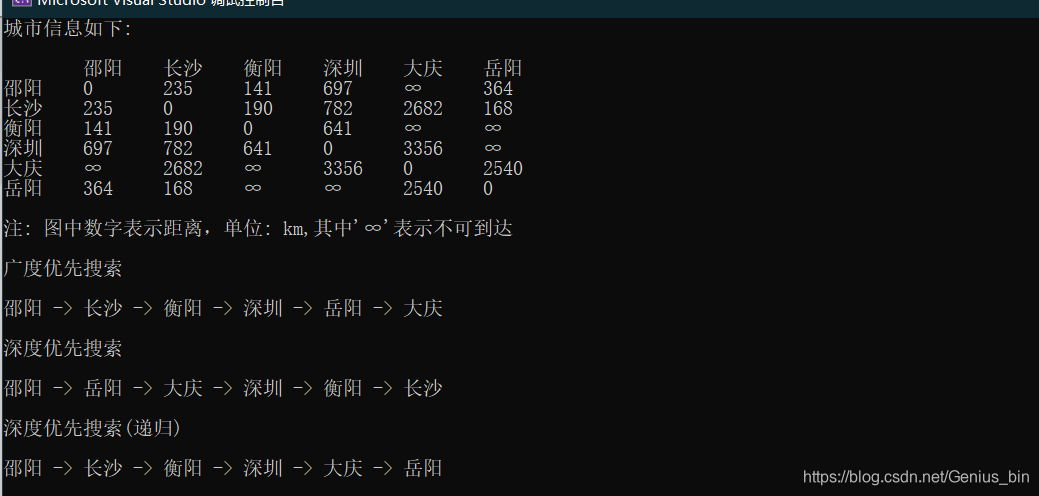
cout << "城市信息如下:\n\n";
//输出临界矩阵
for (auto& city : citys) {
cout << "\t" << city;
}cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cityInf.size(); ++i) {
cout << citys[i] << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < cityInf[i].size(); ++j) {
if (cityInf[i][j] == INFINITE)//无穷大
cout << "\t∞";
else
cout << "\t" << cityInf[i][j];
}cout << endl;
}
cout << "\n注: 图中数字表示距离,单位: km,其中'∞'表示不可到达" << endl;
}
创建后的临接矩阵如下:
∞ 使用一个宏定义来表示:
#define INFINITE 99999999
图的遍历
BFS广度优先
广度以及深度搜索的代码非常相似,只是使用的数据结构有一丢丢差别。直接放上代码
void Graph::BFS(string startCity) {
queue<int> que;
que.push(cityIndex[startCity]);
//记录城市的访问情况: 避免重复加入
vector<bool> visited(cityNum, false);
vector<int> path;
while (que.empty() == 0) {
int cur = que.front();
que.pop();
path.push_back(cur);
visited[cur] = true;
for (int next = 0; next < cityInf.size(); ++next) {
//能够到达且没被加入过
if (visited[next] == false && cityInf[cur][next] > 0 && cityInf[cur][next] != INFINITE) {
que.push(next);
visited[next] = true;//表示已经访问
}
}
}
cout << "\n广度优先搜索\n\t" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; ++i) {
cout << cityName[path[i]] << " -> ";
}
cout << cityName[path[cityNum - 1]] << endl;
}
DFS深度优先
使用STL库中的stack容器实现:
void Graph::DFS(string startCity) {
stack<int> stk;
stk.push(cityIndex[startCity]);
//记录城市的访问情况: 避免重复加入
vector<bool> visited(cityNum, false);
vector<int> path;
while (stk.empty() == 0) {
int cur = stk.top();
stk.pop();
path.push_back(cur);
visited[cur] = true;
for (int next = 0; next < cityInf.size(); ++next) {
//能够到达且没被加入过
if (visited[next] == false && cityInf[cur][next] > 0 && cityInf[cur][next] != INFINITE) {
stk.push(next);
visited[next] = true;//表示已经访问
}
}
}
cout << "\n深度优先搜索\n\t" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; ++i) {
cout << cityName[path[i]] << " -> ";
}
cout << cityName[path[cityNum - 1]] << endl;
}
递归实现:
void Graph::recurDFS(string startCity, vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& path) {
if (path.size() >= cityName.size() - 1) {
//注意,这里在装满所有城市之后不会再进入递归
//此时就差最后一个城市未装入,startCity即为该城市
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; ++i) {
cout << cityName[path[i]] << " -> ";
}
//将最后一个城市输出即可
cout << cityName[cityIndex[startCity]] << endl;
return;
}
int cur = cityIndex[startCity];
visited[cur] = true;
path.push_back(cur);
for (int next = 0; next < cityNum; ++next) {
if (visited[next] == false && cityInf[cur][next] > 0 && cityInf[cur][next] != INFINITE) {
visited[next] = true;
recurDFS(cityName[next], visited, path);
}
}
}
最优二叉生成树
Prim算法
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const Edge* a, const Edge* b) {
return a->distance > b->distance;
}
};
void Graph::primAlgorithm(string startCity) {
int num = cityNum - 1;
int cur = cityIndex[startCity];
vector<bool> visited(cityNum, false);
priority_queue<Edge*, vector<Edge*>, cmp> minEdge;
while (num) {
int minDis = INT_MAX, minNext = -1;//记录最小的距离点
visited[cur] = true;
for (int next = 0; next < cityNum; ++next) {
int nextDis = cityInf[cur][next];
if (visited[next] == false && nextDis != INFINITE && nextDis > 0) {
Edge* newEdge = new Edge(cur, next, cityInf[cur][next]);
minEdge.push(newEdge);//放入最小堆
}
}
while (1) {
Edge* edge = minEdge.top();
minEdge.pop();
if (visited[edge->startCity] == false || visited[edge->endCity] == false) {
//两个点当中只要有一点是第一次访问,那么加入其中进行比较
primEdges.push_back(edge);
cur = edge->endCity;//寻找与该点相连的这些边
break;
}
}
--num;
}
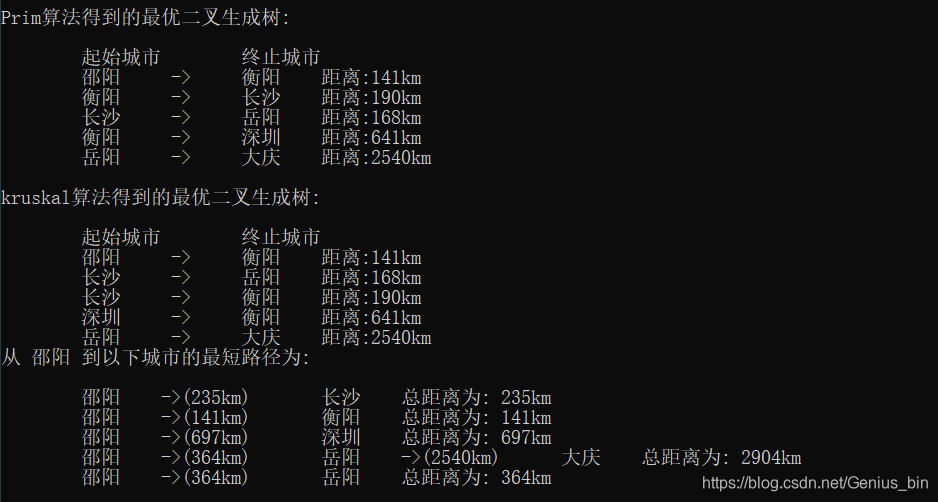
cout << "\nPrim算法得到的最优二叉生成树:\n\n\t起始城市\t终止城市\n";
for (int i = 0; i < primEdges.size(); ++i) {
cout << "\t" << cityName[primEdges[i]->startCity] << "\t ->\t"
<< cityName[primEdges[i]->endCity] << "\t距离:" << primEdges[i]->distance << "km" << endl;
}
}
Kruskal算法
在实现该算法之前需要了解并查集是怎么回事?
推荐一篇非常好的博客:
用故事讲并查集(简单易懂)
并查集结构体定义
struct Node {
string name;
Node(string name) :name(name) {}
};
class Union {
public:
unordered_map<string, Node*> nameToNode;//每个城市对应的节点位置
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> nameLeader;//key:需要寻找"队长"的城市,value:上一级节点
unordered_map<Node*, int> leadNum;//key:队长 value:队伍中成员数量
void init(vector<string>& city);//初始化城市节点
Node* findCaptain(string name);
bool inSameSet(string name1, string name2);
void uniteTwoTeam(string name1, string name2);
vector<int> pre;
};
并查集函数实现
void Union::init(vector<string>& city){
for (int i = 0; i < city.size(); ++i) {
Node* node = new Node(city[i]);
nameToNode[city[i]] = node;//node name哈希表
nameLeader[node] = node;//初始时领导为自己
leadNum[node] = 1;//自成一队,队员数量为1
}
}
Node* Union::findCaptain(string name){
Node* node = nameToNode[name];
vector<Node*> allNode;//收集寻找队长路径上的所有节点
while(node != nameLeader[node]) {
allNode.push_back(node);
node = nameLeader[node];//往上查找
}
for (auto& nodeOnRoad : allNode) {
//将路径上的所有节点都与 "队长" 相连
nameLeader[nodeOnRoad] = node;//node此时已经是队长节点
}
return node;
}
bool Union::inSameSet(string name1, string name2){
Node* captain1 = findCaptain(name1);
Node* captain2 = findCaptain(name2);
return captain1 == captain2;
}
void Union::uniteTwoTeam(string name1, string name2){
Node* captain1 = findCaptain(name1);
Node* captain2 = findCaptain(name2);
if (captain1 == captain2)
return;//已经是一个队长了
int num1 = leadNum[captain1];
int num2 = leadNum[captain2];
Node* smallTeam = num1 > num2 ? captain2 : captain1;//将较小的队伍合并到大队伍中
Node* bigTeam = smallTeam == captain1 ? captain2 : captain1;
nameLeader[smallTeam] = bigTeam;
leadNum[bigTeam] += leadNum[smallTeam];
leadNum.erase(smallTeam);//原来的队伍将被撤销
}
利用并查集实现Kruskal算法
void Graph::kruskalAlgorithm() {
//每次将距离最短的边加入
priority_queue < Edge*, vector<Edge*>, cmp> minEdge;
for (int i = 0; i < cityInf.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cityInf[i].size(); ++j) {
if (cityInf[i][j] > 0 && cityInf[i][j] != INFINITE) {
Edge* edge = new Edge(i, j, cityInf[i][j]);
minEdge.push(edge);
}
}
}
//选择权值最小且不在并查集中的 边
int times = cityName.size() - 1;//共需要取出 times 次
Union ufset;
ufset.init(cityName);
while (times) {
Edge* edge = minEdge.top();
minEdge.pop();
string startCity = cityName[edge->startCity];
string endCity = cityName[edge->endCity];
if (ufset.findCaptain(startCity) != ufset.findCaptain(endCity)) {
kruskalEdges.push_back(edge);//加入结果集
ufset.uniteTwoTeam(startCity, endCity);//加入之后合并两个队伍
--times;
}
}
cout << "\nkruskal算法得到的最优二叉生成树:\n\n\t起始城市\t终止城市\n";
for (int i = 0; i < primEdges.size(); ++i) {
cout << "\t" << cityName[kruskalEdges[i]->startCity] << "\t ->\t"
<< cityName[kruskalEdges[i]->endCity] << "\t距离:" << kruskalEdges[i]->distance << "km" << endl;
}
}
Dijkstra最短路径算法
几月前写过一篇该算法的实现代码,贴一下 Dijkstra算法求解无向图一点到其他各点的最短路径
void Graph::dijkstra(string startCity) {
//求解startCity到其余各城市的最短距离
vector<pair<int,int>> matrix(cityNum);//记录各个城市的信息 first表示前驱城市,
//初始化第一行:第一次选择 startCity作为永久节点
int cur = cityIndex[startCity];
dijkstraPath.push_back(cur);
int next = -1, minDis = INT_MAX;//寻找下一个永久节点
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; ++i) {
//永久节点到自己的距离为 0 前驱节点设这位
matrix[i].first = cur;
matrix[i].second = cityInf[cur][i];
if (matrix[i].second < minDis && i != cur) {
minDis = matrix[i].second;
next = i;
}
}
unordered_set<int> hasJoin;
hasJoin.insert(cur);//永久节点无虚再次访问
cur = next, minDis = INT_MAX;
int row = 1;
while (hasJoin.size() < cityNum) {
hasJoin.insert(cur);
dijkstraPath.push_back(cur);//加入路径中
for (int col = 0; col < cityNum; ++col) {
if (hasJoin.count(col))
continue;//加入过的节点 或者 永久节点无法到达 那么直接跳过
int curDis = cityInf[cur][col] + matrix[cur].second;
if (curDis < matrix[col].second) {
//找到更短路径,更新
matrix[col].first = cur;
matrix[col].second = curDis;
}
if (matrix[col].second < minDis) {//寻找下一个永久节点
minDis = min(minDis, matrix[col].second);
next = col;
}
}
cur = next;
minDis = INT_MAX;
++row;
}
//回溯过程 通过数组往回找这些节点的更新路径
int index = matrix.size() - 1;
int start = cityIndex[startCity];
cout << "从 " << startCity << " 到以下城市的最短路径为:\n\n";
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
//回退到顶点的位置
vector<int> path;
if (i == start)
continue;
int cur = i;
do {
path.push_back(cur);
cur = matrix[cur].first;
} while (cur != start);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
cout << "\t" << startCity << "\t->(" << cityInf[start][path[0]] << "km)" << "\t";
for (int j = 0; j < path.size() - 1; ++j) {
cout << cityName[path[j]] << "\t->(" << cityInf[path[j]][path[j + 1]] << "km)\t";
}
cout << cityName[path[path.size() - 1]] << "\t总距离为: " << matrix[i].second << "km" << endl;
}
}
完整代码
Graph.h
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define INFINITE 99999999
struct Edge {
int startCity;
int endCity;
int distance;
Edge(int start, int end, int dis) :startCity(start), endCity(end), distance(dis) {}
};
struct cityRel {
string startCity;
string endCity;
int distance;
cityRel(string s, string e, int d) :startCity(s), endCity(e), distance(d) {}
};
class Graph {
public:
void createGraph(vector<string>& citys, vector<cityRel*>& cityRelation);
void BFS(string startCity);
void DFS(string startCity);
void recurDFS(string startCity, vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& path);
void primAlgorithm(string startCity);//普里姆算法
void kruskalAlgorithm();
void dijkstra(string startCity);
int cityNum;
vector<string> cityName;//存储所有的城市名
unordered_map<string, int> cityIndex;//kv: 城市名对应的编号
vector<vector<int>> cityInf;//城市间关系矩阵
vector<Edge*> primEdges;//存储通过普利姆算法得到的边
vector<Edge*> kruskalEdges;//存储通过普利姆算法得到的边
vector<int> dijkstraPath;//存储迪杰斯特拉最短路径的装入顺序
};
struct Node {
string name;
Node(string name) :name(name) {}
};
class Union {
public:
unordered_map<string, Node*> nameToNode;//每个城市对应的节点位置
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> nameLeader;//key:需要寻找"队长"的城市,value:上一级节点
unordered_map<Node*, int> leadNum;//key:队长 value:队伍中成员数量
void init(vector<string>& city);//初始化城市节点
Node* findCaptain(string name);
bool inSameSet(string name1, string name2);
void uniteTwoTeam(string name1, string name2);
vector<int> pre;
};
Graph.cpp
#include "Graph.h"
void Graph::createGraph(vector<string>& citys, vector<cityRel*>& cityRelation) {
cityNum = citys.size();
for (auto& city : citys)//数组拷贝
cityName.push_back(city);
/*将cityInf空间设置为 cityNum行,列同行*/
cityInf.resize(cityNum);
for (auto& city : cityInf)
city.resize(cityNum, INFINITE);//默认设置为不可到达
//对每一个城市进行编号,存储到哈希表中
int index = 0;
for (string& city : citys) {
cityIndex[city] = index;
++index;
}
//城市间的信息转换到临界矩阵中
for (auto& city : cityRelation) {
//起始城市索引
int startIndex = cityIndex[city->startCity];
//终止城市索引
int endIndex = cityIndex[city->endCity];
//两城市距离
int distance = city->distance;
//由于是无向图,所以两个方向都需要添加上
cityInf[startIndex][endIndex] = distance;
cityInf[endIndex][startIndex] = distance;
}
//到自身的距离设置为 0
for (int i = 0; i < cityInf.size(); ++i)
cityInf[i][i] = 0;
cout << "城市信息如下:\n\n";
//输出临界矩阵
for (auto& city : citys) {
cout << "\t" << city;
}cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cityInf.size(); ++i) {
cout << citys[i] << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < cityInf[i].size(); ++j) {
if (cityInf[i][j] == INFINITE)//无穷大
cout << "\t∞";
else
cout << "\t" << cityInf[i][j];
}cout << endl;
}
cout << "\n注: 图中数字表示距离,单位: km,其中'∞'表示不可到达" << endl;
}
void Graph::BFS(string startCity) {
queue<int> que;
que.push(cityIndex[startCity]);
//记录城市的访问情况: 避免重复加入
vector<bool> visited(cityNum, false);
vector<int> path;
while (que.empty() == 0) {
int cur = que.front();
que.pop();
path.push_back(cur);
visited[cur] = true;
for (int next = 0; next < cityInf.size(); ++next) {
//能够到达且没被加入过
if (visited[next] == false && cityInf[cur][next] > 0 && cityInf[cur][next] != INFINITE) {
que.push(next);
visited[next] = true;//表示已经访问
}
}
}
cout << "\n广度优先搜索\n\t" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; ++i) {
cout << cityName[path[i]] << " -> ";
}
cout << cityName[path[cityNum - 1]] << endl;
}
void Graph::DFS(string startCity) {
stack<int> stk;
stk.push(cityIndex[startCity]);
//记录城市的访问情况: 避免重复加入
vector<bool> visited(cityNum, false);
vector<int> path;
while (stk.empty() == 0) {
int cur = stk.top();
stk.pop();
path.push_back(cur);
visited[cur] = true;
for (int next = 0; next < cityInf.size(); ++next) {
//能够到达且没被加入过
if (visited[next] == false && cityInf[cur][next] > 0 && cityInf[cur][next] != INFINITE) {
stk.push(next);
visited[next] = true;//表示已经访问
}
}
}
cout << "\n深度优先搜索\n\t" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; ++i) {
cout << cityName[path[i]] << " -> ";
}
cout << cityName[path[cityNum - 1]] << endl;
}
void Graph::recurDFS(string startCity, vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& path) {
if (path.size() >= cityName.size() - 1) {
//注意,这里在装满所有城市之后不会再进入递归
//此时就差最后一个城市未装入,startCity即为该城市
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; ++i) {
cout << cityName[path[i]] << " -> ";
}
//将最后一个城市输出即可
cout << cityName[cityIndex[startCity]] << endl;
return;
}
int cur = cityIndex[startCity];
visited[cur] = true;
path.push_back(cur);
for (int next = 0; next < cityNum; ++next) {
if (visited[next] == false && cityInf[cur][next] > 0 && cityInf[cur][next] != INFINITE) {
visited[next] = true;
recurDFS(cityName[next], visited, path);
}
}
}
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const Edge* a, const Edge* b) {
return a->distance > b->distance;
}
};
void Graph::primAlgorithm(string startCity) {
int num = cityNum - 1;
int cur = cityIndex[startCity];
vector<bool> visited(cityNum, false);
priority_queue<Edge*, vector<Edge*>, cmp> minEdge;
while (num) {
int minDis = INT_MAX, minNext = -1;//记录最小的距离点
visited[cur] = true;
for (int next = 0; next < cityNum; ++next) {
int nextDis = cityInf[cur][next];
if (visited[next] == false && nextDis != INFINITE && nextDis > 0) {
Edge* newEdge = new Edge(cur, next, cityInf[cur][next]);
minEdge.push(newEdge);//放入最小堆
}
}
while (1) {
Edge* edge = minEdge.top();
minEdge.pop();
if (visited[edge->startCity] == false || visited[edge->endCity] == false) {
//两个点当中只要有一点是第一次访问,那么加入其中进行比较
primEdges.push_back(edge);
cur = edge->endCity;//寻找与该点相连的这些边
break;
}
}
--num;
}
cout << "\nPrim算法得到的最优二叉生成树:\n\n\t起始城市\t终止城市\n";
for (int i = 0; i < primEdges.size(); ++i) {
cout << "\t" << cityName[primEdges[i]->startCity] << "\t ->\t"
<< cityName[primEdges[i]->endCity] << "\t距离:" << primEdges[i]->distance << "km" << endl;
}
}
void Graph::kruskalAlgorithm() {
//每次将距离最短的边加入
priority_queue < Edge*, vector<Edge*>, cmp> minEdge;
for (int i = 0; i < cityInf.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cityInf[i].size(); ++j) {
if (cityInf[i][j] > 0 && cityInf[i][j] != INFINITE) {
Edge* edge = new Edge(i, j, cityInf[i][j]);
minEdge.push(edge);
}
}
}
//选择权值最小且不在并查集中的 边
int times = cityName.size() - 1;//共需要取出 times 次
Union ufset;
ufset.init(cityName);
while (times) {
Edge* edge = minEdge.top();
minEdge.pop();
string startCity = cityName[edge->startCity];
string endCity = cityName[edge->endCity];
if (ufset.findCaptain(startCity) != ufset.findCaptain(endCity)) {
kruskalEdges.push_back(edge);//加入结果集
ufset.uniteTwoTeam(startCity, endCity);//加入之后合并两个队伍
--times;
}
}
cout << "\nkruskal算法得到的最优二叉生成树:\n\n\t起始城市\t终止城市\n";
for (int i = 0; i < primEdges.size(); ++i) {
cout << "\t" << cityName[kruskalEdges[i]->startCity] << "\t ->\t"
<< cityName[kruskalEdges[i]->endCity] << "\t距离:" << kruskalEdges[i]->distance << "km" << endl;
}
}
void Graph::dijkstra(string startCity) {
//求解startCity到其余各城市的最短距离
vector<pair<int,int>> matrix(cityNum);//记录各个城市的信息 first表示前驱城市,
//初始化第一行:第一次选择 startCity作为永久节点
int cur = cityIndex[startCity];
dijkstraPath.push_back(cur);
int next = -1, minDis = INT_MAX;//寻找下一个永久节点
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; ++i) {
//永久节点到自己的距离为 0 前驱节点设这位
matrix[i].first = cur;
matrix[i].second = cityInf[cur][i];
if (matrix[i].second < minDis && i != cur) {
minDis = matrix[i].second;
next = i;
}
}
unordered_set<int> hasJoin;
hasJoin.insert(cur);//永久节点无虚再次访问
cur = next, minDis = INT_MAX;
int row = 1;
while (hasJoin.size() < cityNum) {
hasJoin.insert(cur);
dijkstraPath.push_back(cur);//加入路径中
for (int col = 0; col < cityNum; ++col) {
if (hasJoin.count(col))
continue;//加入过的节点 或者 永久节点无法到达 那么直接跳过
int curDis = cityInf[cur][col] + matrix[cur].second;
if (curDis < matrix[col].second) {
//找到更短路径,更新
matrix[col].first = cur;
matrix[col].second = curDis;
}
if (matrix[col].second < minDis) {//寻找下一个永久节点
minDis = min(minDis, matrix[col].second);
next = col;
}
}
cur = next;
minDis = INT_MAX;
++row;
}
//回溯过程 通过数组往回找这些节点的更新路径
int index = matrix.size() - 1;
int start = cityIndex[startCity];
cout << "从 " << startCity << " 到以下城市的最短路径为:\n\n";
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
//回退到顶点的位置
vector<int> path;
if (i == start)
continue;
int cur = i;
do {
path.push_back(cur);
cur = matrix[cur].first;
} while (cur != start);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
cout << "\t" << startCity << "\t->(" << cityInf[start][path[0]] << "km)" << "\t";
for (int j = 0; j < path.size() - 1; ++j) {
cout << cityName[path[j]] << "\t->(" << cityInf[path[j]][path[j + 1]] << "km)\t";
}
cout << cityName[path[path.size() - 1]] << "\t总距离为: " << matrix[i].second << "km" << endl;
}
}
void Union::init(vector<string>& city){
for (int i = 0; i < city.size(); ++i) {
Node* node = new Node(city[i]);
nameToNode[city[i]] = node;//node name哈希表
nameLeader[node] = node;//初始时领导为自己
leadNum[node] = 1;//自成一队,队员数量为1
}
}
Node* Union::findCaptain(string name){
Node* node = nameToNode[name];
vector<Node*> allNode;//收集寻找队长路径上的所有节点
while(node != nameLeader[node]) {
allNode.push_back(node);
node = nameLeader[node];//往上查找
}
for (auto& nodeOnRoad : allNode) {
//将路径上的所有节点都与 "队长" 相连
nameLeader[nodeOnRoad] = node;//node此时已经是队长节点
}
return node;
}
bool Union::inSameSet(string name1, string name2){
Node* captain1 = findCaptain(name1);
Node* captain2 = findCaptain(name2);
return captain1 == captain2;
}
void Union::uniteTwoTeam(string name1, string name2){
Node* captain1 = findCaptain(name1);
Node* captain2 = findCaptain(name2);
if (captain1 == captain2)
return;//已经是一个队长了
int num1 = leadNum[captain1];
int num2 = leadNum[captain2];
Node* smallTeam = num1 > num2 ? captain2 : captain1;//将较小的队伍合并到大队伍中
Node* bigTeam = smallTeam == captain1 ? captain2 : captain1;
nameLeader[smallTeam] = bigTeam;
leadNum[bigTeam] += leadNum[smallTeam];
leadNum.erase(smallTeam);//原来的队伍将被撤销
}
main.cpp
#include "Graph.h"
int main() {
Graph graph;
vector<string> cityName = { "邵阳", "长沙", "衡阳", "深圳", "大庆", "岳阳" };
vector<cityRel*> cityRelation = {
new cityRel("邵阳","长沙",235),
new cityRel("邵阳","衡阳",141),
new cityRel("邵阳","深圳",697),
new cityRel("邵阳","岳阳",364),
new cityRel("长沙","衡阳",190),
new cityRel("长沙","深圳",782),
new cityRel("长沙","大庆",2682),
new cityRel("长沙","岳阳",168),
new cityRel("衡阳","深圳",641),
new cityRel("深圳","大庆",3356),
new cityRel("大庆","岳阳",2540)
};//城市信息
graph.createGraph(cityName, cityRelation);
graph.BFS("邵阳");
graph.DFS("邵阳");
vector<bool> visited(graph.cityNum, false);
vector<int> path;
cout << "\n深度优先搜索(递归)\n\t" << endl;
graph.recurDFS("邵阳", visited, path);
graph.primAlgorithm("邵阳");
graph.kruskalAlgorithm();
graph.dijkstra("邵阳");
return 0;
}
运行示例