从BP神经网络训练模型后,想着换个模型训练训练数据集,于是在SVM和随机森林中选择,最后选择了随机森林。随机森林的原理不在这里做详细解释,有大佬比我讲的要好太多。我仅仅是就这我的代码做一些解释。
导入这次代码所需要的库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime as dt
import sklearn.model_selection as sm
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
import pydot
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
对数据做处理,选择的数据集为上证指数2016年到2021年7月30日日线的数据,csv文件可以从baostock上,通过python直接获取。
random_len=10#随机数种子的数量
est_tree=100#随机森林中树的个数
train_rate=0.7#切分训练组的长度
df=pd.read_csv("F:\大创(k线)\数据//999999.csv")
features=df.filter(['index','open','close','high','low'])
n_f=df.filter(['volume'])
n_f=n_f.values
n_f1=df.filter(['amount'])
n_f1=n_f1.values
scaler=MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1000,10000))#保持成交量和成交额在同一数量级
n_f,n_f1=scaler.fit_transform(n_f),scaler.fit_transform(n_f1)
features['volume']=n_f
features['amount']=n_f1
features['pro_rate']=np.log(features['close'] / features['close'].shift(1))#计算收益率
features=features.replace(np.nan,0)#由于计算收益率时第一行数据没有值,把他变成0
train_data_len=math.floor(len(features)*train_rate)
newdate=features['index']
x_date=newdate[train_data_len:]
数据集准备成这样
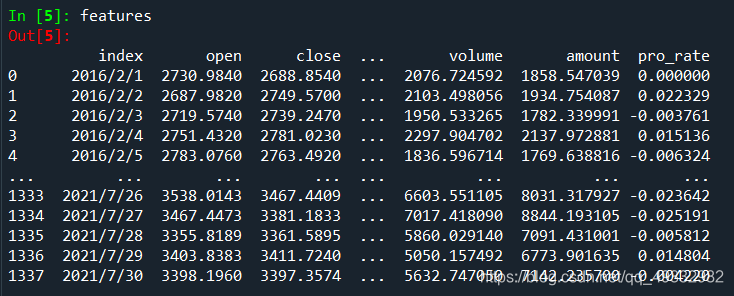
给标签和特征区分数据集,通过定义函数
#准备好标签和特征组
def label_data(features):
labels=np.array(features['pro_rate'])
features=features.drop('pro_rate',axis=1)#从特征值中去除标签列
features=features.drop('index',axis=1)
feature_list=list(features.columns)
features=np.array(features)
return labels,feature_list,features
labels,feature_list,features=label_data(features)
设置随机森林的参数和训练模型,预测
rf=RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=est_tree,random_state=random_len)
rf.fit(train_features,train_labels)
predtion=rf.predict(test_features)
数据可视化
fig,axs=plt.subplots(2,1,sharex=True,figsize=(14,8))
axs[0].plot(x_date,predtion)
axs[0].set_ylabel("prediction")
axs[1].plot(x_date,test_labels)
axs[1].set_ylabel("true")
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0)
plt.xlabel('date')
plt.show()
plt.close()
这里画出的图共享了x轴,这样看起来舒服一点
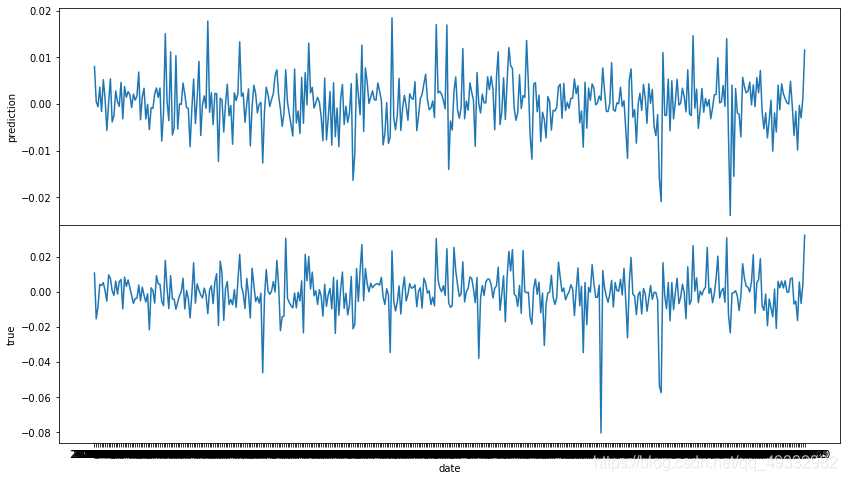
既然有了森林,我们当然要查看一下因子的重要程度
importances=list(rf.feature_importances_)
feature_importances = [(feature, round(importance, 4)) for feature, importance in zip(feature_list, importances)]
feature_importances = sorted(feature_importances, key = lambda x: x[1], reverse = True)
for pair in feature_importances:
print('Variable: {:20} Importance: {}'.format(*pair))
得到的如下:
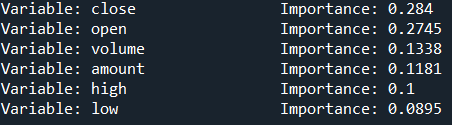
有时我们也需要看一下随机树的内部结构
我们所需要的库为
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
import pydot
值得注意的是graphviz不能在python中通过pip install graphviz命令行去安装到路径中,我们需要去网站下载安装
https://graphviz.org/download/#source-code
下载这个就好:
 下载后安装,记得勾选把其加入到path中,或者之后自己把源文件下bin文件夹加入环境变量也行
下载后安装,记得勾选把其加入到path中,或者之后自己把源文件下bin文件夹加入环境变量也行
如果在运行是报错:"dot" not found in path
则打开pydot.py文件,把这里的dot改成dot.exe
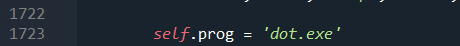
改完之后一定一定要记得重启电脑!!,我翻来覆去查了半小时哪里的问题。
现在就可以输出随机树的结构了
def draw_tree(rf,feature_list):
tree = rf.estimators_[5]
export_graphviz(tree, out_file = 'rf.dot', feature_names = feature_list, rounded = True, precision = 1)
(graph, ) = pydot.graph_from_dot_file('rf.dot')
graph.write_png('rf.png');
draw_tree(rf,feature_list)
(非常局部的)随机树结构为:
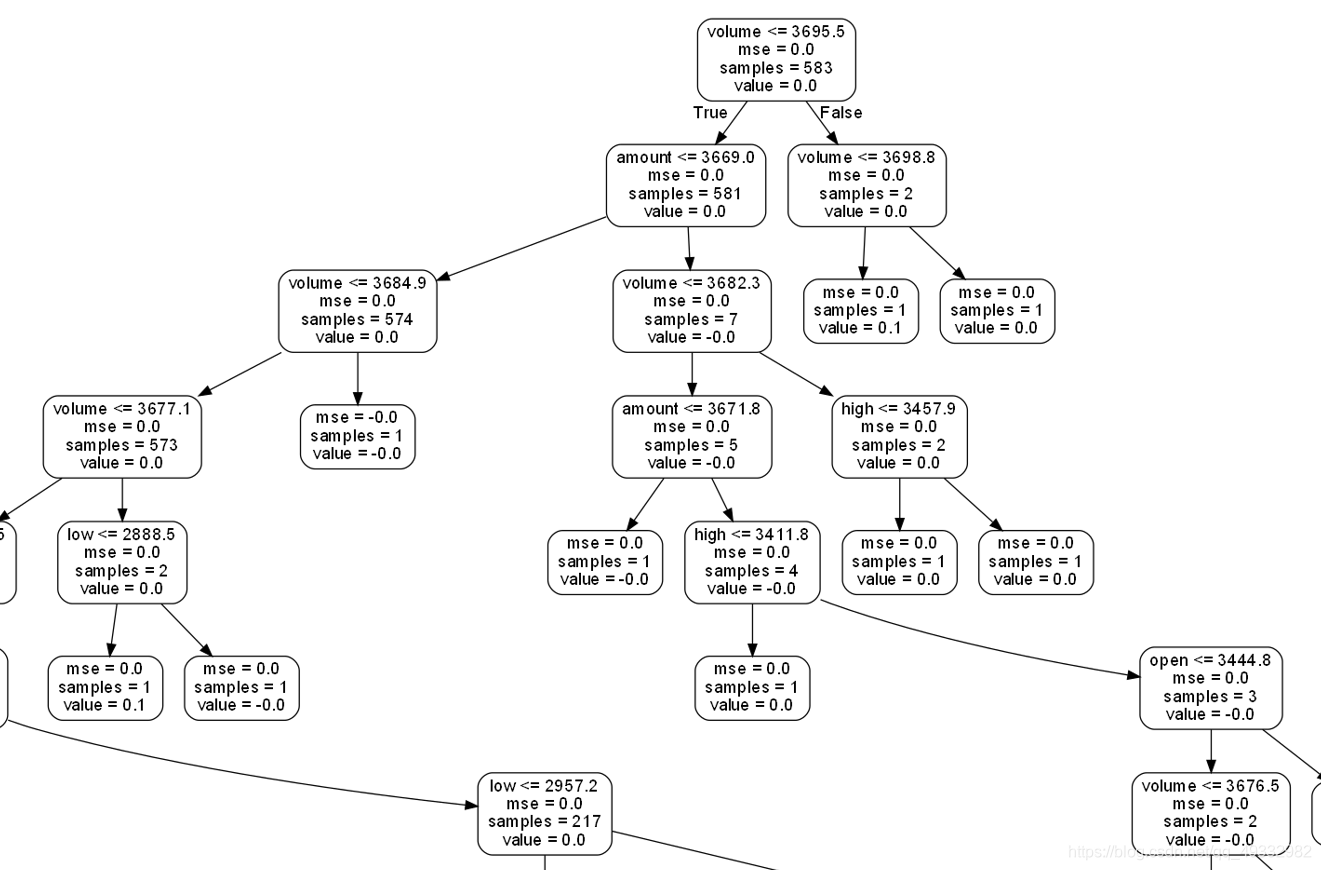
这就是目前写了基本功能的代码,还需改进。