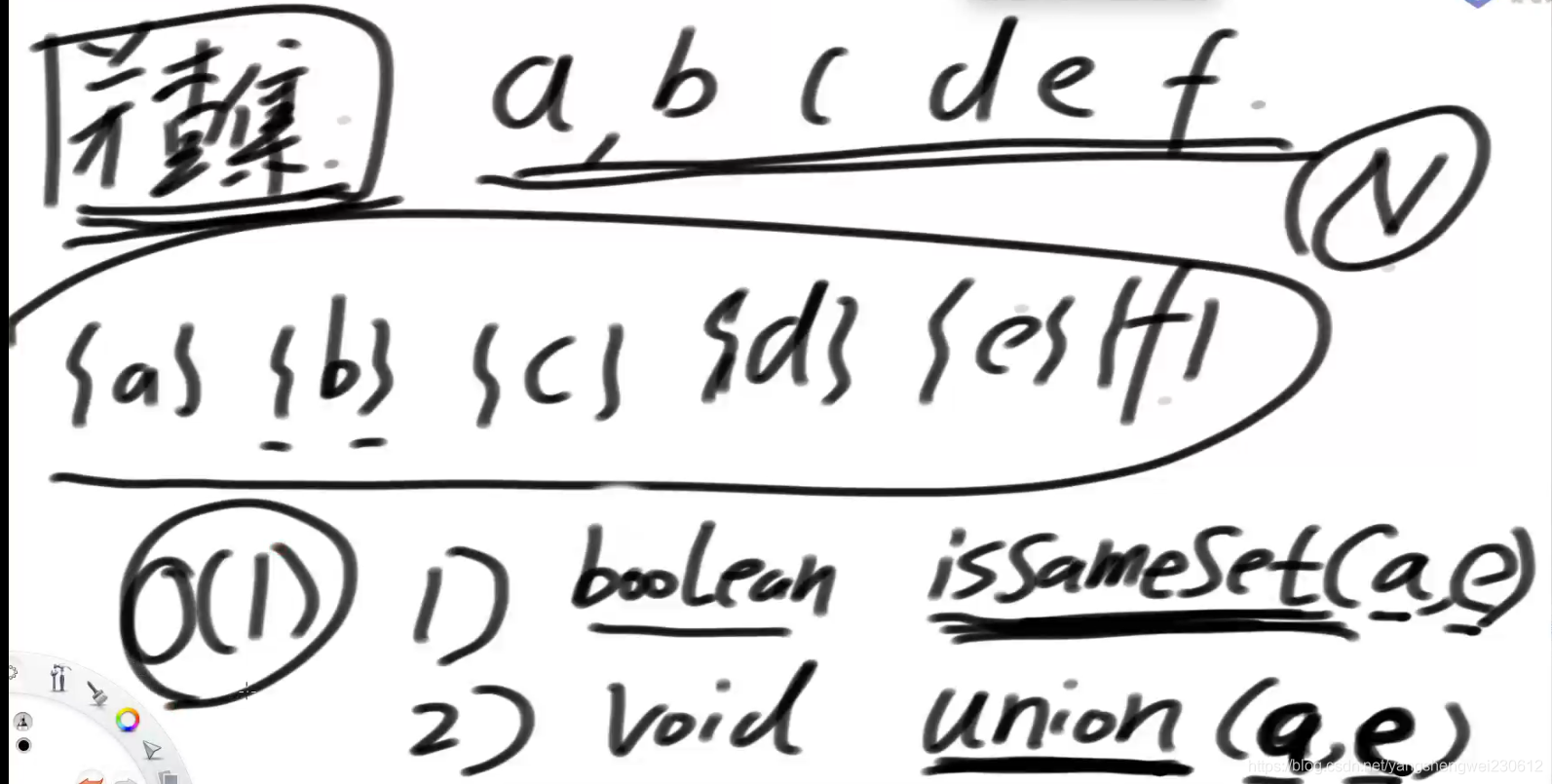
6.并查集
1. 判断两个集合是否属于同一集合
2. 合并两个结合
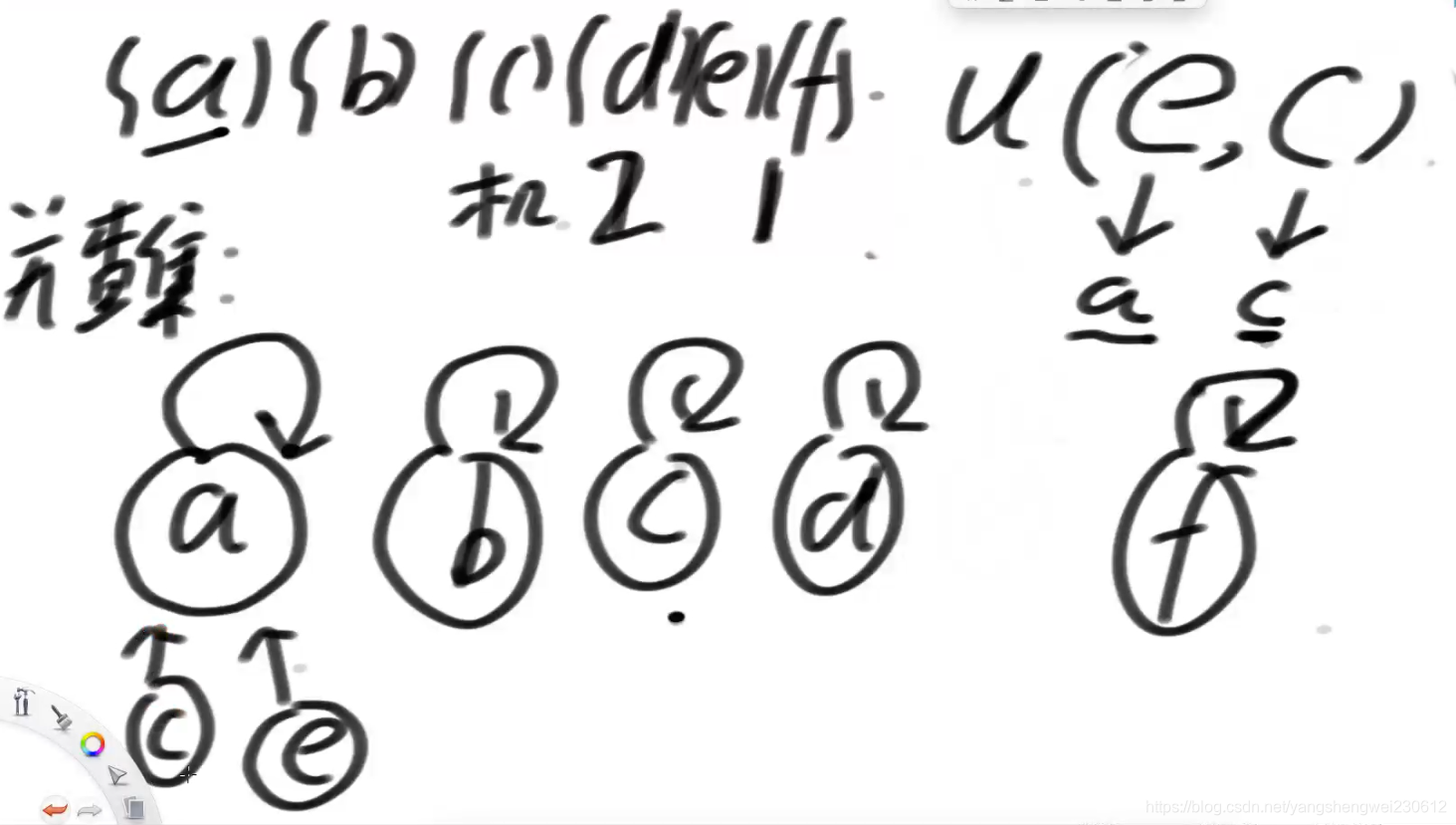

首次生成3张map 表
//包装集合
public HashMap<V, Node<V>> nodes;
//记录本集合下所有节点对应的父节点,即谁的父亲是谁
public HashMap<Node<V>, Node<V>> parents;
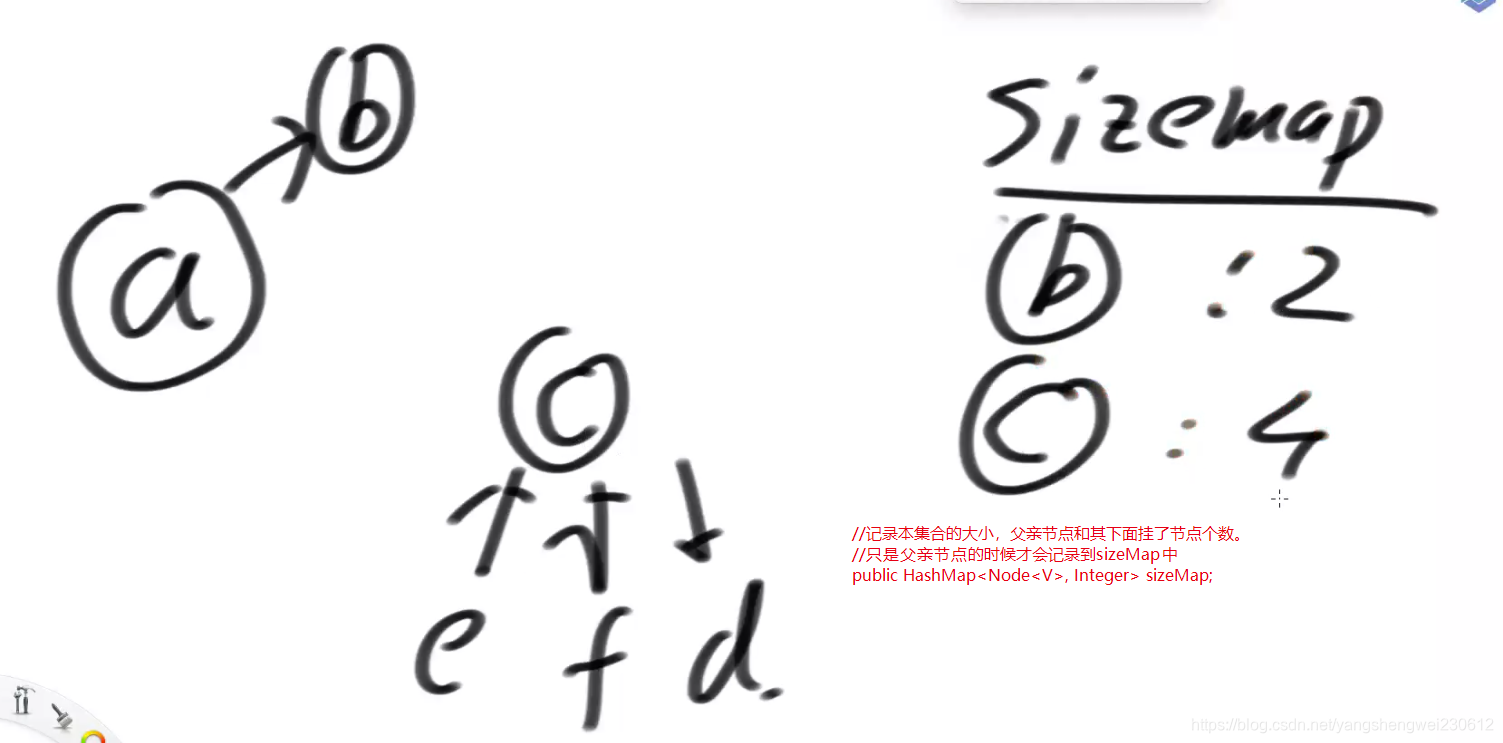
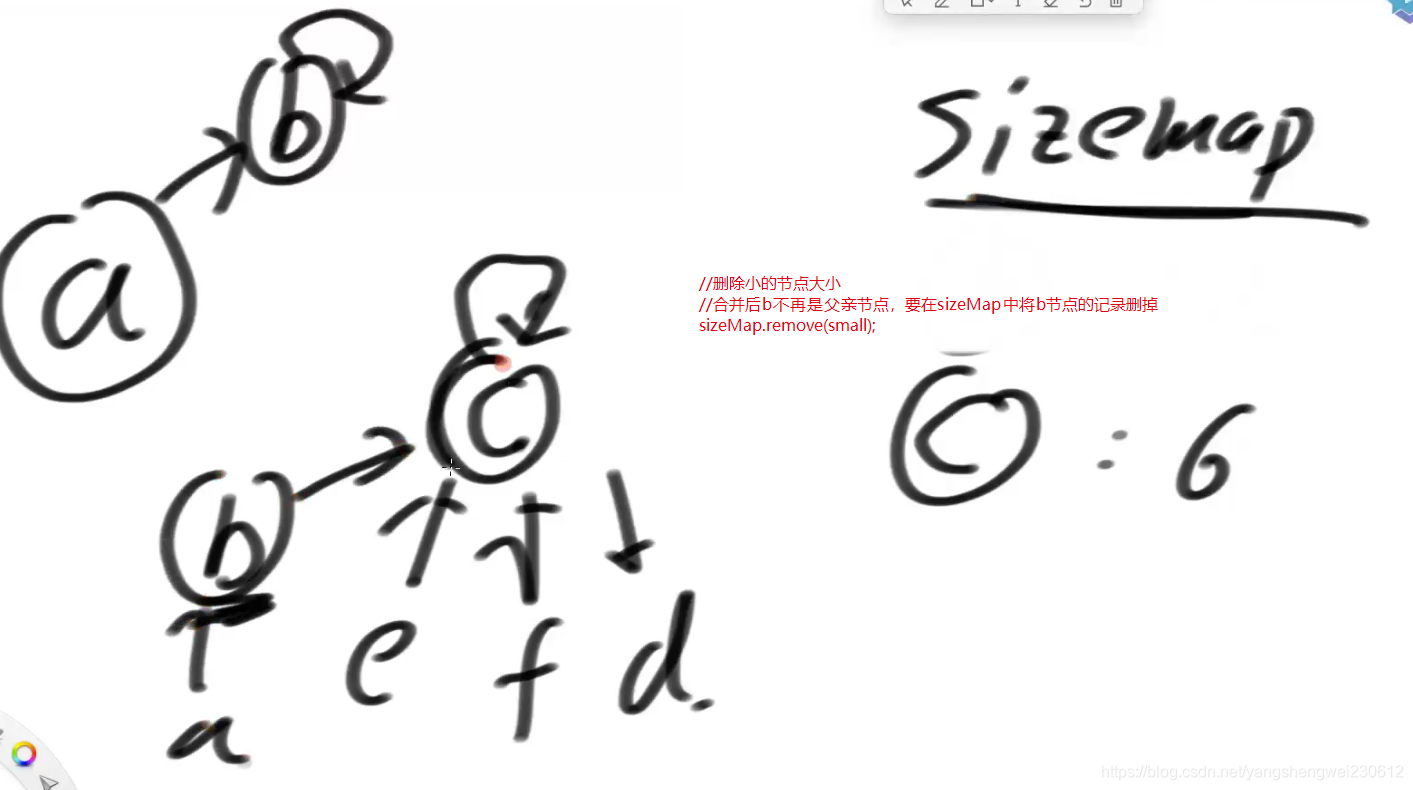
//记录本集合的大小,父亲节点和其下面挂了节点个数。
//只是父亲节点的时候才会记录到sizeMap中
public HashMap<Node<V>, Integer> sizeMap;
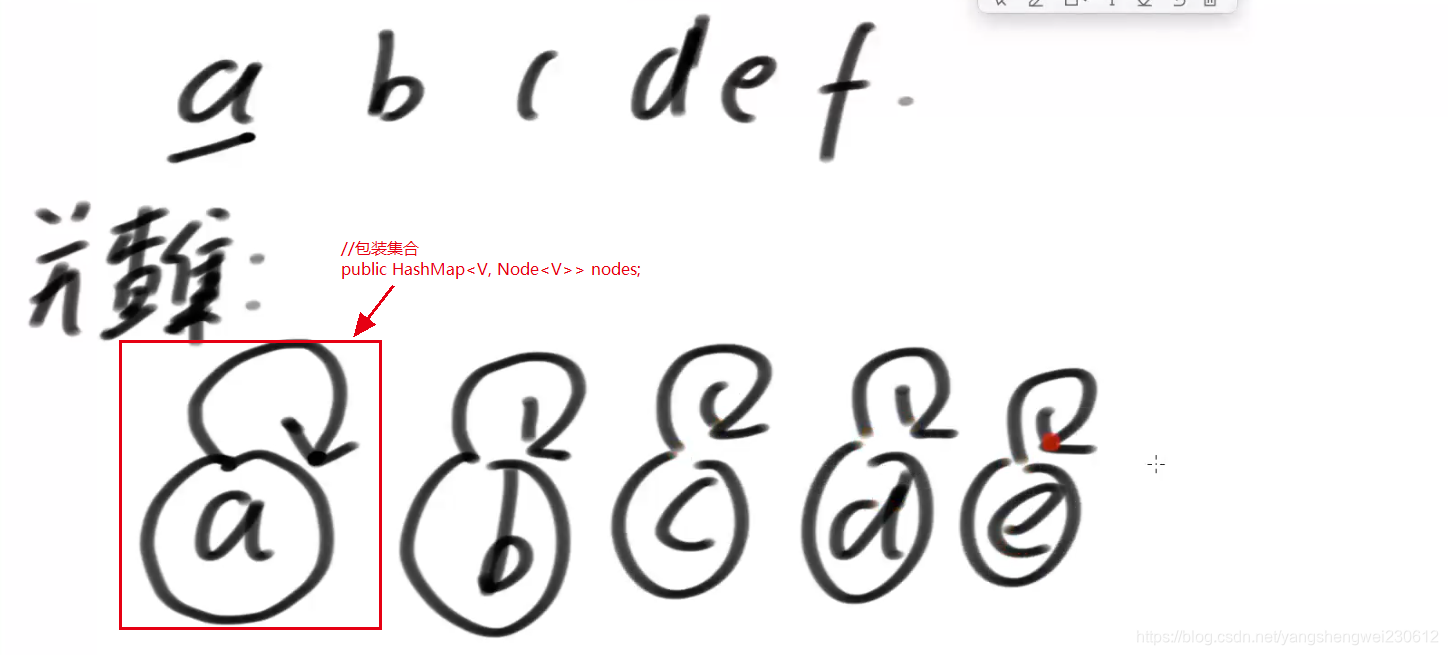


查找父亲节点
Stack<Node<V>> path = new Stack<>();
//自己指向自己即为代表节点
//找到代表节点
while (cur != parents.get(cur)) {
path.push(cur);
cur = parents.get(cur);
}

//合并两个集合
public void union(V a, V b) {
Node<V> aHead = findFather(nodes.get(a));
Node<V> bHead = findFather(nodes.get(b));
if (aHead != bHead) {
int aSetSize = sizeMap.get(aHead);
int bSetSize = sizeMap.get(bHead);
//大小集合重定向
Node<V> big = aSetSize >= bSetSize ? aHead : bHead;
Node<V> small = big == aHead ? bHead : aHead;
//小集合的代表节点指向大集合的代表节点
parents.put(small, big);
sizeMap.put(big, aSetSize + bSetSize);
//删除小的节点大小
sizeMap.remove(small);
}
}
//大小集合重定向
Node<V> big = aSetSize >= bSetSize ? aHead : bHead;
Node<V> small = big == aHead ? bHead : aHead;
//小集合的代表节点指向大集合的代表节点
parents.put(small, big);
package class14;
package class14;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Code05_UnionFind {
public static class Node<V> {
V value;
public Node(V v) {
value = v;
}
}
public static class UnionFind<V> {
//包装集合
public HashMap<V, Node<V>> nodes;
//记录本集合下所有节点对应的父节点,即谁的父亲是谁
public HashMap<Node<V>, Node<V>> parents;
//记录本集合的大小,父亲节点和其下面挂了节点个数。
//只是父亲节点的时候才会记录到sizeMap中
public HashMap<Node<V>, Integer> sizeMap;
public UnionFind(List<V> values) {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
parents = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
for (V cur : values) {
Node<V> node = new Node<>(cur);
nodes.put(cur, node);
//开始都是自己指向自己
parents.put(node, node);
//开始都是都是代表节点,大小为1
sizeMap.put(node, 1);
}
}
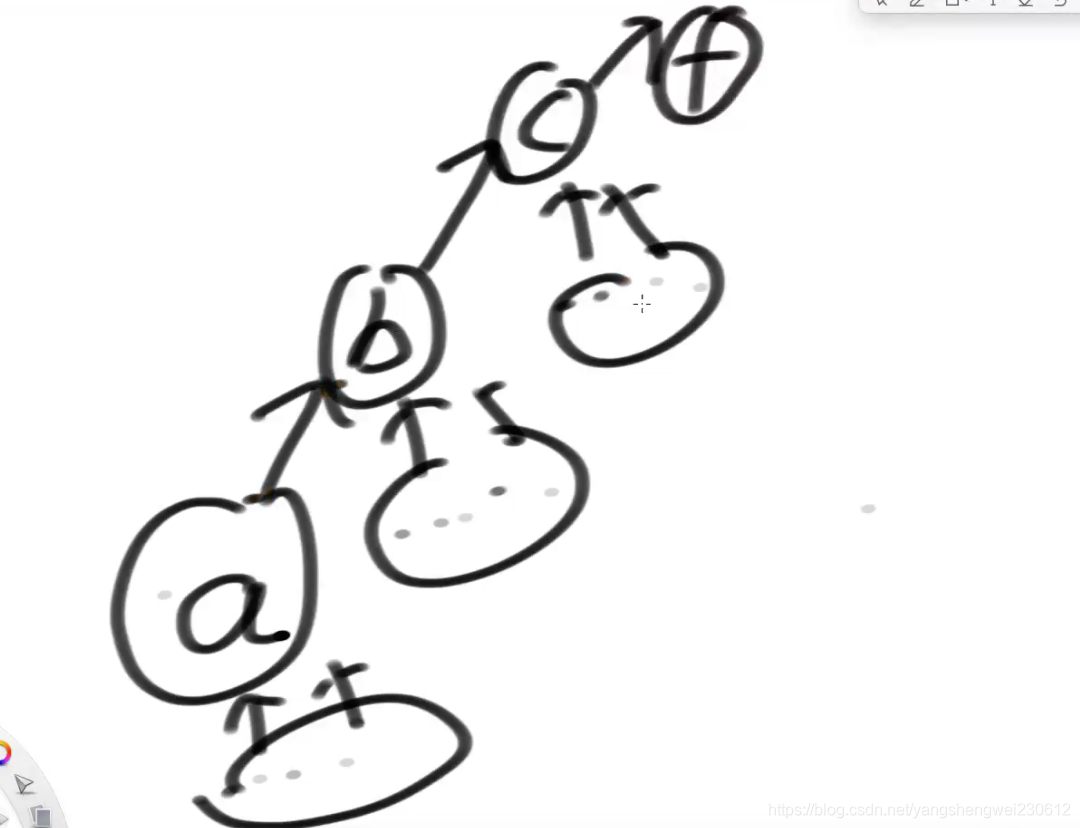
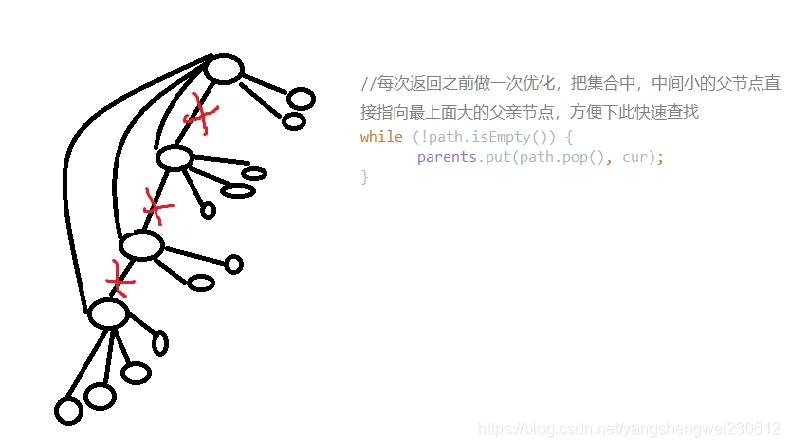
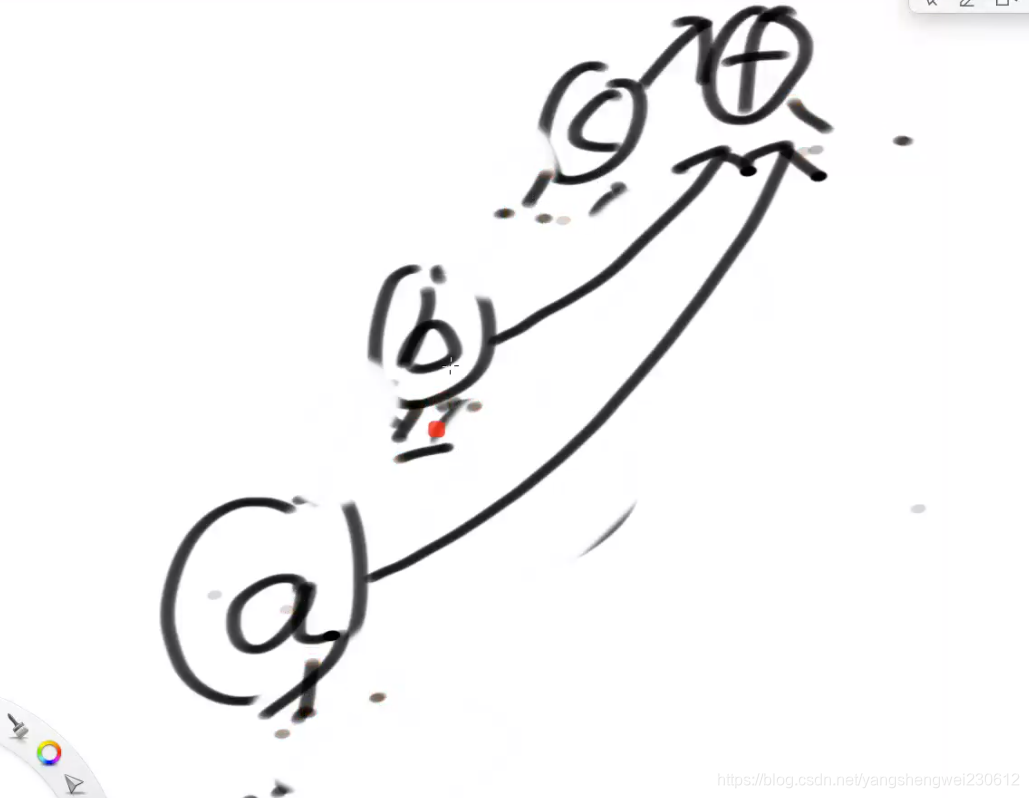
// 给你一个节点,请你往上到不能再往上,把代表返回
//找到给定节点的代表节点
public Node<V> findFather(Node<V> cur) {
Stack<Node<V>> path = new Stack<>();
//自己指向自己即为代表节点
//找到代表节点
while (cur != parents.get(cur)) {
path.push(cur);
cur = parents.get(cur);
}
//每次返回之前做一次优化,把集合中,中间小的父节点直接指向最上面大的父亲节点,方便下此快速查找
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
parents.put(path.pop(), cur);
}
return cur;
}
//判断是否在一个集合
//核心判断两个集合代表节点是否相等,相等则是否属于同一个集合
public boolean isSameSet(V a, V b) {
return findFather(nodes.get(a)) == findFather(nodes.get(b));
}
//合并两个集合
public void union(V a, V b) {
Node<V> aHead = findFather(nodes.get(a));
Node<V> bHead = findFather(nodes.get(b));
if (aHead != bHead) {
int aSetSize = sizeMap.get(aHead);
int bSetSize = sizeMap.get(bHead);
//大小集合重定向
Node<V> big = aSetSize >= bSetSize ? aHead : bHead;
Node<V> small = big == aHead ? bHead : aHead;
//小集合的代表节点指向大集合的代表节点
parents.put(small, big);
sizeMap.put(big, aSetSize + bSetSize);
//删除小的节点大小
//合并small不再是父亲节点,要从sizeMap中删掉
sizeMap.remove(small);
}
}
public int sets() {
return sizeMap.size();
}
}
}
7.贪心算法
局部最优解,是否也是全局最优解

