我的理解
深度优先搜索就是,前方有可选择的路,就一直往前走,知道没有路或只有走过的路为止再原路返回。一直返回到出现了未走过的路,再继续顺着这条路走下去,如此往复,一直走到终点为止。
练习
以下题目均来源于leetcode
二叉树的最大深度
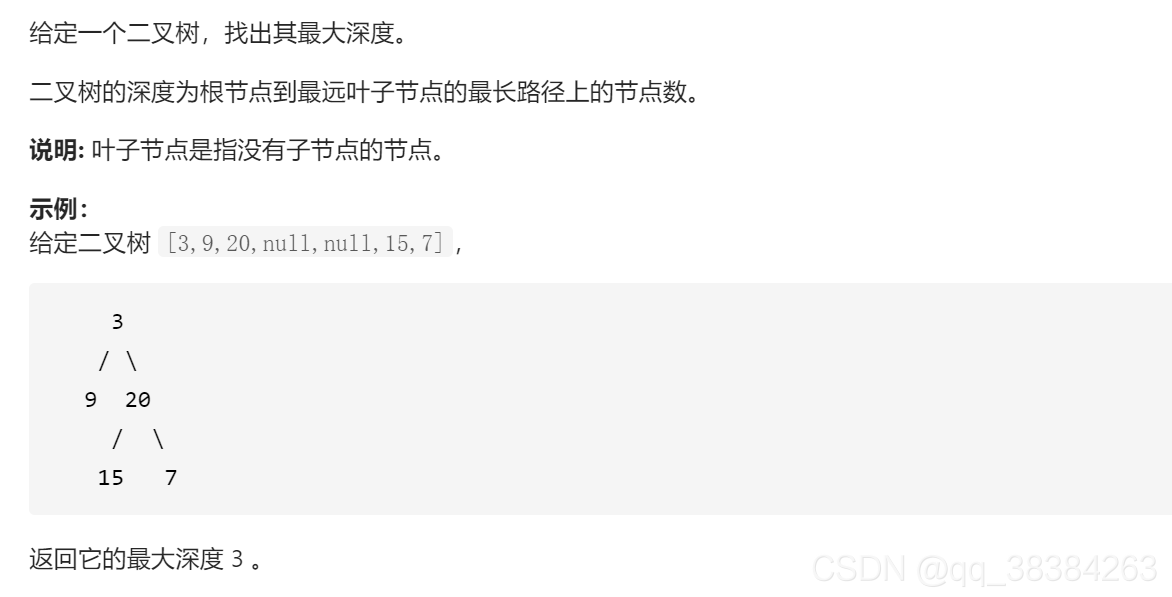
思路:使用深度优先搜索,分别遍历左右子树,每往下一层,深度就+1,直到遇到NULL为止。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
#define Max(a,b) (a>b?a:b)
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int left=maxDepth(root->left)+1;
int right=maxDepth(root->right)+1;
return Max(left, right);
}
二叉树的最小深度
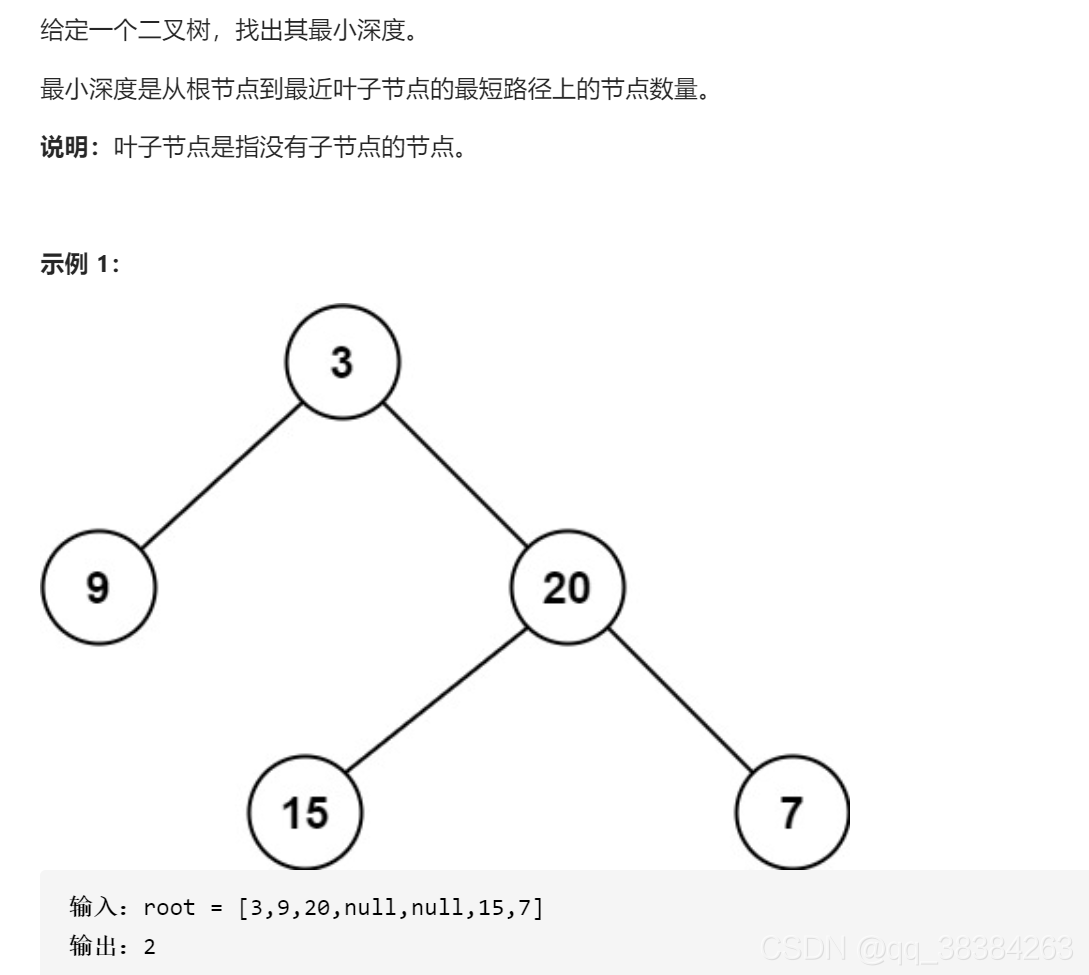
思路:跟上题类似,使用深度优先搜索,分别遍历左右子树,每往下一层,深度就+1,直到遇到NULL为止。不同的是这里输出的是最小值,所以在函数里面要先定义两个很大的变量用来代表左右子树的深度,以便能返回出最小值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
#define Min(a,b) (a<b?a:b)
int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
int left=10000,right=10000;
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}else if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
if(root->left)
{
left=minDepth(root->left)+1;
}
if(root->right)
{
right=minDepth(root->right)+1;
}
return Min(right,left);
}
路径总和
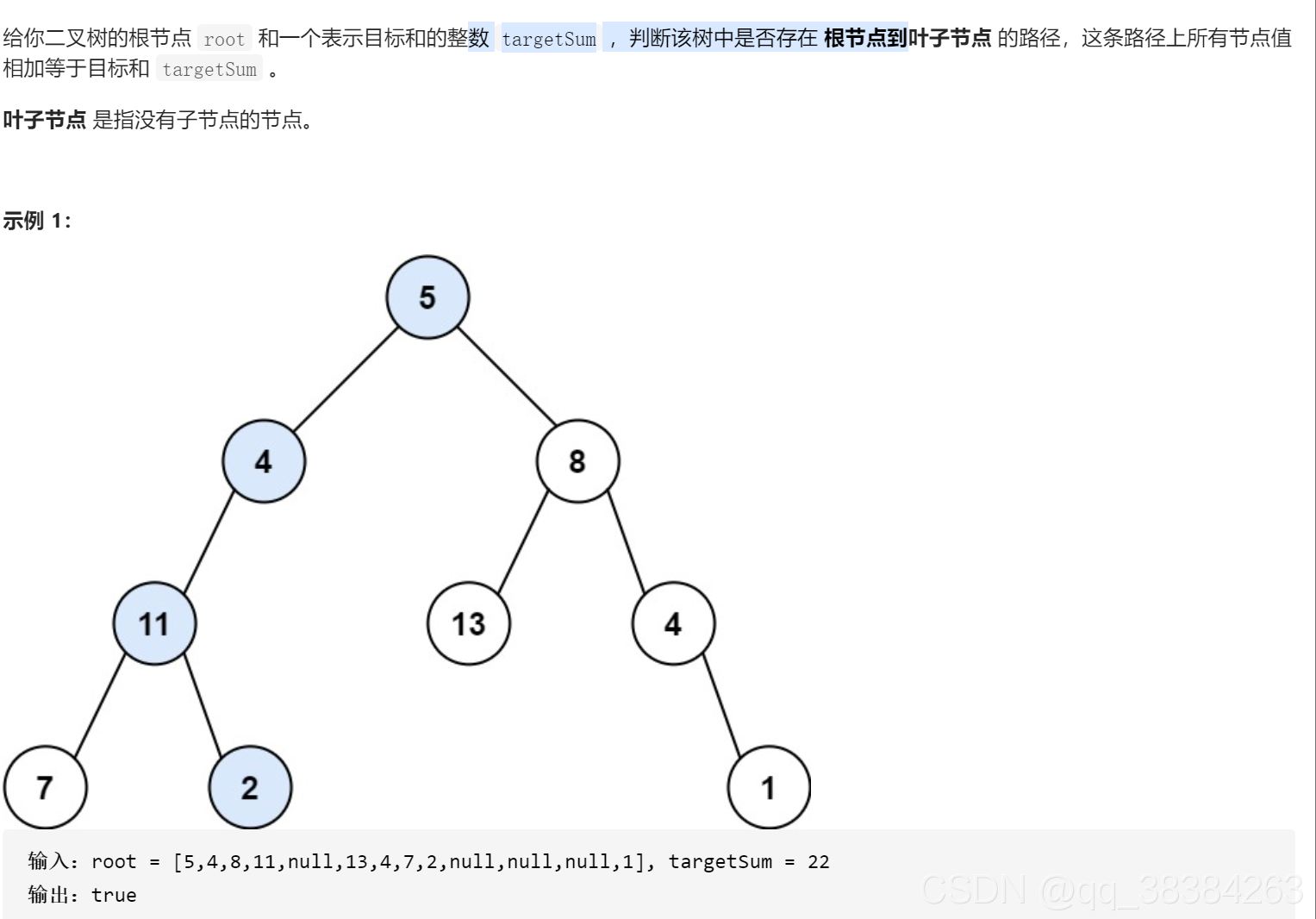
这道题的话是在求从根节点到叶子节点是否有总和等于sum的路线。
思路:构建一个函数,函数的参数有节点,和当前要等于sum。
每次进入这个函数就将sum-节点的值作为参数再次传入函数,一层层嵌套,直到遍历完所有路径,或者是出现一个sum等于0的情况。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
bool left=false,right=false;
if(root)
{
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)
{
if(targetSum-root->val==0)
{
//printf("1,");
return true;
}else
{
//printf("0:%d,",targetSum);
return false;
}
}
if(root->left)
{
left=hasPathSum(root->left,targetSum-root->val);
}
if(root->right)
{
right=hasPathSum(root->right,targetSum-root->val);
}
}
//printf("%d,",left||right);
return left||right;
}
翻转二叉树
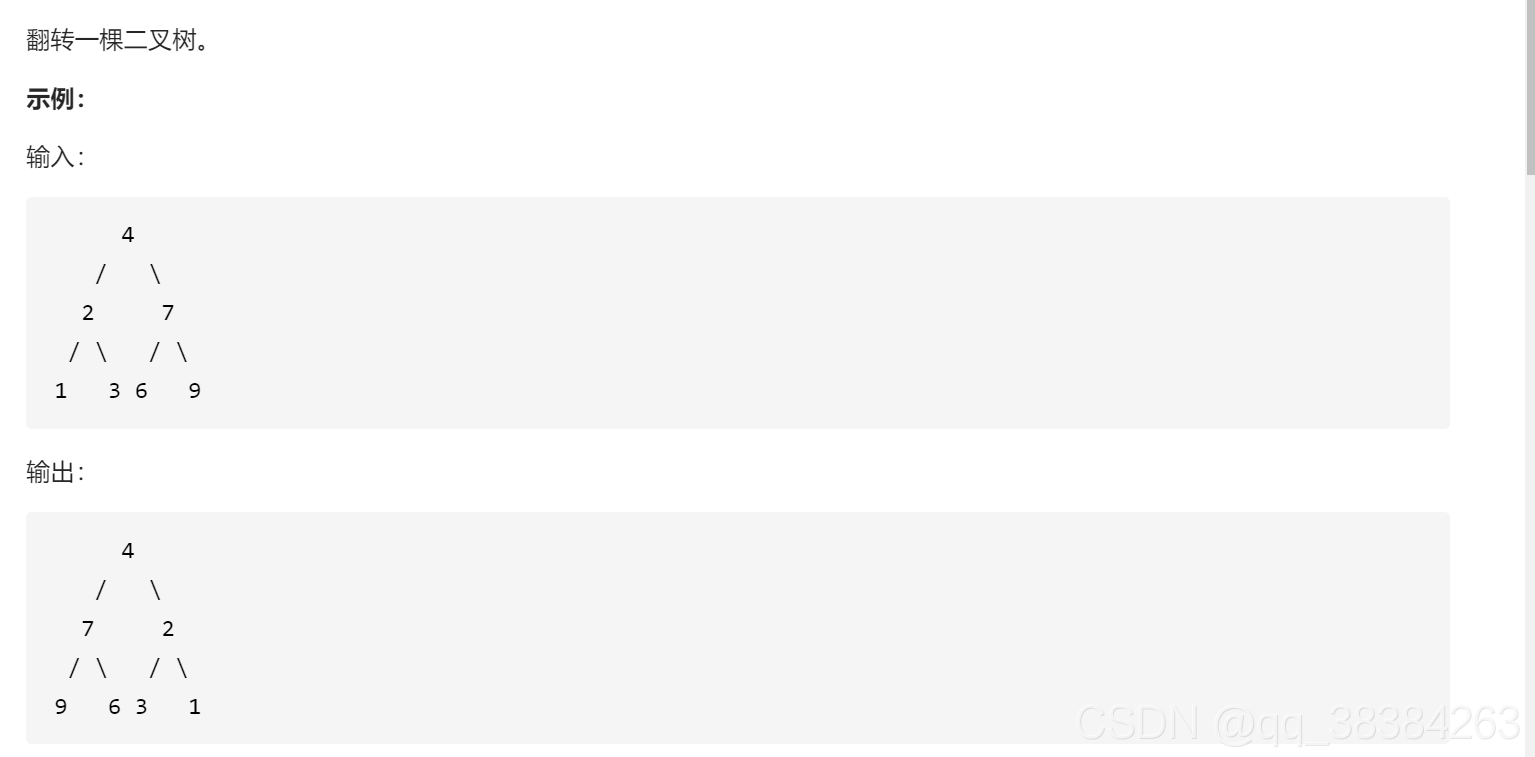
思路:每次进入到一个节点里,如果不为空,就交换其左右节点,再以左右节点为根节点继续向下交换
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
void invert(struct TreeNode *root)
{
if(root)
{
struct TreeNode *p=root->left;
root->left=root->right;
root->right=p;
invert(root->left);
invert(root->right);
}
}
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){
invert(root);
return root;
}
相同的树
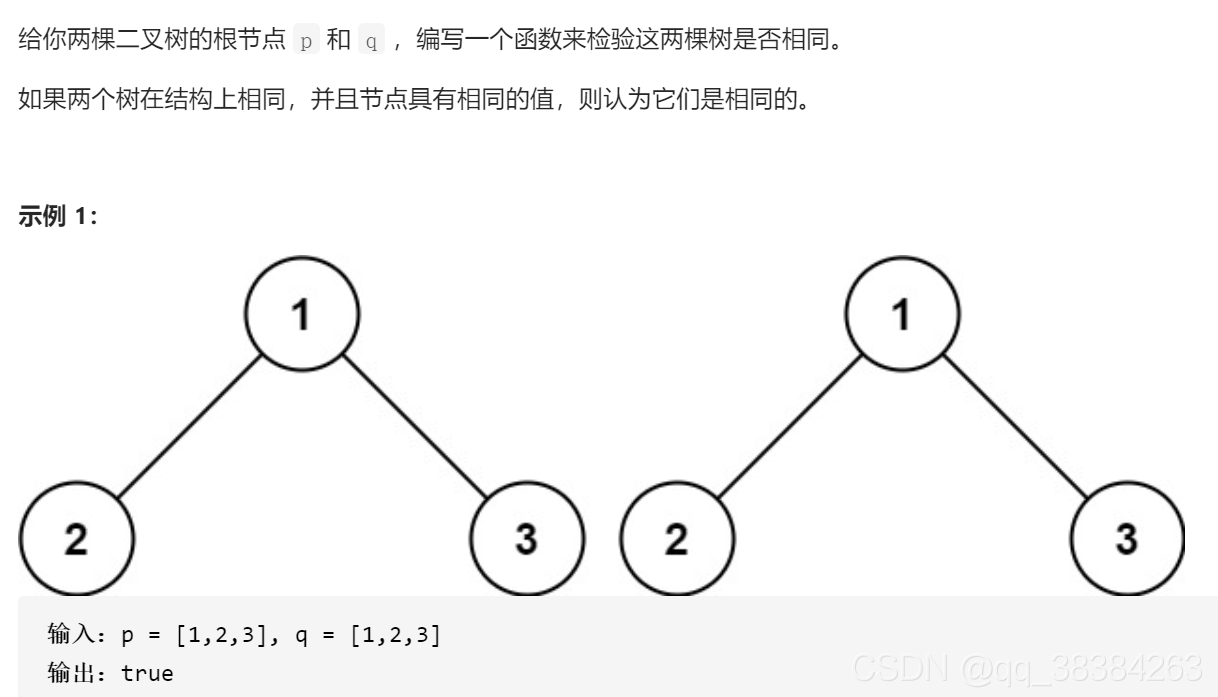
思路:分情况考虑,假如p,q都不为空,就对比p和q的节点值是否相等,如果相等就往下对比p,q的左节点和右节点。否则就返回false。
如果p,q都为空,则返回真
如果p,q只有一个不为空,则返回false。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
bool left=false,right=false;
if(p&&q)
{
if(p->val==q->val)
{
left=isSameTree(p->left,q->left);
right=isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}else
{
return false;
}
}
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)return true;
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)return false;
return right&&left;
}
对称二叉树
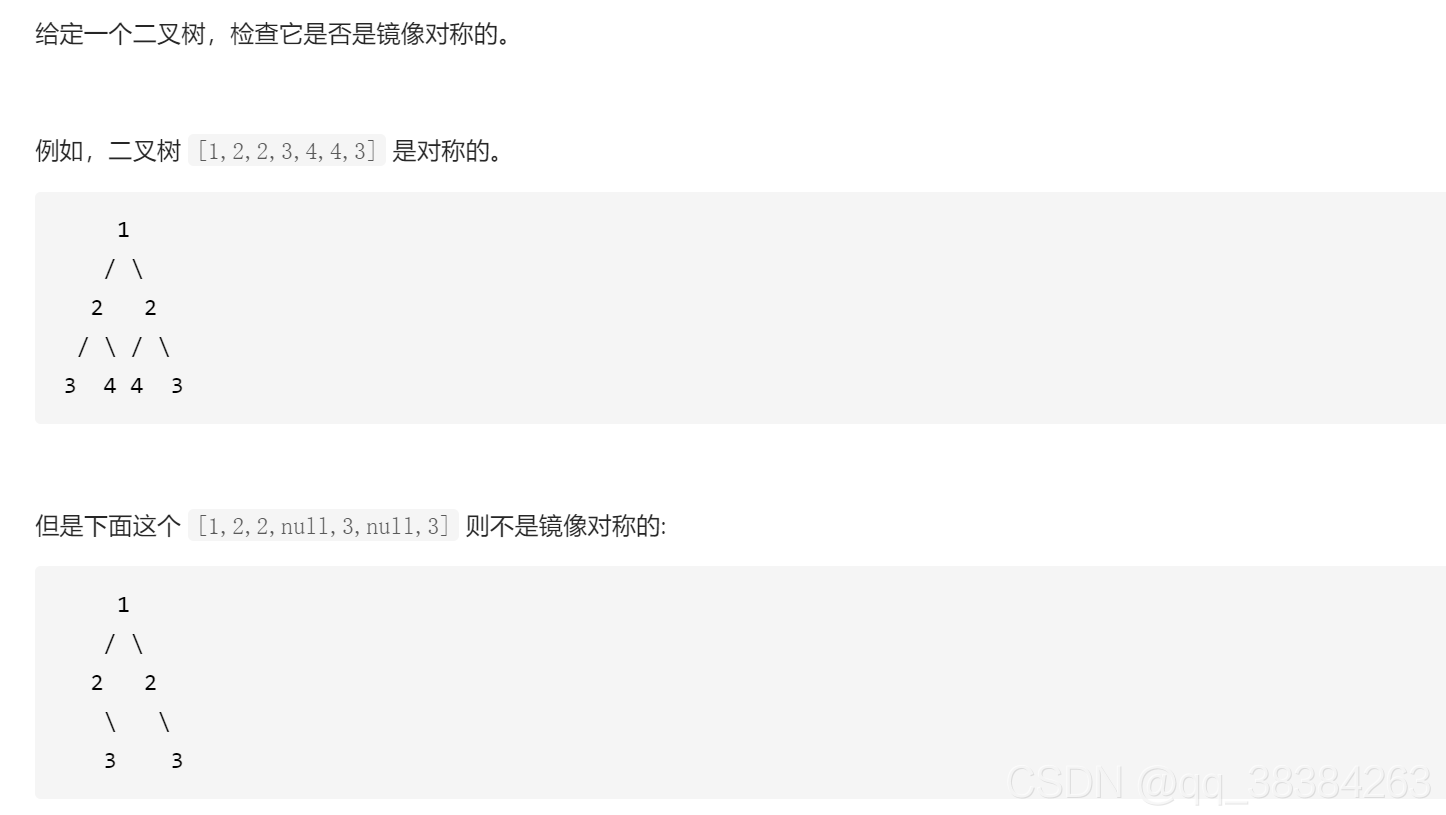
思路,将该题看成是上一个题的变种,将根节点的左节点和右节点当作p,q。只不过是将p的左节点和q的右节点做对比,代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSame(struct TreeNode *p,struct TreeNode *q)
{
bool left=false,right=false;
if(q==NULL&&p==NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p&&q)
{
if(p->val==q->val)
{
left=isSame(p->left,q->right);
right=isSame(p->right, q->left);
}else
{
return false;
}
}else
{
return false;
}
return left&&right;
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root)
{
return isSame(root->left,root->right);
}
return true;
}
求根到叶子节点数字之和
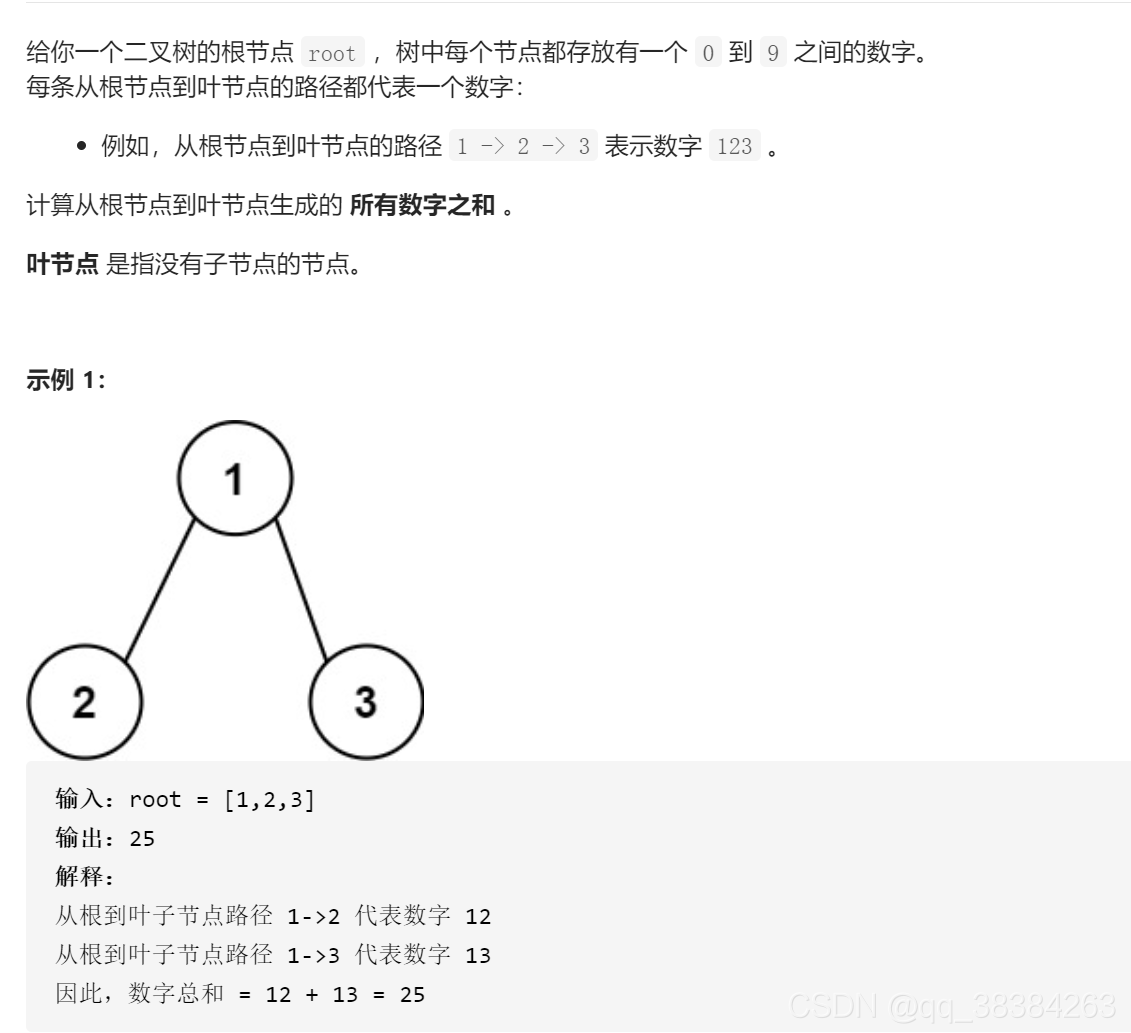
思路:sum一开始设置为0,每次寻到下一层,就*10+当前节点值,再往下遍历左节点和右节点。直到所有节点都遍历完为止,最后返回左右的和
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int sumTree(struct TreeNode* root,int sum)
{
int left=0,right=0;
sum=10*sum+root->val;
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)
{
return sum;
}
if(root->left)
{
left=sumTree(root->left,sum);
}
if(root->right)
{
right=sumTree(root->right,sum);
}
return left+right;
}
int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
return sumTree(root,0);
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先

思路,递归向下搜索,直到收到p或q为止,如果都搜索到了就返回该节点的地址,如果都搜索不到就返回空
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
if(root==p||root==q)
{
return root;
}
if(root==NULL)return NULL;
struct TreeNode* left=lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
struct TreeNode* right=lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
if(left&&right)return root;
if(left)return left;
if(right)return right;
return NULL;
}
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
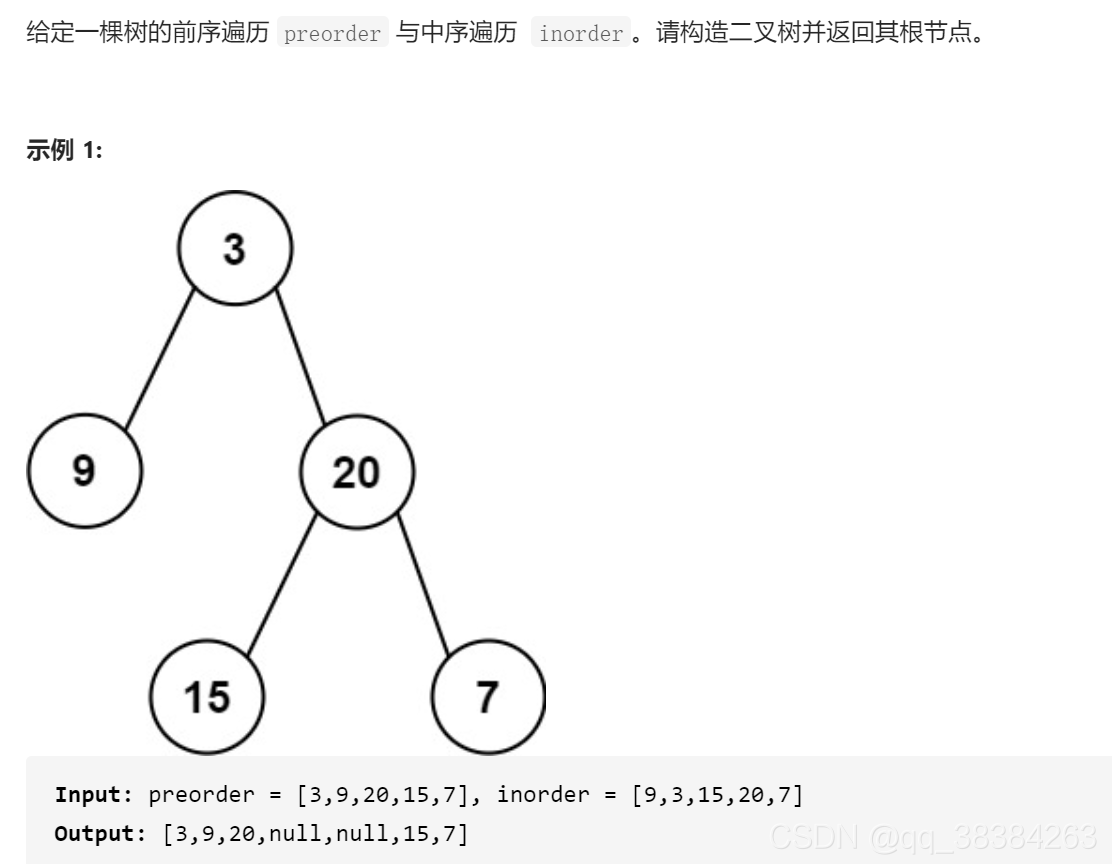
前序=3,9,20,15,7
中序=9,3,15,20,7
思路:前序的第一个数3作为根节点,在中序中寻找根节点3的位置。
由中序遍历特性知:知道了根节点位置后那么根节点左边的就是左子树,右边就是右子树。
3在中序中的索引是1,则说明以3为根节点的树中,左子树共有一个节点,右子树右3个节点。以3为分割点,将中序分成两部分。前序的分割就是去掉根节点取左子树的节点数量作为新的左子树前序,剩余的为右子树前序,分别再以上述方式处理,循环往复,创建二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* inorder, int inorderSize){
int rootVal=0,rootIndex=0;
if(preorderSize==0||inorderSize==0)return NULL;
rootVal=preorder[0];
for(int i=0;i<inorderSize;i++)
{
if(inorder[i]==rootVal)
{
rootIndex=i;
break;
}
}
struct TreeNode *root=calloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode),1);
root->left=NULL;
root->right=NULL;
root->val=rootVal;
struct TreeNode *left=buildTree(&preorder[1],rootIndex,&inorder[0],rootIndex);
struct TreeNode *right=buildTree(&preorder[1+rootIndex],preorderSize-1-rootIndex,&inorder[rootIndex+1],inorderSize-1-rootIndex);
root->left=left;
root->right=right;
return root;
}
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉

思路:和上题类似,后序的最后一个点作为根节点,在中序中寻找左右子树的节点数量,然后分割前序。代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* inorder, int inorderSize, int* postorder, int postorderSize){
int rootVal=0,rootIndex=0;
if(inorderSize==0||postorderSize==0)return NULL;
rootVal=postorder[postorderSize-1];
for(int i=0;i<inorderSize;i++)
{
if(inorder[i]==rootVal)
{
rootIndex=i;
break;
}
}
struct TreeNode *root=calloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode),1);
root->left=NULL;
root->right=NULL;
root->val=rootVal;
struct TreeNode *left=buildTree(&inorder[0],rootIndex,&postorder[0],rootIndex);
struct TreeNode *right=buildTree(&inorder[rootIndex+1],inorderSize-1-rootIndex,&postorder[rootIndex],inorderSize-1-rootIndex);
root->left=left;
root->right=right;
return root;
}
前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
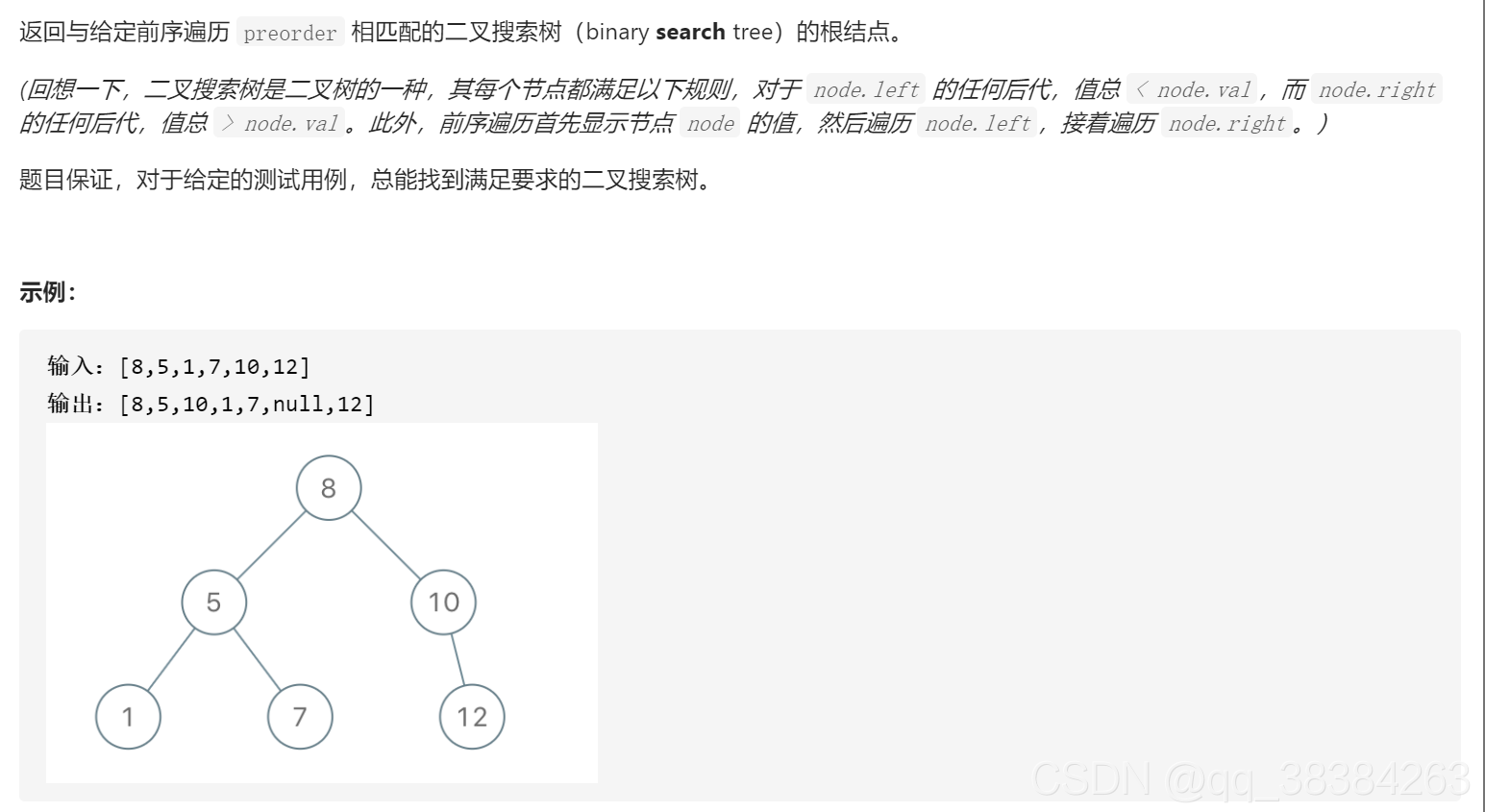
思路:将第一个值作为根节点,往后寻找,直到找到一个值大于根节点的值,这区间就是左子树,剩余的就是右子树。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* bstFromPreorder(int* preorder, int preorderSize){
int rootIndex=preorderSize,rootVal=0;
if(preorderSize==0)return NULL;
rootVal=preorder[0];
struct TreeNode *root=calloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode),1);
root->val=rootVal;
root->left=NULL;
root->right=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<preorderSize;i++)
{
if(preorder[i]>rootVal)
{
rootIndex=i;
break;
}
}
struct TreeNode *left=NULL,*right=NULL;
if(rootIndex-1>0)
{
left=bstFromPreorder(&preorder[1],rootIndex-1);
}
if(preorderSize-rootIndex>0)
{
right=bstFromPreorder(&preorder[rootIndex],preorderSize-rootIndex);
}
root->left=left;
root->right=right;
return root;
}