堆的概念及结构
如果有一个关键码的集合K = 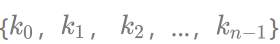
把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储在一个一维数组中,并满足: 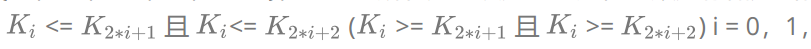
2…,则称为小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆的性质:
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树。

堆的实现
堆向下调整算法
假设父亲的下标是parent,左孩子的下标leftchild就等于2 *parent + 1,右孩子就等于2 *parent + 2
现在我们给出一个数组,逻辑上看做一颗完全二叉树。我们通过从根节点开始的向下调整算法可以把它调整
成一个小堆或大堆。向下调整算法有一个前提:左右子树必须是一个堆,才能调整。
我们以调整小堆为例:
int array[] = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};
- 选出第二层中左右孩子中较小的15,看15与它的父亲27谁小,15<27,所以15与27交换,之后就以第二层为根
- 因为右边子树已经是小堆了,就只看27的两个子节点18和和28谁小,18<28,再将18与27比较,18<27,所以18与27交换位置,之后就以第三层为根
- 因为28的子树已经是小堆了,所以只看27的子树,比较49和25的大小,25<49,再将25与27比较,25<27,所以25与27交换位置,此时整棵树就是一个小堆了
代码:
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int i)
{
int parent = i;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])//小堆
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
堆的创建
下面我们给出一个数组,这个数组逻辑上可以看做一颗完全二叉树,但是还不是一个堆,现在我们通过算
法,把它构建成一个堆。根节点左右子树不是堆,我们怎么调整呢?这里我们从倒数的第一个非叶子节点的
子树开始调整,一直调整到根节点的树,就可以调整成堆。
int a[] = {1,5,3,8,7,6};


堆的插入
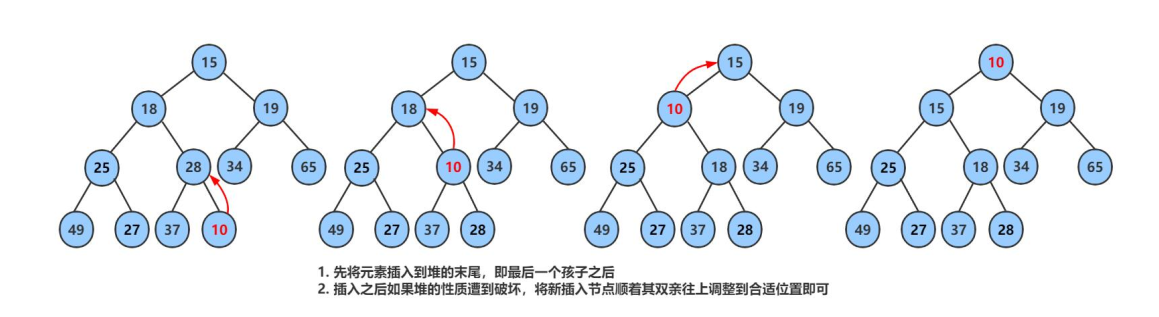
先插入一个10到数组的尾上,再进行向上调整算法,直到满足堆。
堆的删除
删除堆是删除堆顶的数据,将堆顶的数据根最后一个数据一换,然后删除数组最后一个数据,再进行向下调整算法。

堆的代码实现
Heap.h:
typedef int tp;
typedef struct Heap
{
tp* a;
tp capacity;
tp size;
}Heap;
// 堆的构建
void HeapCreate(Heap* hp, tp* a, int n);
// 堆的销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp);
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(Heap* hp,tp x);
// 堆的删除
void HeapPop(Heap* hp);
// 取堆顶的数据
tp HeapTop(Heap* hp);
// 堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
// 堆的判空
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
//打印堆
void HeapPrint(Heap* hp);
Heap.c:
//交换
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//建堆
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int i)
{
int parent = i;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(tp* a, tp child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆的构建(初始化)
void HeapCreate(Heap* hp, tp* a, int n)
{
assert(hp != NULL);
hp->a = (tp*)malloc(sizeof(tp) * n);
if (hp->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(hp->a, a, sizeof(tp) * n);
hp->size = hp->capacity = n;
//建小堆
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(hp->a, n, i);
}
}
// 堆的销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp)
{
free(hp->a);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, tp x)
{
assert(hp != NULL);
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
{
tp* tmp = (tp*)realloc(hp->a, 2 * (hp->capacity) * sizeof(tp));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
tmp = NULL;
HeapDestory(&hp);
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity *= 2;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
//插入后可能要向上调整,只需要调整一条支线
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
}
// 堆的删除,删除堆顶数据,将堆顶数据与最后一个数据交换,再删掉原堆顶数据,最后向下调整
void HeapPop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp != NULL);
assert(!HeapEmpty(&hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
}
// 取堆顶的数据
tp HeapTop(Heap* hp)
{
return hp->a[0];
}
// 堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
{
return hp->size;
}
// 堆的判空
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
{
return hp->size == 0;
}
void HeapPrint(Heap* hp)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < hp->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
int num = 0;
int levelsize = 1;
for (i = 0; i < hp->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
num++;
if (num == levelsize)
{
printf("\n");
num = 0;
levelsize *= 2;
}
}
printf("\n\n");
}
堆的应用
堆排序
堆排序即利用堆的思想来进行排序,总共分为两个步骤:
- 建堆
- 升序:建大堆
- 降序:建小堆
- 利用堆删除思想来进行排序
建堆和堆删除中都用到了向下调整,因此掌握了向下调整,就可以完成堆排序。
TOP-K问题
TOP-K问题:即求数据结合中前K个最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情况下数据量都比较大。
比如:专业前10名、世界500强、富豪榜、游戏中前100的活跃玩家等。
对于Top-K问题,能想到的最简单直接的方式就是排序,但是:如果数据量非常大,排序就不太可取了(可能
数据都不能一下子全部加载到内存中)。最佳的方式就是用堆来解决,基本思路如下:
- 用数据集合中前K个元素来建堆
- 前k个最大的元素,则建小堆
- 前k个最小的元素,则建大堆
- 用剩余的N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素来比较,不满足则替换堆顶元素
将剩余N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素比完之后,堆中剩余的K个元素就是所求的前K个最小或者最大的元素。
下列代码调用的函数是上面实现堆里面实现的接口
void TestTopK()
{
int *a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)* 10000) ;
srand(time(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10000; ++i)
{
a[i] = rand() % 10000;
}
a[5] = 10000 + 2;
a[32] = 10000 + 3;
a[35] = 10000 + 9;
a[19] = 10000 + 1;
a[999] = 10000 + 10;
a[25] = 10000 + 22;
a[52] = 10000 + 4;
int k = 7;
hp h;
HeapInit(&h, a, k);
HeapPrint(&h);
printf("\n");
//将k个最大的数放在堆里
for (int j = k; j < 10000; ++j)
{
int top = HeapTop(&h);
if (a[j] > top)
{
HeapPop(&h);
HeapPush(&h, a[j]);
}
}
printf("\n");
HeapPrint(&h);
while (!HeapEmpty(&h) && k > 0)
{
printf("%d ", HeapTop(&h));
HeapPop(&h);
--k;
}
HeapDestroy(&h);
}
int main()
{
//建小堆
TestTopK();
return 0;
}