一些碎碎念:其实以前听过清华大学的 数据结构 OJ小记录(差不多快正好一年前了),而且也看到过一个博主曾经这两门课都上过对比过不同【清华看重课程深层的理论,浙大更轻松易懂一点】,可惜清华大学的上到上半段后就没有坚持下去搞完(主要是又看其他的课去了 热度变得好快哦 😂) 这次的笔记也主要是关于编程作业和自己一开始理解错了的地方。希望这次重拾能更深刻一点,这次尽量不像上次一样遇到不会就搜 至少我先挣扎个2小时… 不过做完一般我都会对比优劣和简易 如果有的话 wa 眼前一亮的那种 我会再次引用说明
之所以没有直接刷算法题,是因为我还是想从理论抓起的感觉会更扎实一点?虽然刷算法题也能接触到
【MOOC课程】浙大数据结构记录(上) 在这里:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39537898/article/details/113006713
其实有想过把他们合并,但是太太太太长了 hhhh 所以就还是分一下上下 当做自我记录了。
giteee代码链接:https://gitee.com/kin_zhang/data-structure
第七周:图(最短路径问题)
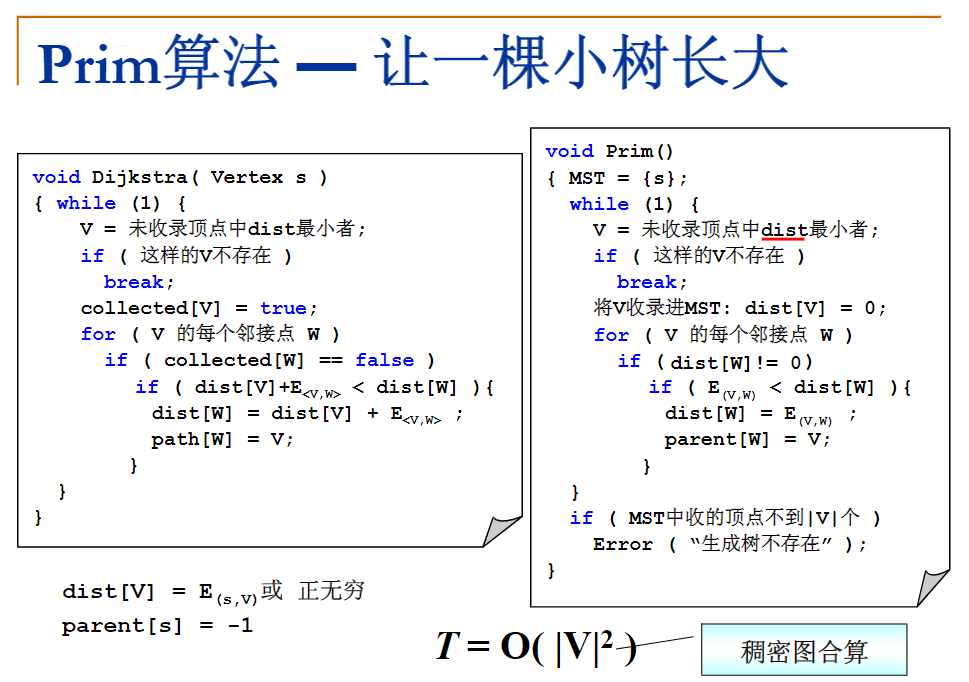
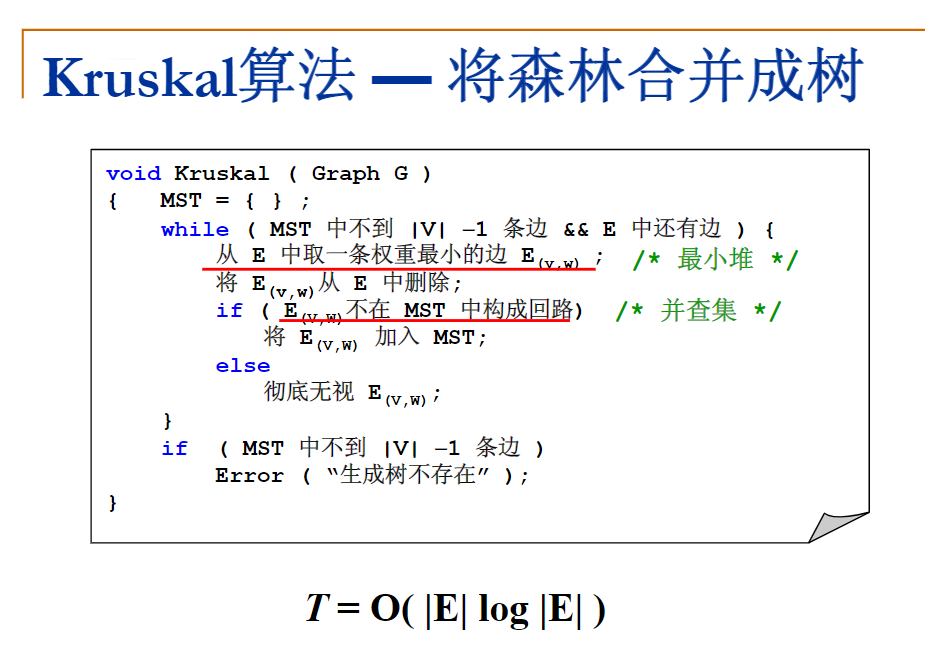
这一节前面都在讲前面的几道题目,我就没有放在这里了,而是放在对应的题目下,详情请跳转到各自的题底下查看吧;题目果然做一道忘一道,我感觉没做完多久我连Huffman Codes的构建都给忘了 emmm;好了 回到这节课的内容 最短路径问题,然后发现自己听的时候根本没做笔记 emm,然后为了后续方便我还是截个图放一下伪代码 以后自己查起来也方便
BFS DFS
编程作业
那就直接进入编程题吧:
- 哈利·波特的考试 是很基本的算法应用,一定要做。如果不会,那么看看小白专场,会详细介绍C语言的实现方法;
- Saving James Bond - Hard Version 有余力的话,好人做到底,如果上周已经尝试着救过007了,这周就继续给他建议吧;
- 旅游规划 Dijkstra算法的变形——姥姥只能帮你到这里了,自己动脑筋想一下怎么改造经典去解决这个问题?实在不会也不要急,再下周会讲算法的。
07-图4 哈利·波特的考试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define INFINITY 10000
#define MAX_SIZE 100
int MGraph[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
typedef struct ENode *PtrToENode;
struct ENdode{
int v1, v2;
int weight;
};
int main()
{
int N, M;
int v1, v2, weight;
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
//init MGraph
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N;j++)
MGraph[i][j] = INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &weight);
//construct graph
v1--;
v2--;
MGraph[v1][v2] = weight;
MGraph[v2][v1] = weight;
}
//floyd matrix
for (int k = 0; k < N;k++)
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N;j++)
if (MGraph[i][k] + MGraph[k][j] < MGraph[i][j])
MGraph[i][j] = MGraph[i][k] + MGraph[k][j];
//i,k k,j -> i,j compare with i,j direct
int Min_dis = 1000, Max_dis = 0;
int record;
//analysis
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N;j++)
{
if(i!=j && Max_dis< MGraph[i][j])
Max_dis = MGraph[i][j];
}
if(Max_dis==INFINITY)
{
printf("0");
break;
}
if(Min_dis > Max_dis)
{
Min_dis = Max_dis;
record = i + 1;
}
Max_dis = 0;
}
if(Max_dis!=INFINITY)
printf("%d %d", record, Min_dis);
return 0;
}
07-图5 Saving James Bond - Hard Version
做这个题的时候发现自己上次写这个写了一个Bug,我看成半径了所以那个第一次Jump是得改一下的emmm 问题不大 hhh
还有就是这道题 emmm 我做了两个小时,感觉骚操作有点多啊 emmm 但是没有通过全部例子,而且也没想到为啥没通过,特别是最后一个 一步到达的 我感觉我考虑进去了。先把自己代码贴上吧 后面我看看有没有讲解这题(没有的话 我就去找一个简版的)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100
typedef struct SVNode *PtrToSVNode;
struct SVNode{
int x;
int y;
};
typedef struct VNode *PtrToVNode;
struct VNode{
int x;
int y;
int pre_id;
PtrToVNode Next;
};
typedef struct Graph{
int id;
int pre_id;
int x;
int y;
PtrToVNode Next;
} AdjList[MaxVertexNum];
bool VM[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
bool Jump(int now_x, int now_y, int next_x, int next_y, int D);
bool FirstJump(int x, int y, int D);
bool IsSafe(int x, int y, int D);
int main()
{
AdjList LGraph;
int N, D;
int x_, y_;//location of a crocodile
scanf("%d %d", &N, &D);
PtrToVNode NewNode;
PtrToSVNode tempV;
//construct graph
queue<PtrToVNode> myqueue;
LGraph[0].x = 0;
LGraph[0].y = 0;
LGraph[0].id = 0;
LGraph[0].pre_id = -1;
queue<PtrToSVNode> vertex_queue;
for (int i = 0; i < MaxVertexNum;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < MaxVertexNum;j++)
VM[i][j] = false;
int N_num = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &x_, &y_);
if (FirstJump(x_, y_, D))
{
//nodes for first jump can reach
NewNode = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct VNode));
NewNode->x = x_;
NewNode->y = y_;
NewNode->pre_id = 0;
VM[x_ + 50][y_ + 50] = true;
VM[y_ + 50][x_ + 50] = true;
myqueue.push(NewNode);
NewNode->Next = LGraph[0].Next;
LGraph[0].Next = NewNode;
N_num--;
}
else
{
//nodes for unvisited at first
tempV = (PtrToSVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct SVNode));
tempV->x = x_;
tempV->y = y_;
vertex_queue.push(tempV);
}
}
PtrToVNode W;
int LG = 1;
bool Have = false;
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
W = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
x_ = W->x;
y_ = W->y;
VM[x_ + 50][y_ + 50] = true;
LGraph[LG].id = LG;
LGraph[LG].pre_id = W->pre_id;
LGraph[LG].x = x_;
LGraph[LG].y = y_;
if(IsSafe(x_, y_, D))
{
Have = true;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N_num;i++)
{
tempV = vertex_queue.front();
vertex_queue.pop();
if (!VM[tempV->x + 50][tempV->y + 50] && Jump(x_, y_, tempV->x, tempV->y, D))
{
NewNode = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct VNode));
NewNode->x = tempV->x;
NewNode->y = tempV->y;
VM[tempV->x + 50][tempV->y + 50] = true;
VM[tempV->y + 50][tempV->x + 50] = true;
NewNode->pre_id = LGraph[LG].id;
NewNode->Next = LGraph[LG].Next;
LGraph[LG].Next = NewNode;
N_num--;
myqueue.push(NewNode);
}
else
{
vertex_queue.push(tempV);
}
}
LG++;
}
if(Have)
{
//output result
int con = LGraph[LG].id;
stack<PtrToSVNode> result;
int cout = 0;
while(con!=-1)
{
tempV = (PtrToSVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct SVNode));
tempV->x = LGraph[con].x;
tempV->y = LGraph[con].y;
result.push(tempV);
cout++;
con = LGraph[con].pre_id;
}
printf("%d\n", cout-1);
result.pop();
while(!result.empty())
{
tempV = result.top();
printf("%d %d\n", tempV->x, tempV->y);
result.pop();
}
}
else
{
printf("0");
}
return 0;
}
bool Jump(int now_x, int now_y, int next_x, int next_y, int D)
{
if ((now_x - next_x) * (now_x - next_x) + (now_y - next_y) * (now_y - next_y) <= D * D)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool FirstJump(int x, int y, int D)
{
if ((x * x + y * y) <= (7.5 + D) * (7.5 + D))
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool IsSafe(int x, int y, int D)
{
if (abs(abs(x) - 50) <= D || abs(abs(y) - 50) <= D)
return true;
else
return false;
}
我似乎知道我一开始的问题出在哪里了,我是直接按照鳄鱼进来的顺序,来直接决定这个queue队列的,我看了其他人还会根据鳄鱼的距离进行整体的排序,直接是通过和原点的距离进行排序,然后再进行BFS操作,参考地址:
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38677814/article/details/80036587
- https://www.cnblogs.com/minesweeper/p/5954733.html 我发现这两好像是一样的,但是博客园里说明了解题思路
大致看完思路后 重新的一版,仔细看了一下问题:
- 没有考虑,直接一跳就能到岸的情况,这种情况也没说应该输出什么呀,直接输出
1作为跳跃次数而不需要鳄鱼嘛? - 输出最小一跳的,需要在BFS第一跳按距离进行排序(本来我想用qsort直接一个队列内解决,但是好像使用错误了 所以就拿熟悉的priority_queue来处理的),之所以使用BFS是因为要求跳的次数最少,而不是跳的距离最短,如果距离最短的话 dijkstra 更好
- 一开始直接拿我上次的一些函数做Safe判断,后面才发现哦吼,这个不是数组,所以不需要-50啥的操作
- 鳄鱼在岛内和岸上的要在一开始就去掉
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct crocodile *Ptrtocro;
typedef struct crocodile
{
int x;
int y;
double d;
bool v;
int pre_id;
int my_id;
}croco[MAX_SIZE];
// function
bool FirstJump(int x, int y, int D);
bool Jump(int now_x, int now_y, int next_x, int next_y, int D);
bool IsSafe(int x, int y, int D);
bool cmp(crocodile a, crocodile b);
int main()
{
int N, D, x_, y_, step = 0, temp_id;
croco Allcroco;
// 为了更好使用sort直接排序,使用vector
vector<crocodile> myqueue;
stack<int> mystack;
crocodile now;
bool Safe = false;
scanf("%d %d", &N, &D);
// 一步就能跳到岸上 不需要经过鳄鱼
if (D >= 25)
printf("1\n");
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &x_, &y_);
// init
Allcroco[i].d = x_ * x_ + y_ * y_;
Allcroco[i].x = x_;
Allcroco[i].y = y_;
Allcroco[i].pre_id = -1;
Allcroco[i].my_id = i;
Allcroco[i].v = false;
// init
// 岛内和边界的都直接以访问过再后续被去掉
if (Allcroco[i].d <= 7.5 * 7.5 || abs(x_) >= 50 || abs(y_) >= 50)
Allcroco[i].v = true;
else if (FirstJump(x_, y_, D))
{
Allcroco[i].pre_id = 0;
myqueue.push_back(Allcroco[i]);
Allcroco[i].v = true;
}
}
// 如果没有第一步的落脚点 直接失败
if(myqueue.empty())
printf("0\n");
else
{
sort(myqueue.begin(), myqueue.end(), cmp);
/* ---------------------------- BFS ------------------------ */
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
now = myqueue.front();
myqueue.erase(myqueue.begin());
if(IsSafe(now.x, now.y, D))
{
Safe = true;
break;
}
// 判断是否相邻并可跳
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
crocodile next = Allcroco[i];
if(!next.v && Jump(now.x, now.y, next.x, next.y, D))
{
myqueue.push_back(next);
Allcroco[i].v = true;
Allcroco[i].pre_id = now.my_id;
}
}
}
if(Safe)
{
mystack.push(now.my_id);
step = 1;
while(true)
{
temp_id = Allcroco[now.my_id].pre_id;
step++;
if(temp_id == 0)
break;
mystack.push(temp_id);
now = Allcroco[temp_id];
}
printf("%d\n", step);
while(!mystack.empty())
{
temp_id = mystack.top();
now = Allcroco[temp_id];
printf("%d %d\n", now.x, now.y);
mystack.pop();
}
}
else
printf("0");
}
}
return 0;
}
bool FirstJump(int x, int y, int D)
{
if ((x * x + y * y) <= (7.5 + D) * (7.5 + D))
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool Jump(int now_x, int now_y, int next_x, int next_y, int D)
{
if ((now_x - next_x) * (now_x - next_x) + (now_y - next_y) * (now_y - next_y) <= D * D)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool IsSafe(int x, int y, int D)
{
if (abs(x) + D >= 50 || abs(y) + D >= 50)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool cmp(crocodile a, crocodile b)
{
return a.d < b.d;
}
07-图6 旅游规划
这个题本身不难,然而我找了一上午的为啥么priority_queue的样子不对,后面才知道,样子是不对,就是存在里面的顺序,但是top和pop是对的,也就是说你看到的top不一定是真正top出来的,然后Dijkstra算法被我随着这个priority_queue进行了修改,去掉了visit因为我每次都在接近最近的那个 有点像A*了噢,没错 我又似乎做了一整个天:
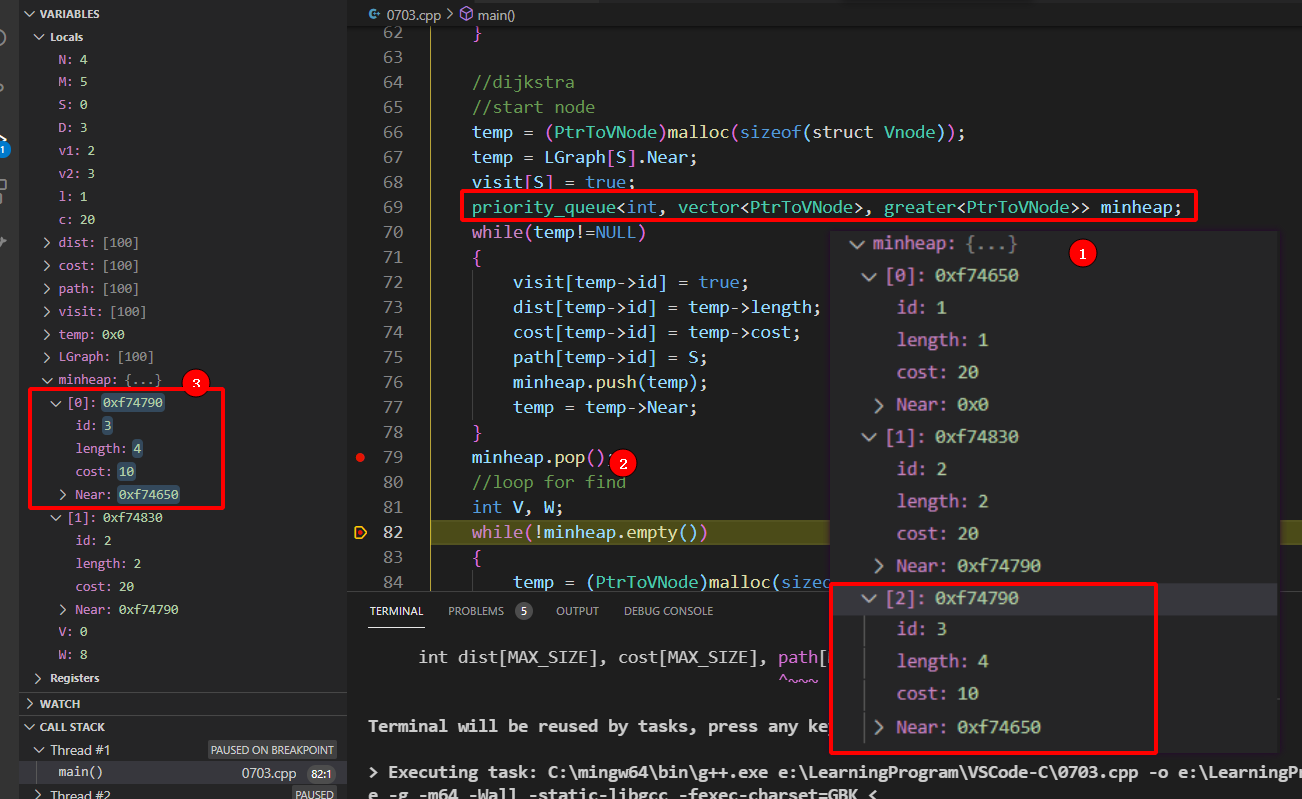
- 重载运算符需要放在外面,而不是struct结构体里面
prioriy_queue的样子可能不会是以排序好的,但是对于输出的一定是排好的
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 500
#define INF 10000
typedef struct Vnode *PtrToVNode;
struct Vnode
{
int id;
int length;
int cost;
PtrToVNode Near;
};
//重载运算符 以适用priority_queue的greater按length来排
bool operator<(Vnode a,Vnode b)
{
if(a.length == b.length)
return a.cost < b.cost;
return a.length < b.length;
}
bool operator>(Vnode a,Vnode b)
{
if(a.length == b.length)
return a.cost > b.cost;
return a.length > b.length;
}
typedef struct LGraph
{
PtrToVNode Near;
}AdjList[MAX_SIZE];
int main()
{
int N, M, S, D, v1, v2, l, c;
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &N, &M, &S, &D);
int cost[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE],dis[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
PtrToVNode temp,temp_near;
AdjList LGraph;
priority_queue<Vnode, vector<Vnode>, greater<Vnode>> minheap;
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
LGraph[i].Near = NULL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N;j++)
{
cost[i][j] = INF;
dis[i][j] = INF;
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &l, &c);
cost[v1][v2] = c;
cost[v2][v1] = c;
dis[v1][v2] = l;
dis[v2][v1] = l;
temp = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Vnode));
temp->id = v2;
temp->length = INF;
temp->cost = INF;
temp->Near = LGraph[v1].Near;
LGraph[v1].Near = temp;
//无向图 双边连接
temp = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Vnode));
temp->id = v1;
temp->length = INF;
temp->cost = INF;
temp->Near = LGraph[v2].Near;
LGraph[v2].Near = temp;
}
//dijkstra -> but with min heap modify no visit
//start node insert heap
temp = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Vnode));
temp->id = S;
temp->length = 0;
temp->cost = 0;
temp->Near = LGraph[S].Near;
minheap.push(*temp);
// init some temp variables
int V, W;
//from start node
while(minheap.top().id != D)
{
temp = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Vnode));
temp_near = (PtrToVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Vnode));
*temp_near = minheap.top();
minheap.pop();
temp = LGraph[temp_near->id].Near;
V = temp_near->id;
//insert all around nodes
while(temp!=NULL)
{
W = temp->id;
if (temp_near->length + dis[V][W] < temp->length)
{
temp->length = temp_near->length + dis[V][W];
temp->cost = temp_near->cost + cost[V][W];
minheap.push(*temp);
}
temp = temp->Near;
}
}
printf("%d %d", minheap.top().length, minheap.top().cost);
return 0;
}
第八周:图(最小生成树 拓扑排序)
最小生成树
-
是一棵树
- 无回路
- ∣ V ∣ |V| ∣V∣个顶点一定有 ∣ V ∣ ? 1 |V|-1 ∣V∣?1条边
-
是生成树
- 包含全部顶点
- ∣ V ∣ ? 1 |V|-1 ∣V∣?1条边都在图里
-
边的权重和最小
拓扑排序
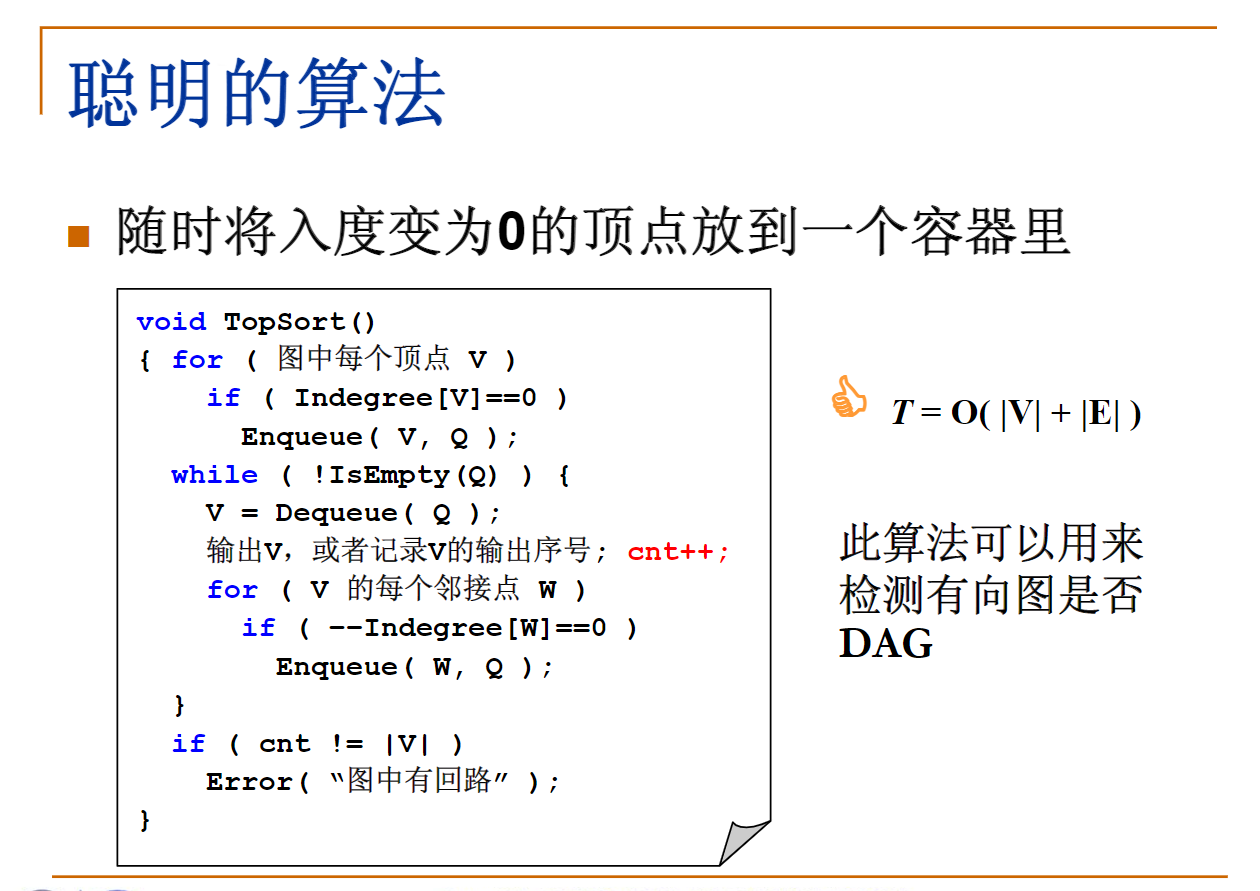
- 拓扑序:如果图中从 V V V 到 W W W 有一条有向路径,则 V V V 一定排在 W W W 之前。满足此条件的顶点序列称为一个拓扑序
- 获得一个拓扑序的过程就是拓扑排序
- AOV (Activity on vertex) 如果有合理的拓扑序,则必定是有向无环图 (Directed Acyclic Graph, DAG)
本周编程题跟之前的题目相比,难度略高,所以都是选做的:
- 公路村村通 非常直白的最小生成树问题,但编程量略大,选做 —— 有时间就写写
- How Long Does It Take 拓扑排序的变形,程序不算复杂,建议尝试;
- 关键活动 在听完课以后,这题的思路应该比较清晰了,只需要在前面一题的程序基础上增加一些内容。不过编程量还是有一些的,根据自己的时间决定,慎入。
08-图7 公路村村通
wc 兴奋,记录一下 我最快写完的一道题,可能整体连起来一个小时都不到,而且一次就过了 芜湖!看来是前面的时间都是给后面来打基石的,主要是最小堆的实在太太太好用了hhhh
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 1000
typedef struct VNode *PtrToNode;
struct VNode {
int id;
PtrToNode Near;
};
typedef struct LGraph{
PtrToNode Near;
} Adj[MAX_SIZE];
typedef struct input *PtrToi;
struct input{
int v1;
int v2;
int cost;
};
//重载运算符 给priority用
bool operator < (input a, input b)
{
return a.cost < b.cost;
}
bool operator > (input a, input b)
{
return a.cost > b.cost;
}
bool CheckU(int S[], int v1, int v2);
void Union(int S[], int v1, int v2);
int Find(int S[], int X);
int main()
{
int N, M,v1,v2,cost;
int SumCost = 0;
int S[MAX_SIZE];//并查集所用
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
Adj LGraph;
priority_queue<input, vector<input>, greater<input>> minheap;
PtrToi temp = (PtrToi)malloc(sizeof(input));
PtrToNode NewNode;
for (int i = 0; i < M;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &cost);
v1--;
v2--;
NewNode = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(VNode));
NewNode->id = v2;
NewNode->Near = LGraph[v1].Near;
LGraph[v1].Near = NewNode;
NewNode = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(VNode));
NewNode->id = v1;
NewNode->Near = LGraph[v2].Near;
LGraph[v2].Near = NewNode;
temp->v1 = v1;
temp->v2 = v2;
temp->cost = cost;
minheap.push(*temp);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
S[i] = -1;
}
while (!minheap.empty())
{
*temp = minheap.top();
minheap.pop();
v1 = temp->v1;
v2 = temp->v2;
if (CheckU(S,v1,v2))
SumCost = SumCost + temp->cost;
}
int cout = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(S[i]<0)
cout++;
if(cout>1)
break;
}
if(cout>1)
printf("-1");
else
printf("%d", SumCost);
return 0;
}
bool CheckU(int S[],int v1,int v2)
{
int Root1, Root2;
Root1 = Find(S, v1);
Root2 = Find(S, v2);
if (Root1 == Root2)
return false;
else
Union(S, Root1, Root2);
return true;
}
void Union(int S[],int v1,int v2)
{
if(S[v1]<S[v2])//集合1大
{
S[v1] += S[v2];//并入
S[v2] = v1;//根换成v1
}
else
{
S[v2] += S[v1];
S[v1] = v2;
}
}
int Find(int S[],int X)
{
if(S[X]<0)
return X;
else
return S[X] = Find(S, S[X]);
}
08-图8 How Long Does It Take
做这个题挺快的吧(但是应该也有两小时,主要是后面找错误,所以我也顺便贴两份),原因:
- 第一份我在一开始的时候就开始计算Cost,没有考虑到输入可能不是从小到大进行输入的
- 所以第二份我直接将Cost计算放到了dequeue inqueue的步骤
有错误版:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 101
#define MY_MAX(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y))
typedef struct Vnode *PtrToV;
struct Vnode
{
int id;
PtrToV Near;
};
typedef struct LGraph
{
PtrToV Near;
} AdjList[MAX_SIZE];
int compare(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int main()
{
int N, M, v1, v2, cost, temp_v;
int num_V = 0;//all node num
int In_degree[MAX_SIZE], Cost[MAX_SIZE];
AdjList LGraph;
PtrToV NewNode;
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
In_degree[i] = 0;
Cost[i] = 0;
LGraph[i].Near = NULL;
}
queue<int> myqueue;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &cost);
In_degree[v2]++;
Cost[v2] = MY_MAX(Cost[v1] + cost, Cost[v2]);
//有向图
NewNode = (PtrToV)malloc(sizeof(Vnode));
NewNode->id = v2;
NewNode->Near = LGraph[v1].Near;
LGraph[v1].Near = NewNode;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if(In_degree[i]==0)
myqueue.push(i);
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
temp_v = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
num_V++;
NewNode = (PtrToV)malloc(sizeof(Vnode));
NewNode = LGraph[temp_v].Near;
while(NewNode!=NULL)
{
if(--In_degree[NewNode->id]==0)
myqueue.push(NewNode->id);
NewNode = NewNode->Near;
}
}
if(num_V == N)
{
qsort(Cost, N, sizeof(int), compare);
printf("%d", Cost[N - 1]);
}
else
printf("Impossible");
return 0;
}
可通过全部案例版:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 101
#define MY_MAX(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y))
typedef struct Vnode *PtrToV;
struct Vnode
{
int id;
PtrToV Near;
};
typedef struct LGraph
{
PtrToV Near;
} AdjList[MAX_SIZE];
int compare(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int main()
{
int N, M, v1, v2, cost, temp_v;
int num_V = 0;//all node num
int In_degree[MAX_SIZE], Cost[MAX_SIZE], ALLCOST[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
AdjList LGraph;
PtrToV NewNode;
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
In_degree[i] = 0;
Cost[i] = 0;
LGraph[i].Near = NULL;
}
queue<int> myqueue;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &cost);
In_degree[v2]++;
ALLCOST[v1][v2] = cost;
// Cost[v2] = MY_MAX(Cost[v1] + cost, Cost[v2]);
//有向图
NewNode = (PtrToV)malloc(sizeof(Vnode));
NewNode->id = v2;
NewNode->Near = LGraph[v1].Near;
LGraph[v1].Near = NewNode;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if(In_degree[i]==0)
myqueue.push(i);
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
v1 = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
num_V++;
NewNode = (PtrToV)malloc(sizeof(Vnode));
NewNode = LGraph[v1].Near;
while(NewNode!=NULL)
{
v2 = NewNode->id;
if(--In_degree[v2]==0)
myqueue.push(v2);
Cost[v2] = MY_MAX(Cost[v1] + ALLCOST[v1][v2], Cost[v2]);
NewNode = NewNode->Near;
}
}
if(num_V == N)
{
qsort(Cost, N, sizeof(int), compare);
printf("%d", Cost[N - 1]);
}
else
printf("Impossible");
return 0;
}
08-图9 关键活动
这个我写了还挺久的,主要是总是考虑不全,写了起码三种方案,主要是多起点和多终点的关键活动是否应该包含其他终点的;然后还有可行除了第0个case和样例能输出对,其他的并没有输出对,暂时找不到什么原因,可能后面看其他人的回来再补原因吧
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 101
#define MY_MAX(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y))
typedef struct Vnode *PtrToV;
struct Vnode
{
int id;
PtrToV Near;
};
typedef struct LGraph
{
PtrToV Near;
} AdjList[MAX_SIZE];
int compare(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int main()
{
int N, M, v1, v2, cost;
int num_V = 0;//all node num
int In_degree[MAX_SIZE], Cost[MAX_SIZE], ALLCOST[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
int NoChange_Indegree[MAX_SIZE],NoChange_Cost[MAX_SIZE];
int record_from[MAX_SIZE];
AdjList LGraph;
PtrToV NewNode;
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
In_degree[i] = 0;
NoChange_Indegree[i] = 0;
Cost[i] = 0;
LGraph[i].Near = NULL;
record_from[i] = -1;
}
queue<int> myqueue;
queue<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &cost);
v1--;
v2--;
In_degree[v2]++;
NoChange_Indegree[v2]++;
ALLCOST[v1][v2] = cost;
//有向图
NewNode = (PtrToV)malloc(sizeof(Vnode));
NewNode->id = v2;
NewNode->Near = LGraph[v1].Near;
LGraph[v1].Near = NewNode;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if(In_degree[i]==0)
myqueue.push(i);
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
v1 = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
num_V++;
NewNode = (PtrToV)malloc(sizeof(Vnode));
NewNode = LGraph[v1].Near;
while(NewNode!=NULL)
{
v2 = NewNode->id;
if(--In_degree[v2]==0)
myqueue.push(v2);
if(Cost[v1] + ALLCOST[v1][v2] > Cost[v2])
record_from[v2] = v1;
Cost[v2] = MY_MAX(Cost[v1] + ALLCOST[v1][v2], Cost[v2]);
NewNode = NewNode->Near;
}
}
//record no change cost to find max time from which task
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
NoChange_Cost[i] = Cost[i];
int record_i;
stack<int> temp_result;
if (num_V == N)
{
qsort(Cost, N, sizeof(int), compare);
printf("%d\n", Cost[N - 1]);
// find the max num
for (record_i = N - 1; record_i > 0; record_i--)
if(NoChange_Cost[record_i] == Cost[N-1])
break;
temp_result.push(record_i);
while(record_i != -1)
{
temp_result.push(record_from[record_i]);
record_i = record_from[record_i];
}
//remove -1
temp_result.pop();
//get task connect
v1 = temp_result.top();
temp_result.pop();
while(!temp_result.empty())
{
v2 = temp_result.top();
temp_result.pop();
printf("%d->%d\n", v1 + 1, v2 + 1);
v1 = v2;
}
}
else
printf("0");
return 0;
}
然后回来的时候 我已经忘了 我的整体思路过程了,但是大概从对比来看,我并没有记录最早实现时间,只是将Cost进行记录,缺少了一个信息点?
参考地址,我的参考标准一般都是行数比较少/有点注释,思路的,这样看起来比较快
然后整理了一下思路,整体和拓扑排序差不多,注意出入度的记录,外加的需要注意时间(最早最晚的完成时间记录)以对比关键任务;发现之前缺少了一个 从小到大输出,如果一致与输入的任务顺序相反这点需要 记录输入的顺序,来看的,也就是入度是有顺序的
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#define MAX_SIZE 101
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int N, M, v1, v2, cost, tv1, tv2, num_task = 0;
int finalc[MAX_SIZE]={0}, judgec[MAX_SIZE]={0};
int costmap[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
int indegree[MAX_SIZE] = {0};
vector<int> connect[MAX_SIZE];
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &cost);
indegree[v2]++;
costmap[v1][v2] = costmap[v2][v1] = cost;
connect[v1].push_back(v2);
}
queue<int> myqueue;
stack<int> mystack;
// 开始进入出入度的队列入队
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
if (indegree[i] == 0)
myqueue.push(i);
// 循环并计算
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
// 用来看是否所有任务都可以达到
num_task++;
tv1 = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
mystack.push(tv1);
for (int i = 0; i < connect[tv1].size(); i++)
{
tv2 = connect[tv1][i];
if (--indegree[tv2] == 0)
myqueue.push(tv2);
if (finalc[tv2] < finalc[tv1] + costmap[tv1][tv2])
finalc[tv2] = finalc[tv1] + costmap[tv1][tv2];
}
}
// 如果队列走完了数量不对 那就是有不连通的点
if (num_task != N)
{
printf("0");
return 0;
}
printf("%d\n", finalc[mystack.top()]);
// init all judgec
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
judgec[i] = finalc[mystack.top()];
while(!mystack.empty())
{
tv1 = mystack.top();
mystack.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < connect[tv1].size(); i++)
{
tv2 = connect[tv1][i];
if(judgec[tv1] > judgec[tv2] - costmap[tv1][tv2])
judgec[tv1] = judgec[tv2] - costmap[tv1][tv2];
}
}
// 编号小的开始
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = connect[i].size() - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
tv2 = connect[i][j];
// 判断是否有冗余时间,如果没有就是关键任务
if (judgec[tv2] - finalc[i] - costmap[i][tv2] == 0)
printf("%d->%d\n", i, tv2);
}
return 0;
}
第九周:排序(上)
冒泡和插入排序应该很熟悉了,但是我还是做个搬运工贴一下各个的实现大致代码,冒泡的一开始我一直没数对,主要是冒上来后都是从0开始的,从冒后的–结束
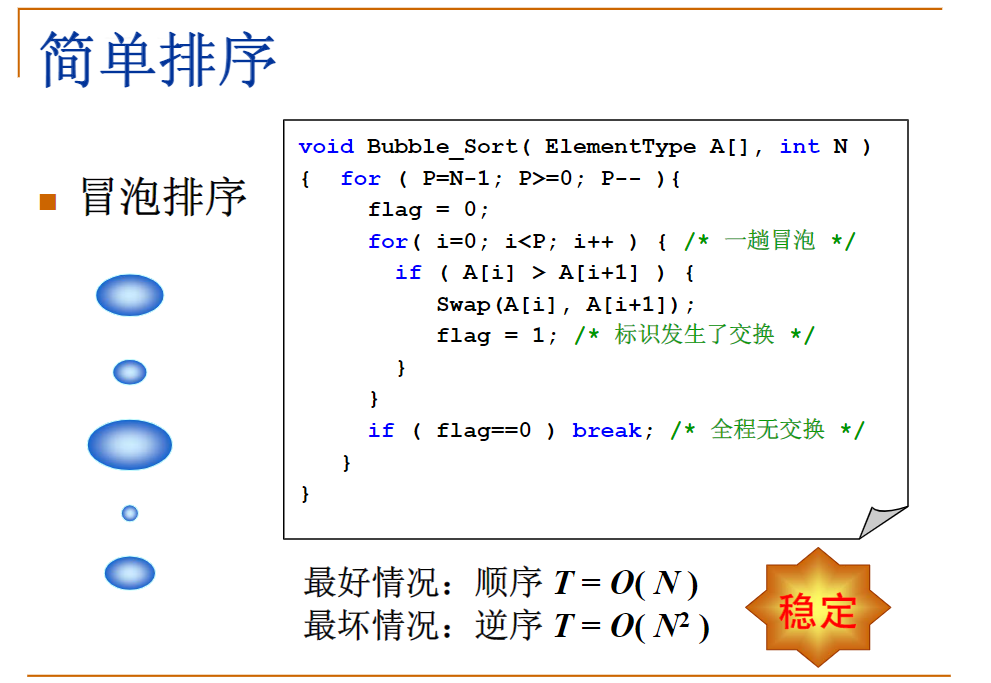


这里令我一开始比较惊讶的是:希尔排序不是稳定的 emmm。然后查了查,原来是分组的问题
对于相同的两个数,可能由于分在不同的组中而导致它们的顺序发生变化。
算法稳定性 – 假设在数列中存在a[i]=a[j],若在排序之前,a[i]在a[j]前面;并且排序之后,a[i]仍然在a[j]前面。则这个排序算法是稳定的!
这里还有两种关于不同间隔的,看的时候觉得 哇塞都好聪明啊


编程作业
09-排序1 排序
hhh 这题我投机取巧了 直接在网页上写了qsort,不过后面看课的时候发现,人家设置这题的本意是各个排序算法都试一下,所以等我再写写,单独总结一份(我看其实讨论区也有大佬贴了自己的想法和各个算法的运行情况)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100000
int Tree[MAX_SIZE];
int compare(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &Tree[i]);
}
qsort(Tree, N, sizeof(int), compare);
printf("%d", Tree[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
printf(" %d", Tree[i]);
}
}
09-排序2 Insert or Merge
最小N, Ins 第一步没变 主要是这个测试案例一直过不了,我把我两次写的都注释了CASE 1 CASE 2,后面我看了一下别人的做法,发现是先判断是否一致,然后跳出来进行下一步迭代,而我的做法是:先判断 然后迭代一下 然后跳出
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
bool Check(int N, int P[], int A[]);
void Insert_sort(int i, int Num[]);
void Merge_pass(int A[], int TmpA[], int N, int len);
int main()
{
int Sort_N[MAX_SIZE], Num[MAX_SIZE], Partial_N[MAX_SIZE];
int N, temp, len = 1, record_i, j, insert_num;
int *TempA;
bool flag = false;
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &Num[i]);
Sort_N[i] = Num[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &Partial_N[i]);
//Check for Insertion
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
//-------------- CASE 3
Insert_sort(i, Num);
flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Num);
if (flag)
{
Insert_sort(++i, Num);
break;
}
//-------------- CASE 2
// insert_num = Num[i];
// for (j = i; j > 0 && Num[j-1] > insert_num;j--)
// Num[j] = Num[j - 1];
// Num[j] = insert_num;
// flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Num);
// if (flag)
// {
// record_i = i;
// break;
// }
//-------------- CASE 1
// int tempi = i;
// for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
// {
// if(Num[j]>Num[tempi])
// {
// temp = Num[tempi];
// Num[tempi] = Num[j];
// Num[j] = temp;
// tempi = j;
// }
// }
// flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Num);
// if (flag)
// {
// record_i = i;
// break;
// }
}
if(!flag)
{
//definitely merge
TempA = (int *)malloc(N * sizeof(int));
if(TempA!=NULL)//确保内存分配生效
{
while(len<N)
{
//front
flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Sort_N);
Merge_pass(Sort_N, TempA, N, len);
len *= 2;
if(flag)
break;
//back
flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Sort_N);
Merge_pass(TempA, Sort_N, N, len);
len *= 2;
if(flag)
break;
}
free(TempA);
}
printf("Merge Sort\n");
printf("%d", Sort_N[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < N;i++)
{
printf(" %d", Sort_N[i]);
}
}
else
{
printf("Insertion Sort\n");
printf("%d", Num[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < N;i++)
{
printf(" %d", Num[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
bool Check(int N, int P[], int A[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
if(P[i]!=A[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Merge(int A[], int TmpA[], int L, int R, int R_end)
{
int L_end = R - 1;//左边终点位置即右点
int tmp = L;
int NumElements = R_end - L + 1;
while (L <= L_end && R <= R_end)
{
if(A[L]<=A[R])
TmpA[tmp++] = A[L++];
else
TmpA[tmp++] = A[R++];
}
while(L<=L_end)//直接复制左边剩下的
TmpA[tmp++] = A[L++];
while(R<=R_end)
TmpA[tmp++] = A[R++];
for (int i = 0; i < NumElements; i++, R_end--)
A[R_end] = TmpA[R_end];
}
void Merge_pass(int A[], int TmpA[], int N, int len)
{
int i, j;
//归并前面的
for (i = 0; i <= N - 2 * len; i += 2 * len)
Merge(A, TmpA, i, i + len, i + 2 * len - 1);
//归并最后两个子列
if(i+len<N)
Merge(A, TmpA, i, i + len, N - 1);
else
for (j = i; j < N;j++)
TmpA[j] = A[j];
}
void Insert_sort(int i, int Num[])
{
int temp;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if(Num[j]>Num[i])
{
temp = Num[i];
Num[i] = Num[j];
Num[j] = temp;
}
}
}
还有写Merge的时候基本对着PPT直接写的 emmm 看来还是得自己捋一捋这个下标(我每次都下标搞混)
回过头看最后一讲的习题选讲,发现原来可以按照现归并排序的长度来进行,而不需要归并一次,对比一次(没错 我是这么干的)
09-排序3 Insertion or Heap Sort
emmm 这题和上题连在一起的话 不就… 插入、归并、堆排序都写了嘛 emmm 那就差希尔排序了?
这道题期间本来应该一天搞定的 然而我… 身体原因肌肉拉伤 emmm 提醒大家:不要久坐啊----。回归正题:主要是堆排序一开始我一直没理解,我以为是直接最大堆上来 寻思了好久 这 这 示例的输出是为啥呀;然后我就看了一下课后的伪代码 一步步直接写了一遍 就悟了,原来是拿完全二叉树来做的,难道是我用priority_queue(greater) 用太多了 而没有在意实际的最大堆的构建过程
那就直接贴吧,Insert_sort我是直接拿的上面那段复制了,heap_sort是根据伪代码写的(基本一致),再贴一下我的笔记路程吧,应该说是草稿
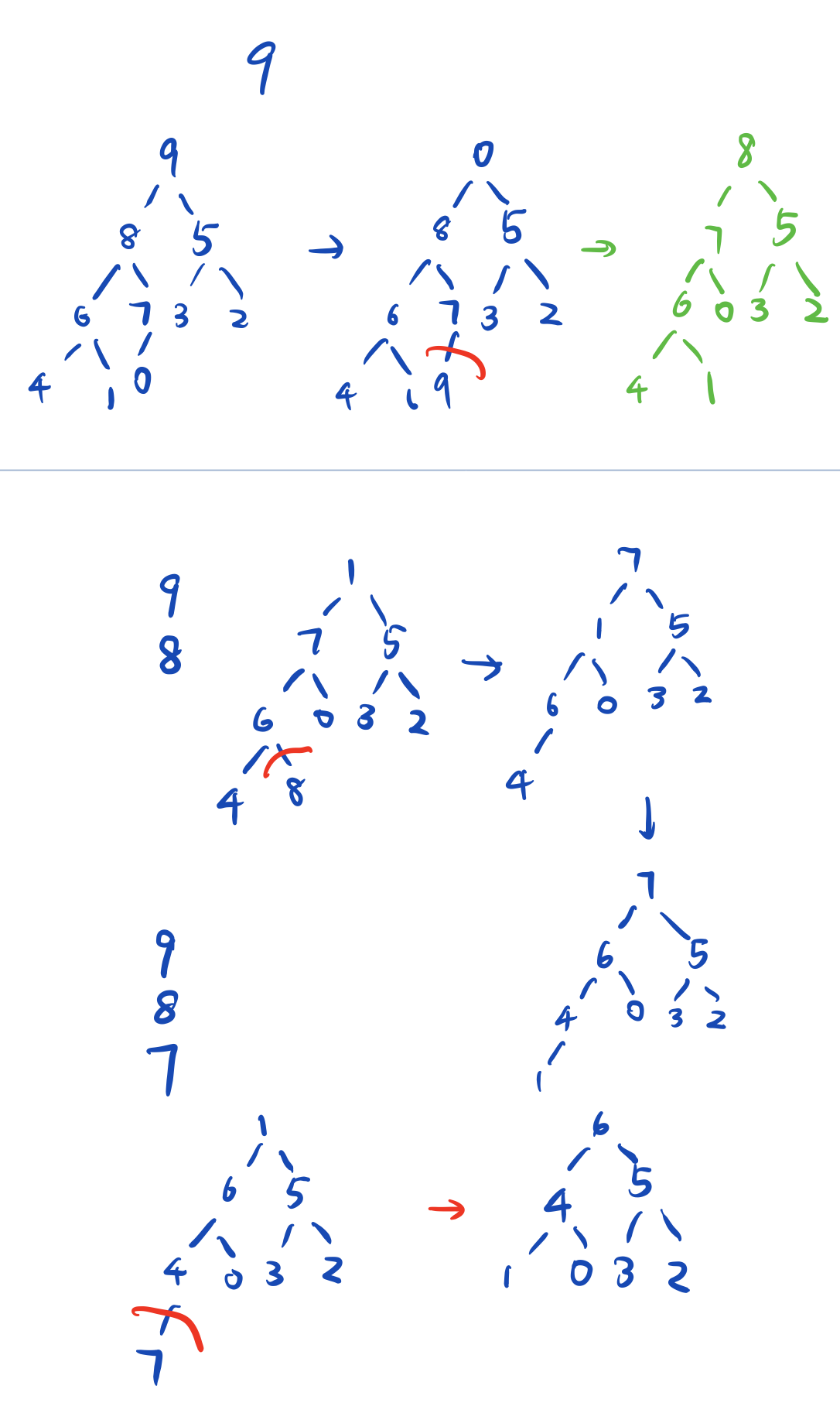
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
bool Check(int N, int P[], int A[]);
void Insert_sort(int i, int Num[]);
void Heap_sort(int A[], int N, int start);
void PercDown(int A[], int p, int N);
int main()
{
int Sort_N[MAX_SIZE], Num[MAX_SIZE], Partial_N[MAX_SIZE];
int N, len;
bool flag = false; // 1. check if Insert sort; 2. check if finished sort
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &Num[i]);
Sort_N[i] = Num[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &Partial_N[i]);
//Check for Insertion
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
Insert_sort(i, Num);
flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Num);
if (flag)
{
Insert_sort(++i, Num);
break;
}
}
if(!flag)
{
// From slides 9.3 堆排序
int i;
// build max heap with binary tree
for (i = N / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
PercDown(Sort_N, i, N);
//definitely heap
for (len = N - 1; len > 0; len--)
{
flag = Check(N, Partial_N, Sort_N);
Heap_sort(Sort_N, N, len);
if(flag)
break;
}
printf("Heap Sort\n");
printf("%d", Sort_N[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < N;i++)
printf(" %d", Sort_N[i]);
}
else
{
printf("Insertion Sort\n");
printf("%d", Num[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < N;i++)
{
printf(" %d", Num[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
bool Check(int N, int P[], int A[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
if(P[i]!=A[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
void PercDown(int A[], int p, int N)
{
// From slides 9.3 堆排序
/* 将N个元素的数组中以A[p]为根的子堆调整为最大堆 */
int Parent, Child;
int X;
X = A[p];
for (Parent = p; Parent * 2 + 1 < N; Parent = Child)
{
Child = Parent * 2 + 1;
//首先确保child下标没超,然后对比哪个更大
if ((Child != N - 1) && (A[Child] < A[Child + 1]))
Child++;
if (X >= A[Child])
break; //找到了位置
else
A[Parent] = A[Child];//否则进入下一层继续看
}
A[Parent] = X;
}
void Heap_sort(int A[], int N, int start)
{
//swap max value and delete
int temp = A[0];
A[0] = A[start];
A[start] = temp;
PercDown( A, 0, start );
}
void Insert_sort(int i, int Num[])
{
int temp;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if(Num[j]>Num[i])
{
temp = Num[i];
Num[i] = Num[j];
Num[j] = temp;
}
}
}
第十周:排序(下)
快速排序
伪代码贴一下好了,因为… 刚刚刷脉脉动态看到有人考快排,评论区了都是sort hhh 是我了
/* 快速排序 */
ElementType Median3( ElementType A[], int Left, int Right )
{
int Center = (Left+Right) / 2;
if ( A[Left] > A[Center] )
Swap( &A[Left], &A[Center] );
if ( A[Left] > A[Right] )
Swap( &A[Left], &A[Right] );
if ( A[Center] > A[Right] )
Swap( &A[Center], &A[Right] );
/* 此时A[Left] <= A[Center] <= A[Right] */
Swap( &A[Center], &A[Right-1] ); /* 将基准Pivot藏到右边*/
/* 只需要考虑A[Left+1] … A[Right-2] */
return A[Right-1]; /* 返回基准Pivot */
}
void Qsort( ElementType A[], int Left, int Right )
{ /* 核心递归函数 */
int Pivot, Cutoff, Low, High;
if ( Cutoff <= Right-Left ) { /* 如果序列元素充分多,进入快排 */
Pivot = Median3( A, Left, Right ); /* 选基准 */
Low = Left; High = Right-1;
while (1) { /*将序列中比基准小的移到基准左边,大的移到右边*/
while ( A[++Low] < Pivot ) ;
while ( A[--High] > Pivot ) ;
if ( Low < High ) Swap( &A[Low], &A[High] );
else break;
}
Swap( &A[Low], &A[Right-1] ); /* 将基准换到正确的位置 */
Qsort( A, Left, Low-1 ); /* 递归解决左边 */
Qsort( A, Low+1, Right ); /* 递归解决右边 */
}
else InsertionSort( A+Left, Right-Left+1 ); /* 元素太少,用简单排序 */
}
void QuickSort( ElementType A[], int N )
{ /* 统一接口 */
Qsort( A, 0, N-1 );
}
表排序
主要是由于排序的数据结构大,所引出的一种排序方式,添加一个table来做假移动,最后物理排序因为
N个数字的排列由若干个独立的环组成
基数排序/桶排序
有一说一其实我没听懂这个桶排序的过程,主要是主次位的排序意义可能没get到,估计需要在自己走一遍伪代码(所以我这次编程作业基本 qsort compare改一下 hhh)
/* 基数排序 - 主位优先 */
/* 假设元素最多有MaxDigit个关键字,基数全是同样的Radix */
#define MaxDigit 4
#define Radix 10
/* 桶元素结点 */
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node{
int key;
PtrToNode next;
};
/* 桶头结点 */
struct HeadNode {
PtrToNode head, tail;
};
typedef struct HeadNode Bucket[Radix];
int GetDigit ( int X, int D )
{ /* 默认次位D=1, 主位D<=MaxDigit */
int d, i;
for (i=1; i<=D; i++) {
d = X%Radix;
X /= Radix;
}
return d;
}
void MSD( ElementType A[], int L, int R, int D )
{ /* 核心递归函数: 对A[L]...A[R]的第D位数进行排序 */
int Di, i, j;
Bucket B;
PtrToNode tmp, p, List = NULL;
if (D==0) return; /* 递归终止条件 */
for (i=0; i<Radix; i++) /* 初始化每个桶为空链表 */
B[i].head = B[i].tail = NULL;
for (i=L; i<=R; i++) { /* 将原始序列逆序存入初始链表List */
tmp = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
tmp->key = A[i];
tmp->next = List;
List = tmp;
}
/* 下面是分配的过程 */
p = List;
while (p) {
Di = GetDigit(p->key, D); /* 获得当前元素的当前位数字 */
/* 从List中摘除 */
tmp = p; p = p->next;
/* 插入B[Di]号桶 */
if (B[Di].head == NULL) B[Di].tail = tmp;
tmp->next = B[Di].head;
B[Di].head = tmp;
}
/* 下面是收集的过程 */
i = j = L; /* i, j记录当前要处理的A[]的左右端下标 */
for (Di=0; Di<Radix; Di++) { /* 对于每个桶 */
if (B[Di].head) { /* 将非空的桶整桶倒入A[], 递归排序 */
p = B[Di].head;
while (p) {
tmp = p;
p = p->next;
A[j++] = tmp->key;
free(tmp);
}
/* 递归对该桶数据排序, 位数减1 */
MSD(A, i, j-1, D-1);
i = j; /* 为下一个桶对应的A[]左端 */
}
}
}
void MSDRadixSort( ElementType A[], int N )
{ /* 统一接口 */
MSD(A, 0, N-1, MaxDigit);
}
所有排序的全部总结
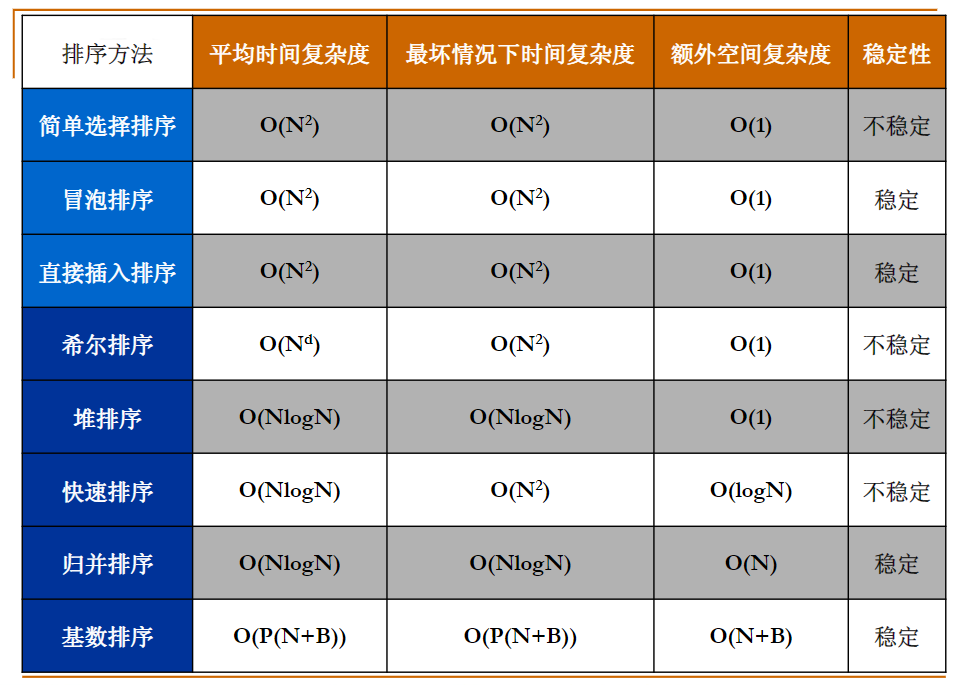
编程作业
- 统计工龄 非常简单的练习,想一下用哪种排序效率最高?此题一定要做;
- PAT Judge 2014年PAT春季考试真题,供备考的同学练练手;
- Sort with Swap(0, i) 2013年免试研究生上机考试真题,需要思考一下,想通了就很容易 —— 于是有时间就想想吧~ 实在想不出也不要紧,最后一次课会专门讲的。
10-排序4 统计工龄
恕我直言,这道题是我近期做的最快的一道题,而且还是在我爸硬是要聊天的氛围下做完的,大概5分钟?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 51
int main()
{
int N, input_num;
int All_Count[MAX_SIZE];
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)
All_Count[i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &input_num);
All_Count[input_num]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)
{
if (All_Count[i] != 0)
printf("%d:%d\n", i, All_Count[i]);
}
return 0;
}
10-排序5 PAT Judge
我以为大概很快能做完,然后还是做了一小时以上,构思方向上挺简单的,就是结构体然后再对里面的key排序,时间花费主要是:
- rank输出 并列分数的排名是一样的,这一点我一直没发现,直到我对比样例的时候才发现
- full_mark可以多次提交,但是这点我针对性的加了判断,也没能过最后一个案例
- K最小,有0分这一条案例始终不知道为什么没过,还有要求是最少要输出一个 那就0分里面肯定是00001号?
后面回过头来再看问题吧,先继续旅程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10001
typedef struct User
{
int id;
int score[5];
int sum_score;
int full_p;
bool full_count[5];
} ArrayUser[MAX_SIZE];
int compare2key(const void *a, const void *b)
{ /* 比较两种键值:按key1非升序排列;如果key1相等,则按key2非降序排列 */
int k;
if ( ((const User *)a)->sum_score > ((const User *)b)->sum_score )
k = 1;
else if ( ((const User *)a)->sum_score < ((const User *)b)->sum_score )
k = -1;
else
{ /* 如果key1相等 */
if ( ((const User *)a)->full_p > ((const User *)b)->full_p)
k = 1;
else if ( ((const User *)a)->full_p < ((const User *)b)->full_p)
k = -1;
else
{
if ( ((const User *)a)->id < ((const User *)b)->id)
k = 1;
else
k = -1;
}
}
return -k;
}
int main()
{
int N, K, M;
int full_mark[5];
int user_id, p_id, p_score;
ArrayUser all_user;
scanf("%d %d %d", &N, &K, &M);
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++)
scanf("%d", &full_mark[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
all_user[i].sum_score = 0;
all_user[i].full_p = 0;
all_user[i].id = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
all_user[i].score[j] = -1;
all_user[i].full_count[j] = false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &user_id, &p_id, &p_score);
p_id--;
user_id--;
all_user[user_id].id = user_id + 1;
if(all_user[user_id].score[p_id] == -1)
{
all_user[user_id].score[p_id] = p_score>0?p_score:0;
all_user[user_id].sum_score += all_user[user_id].score[p_id];
}
else if (all_user[user_id].score[p_id] < p_score)
{
all_user[user_id].sum_score += (p_score - all_user[user_id].score[p_id]);
all_user[user_id].score[p_id] = p_score;
}
if (all_user[user_id].score[p_id] == full_mark[p_id] && !all_user[user_id].full_count[p_id])
{
all_user[user_id].full_p++;
all_user[user_id].full_count[p_id] = true;
}
}
qsort(all_user, N, sizeof(User), compare2key);
bool flag = true;
int temp_rank;
// for first one or at least one
printf("%d %05d %d", 1, all_user[0].id, all_user[0].sum_score);
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
if(all_user[0].score[j]!=-1)
printf(" %d", all_user[0].score[j]);
else
printf(" -");
if (j == (K - 1))
printf("\n");
}
// for next
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
if (all_user[i].sum_score != 0)
{
if (flag && all_user[i].sum_score == all_user[i - 1].sum_score)
{
temp_rank = i;
flag = false;
}
else if (all_user[i].sum_score != all_user[i - 1].sum_score)
flag = true;
if(!flag)
printf("%d %05d %d", temp_rank, all_user[i].id, all_user[i].sum_score);
else
printf("%d %05d %d", i + 1, all_user[i].id, all_user[i].sum_score);
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
if(all_user[i].score[j]!=-1)
printf(" %d", all_user[i].score[j]);
else
printf(" -");
if (j == (K - 1))
printf("\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
回头又找到问题了,找到以下问题:
- compare函数里手误写错了对比id的地方
- 当有人提交了通过了编译器分数为0时,应该参与排名的,所以得加个submit的flag来判断
- full_mark有等于-1的情况!这也太狗了啊!
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10000
typedef struct User
{
int id;
int score[5];
int sum_score;
int full_p;
bool submit;
} ArrayUser[MAX_SIZE];
int compare2key(const void *a, const void *b)
{ /* 比较两种键值:按key1非升序排列;如果key1相等,则按key2非降序排列 */
int k;
if ( ((const User *)a)->sum_score < ((const User *)b)->sum_score )
k = 1;
else if ( ((const User *)a)->sum_score > ((const User *)b)->sum_score )
k = -1;
else
{ /* 如果key1相等 */
if ( ((const User *)a)->full_p < ((const User *)b)->full_p)
k = 1;
else if ( ((const User *)a)->full_p > ((const User *)b)->full_p)
k = -1;
else
{
if ( ((const User *)a)->id < ((const User *)b)->id)
k = -1;
else
k = 1;
}
}
return k;
}
int main()
{
int N, K, M, full_mark[5], user_id, p_id, p_score;
ArrayUser all_user;
scanf("%d %d %d", &N, &K, &M);
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++)
scanf("%d", &full_mark[i]);
// init
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
all_user[i].sum_score = 0;
all_user[i].full_p = 0;
all_user[i].id = i + 1;
all_user[i].submit = false;
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
all_user[i].score[j] = -1; // non-visited
}
// init
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &user_id, &p_id, &p_score);
if (all_user[--user_id].score[--p_id] <= p_score)
{
all_user[user_id].score[p_id] = p_score > 0 ? p_score : 0;
if (p_score > -1)
all_user[user_id].submit = true;
}
}
// 重新整体计算 分数总和和满分题目
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
if (all_user[i].score[j] > 0)
{
if (all_user[i].score[j] == full_mark[j])
all_user[i].full_p++;
all_user[i].sum_score += all_user[i].score[j];
}
qsort(all_user, N, sizeof(User), compare2key);
int LastScore = all_user[0].sum_score, LastRank = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(all_user[i].submit)
{
// 当分数不相等时,需要更新一个记录到last
if (LastScore != all_user[i].sum_score)
{
LastScore = all_user[i].sum_score;
LastRank = i + 1;
}
printf("%d %05d %d", LastRank, all_user[i].id, all_user[i].sum_score);
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
if (all_user[i].score[j] >= 0)
printf(" %d", all_user[i].score[j]);
else
printf(" -");
if (j == (K - 1))
printf("\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
10-排序6 Sort with Swap(0, i)
一开始自己在草稿上画画看了看过程,意识到是一个找环,但是环必须像题目介绍那样从0开始吗?
这题做的特别梦幻中途去吃了个饭,但是大致时长没有超过一小时,梦幻的意思是,一开始过不了两个案例,然后我想了想我的do while也可以不do while 顺着写一个while就好了,然后 然后就发现全过了… hhhh 也就是自己都没发现上次的到底有啥问题 (可能就是do while的先操作问题吧)
我贴一下我的思考笔记。这个真的就有点乱,我基本后面操作的时候都是单步调试看看有没有对上我的思路,主要是swap操作有点骚 ,y因为我的数组下标是指的数值,数组内部的数字是排列的顺序,也就是输入进来的位置,不知道你们看这句话能不能get到
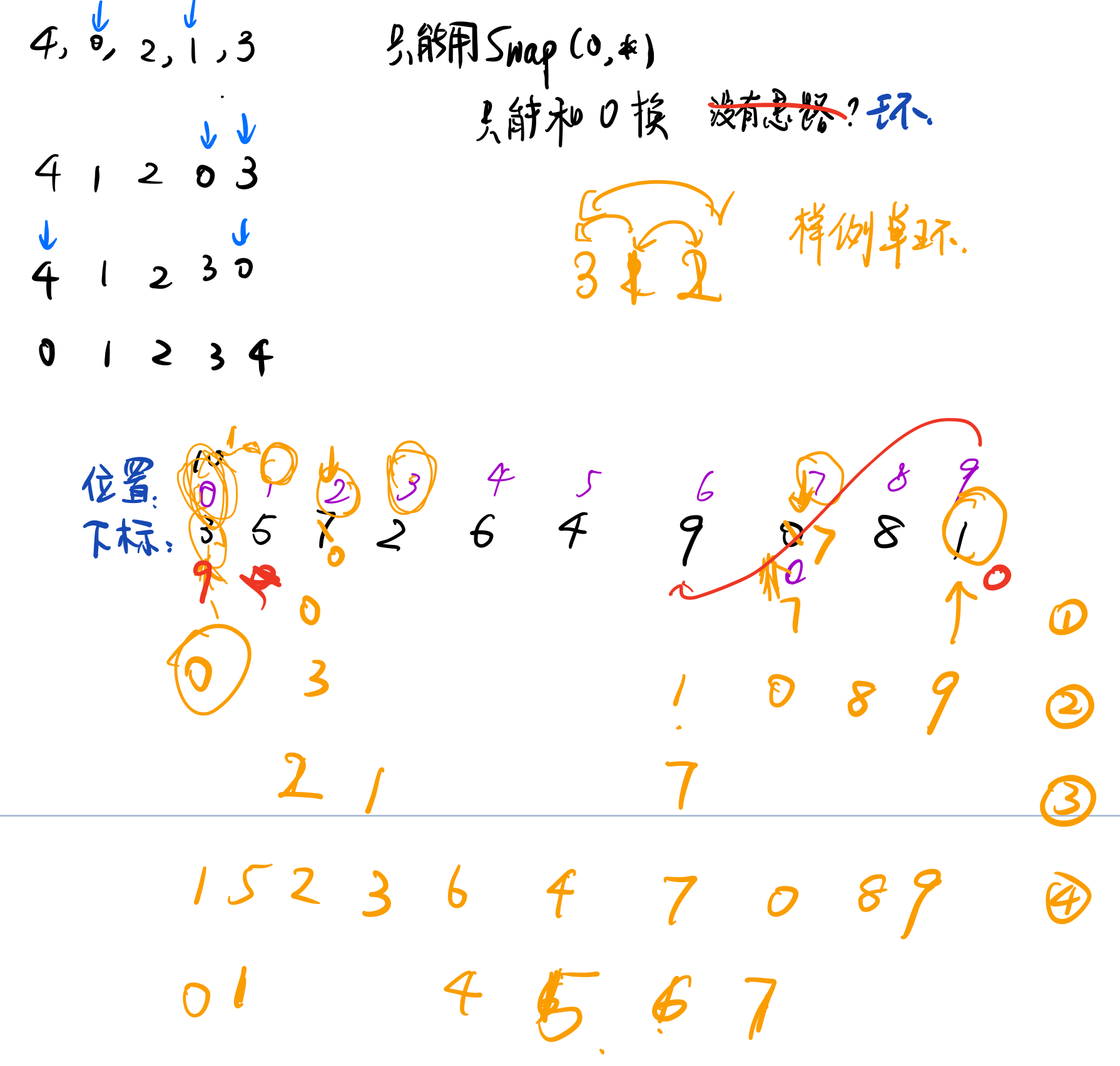
真的就像陈姥姥说的 只要想通了 程序上很简单 emmm 甚至我自己其实也有点蒙蒙的 但是大致就是这样?蒙蒙的理由主要在:环如果出现多个的时候,我是直接把0放到下一个不对的位置上,但是如果min的步骤 是否应该考虑放哪个不对的位置上产生的min最小还是说无论放哪里都是一样的,所以直接下一个就好了? -> 根据课上的环的道理来说,是一样的。
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100000
int main()
{
int N, ind, temp[MAX_SIZE], start;
int count = 0, Temp;
int s_count = 0;
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &ind);
temp[ind] = i;
if (ind == 0)
start = i;
}
while(1)
{
while (temp[s_count] != s_count)
{
//swap
Temp = temp[start];
temp[start] = start;
temp[s_count] = Temp;
start = Temp;
count++;
}
while(temp[++s_count] == s_count);
if(s_count>=N)
break;
//swap two num and count for another loop
temp[start] = temp[s_count];
temp[s_count] = 0;
count++;
}
printf("%d", count);
return 0;
}
回看最后一周的习题讲解,我觉得我的解法更聪明 hhhh 因为不需要另一个指针数组,我直接将下标代表的输入数字,然后存的是原下标,这样找起来就更方便了
第十一周:散列查找
啊!我终于到最后拉!啊!我的flag终于没有半途而废,(虽然是半途拾起 priority_queue qsort 等一系列骚操作,但是总算是 认认真真 完完全全的自己!刷完了一遍!)🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉 最后一章 冲啊!然后我发现原来还有一周的课 emmm 只是因为在明天发布 我没看到而已 hhh 没事 结束前一节也可以提前庆祝一番,好了 回归正题
“散列” 基本思想
- 以关键字 key 为自变量,通过一个确定的函数 h (散列函数) 计算出对应的函数值h(key), 作为数据对象的存储地址
- 可能不同的关键字会映射到同一个散列地址上,即 h ( k e y i ) = h ( k w y j ) h(key_i)=h(kwy_j) h(keyi?)=h(kwyj?) 当 k e y i =? k e y j key_i \not = key_j keyi??=keyj?,称为冲突(collision) 也就需要某种冲突解决策略
构造方法
1. 直接定址法
取关键词的某个线性函数值为散列地址,即
h
(
k
e
y
)
=
a
×
k
e
y
+
b
h(key) = a \times key +b
h(key)=a×key+b
比如这样的:
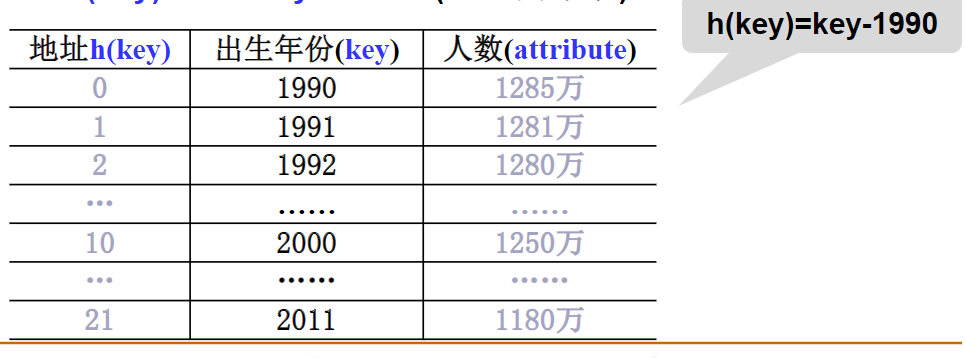
2. 除留余数法
散列函数为:h(key) = key mod p
3. 数字分析法
分析数字关键字在各位上的变化情况。取比较随机的位作为散列地址。
-
比如:取11位手机号码key的后4位作为地址:
散列函数为: h(key) = atoi(key+7) (char *key)
其中atoi的意思是整个key是字符串,然后往后移了7位,也就是取最后4个数作为地址
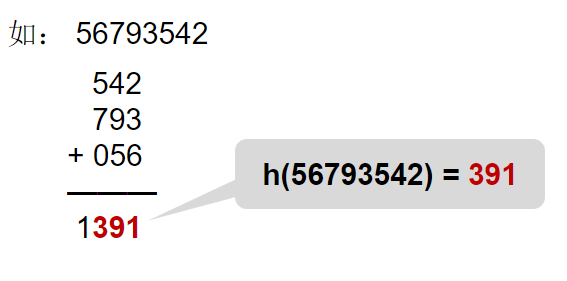
4. 折叠法
把关键词分割成位数相同的几个部分,然后叠加
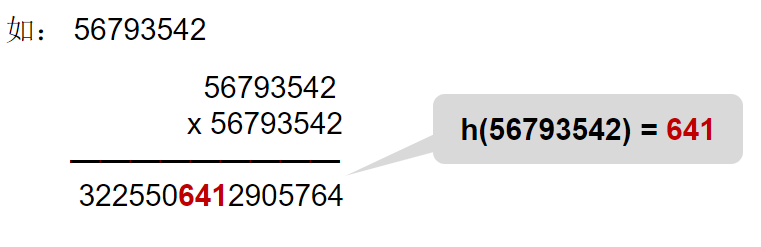
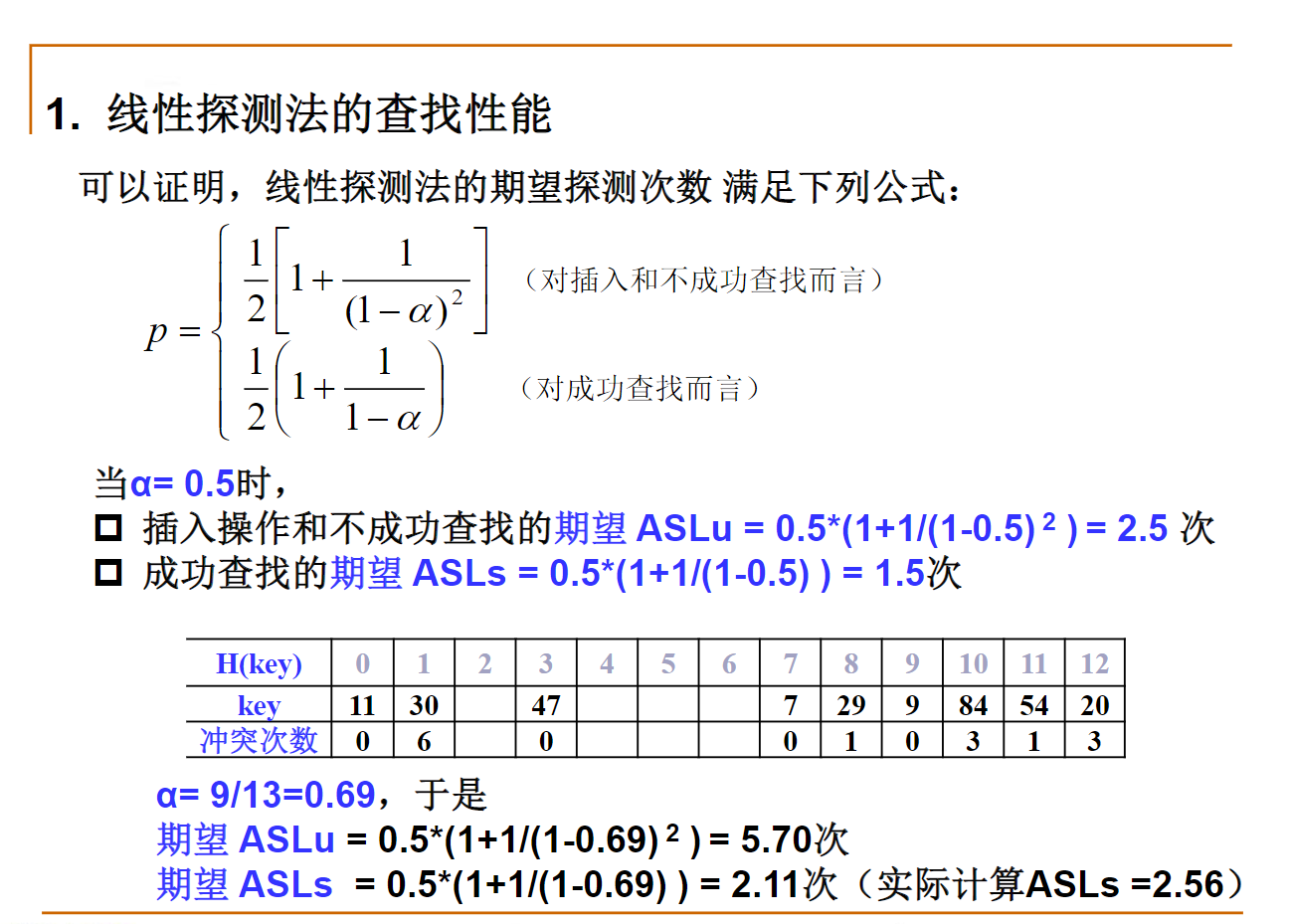
5. 平方取中法
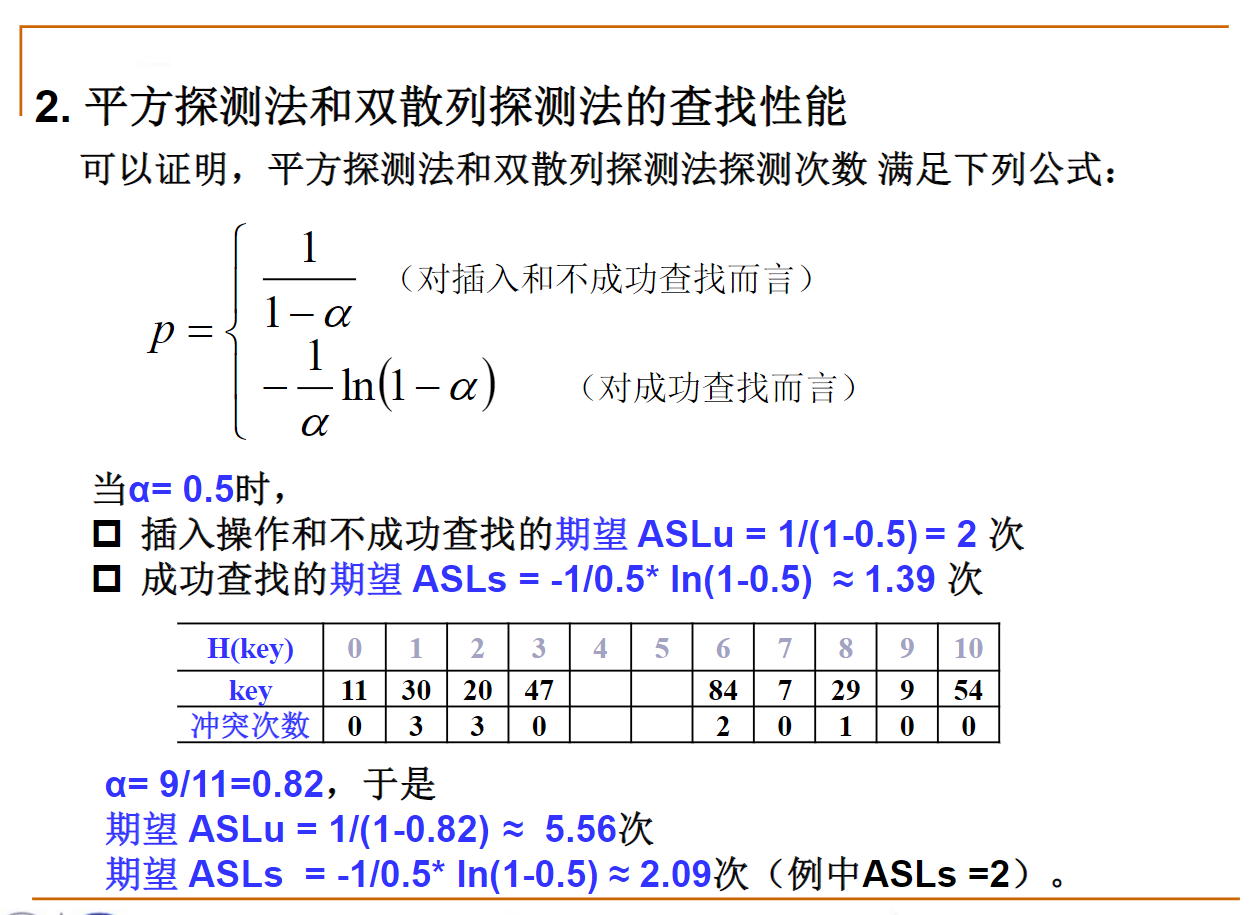

编程作业
- **电话聊天狂人 一定要做。**如果不知道怎么下手,可以看“小白专场”,将详细给出C语言实现的方法;
- Hashing 2014年考研上机复试真题,比较直白,一定要做;
- QQ帐户的申请与登陆 数据结构教材中的练习题,可以用散列,也可以用排序,有兴趣+有时间的,建议两种都试一下。选做;
- Hashing - Hard Version 很好玩的一道题哦,需要思考一下,想通了就很容易 —— 于是有时间就想想吧~ 实在想不通也没关系,下周习题课会讲的。
11-散列1 电话聊天狂人
由小白专场里层提到过挺多种解法的 其中关于解法二是我第一次看到就去查了查行不行的 hhhh 确实耗内存太大了,不过我的想法还再加一层 Hash后内存,不怎么喜欢用链表操作 lol 但是看起来好像是要喜欢起来
好了我放弃了 我写了一版,虽然找了几个bug出来,但是还是始终没能过最后一个最大N的案例,实属想不到为什么啊~
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 200000
#define KEY 11 // phone number length
#define TAIL 6
typedef struct SData
{
bool have;
char phone[KEY + 1];
int count;
} AData[MAX_SIZE];
int Hash(char *string);
int main()
{
int N, temp_hash, max_count = 0;
AData All;
int Ccount = 1;
bool SAME_F = false;
char phone_n[KEY + 1], cray_phone[KEY + 1];
// cray_phone[0] = '\0';
scanf("%d", &N);
// Initial Data
for (int i = 0;i<MAX_SIZE;i++)
{
All[i].have = false;
All[i].count = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2*N; i++)
{
scanf("%s", &phone_n);
temp_hash = Hash(phone_n);
//放入Hash表内
if (!All[temp_hash].have)
{
strcpy(All[temp_hash].phone, phone_n);
All[temp_hash].count = 1;
All[temp_hash].have = true;
}
else if (strcmp(phone_n, All[temp_hash].phone) == 0)
All[temp_hash].count++;
else //解决冲突下一个Hash num
{
while (All[++temp_hash].have)
{
if (strcmp(phone_n, All[temp_hash].phone) == 0)
{
All[temp_hash].count++;
SAME_F = true;
break;
}
if (temp_hash >= MAX_SIZE - 1)
temp_hash = -1;
}
if(!SAME_F)
{
strcpy(All[temp_hash].phone, phone_n);
All[temp_hash].count = 1;
All[temp_hash].have = true;
}
SAME_F = false;
}
//找到最大的
if(All[temp_hash].count>max_count)
{
max_count = All[temp_hash].count;
strcpy(cray_phone, phone_n);
Ccount = 1;
}
else if (All[temp_hash].count == max_count && strcmp(cray_phone, phone_n) > 0)
{
strcpy(cray_phone, phone_n);
Ccount++;
}
}
printf("%s %d", cray_phone, max_count);
if (Ccount != 1)
printf(" %d", Ccount);
return 0;
}
int Hash(char *phone)
{
char ctemp[KEY - TAIL];
strncpy(ctemp, phone, KEY - TAIL);
int front = atoi(ctemp);
int tail = atoi(phone + KEY - TAIL);
return (front + tail) % MAX_SIZE;
// int tail = atoi(phone + KEY - TAIL);
// return tail % MAX_SIZE;
}
好吧,我找了半小时还是没发现什么问题,但是大概知道了原来C++里有unorder_map去做哈希表的 hhhh 这是跳转链接:CSDN博客;不过最后正儿八经还是得走小白专场那样的链表形式吧,主要是我找不到问题,最大N的特点也没有什么说明,随机… emmm 很苦恼啊
但是 我就不是哎,看完之后,我决定用一下C++ STL库里的unodered_map来玩!真香。不过还是参考的其他人的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//reference: https://blog.csdn.net/Van0512/article/details/53125103
int main()
{
int N;
unordered_map<string, int> dict;
char s[12];
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * N; i++)
{
scanf("%s", s);
dict[s]++;
}
auto it = dict.cbegin();
string minStr = it->first;
int num = 1;
int callCnt = it->second;
for (++it; it != dict.cend(); ++it)
{
if(it->second > callCnt)
{
callCnt = it->second;
minStr = it->first;
num = 1;
}
else if (it->second == callCnt)
{
num++;
if (it->first < minStr)
minStr = it->first;
}
}
cout << minStr << " " << callCnt;
if (num > 1)
cout << " " << num;
}
11-散列2 Hashing
我好像知道上一个为什么了,我发现我理解错 冲突解决方法的计算了,具体可以见我一开始注释的部分,对了这个题有两个需要注意的点:
- 最小素数是2
- 冲突解决方法是 加了之后在取余不是 取余后发现冲突再加
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10000
int MPrime(int n);
int Hash(int ts, int n);
bool have[MAX_SIZE];
int main()
{
int MSize, N;
int num, result; //input num
scanf("%d %d", &MSize, &N);
MSize = MPrime(MSize);
for (int i = 0; i < MSize; i++)
have[i] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N-1; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &num);
result = Hash(MSize, num);
if (result != -1)
printf("%d ", result);
else
printf("- ");
}
scanf("%d", &num);
result = Hash(MSize, num);
if (result != -1)
printf("%d", result);
else
printf("-");
return 0;
}
//求素数
int MPrime(int n)
{
//最小的情况需要考虑 最小素数为 2
if (n == 1)
return 2;
n--;//把n包含进来
int i, p = (n % 2) ? n + 2 : n + 1;//下一个奇数开始
while (1)
{
for (i = (int)sqrt(p); i > 2; i--)
if (!(p % i))
break;
if(i==2)
break;
else
p += 2;
}
return p;
}
int Hash(int ts, int n)
{
int key;
int qp = 0, i;
for (i = 0; i < ts; i++)
{
key = (n + i * i) % ts;
if(!have[key])
{
have[key] = true;
return key;
}
}
return -1;
}
// wrong case
// int Hash(int ts, int n)
// {
// int key = n % ts;
// int qp = 1, i;
// if(!have[key])
// {
// have[key] = true;
// return key;
// }
// else
// {
// while (qp * qp < ts)
// {
// key += qp * qp;
// qp++;
// if (key >= ts)
// key -= ts;
// if (!have[key])
// {
// have[key] = true;
// return key;
// }
// }
// return -1;
// }
// }
11-散列3 QQ帐户的申请与登陆
这个题估计整体时长半小时,主要是有前面两道题铺垫,基本bug都踩了一遍;但是即使这样我还是没能找出我电话狂人那道题的bug。这道题基本写完就直接提交了,这其中主要是处理输入的第一个字符花了几分钟看到这个bug,其他的基本一气呵成。真不错
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100000
typedef struct QQ
{
bool have;
char num[11];
char pwd[17];
} All_QQ[MAX_SIZE];
All_QQ DataSet;
int Check(char *QQ, char *pwd, int size);
int Create(char *QQ, char *pwd, int size);
int Hash(char *QQ, int N);
int MPrime(int n);
int main()
{
char cmd='\n', QQ_num[11], pwd[17];
int flag;
int N, MSize;
scanf("%d\n", &N);
MSize = MPrime(N);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE;i++)
DataSet[i].have = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
while(cmd == '\n')
scanf("%c", &cmd);
if (cmd == 'L') //login in
{
scanf("%s %s", &QQ_num, &pwd);
flag = Check(QQ_num, pwd, MSize);
switch (flag)
{
case 1:
printf("Login: OK\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("ERROR: Wrong PW\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("ERROR: Not Exist\n");
break;
default:
printf("error\n");
break;
}
}
else if(cmd == 'N')//create new
{
scanf("%s %s", &QQ_num, &pwd);
flag = Create(QQ_num, pwd, MSize);
switch(flag)
{
case 1:
printf("New: OK\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("ERROR: Exist\n");
break;
default:
printf("error\n");
break;
}
}
cmd = '\n';
}
return 0;
}
int Create(char *QQ, char *pwd, int size)
{
int hash_num = Hash(QQ, size);
if(!DataSet[hash_num].have)
{
strcpy(DataSet[hash_num].num, QQ);
strcpy(DataSet[hash_num].pwd, pwd);
DataSet[hash_num].have = true;
return 1;
}
else if(strcmp(pwd, DataSet[hash_num].pwd) == 0)
return 2;
}
int Check(char *QQ, char *pwd, int size)
{
int hash_num = Hash(QQ, size);
if(!DataSet[hash_num].have)
return 3;
else if(DataSet[hash_num].have)
{
if(strcmp(pwd, DataSet[hash_num].pwd) == 0)
return 1;
else
return 2;
}
}
int Hash(char *QQ, int N)
{
long unsigned int tail = atoi(QQ);
int hash_num;
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
hash_num = (tail + i) % N;
if(!DataSet[hash_num].have)
return hash_num;
else if(strcmp(QQ, DataSet[hash_num].num) == 0)
return hash_num;
}
return -1;
}
//求素数
int MPrime(int n)
{
//最小的情况需要考虑 最小素数为 2
if (n == 1)
return 2;
n--;//把n包含进来
int i, p = (n % 2) ? n + 2 : n + 1;//下一个奇数开始
while (1)
{
for (i = (int)sqrt(p); i > 2; i--)
if (!(p % i))
break;
if(i==2)
break;
else
p += 2;
}
return p;
}
11-散列4 Hashing - Hard Version
写了大概一小时,主要是在构思思路,但是又像狂人那题一样,我找不到bug,就是为什么通不过最大N的案例,emmm 是我哪里的认知又不对了嘛,我感觉我的想法应该是对的才对… emm 而且自认为还挺聪明的那种 hhh
找到了一个方法和我差不多 甚至比我还聪明点,考虑更周全点的:11-散列4 Hashing - Hard Version (30分)_语阑的博客-CSDN博客 可能是因为我并不考虑顺序,但是我以为的是,在我进行sort数字的输入的时候就在考虑顺序问题了?
- 找到一个bug 是没认真看题,题目说的是空位放负数!
但是都有最大N可以过了,为啥 随机那个还是过不了… emm 找不到问题所在了
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1000
typedef struct SNum
{
int real;
int sort;
} TNum[MAX_SIZE];
int compare2key(const void *a, const void *b)
{ /* 比较两种键值*/
int k;
if (((const struct SNum *)a)->sort > ((const struct SNum *)b)->sort)
k = 1;
else if(((const struct SNum *)a)->sort < ((const struct SNum *)b)->sort)
k = -1;
else
{
if(((const struct SNum *)a)->real < ((const struct SNum *)b)->real)
k = -1;
else
k = 1;
}
return k;
}
int main()
{
int N, temp;
TNum All;
bool once = true;
bool from_pre = false;
scanf("%d", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
All[i].real = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
scanf("%d", &All[i].real);
All[i].sort = All[i].real;
// -1 无值 跳过
if (All[i].real == -1)
continue;
// -1 无值 跳过
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
int hash_n = (All[i].real + j) % N;
if (i == hash_n && once)
{
All[i].sort = All[i].real;
break;
}
else if(i == hash_n)
break;
else
{
if (All[hash_n].real + 1 >= All[i].sort)
{
All[i].sort = All[hash_n].real + 1;
from_pre = true;
}
else if(from_pre)
All[i].sort++;
once = false;
}
}
once = true;
from_pre = false;
}
qsort(All, N, sizeof(struct SNum), compare2key);
for (int i = 0; i < N-1; i++)
{
if (All[i].sort != -1)
printf("%d ", All[i].real);
}
printf("%d", All[N - 1].real);
return 0;
}
虽然我看到了用拓扑排序做,但是我还是想不清楚我的到底出了啥问题,算是一种权重加上去的排序方式吧,不过在看完后 我还是再写一遍拓扑的吧,毕竟这道题也太太太精彩了 融合散列和拓扑
然而计算这样子来一遍我还是没找到我自己的那个版本的问题,但是按照参考:11-散列4 Hashing - Hard Version (30 分) - 王清河 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) 来写的一版,写的时候觉得!这人太聪明了!相邻的点竟然是用vector vector来做,加之hash做标,入度在前hash值上;这样出入度都非常好弄了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 1001
using namespace std;
// reference: https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghao-boke/p/10043281.html
int N, Num[MAX_SIZE];
// 以hash来做标,数值来进行对比
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(int i, int j)
{
return Num[i] > Num[j];
}
};
int main()
{
int origin_hash, temp = 1;
bool first = true;
int indegree[MAX_SIZE] = {0};
scanf("%d", &N);
vector<vector<int>> graph(N);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp> q;
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
scanf("%d", &Num[i]);
// 负数不算入
if (Num[i] < 0)
continue;
origin_hash = Num[i] % N;
if (origin_hash == i)
q.push(i);
else
{
do
{
// 以上一个点hash引做标 输入现在的值
graph[origin_hash].push_back(i);
// 线性探测到下一个
origin_hash = (Num[i] + temp) % N;
temp++;
indegree[i]++;
} while (origin_hash != i);
}
temp = 1;
}
while(!q.empty())
{
temp = q.top();
q.pop();
if(first)
{
printf("%d", Num[temp]);
first = false;
}
else
printf(" %d", Num[temp]);
for (int i = 0; i < graph[temp].size(); i++)
if (--indegree[graph[temp][i]] == 0)
q.push(graph[temp][i]);
}
return 0;
}
第十二周:KMP 串
什么是串? → 线性存储的一组数据(默认是字符)
特殊的操作集:
- 求串的长度
- 比较两串是否相等
- 两串相接
- 求子串
- 插入子串
- 匹配子串 (有难度的操作)
- 删除子串
这个KMP 非常六啊,但是这个子串的match构建有点绕,我理一理
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int Position;
#define NotFound -1
void BuildMatch( char *pattern, int *match )
{
Position i, j;
int m = strlen(pattern);
match[0] = -1;
for ( j=1; j<m; j++ ) {
i = match[j-1];
while ( (i>=0) && (pattern[i+1]!=pattern[j]) )
i = match[i];
if ( pattern[i+1]==pattern[j] )
match[j] = i+1;
else match[j] = -1;
}
}
Position KMP( char *string, char *pattern )
{
int n = strlen(string);
int m = strlen(pattern);
Position s, p, *match;
if ( n < m ) return NotFound;
match = (Position *)malloc(sizeof(Position) * m);
BuildMatch(pattern, match);
s = p = 0;
while ( s<n && p<m ) {
if ( string[s]==pattern[p] ) {
s++; p++;
}
else if (p>0) p = match[p-1]+1;
else s++;
}
return ( p==m )? (s-m) : NotFound;
}
int main()
{
char string[] = "This is a simple example.";
char pattern[] = "simple";
Position p = KMP(string, pattern);
if (p==NotFound) printf("Not Found.\n");
else printf("%s\n", string+p);
return 0;
}
编程作业
KMP 串的模式匹配
如果是看着课后的代码写 基本无难度,只在于return的格式需要稍作修改;如果不看的话,主要难点:
- 构造
match数组的过程,特别是有前子串相等的后 后子串的跳转,这一点我建议先看一下课,然后一定要自己画一遍过程 emmm;这里我画的太乱了 我感觉应该不好看懂 - 记得修改返回的格式是char *
- (提醒点) 虽然题目是 1 0 6 10^6 106 但是因为结束符也要占一个,所以其实最大size应该是1000001
我写的为了与strstr方法做对比,保持了输入输出一致,这样注释任意一个即可。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1000001
#define NotFound NULL
char *KMP(char *ostring, char *pattern);
void BuildMatch(char *pattern, int *match);
int main()
{
char ostring[MAX_SIZE];
char pattern[MAX_SIZE];
int N;
scanf("%s\n", &ostring);
scanf("%d\n", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// input pattern
scanf("%s", &pattern);
// method from strstr
// char *p = strstr(ostring, pattern);
// KMP compare
char *p = KMP(ostring, pattern);
// Result output
if (p == NotFound)
printf("Not Found\n");
else
printf("%s\n", p);
}
return 0;
}
char *KMP(char *ostring, char *pattern)
{
int n = strlen(ostring);
int m = strlen(pattern);
int s, p, *match;
if (n < m)
return NotFound;
match = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * m);
BuildMatch(pattern, match);
s = p = 0;
while (s < n && p < m)
{
if(ostring[s]==pattern[p])
{
s++;
p++;
}
else if (p > 0)
p = match[p - 1] + 1;
else
s++;
}
return (p == m) ? ostring + s - p : NotFound;
}
void BuildMatch(char *pattern, int *match)
{
int i, j;
int m = strlen(pattern);
match[0] = -1;
for (j = 1; j < m; j++)
{
i = match[j - 1];
while (i >= 0 && pattern[i + 1] != pattern[j])
i = match[i];
if (pattern[i + 1] == pattern[j])
match[j] = i + 1;
else
match[j] = -1;
}
}
运行结果对比:这么看内存上耗的也是挺大的吼,可能是因为开了match的数组
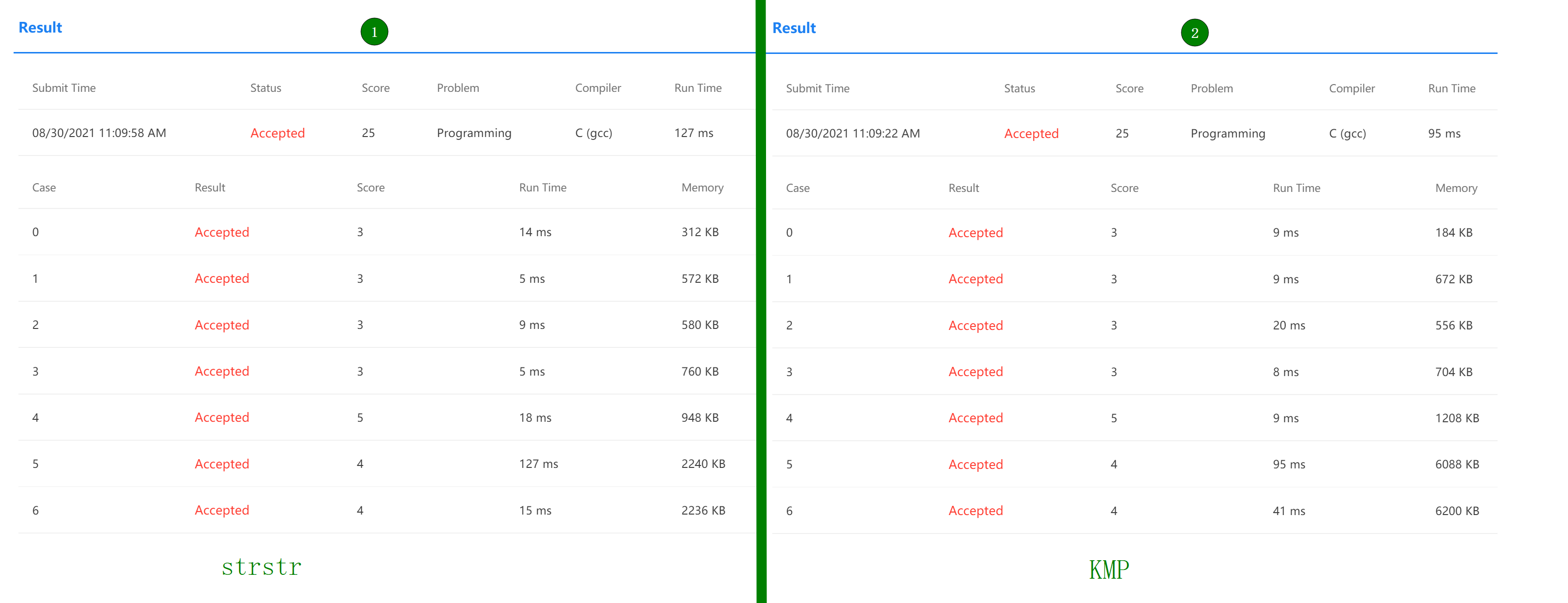
结束啦
至此!数据结构,我终于在三次半途而废之后,刷完了;不得不说学到了太多了,虽然还有几个地方是似懂非懂的,比如某些题要想到拓扑排序,还有三个题 自己的bug还没找到;但是呢,这一趟的旅程弥补了我一直没有打下的数据结构的坚实基础。虽然可能后面不用又给忘了,加之这里面很多都在STL库里有实现,可以直接调用的方式更快。对比与清华大学的邓俊辉教授的,陈姥姥和何钦铭老师的课更循序渐进一点,包括题目也是;清华大学的课后每个只有一道题,但那一道题真的很难很难,有时候思路理的会怀疑人生(也可能是当时我太菜了);这次陈姥姥这个 一边写一边也会记录自己的花费时间,为什么花费这么长的时间,和一些Bug的原因等,也算是给自己留下的总结吧,但是其实很多时候忘得也快。比如Coursera上我上了深度学习、自动驾驶的课,也做了笔记,但是忘得 那叫一个快呀 hhhh 好了下一阶段是C++基础和设计模式居多,再加上 专业领域的数学知识补充 and 看论文!冲 聪明
属实没有想到 这门课竟然断断续续有一年半的战线长度,但是年前的flag总算是实现了一个 欧耶!截图证明,终于还是补完了。
9/4,今天是真的结束了,做完了期末,但是好像也得总结期末题目?
先备用一下吧,这是我一边做期末题目,一边记下来的哪些地方忘记了的点,自我备用,可忽略:
- 将 {28, 15, 42, 18, 22, 5, 40} 逐个按顺序插入到初始为空的最小堆(小根堆)中。则该树的前序遍历结果为 -> 没想到最后这个还对了
- 最小堆的构树部分需要着重复习
- 散列部分的分离连接法需要看一下插入后的下标走势
- 初始步长为4的希尔排序法
- 最小生成树算法 Primer需要进一步加深印象
- 哈夫曼树是啥?hhh 忘得可真快啊
编程部分,哦吼 这可真不巧 都是… 我不是很有把我的
-
堆排序 用priority_queue用惯了 基本全忘了 照着伪代码写的 emm 都有些看不懂了
-
还原二叉树,恕我直说 我的二叉树层序 中序 后序学的那个叫… emmm 一言难尽;然后我一搜 csdn看到的瞬间好像又悟了 emmm hhhh 我确实悟了 发现了问题,只要找到根节点,输入len长度不断递归处理就行了,主要可能是一开始没get到先序和中序的感觉
参考于:https://blog.csdn.net/SASAKI_130/article/details/106284885
至此 23:39 2021/09/04 张聪明同学终于完完整的搞完了,flag还是实现了的,就是期末这一做发现 有些地方得回顾不然忘得真的快,特别是二叉树下的堆排序当时我还弄了一下午,然而… 还是忘了 emmm 只记得那一下午 画树 提min到顶堆 emmm
后面有空再回来看看错题自我总结一波吧