Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Examples
Example 1:
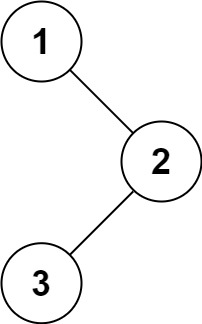
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 4:
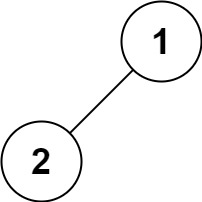
Input: root = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Example 5:
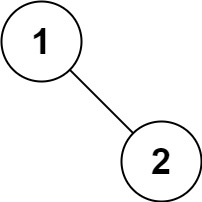
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
思路
这个就是普通的深搜,中序遍历
但是题目给出了思考说希望 “do it iteratively”
那就是要引入堆栈(深搜→堆栈;广搜→队列)
discussion里面有一张图解释的很好,就直接拿过来用了
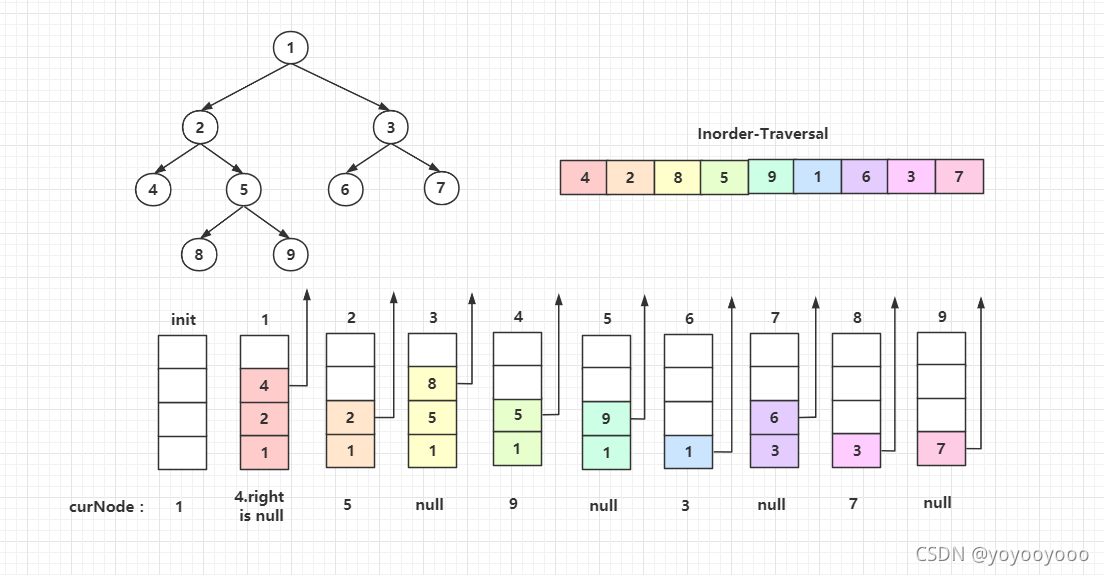
代码
- 普通深搜
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> answer;
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
answer.add(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
}
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
answer = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root);
return answer;
}
}
- 用堆栈
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stackNodes = new Stack<>();
while(root != null || !stackNodes.empty()){
while (root != null){
stackNodes.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stackNodes.pop();
answer.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return answer;
}
}