? ? ? ? ? 链表(linked-list)在所有的数据结构中属于容易理解,难以应用的一种数据结构,这次只是为介绍栈、队列提供一个基础。链表主要联系题在进阶课进行讲解。
一、链表(linked-list)
????????链表其实就是线性表的链式存储方式,而线性表(list)也叫作顺序表,它是最基础、最简单、最常用的一种基本数据结构,线性表总存储的每个数据称为一个元素,各个元素及其索引是一一对应的关系。线性表有两种存储方式:顺序存储方式和链式存储方式。虽然链表是一种有序的,但是要明白在实际的物理存储结构上是非连续、非顺序的存储结构。链表的内存是不连续的,前一个元素存储地址的下一个地址中存储的不一定是下一个元素。链表通过指向下一个元素地址的引用将链表中的元素串起来。?
? ? ? ? 根据链表中存储的元素的方式,可以得出链表的俩个基本组成:指针和自己存储的值。
//单向链表节点结构(可以实现成范型)
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
value = data;
}
}
????????链表大体分为单向链表(Singly linked lis)、双向链表(Doubly linked list)、循环链表(Circular Linked list)。其中循环链表夹杂在单双向链表中讲解,其实循环链表就是头尾指针的指向问题。
? ? ? 1、单向链表
? ? ? ??单向链表是最简单的链表形式。我们将链表中最基本的数据称为节点(node),每一个节点包含了数据块和指向下一个节点的指针。在单向链表中我们首先要确认头结点,通过头结点的next指针找到以下节点,下图为最简单的单向链表结构和循环单向链表结构。同时单向链表一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
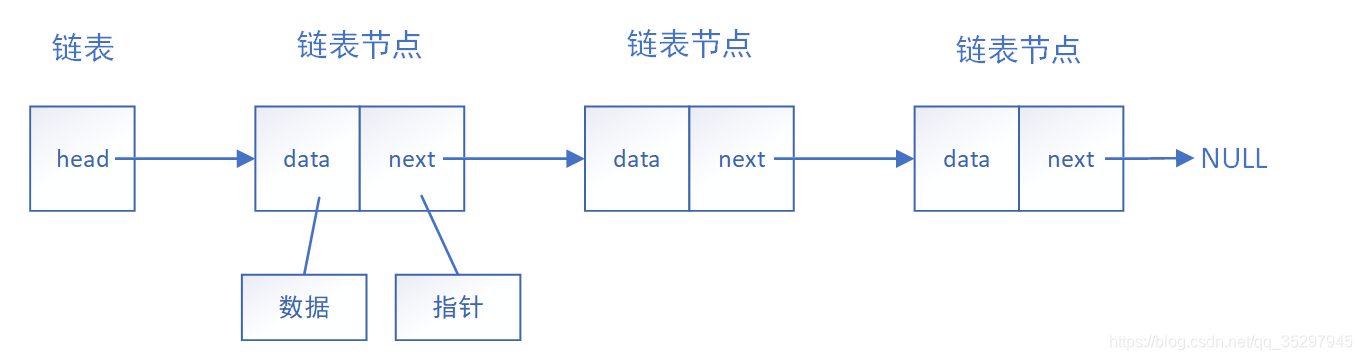
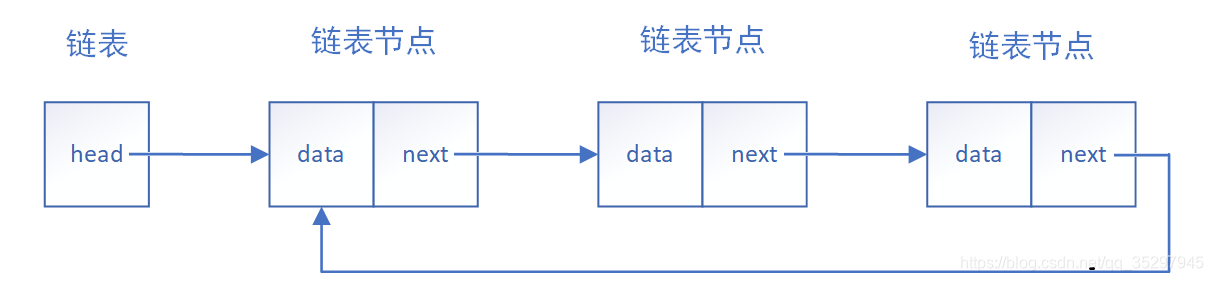
?下面做一个单向链表简单的联系题加深理解:
????????1.单向链表的反转
package com.zcm.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @ClassName: ReverseList
* @Author: zhangchunming
* @Date: 2021/9/1 22:07
* @Description: 单向链表的反转:主要思路就是修改头结点以及其他节点的next指向
**/
public class ReverseList {
// 链表的基本节点
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
value = data;
}
}
/**
* @Author zhangchunming
* @Description //TODO 交换节点位置
**/
public static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) {
// 创建容器pre和next分别存储当前节点以及指向的下一个节点
// pre存储当前节点,为下一次循环到的节点next提供指向
Node pre = null;
// next存储当前节点下一个节点,主要是为了节点信息的转换,使head节点可以改变
Node next = null;//下一个节点
while (head != null) {
// 将a的下一个b进行存储,用于之后赋值为pre
// next = b; next = null
next = head.next;
// a -> null ; b -> a
head.next = pre;
// pre = a ; pre =b
pre = head;
// a = b ; b = null 退出循环此时变为b -> a
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
/**
* @Author zhangchunming
* @Description //TODO 对数器:判断上边自己的代码是否正确
**/
public static Node testReverseLinkedList(Node head) {
// head为null 反转也是null
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null) {
// 因为单向链表是有序的,所以直接存储在list中,list中的顺序就是节点的顺序
list.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
// 头变尾结点
list.get(0).next = null;
int N = list.size();
// 顺序反转
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
list.get(i).next = list.get(i - 1);
}
return list.get(N - 1);
}
/**
* @Author zhangchunming
* @Description //TODO 自动生成链表
* @Param [len, value] 链表最大长度以及节点最大值
**/
public static Node generateRandomLinkedList(int len, int value) {
// 生成随机长度
int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
//创建头结点
Node head = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));
// 判断是否只有头结点
size--;
Node pre = head;
while (size != 0) {
// 指向的节点
Node cur = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));
pre.next = cur;
pre = cur;
size--;
}
return head;
}
// 判断俩个链表是否相等
// 如果是循环单向链表,那么会出现死循环,head1 != null && head2 != null这个永远不会满足
public static boolean checkLinkedListEqual(Node head1, Node head2) {
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
// 相等继续,不等说明我们的算法出现错误
if (head1.value != head2.value) {
return false;
}
// 同时移到下一位
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
// 循环结束,说明全部相等
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len = 50;
int value = 100;
int testTime = 100000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
Node node1 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value);
Node reverse1 = reverseLinkedList(node1);
// 对数器,判断我们反转的reverse1链表反转之后是否和原来的node1链表完全一致
Node back1 = testReverseLinkedList(reverse1);
if (!checkLinkedListEqual(node1, back1)) {
System.out.println("算法出现错误,反转与原链表不相等!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("算法完全正确!");
}
}
? ? ?2、双向链表
? ? ? ?双向链表各个内存结构通过指针 Next 和指针 Prev 链接在一起组成,每一个内存结构都存在前驱内存结构和后继内存结构【链头没有前驱,链尾没有后继】,内存结构由数据域、Prev 指针域和?Next 指针域组成。结构较为复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了。
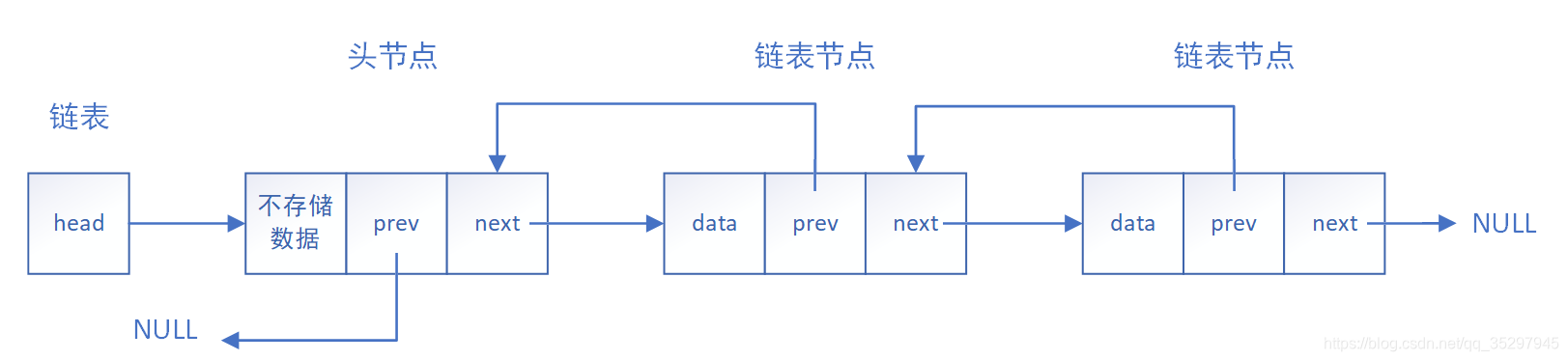
?
同样通过练习题深入理解:
? ? ? ? 1.双向链表的反转
package com.zcm.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @ClassName: DoubleReverseList
* @Author: zhangchunming
* @Date: 2021/9/7 22:06
* @Description:
**/
public class DoubleReverseList {
//双向链表基础结构
public static class DoubleNode {
public int value;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int data) {
value = data;
}
}
/**
* @Author zhangchunming
* @Description //TODO 交换节点位置
**/
public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {
// 为下一次循环的节点的next提供指向
DoubleNode pre = null;
// 1.一开始给当前节点的last提供指向;2.为循环提供进行下去的条件为下一个head赋值
DoubleNode next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
head.last = next;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 对数器
public static DoubleNode testReverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ArrayList<DoubleNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null) {
list.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
list.get(0).next = null;
DoubleNode pre = list.get(0);
int N = list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
DoubleNode cur = list.get(i);
cur.last = null;
cur.next = pre;
pre.last = cur;
pre = cur;
}
return list.get(N - 1);
}
public static DoubleNode generateRandomDoubleList(int len, int value) {
int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
size--;
DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));
DoubleNode pre = head;
while (size != 0) {
DoubleNode cur = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));
pre.next = cur;
cur.last = pre;
pre = cur;
size--;
}
return head;
}
// 判断相等,循环双向链表出现死循环
public static boolean checkDoubleListEqual(DoubleNode head1, DoubleNode head2) {
boolean null1 = head1 == null;
boolean null2 = head2 == null;
if (null1 && null2) {
return true;
}
if (null1 ^ null2) {
return false;
}
if (head1.last != null || head2.last != null) {
return false;
}
DoubleNode end1 = null;
DoubleNode end2 = null;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.value != head2.value) {
return false;
}
end1 = head1;
end2 = head2;
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
if (head1 != null || head2 != null) {
return false;
}
while (end1 != null && end2 != null) {
if (end1.value != end2.value) {
return false;
}
end1 = end1.last;
end2 = end2.last;
}
return end1 == null && end2 == null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len = 50;
int value = 100;
int testTime = 100000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
DoubleNode node2 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value);
DoubleNode reverse2 = reverseDoubleList(node2);
DoubleNode back2 = testReverseDoubleList(reverse2);
if (!checkDoubleListEqual(node2, back2)) {
System.out.println("oops!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("finish!");
}
}
