树的遍历
1 遍历方式
1.1 前序遍历
前序遍历定义:在前序遍历中,先访问根节点,然后递归地前序遍历左子树,最后递归地的前序遍历右子树。

1.2 中序遍历
中序遍历定义:在中序遍历中,先递归地中序遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后递归地中序遍历右子树。
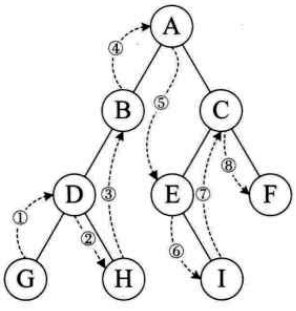
1.3 后序遍历
后序遍历定义:在后序遍历中,先递归地后序遍历左子树,然后递归地后序遍历右子树,最后访问根节点。

1.4 层序遍历
层序遍历定义:按层从左至右

2 案例

3 代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
//二叉树类
class BinaryTree {
public:
BinaryTree(string val) {
this->val = val;
this->leftChild = nullptr;
this->rightChild = nullptr;
}
void insertLeft(string newNode) {
if (this->leftChild == nullptr) {
this->leftChild = new BinaryTree(newNode);
}
else {
BinaryTree* t = new BinaryTree(newNode);
t->leftChild = this->leftChild;
this->leftChild = t;
}
}
void insertRight(string newNode) {
if (this->rightChild == nullptr) {
this->rightChild = new BinaryTree(newNode);
}
else {
BinaryTree* t = new BinaryTree(newNode);
t->rightChild = this->rightChild;
this->rightChild = t;
}
}
BinaryTree* getleftChild() {
return this->leftChild;
}
BinaryTree* getRightChild() {
return this->rightChild;
}
void setRootVal(string val) {
this->val = val;
}
string getRootVal() {
return this->val;
}
string val;
BinaryTree* leftChild;
BinaryTree* rightChild;
};
//把数据以二叉树的形式存储
BinaryTree* buildBinaryTree(BinaryTree* root, vector<string>& vec, int i) {
if (i < vec.size()) {
if (vec[i] == "#") {
return nullptr;
}
else {
BinaryTree* root = new BinaryTree(vec[i]);
root->leftChild = buildBinaryTree(root->leftChild, vec, 2 * i + 1);
root->rightChild = buildBinaryTree(root->rightChild, vec, 2 * i + 2);
return root;
}
}
return root;
}
//前序遍历
void preOrder(BinaryTree* root) {
if (root != nullptr) { //访问根节点,判断其是否空
cout << root->val << endl; //访问根节点, 并输出每个节点的值
preOrder(root->leftChild); //递归地前序遍历左子树
preOrder(root->rightChild); //递归地前序遍历右子树
}
}
//中序遍历
void inOrder(BinaryTree* root) {
if (root != nullptr) { //访问根节点,判断其是否空
inOrder(root->leftChild); //递归地前序遍历左子树
cout << root->val << endl; //访问根节点, 并输出每个节点的值
inOrder(root->rightChild); //递归地前序遍历右子树
}
}
//后序遍历
void postOrder(BinaryTree* root) {
if (root != nullptr) { //访问根节点,判断其是否空
postOrder(root->leftChild); //递归地前序遍历左子树
postOrder(root->rightChild); //递归地前序遍历右子树
cout << root->val << endl; //访问根节点, 并输出每个节点的值
}
}
//层序遍历 使用队列完成
void layerOrder(BinaryTree* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
queue<BinaryTree*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
cout << que.front()->val << endl;
if (que.front()->leftChild != nullptr) {
que.push(que.front()->leftChild);
}
if (que.front()->rightChild != nullptr) {
que.push(que.front()->rightChild);
}
que.pop();
}
}
void test01() {
vector<string> myVec = { "书", "第1章", "第2章", "1.1节", "1.2节", "2.1节", "2.2节", "#", "#", "1.2.1节", "1.2.2节", "#", "#", "2.2.1节", "2.2.2节", "#", "#",
"#", "#", "#", "#", "#", "#" };
BinaryTree* root = buildBinaryTree(nullptr, myVec, 0);
cout << "前序遍历:" << endl;
preOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "中序遍历:" << endl;
inOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "后序遍历:" << endl;
postOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "层序遍历:" << endl;
layerOrder(root);
cout << endl;
}
void main() {
test01();
system("pause");
}
输出结果:
前序遍历:
书
第1章
1.1节
1.2节
1.2.1节
1.2.2节
第2章
2.1节
2.2节
2.2.1节
2.2.2节
中序遍历:
1.1节
第1章
1.2.1节
1.2节
1.2.2节
书
2.1节
第2章
2.2.1节
2.2节
2.2.2节
后序遍历:
1.1节
1.2.1节
1.2.2节
1.2节
第1章
2.1节
2.2.1节
2.2.2节
2.2节
第2章
书
层序遍历:
书
第1章
第2章
1.1节
1.2节
2.1节
2.2节
1.2.1节
1.2.2节
2.2.1节
2.2.2节
4 总结
总结:前、中、后序遍历用递归实现,层序遍历用队列