? ? ? ?在介绍了单链表结构后,我们发现链表结构在使用过程相对数组具有更优的存储性能,但是其存在的不足就是吗,每次需要访问当前节点的前一个节点时需要从头在访问,这大大降低了链表的存储性能,因此引出了双链表结构来存储当前节点的前一个节点。
? ? ? ?双链表结构较单链表结构多了prev字段,让我们可以更加方便的获取前一个节点:
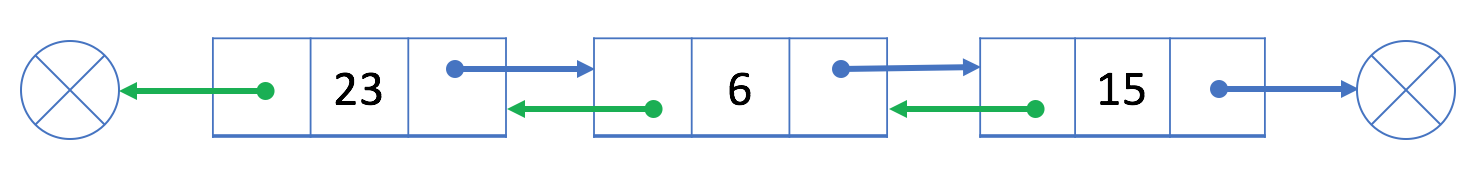
?PS:上图中的绿色箭头就代表prev节点的运行原理,其中双链表的典型定义如下:
// Definition for doubly-linked list.
struct DoublyListNode {
int val;
DoublyListNode *next, *prev;
DoublyListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL), prev(NULL) {}
};1.添加双链表
我们可以将该插入操作分为两个部分:
- 链接cur与next和prev,next是prev原始的下一个节点
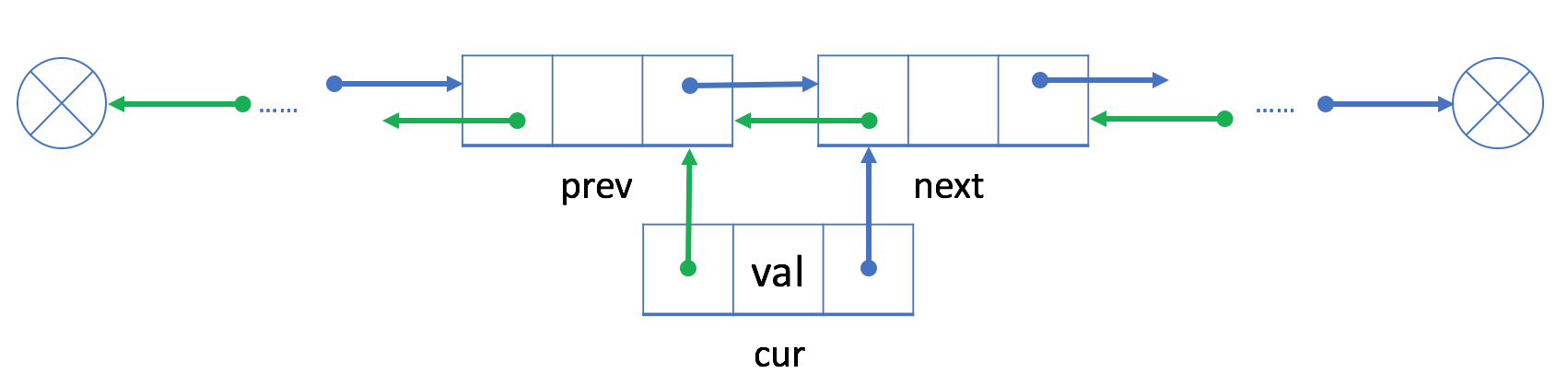
- ??使用cur重新链接prev和next

? ? ? ?这里在刚开始写的过程中我总是直接把next->prev直接赋给prev->next,这样会导致出错,而正确写法应当是将prev和next的赋值分开进行。
- cur->next = p-next;
- p->next->prev = cur,
- p->next = cur;
- cur->prev = p.
2.删除双链表
? ? ? ?如果想要删除一个双链表节点cur,我们只需要将当前cur前一个节点的next与cur下一个节点的prev链接起来即可。即:

? ? ? ?如果要删除上图中的节点6,可以将节点23的next与15的prev分别链接即可:
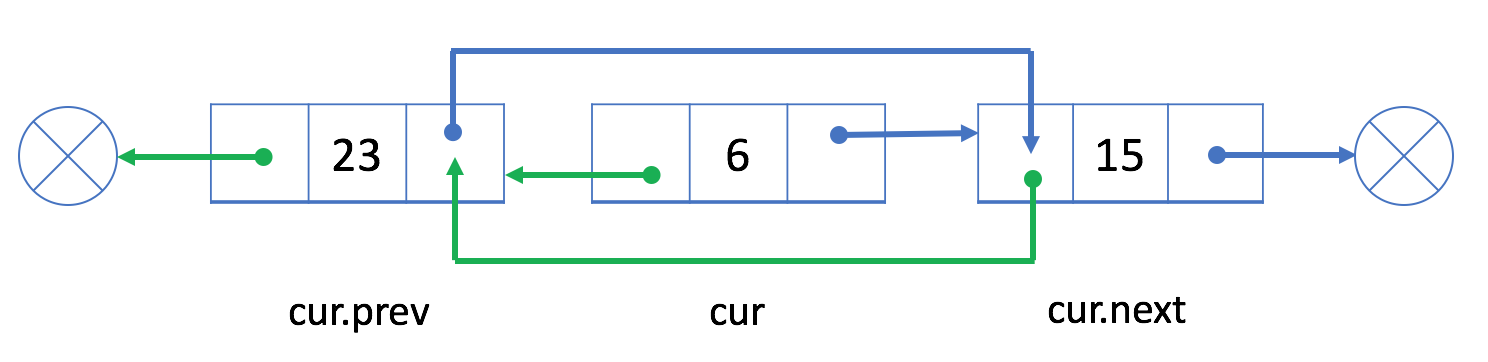
? ? ?PS:以上删除和插入操作因为prev节点,所以时间和空间复杂度均是O(1)。
注意:
? ? ?在删除和插入操作中,我们对于在头结点插入和删除,尾结点插入和删除的操作都需要特别注意:
- 头结点在插入和删除后需要将头节点重新定义赋值,即head = cur;
- 尾部插入和删除我们需要在尾部的赋空值,即cur->next = NULL;
3. 设计双链表?
class MyLinkedList {
public:
struct ListNode{
ListNode *next,*pred;
int val;
ListNode(int x)
{
val=x;
next=NULL;
pred=NULL;
}
};
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyLinkedList() {
head = new ListNode(0);
size = 0;
}
/** Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. */
// int get(int index) {
// if(index<0||index>=size){
// return -1;
// }
// ListNode *cur = head->next; //从头节点的下一个开始
// if(cur == NULL) return -1;
// while(index--)
// {
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// return cur->val;
// }
int get(int index) {
if(index<0||index>=size)//
return -1;
ListNode *p=head->next;
if(p==NULL)
return -1;
while(index--)
p=p->next;
return p->val;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. */
void addAtHead(int val) { //next和pred的赋值是分开进行的
ListNode *cur = new ListNode(val);
cur->next = head->next;
if(head->next)
{
head->next->pred = cur->next;
}
head->next = cur;
cur->pred = head;
size++;
}
/** Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. */
void addAtTail(int val) { //bingo
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);
while(cur!=NULL) cur = cur->next;
if(cur==NULL) return;
cur->next = newNode;
newNode->pred = cur;
newNode->next = NULL;
size++;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. */
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(index>size) return;
else if(index==size) addAtTail(val);
else if(index <= 0) addAtHead(val);
else{
while(index--)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if(cur==NULL&&cur->next==NULL) return;
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next->pred = newNode;
cur->next = newNode;
newNode->pred = cur;
size++;
}
}
/** Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. */
void deleteAtIndex(int index) { //区别删除的是否为开始节点 head删除后需要调整head节点
ListNode *cur = head;
if(index<0||index>=size)
return;
if(index==0)
{
if(head!=NULL&&head->next!=NULL&&head->next->next!=NULL)
{
head->next = head->next->next;
head->next->pred = head;
}
else{
head->next = NULL;
}
}
else{
while(index--)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if(cur==NULL||cur->next==NULL) return;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
//cur->next->next->pred = cur; 注意已经交换结束后直接为cur->next
if(cur->next)
cur->next->pred = cur;
}
size--;
}
private:
int size;
ListNode *head;
};