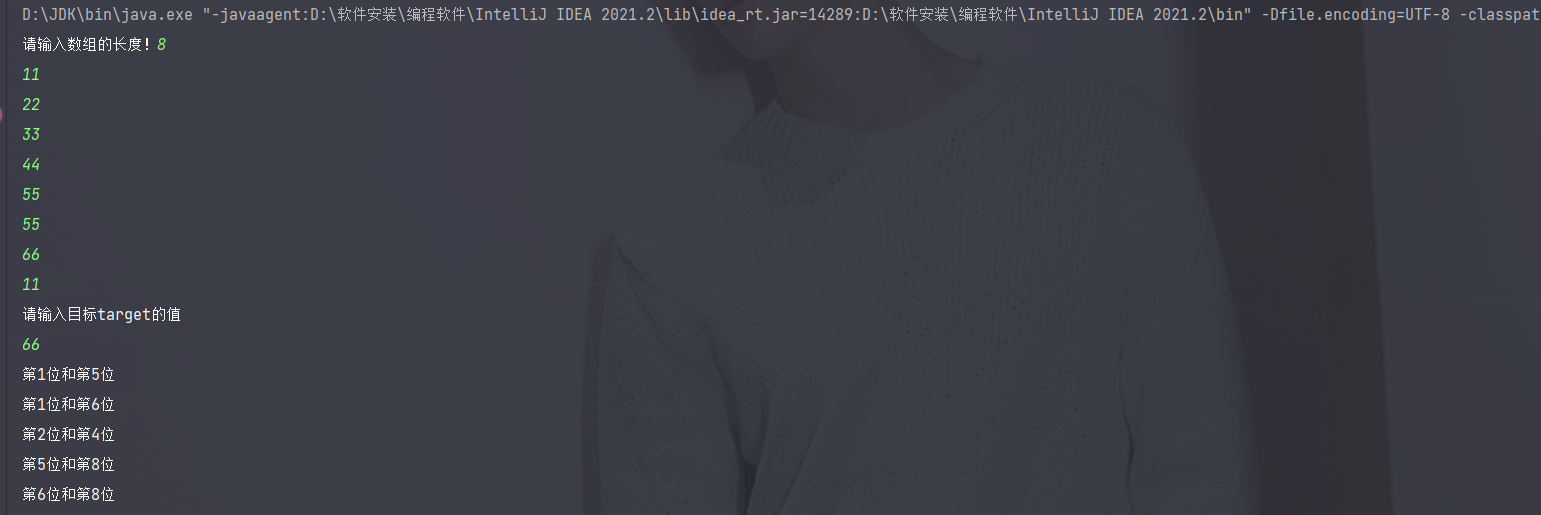
例题:输入行号打印以下图形

观察图型找规律。
发现每一行的
空格=总行数 - 行号
星星的个数 = 2*行号-1
都与行号有关,所以外层循环遍历行号

package com.zsq;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in );
System.out.println("请输入行数");
int rows = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1;i<=rows;i++) {
for (int col = 1; col <=rows-i; col++) { //行数的空格是:行数-行号
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int col = 1; col <= i*2-1; col++) { //星星的个数 = 2*行号-1
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
例题:阶乘 输出以下内容

举个🌰🌰🌰
阶乘的题用递归。递归就是自己调用自己。由于要求和,那么可以写俩个函数,一个递归函数写阶乘,一个递归函数写阶乘相加求总和
package com.zsq;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author大胆刁民
* @create 2021-09-2021/9/25-9:27
**/
public class demo2 {
public static int f(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * f(n - 1);
}
}
public static int sum(int n) { //求阶乘和
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return f(n) + sum(n - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
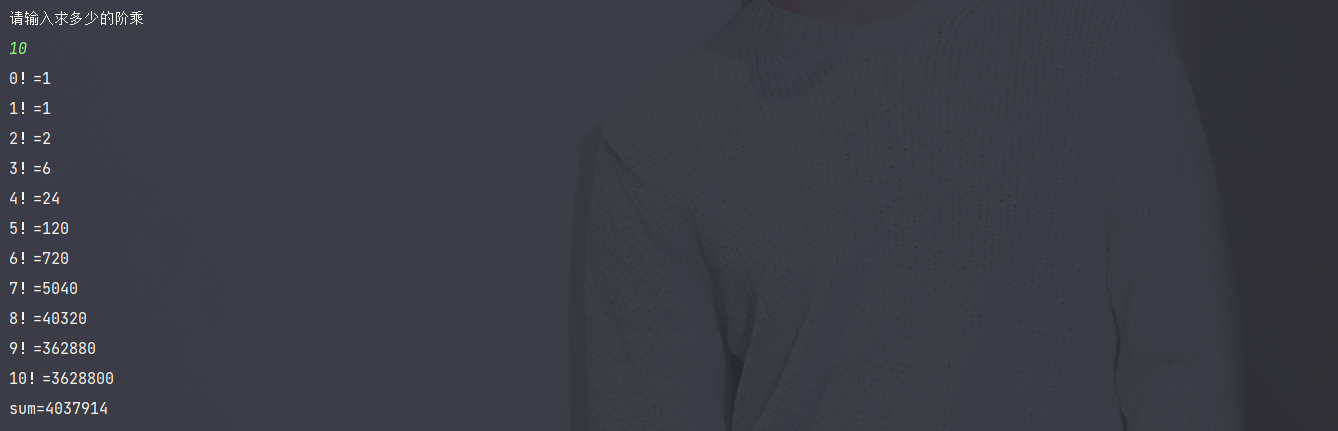
System.out.println("请输入求多少的阶乘");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int s = scanner.nextInt();
int j = 0;
for (int i = s; i >= 0; i--) {
int sum;
sum = j++;
System.out.println(sum + "!=" + f(sum));
}
System.out.println("sum=" + sum(s));
}
}
例题:写一个简单的系统,系统具有读写文件功能

package com.zsq;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author大胆刁民
* @create 2021-09-2021/9/24-20:31
**/
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
information();
System.out.println("请输入执行程序的代码:");
switch (scanner.nextInt()) {
case 1:
writeTxt();
break;
case 2:
setReader();
break;
case 3:
System.exit(0);
default:
System.out.println("无效代码");
}
}
}
public static void writeTxt() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入写入文件的名称:");
File file = new File(scanner.next() + ".txt"); // 相对路径,如果没有则要建立一个新的output。txt文件
try {
boolean newFile = file.createNewFile();// 创建新文件
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file, true); 后面的 true 是让源文件内容不会被再次输入的内容给覆盖掉
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
System.out.println("请输入");
out.write(scanner.next() + "\r\n"); // \r\n即为换行
System.out.println("写入成功!");
out.flush(); // 把缓存区内容压入文件
out.close(); // 最后记得关闭文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void setReader() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入读取文件的名称:");
String pathname = scanner.next() + ".txt"; // 绝对路径或相对路径都可以,写入文件时演示相对路径,xxxx.txt文件
//防止文件建立或读取失败,用catch捕捉错误并打印,也可以throw;
//不关闭文件会导致资源的泄露,读写文件都同理
FileReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(pathname);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); // 建立一个对象,它把文件内容转成计算机能读懂的语言
String line;
//网友推荐更加简洁的写法
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 一次读入一行数据
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void information() {
System.out.println("1:写入文件");
System.out.println("2:读取文件");
System.out.println("3:退出程序");
System.out.println();
}
}
例题:基于Java文件输入输出流技术,实现将in.txt文件的内容复制到out.txt文件中
举个🌰🌰🌰
package com.zsq;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author大胆刁民
* @create 2021-09-2021/9/25-10:12
**/
public class demo3 {
public static void reader(){
String path = "in.txt";
try {
FileReader fileReader=new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line;
//网友推荐更加简洁的写法
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 一次读入一行数据
writer(line);
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void writer(String line){
try {
String path1="out.txt";
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(path1,true);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
bufferedWriter.write(line+ "\r\n"); // \r\n即为换行
bufferedWriter.flush();
File file = new File(path1);
if (0 == file.length() || !file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件为空!");
}
bufferedWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
reader();
}
}
例题:给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
举个🌰🌰🌰
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
package com.zsq;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author大胆刁民
* @create 2021-09-2021/9/25-18:39
**/
//给定一个整数数组 `nums` 和一个整数目标值 `target`,请你在该数组中找出 **和为目标值** *`target`* 的那 **两个** 整数,并返回它们的数组下标.
public class demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
}
public static void input() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入数组的长度!");
int sc = scanner.nextInt();
int a[] = new int[sc];
for (int i = 0; i < sc; i++) {
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("请输入目标target的值");
int target = scanner.nextInt();
finds(a, target);
}
public static void finds(int[] a, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[i] + a[j] == target) {
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"位和第"+ (j+1)+"位");
}
}
}
}
}