搜索树,图算法,深度搜索与广度搜索
一、深度搜索与广度搜索
已知连接关系,查出与这个人有直接联系或间接联系的人。
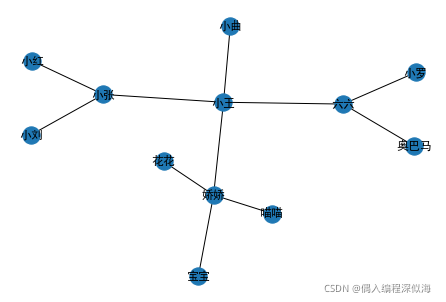
social_network = {
'小张': ['小刘', '小王', '小红'],
'小王': ['六六', '娇娇', '小曲'],
'娇娇': ['宝宝', '花花', '喵喵'],
'六六': ['小罗', '奥巴马']
}
def search_graph(graph, start, expand_position):
need_to_check = [start]
expanded = [] # you can change this to a set
while need_to_check:
# pop(0) 先进先出 队列 实现广度
# pop(-1) 先进后出 堆栈 实现深度
person = need_to_check.pop(expand_position)
if person in expanded: continue
connect_person = graph.get(person, {})
need_to_check += connect_person
expanded.append(person)
return expanded
def bfs(graph, start): return search_graph(graph, start, expand_position=0)
def dfs(graph, start): return search_graph(graph, start, expand_position=-1)
// 测试
dfs(social_network, '小张')
1.1 如连接关系的数据格式变化为元组
输入变为元组的代码实现
social_network_with_tuple = (
('小张', '小刘', '小王', '小红'),
('小王', '六六', '娇娇', '小曲'),
('娇娇', '宝宝', '花花', '喵喵'),
('六六', '小罗', '奥巴马'),
)
def search_graph_tuple(graph, start, expand_position):
need_to_check = [start]
expanded = [] # you can change this to a set
while need_to_check:
person = need_to_check.pop(expand_position)
if person in expanded: continue
connect_tuple = list(filter(lambda x: x[0] == person, social_network_with_tuple))
if len(connect_tuple) != 0:
need_to_check += connect_tuple[0][1:]
expanded.append(person)
return expanded
二、 代码练习
2.1 需求描述
已知,城市的经纬度,给出起点与终点,每天最多开600km, 规划通行的路径。
2.1.1 数据处理部分
使用正则表达式。将数据解析为字典。
coordination_source = """
{name:'兰州', geoCoord:[103.73, 36.03]},
{name:'嘉峪关', geoCoord:[98.17, 39.47]},
{name:'西宁', geoCoord:[101.74, 36.56]},
{name:'成都', geoCoord:[104.06, 30.67]},
{name:'石家庄', geoCoord:[114.48, 38.03]},
{name:'拉萨', geoCoord:[102.73, 25.04]},
{name:'贵阳', geoCoord:[106.71, 26.57]},
{name:'武汉', geoCoord:[114.31, 30.52]},
{name:'郑州', geoCoord:[113.65, 34.76]},
{name:'济南', geoCoord:[117, 36.65]},
{name:'南京', geoCoord:[118.78, 32.04]},
{name:'合肥', geoCoord:[117.27, 31.86]},
{name:'杭州', geoCoord:[120.19, 30.26]},
{name:'南昌', geoCoord:[115.89, 28.68]},
{name:'福州', geoCoord:[119.3, 26.08]},
{name:'广州', geoCoord:[113.23, 23.16]},
{name:'长沙', geoCoord:[113, 28.21]},
//{name:'海口', geoCoord:[110.35, 20.02]},
{name:'沈阳', geoCoord:[123.38, 41.8]},
{name:'长春', geoCoord:[125.35, 43.88]},
{name:'哈尔滨', geoCoord:[126.63, 45.75]},
{name:'太原', geoCoord:[112.53, 37.87]},
{name:'西安', geoCoord:[108.95, 34.27]},
//{name:'台湾', geoCoord:[121.30, 25.03]},
{name:'北京', geoCoord:[116.46, 39.92]},
{name:'上海', geoCoord:[121.48, 31.22]},
{name:'重庆', geoCoord:[106.54, 29.59]},
{name:'天津', geoCoord:[117.2, 39.13]},
{name:'呼和浩特', geoCoord:[111.65, 40.82]},
{name:'南宁', geoCoord:[108.33, 22.84]},
//{name:'西藏', geoCoord:[91.11, 29.97]},
{name:'银川', geoCoord:[106.27, 38.47]},
{name:'乌鲁木齐', geoCoord:[87.68, 43.77]},
{name:'香港', geoCoord:[114.17, 22.28]},
{name:'澳门', geoCoord:[113.54, 22.19]}
"""
def get_city_info(city_coordination):
city_loaction = {}
for city in city_coordination.split("\n"):
if city.startswith("//"): continue
if city.strip() == "": continue
city_name = re.findall(r"name:'(\w+)'", city)[0]
loaction = re.findall(r'geoCoord:\[(\d+.\d+),\s(\d+.\d+)\]', city)[0]
city_loaction[city_name] = tuple(map(float,loaction))
return city_loaction
city_info = get_city_info(coordination_source)
2.1.2 城市直接距离计算
使用球面坐标的距离计算公式,得到城市直接距离。
import math
def geo_distance(origin, destination):
"""
Calculate the Haversine distance.
Parameters
----------
origin : tuple of float
(lat, long)
destination : tuple of float
(lat, long)
Examples
--------
>>> origin = (48.1372, 11.5756) # Munich
>>> destination = (52.5186, 13.4083) # Berlin
>>> round(distance(origin, destination), 1)
504.2
"""
lat1, lon1 = origin
lat2, lon2 = destination
radius = 6371 # km
dlat = math.radians(lat2 - lat1)
dlon = math.radians(lon2 - lon1)
a = (math.sin(dlat / 2) * math.sin(dlat / 2) +
math.cos(math.radians(lat1)) * math.cos(math.radians(lat2)) *
math.sin(dlon / 2) * math.sin(dlon / 2))
c = 2 * math.atan2(math.sqrt(a), math.sqrt(1 - a))
d = radius * c
return d
def get_city_distance(city1,city2):
return geo_distance(city_info[city1],city_info[city2])
get_city_distance("杭州","上海")
2.1.3 计算可以到达的城市关系
# 绘制当前图像
city_graph = nx.Graph()
city_graph.add_nodes_from(list(city_info.keys()))
nx.draw(city_graph, city_info, with_labels=True, node_size=10)
#
threshold = 600
from collections import defaultdict
def build_connection(city_info):
cities_connection = defaultdict(list)
cities = list(city_info.keys())
for c1 in cities:
for c2 in cities:
if c1 == c2 : continue
if get_city_distance(c1,c2) < threshold:
cities_connection[c1].append(c2)
return cities_connection
# 得到能够到达的城市关系
cities_connection = build_connection(city_info)
2.1.4 查找相互连接的城市路径
BFS 1 version
def search_1(graph,start,destination):
pathes = [[start]]
visited = set()
while pathes:
path = pathes.pop(0)
froniter = path[-1]
if froniter in visited: continue
successsors = graph[froniter]
for city in successsors:
if city in path: continue # check loop
new_path = path+[city]
pathes.append(new_path) #bfs
#pathes = [new_path] + pathes #dfs
if city == destination:
return new_path
visited.add(froniter)
search_1(cities_connection,"上海","香港")
# ['上海', '合肥', '香港']
Optimal search using variation of BFS
def search_2(graph,start,destination,search_strategy):
pathes = [[start]]
#visited = set()
while pathes:
path = pathes.pop(0)
froniter = path[-1]
#if froniter in visited : continue
#if froniter == destination:
# return path
successsors = graph[froniter]
for city in successsors:
if city in path: continue # check loop
new_path = path+[city]
pathes.append(new_path) #bfs
pathes = search_strategy(pathes)
# visited.add(froniter)
if pathes and (destination == pathes[0][-1]):
return pathes[0]
当存在多个路径时,按照城市的距离进行排序操作。
def sort_by_distance(pathes):
def get_distance_of_path(path):
distance = 0
for i,_ in enumerate(path[:-1]):
distance += get_city_distance(path[i],path[i+1])
return distance
return sorted(pathes,key=get_distance_of_path)
功能实现
search_2(cities_connection,"北京","上海",search_strategy=sort_by_distance)
# ['北京', '天津', '上海']
三、 编辑距离的练习


def Levenshtein_Distance_Recursive(str1, str2):
if len(str1) == 0: return len(str2)
elif len(str2) == 0: return len(str1)
elif str1 == str2: return 0
d = 0 if str1[len(str1)-1] == str2[len(str2)-1] else 1
return min(Levenshtein_Distance_Recursive(str1, str2[:-1]) + 1, Levenshtein_Distance_Recursive(str1[:-1], str2) + 1, Levenshtein_Distance_Recursive(str1[:-1], str2[:-1]) + d)
四、总结
搜索算法可以解决: 路径规划,国家象棋,象棋等问题。
围棋的搜索时间复杂度太高,搜索解决不了后来人们就发明出了新的算法,新的算法,时间复杂度更低。
- 深度学习
- 深度强化学习