5.2.1 一维数组定义
数组特点:
1.放在一块连续的内存空间中
2.数组中每个元素都是相同数据类型
定义方式:
1. 数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//数组
//1. 数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ]
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
arr[2] = 30;
arr[3] = 40;
arr[4] = 50;
//访问数据元素
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ] = {值1,值2 ...};
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//数组
//2. 数据类型 数组名[ 数组长度 ] = {值1,值2 ...};
int arr[5] = { 10,20,30,40,50};
int arr2[5] = { 10,20,30 };
//如果在初始化数据时,没有全部填写完,会用0来填补剩余数据
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
//cout << arr[i] << endl;
cout << arr2[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.数据类型 数组名[ ] = {值1,值2 ...};
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//数组
//3. 数据类型 数组名[ ] = {值1,值2 ...};
int arr[] = { 10,20,30,40,50};
int arr2[] = { 10,20,30 };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
//cout << arr[i] << endl;
cout << arr2[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
注意:
1.数组的命名不要和变量重名
2.数组的下标是从0开始索引的
5.2.2 一维数组数组名
一维数组名称的用途:
1.可以统计整个数组在内存中的长度
2.可以获取数组在内存中的首地址
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "整个数组所占的内存空间为"<<sizeof(arr) << endl;//统计整个数组所占内存空间
cout << "每个元素所占的内存空间为:"<<sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;//统计某个元素所占内存空间
cout << "数组中元素的个数为:"<< sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;//统计数组的元素个数
//通过数组名查看数组的首地址
cout << "数组首地址为:" << arr << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习实例:冒泡排序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int temp;
int arr[9] = { 4,2,8,0,5,7,1,3,9 };
//排序前
cout << "排序前:" << endl;
for (int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
cout << arr[k]<<" ";
}
//开始冒泡排序
//总排序轮数为 元素个数 - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 9 - 1; i++)
{
//内层循环对比次数 = 元素个数 - 当前排序轮数 - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 9 - i - 1; j++)
{
//如果第一个数字,比第二个数字大,交换两个数字
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
//排序后
cout << endl << "排序后:" << endl;
for (int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
cout << arr[k] << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.3 二维数组
5.3.1 二维数组的定义方式
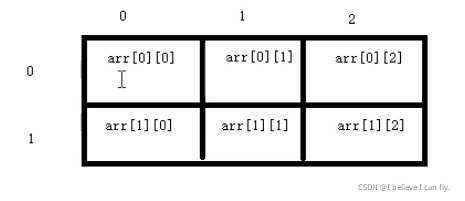
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//二维数组定义方式
//1.数据类型 数组名[ 行数 ][ 列数 ];
int arr[2][3];
arr[0][0] = 1;
arr[0][1] = 2;
arr[0][2] = 3;
arr[1][0] = 4;
arr[1][1] = 5;
arr[1][2] = 6;
//外层循环打印行数,内层循环打印列数
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//2.数据类型 数组名[ 行数 ][ 列数 ] = {{数据1,数据2},{数据3,数据4}};
int arr2[2][3] =
{
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
cout << arr2[i][j] <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//4.数据类型 数组名[ ][ 列数 ] = {数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4};
int arr3[][3] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
cout << arr3[i][j] <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
注意:定义二维数组时,如果初始化了数据,可以省去行数,但列数不能省去
5.3.2 二维数组数组名
作用:
1.查看二维数组所占内存空间大小
2.获取二维数组首地址
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//二维数组名称用途
int arr[2][3] =
{
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
cout << "二维数组所占内存空间为:" << sizeof(arr) << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一行所占内存为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一个元素占用内存为:" << sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组的行数为:"<<sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组的列数为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
//2.查看二维数组的首地址
cout << "二维数组首地址为:"<<(int)arr << endl;//(int)将16进制数据转换成10进制数据
cout << "二维数组第一行首地址:" << (int)arr[0] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第二行首地址为:" << (int)arr[1] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一个元素的首地址:" << (int)&arr << endl;
cout << "二维数组第二个元素的首地址:" << (int)&arr[0][1] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.3.3 二维数组应用案例

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
int main()
{
//1.创建二维数组,3行3列
//2.统计考试成绩,让每行的3列相加,统计出总和
//创建二维数组
int arr[3][3] =
{
{100,100,100},
{90,50,100},
{60,70,80}
};
//统计每个人的总和分数
//给出每个人的名字数组,
string names[3] = { "张三","李四","王五" };//使用string函数时需要添加<string>头文件
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
sum = sum + arr[i][j];
}
cout <<names[i]<<"的总分为:"<< sum << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6. 函数
6.1? 函数概述
作用:将一组经常使用的代码进行封装,减少重复代码
一个较大的程序,一般分为若干个程序块,每个程序块实现特定的功能
6.2 函数定义
函数定义一般有5个主要步骤:
1.返回值类型
2.函数名
3.参数表列
4.函数体语句
5.return表达式

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//加法函数,实现两个整形相加,并且将相加的结果进行返回
int add(int num1, int num2)
{
int sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}
?6.3 函数的调用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
//加法函数,实现两个整形相加,并且将相加的结果进行返回
//函数定义的时候,num1和num2并没有真实数据
//它们只是一个形式上的参数,简称形参
int add(int num1, int num2)
{
int sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
//main函数中调用add函数
int a = 20;
int b = 20;
//函数调用语法:函数名称(参数)
int c = add(a, b);
//a和b称为实际参数,简称实参
//当调用函数的时候,实际参数的值会传递给形参
cout << c << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6.4 值传递
值传递时,函数的形参发生改变,并不会影响实参
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//值传递
//定义函数,实现两个数字进行交换的函数
//如果函数不需要返回值,声明的时候可以写void
void swap(int num1, int num2)
{
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;
int temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;
return;//返回值不需要的时候可以不写return或写return;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
//值传递时,函数的形参发生改变,并不会影响实参
swap(a, b);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.5 函数的常见样式
常见的函数样式:

?