排序衍生
^运算符
^ 异或操作,理解为不进位相加
有交换率。
a^a=0
a^0=a
public static void sway(int[] arr,int i,int j){
if(i!=j){
//不能两个值指向同一地址
arr[i]=arr[i]^arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[i]^arr[j];//就是arr[i]^arr[j]^arr[j]就表示a
arr[i]=arr[i]^arr[j];//表示arr[i]^arr[j]^arr[i]^arr[j]^arr[j]就是b
}
}
找一个单数
一组数只有一个数出现一次,其他出现两次,找出这个数:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {2, 2, 4, 4, 6, 8, 99, 99, 6, 8, 43, 76, 43, 76, 111};
int med=0;
for (int a:ints){
med^=a;//两次出现就会变成0,单数就保留
}
System.out.println(med);
}
找两个个单数
一组数只有两个数出现一次,其他出现两次,找出这两个数:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {2, 2, 4, 4, 6, 8, 99, 99, 6, 8, 43, 76, 43, 76, 111,333};
int med=0;
for (int a:ints){
med^=a;//两个不同的单数^最后得到med
}
int rightOne=med&(~med+1);//取出med中二进制为1的位值(必存在,因为不同值)
int med1=0;
for (int a:ints){
//对应位为1的值取出进行^最后的到两个单数对应位为1的
// (a&rightOne)== 0得到对应位为0
if ((a&rightOne)== rightOne){
med1^=a;
}
}
System.out.println(med1);//两个单数其中一个值
System.out.println(med^med1);//两个单数令一个值
}
基于归并排序的小数和
数组的每个值前比他本身小的和的总和。求数组的小数和
public static int mergeSortTest(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp){
if(left<right){
int m=(left+right)/2;
return
mergeSortTest(arr,left,m,temp)+
mergeSortTest(arr,m+1,right,temp)+
mergeTest(arr,left,m,right,temp);
}
return 0;
}
private static int mergeTest(int[] arr, int left, int m, int right, int[] temp) {
int i=left;
int j=m+1;
int tempIndex=0;
int res=0;
while (i<=m&&j<=right){
res+=arr[i]<arr[j]?arr[i]*(right-j+1):0;//若左小,就是会出现小数的位置。个数有右侧确定。
temp[tempIndex++]=arr[i]<arr[j]?arr[i++]:arr[j++];
}
while (i<=m)
temp[tempIndex++]=arr[i++];
while (j<=right)
temp[tempIndex++]=arr[j++];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, left, tempIndex);
return res;
}
二分衍生
查找极小值
该值比左右的值都小,如果是在数组两侧则只比较一点即可。
在无序数组中找到该极小值
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(limitMin(new int[]{235, 34,53, 53, 354, 454, 45, 65}, 0, 7));
}
public static int limitMin(int[] arr,int left,int right){
if(arr[left]<arr[left+1]){
return arr[left];
}else if (arr[right]<arr[right-1]){
return arr[right];
}
int med=(left+right)/2;
if(arr[med+1]>arr[med]){
return limitMin(arr,left,med);
}else {
return limitMin(arr,med,right);
}
}
}
链表衍生
判断链表的回文
package Test;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.add(1);
list.add(5);
list.add(3);
list.add(7);
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(1);
LinkedList list1 = new LinkedList();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(4);
list1.add(4);
list1.add(1);
System.out.println(IsTrue.isTrue_1(list.header));
System.out.println(IsTrue.isTrue_2(list.header));
System.out.println(IsTrue.isTrue_1(list1.header));
System.out.println(IsTrue.isTrue_2(list1.header));
System.out.println(IsTrue.isTrue_3(list1.header));
System.out.println(IsTrue.isTrue_3(list.header));
}
}
class IsTrue{
public static boolean isTrue_1(Node header){
if (header==null)throw new RuntimeException("空");
Node tail=header;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (tail!=null){
stack.push(tail);
tail=tail.next;
}
tail=header;
while (tail!=null){
if (tail.num!=stack.pop().num)
return false;
tail=tail.next;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isTrue_2(Node header){
if (header==null||header.next==null)return true;
Node slow=header;
Node quick=header;
while (quick.next!=null&&quick.next.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
quick=quick.next.next;
}
slow=slow.next;
Stack<Node> nodes = new Stack<Node>();
while (slow!=null){
nodes.push(slow);
slow=slow.next;
}
slow=header;
while (!nodes.isEmpty()){
if (slow.num!=nodes.pop().num)
return false;
slow=slow.next;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isTrue_3(Node header) {
if (header == null || header.next == null) return true;
Node node1 = header;
Node node2 = header;
while (node2.next != null && node2.next.next != null) {
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next.next;
}
node2 = node1.next;
node1.next = null;
Node node3;
//将后一半链表指向反向
while (node2 != null) {
node3 = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
node1 = node2;
node2 = node3;
}
node2 = header;
node3 = node1;
boolean flag = true;
//从两头进行判断
while (node2 != null&&node3!=null) {//node3!=null多余,因为node2链表节点必定不少于node3节点
if (node3.num!=node2.num){
flag=false;
break;
}
node3 = node3.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
node3 = node1.next;
node1.next = null;
//将后面一半反向后再反过来(恢复)
while (node3 != null) {
node2 = node3.next;
node3.next = node1;
node1 = node3;
node3 = node2;
}
return flag;
}
}
//链表的类
class LinkedList{
Node header;
public void add(int num){
if (header==null){
header=new Node(num,null);
return;
}
Node tail=header;
while (tail.next!=null){
tail=tail.next;
}
tail.next=new Node(num,null);
}
}
class Node{
int num;
Node next;
public Node(int num, Node next) {
this.num = num;
this.next = next;
}
}
复制随机指向的链表

package Test;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node header=new Node(0);
Node node1=new Node(1);
Node node2=new Node(2);
Node node3=new Node(3);
Node node4=new Node(4);
Node node5=new Node(5);
header.next=node1;
node1.next=node2;
node2.next=node3;
node3.next=node4;
node4.next= node5;
node1.rand=node4;
node3.rand=node2;
node5.rand=node1;
CopyLinkedList.copy_1(header);
CopyLinkedList.copy_2(header);
}
}
class CopyLinkedList{
public static Node copy_1(Node header){
if (header==null)return null;
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
Node tail=header;
while (tail!=null){
//遍历填入哈希表
map.put(tail,new Node(tail.value));
tail=tail.next;
}
tail=header;
while (tail!=null){
map.get(tail).next=map.get(tail.next);
map.get(tail).rand=map.get(tail.rand);
tail=tail.next;
}
return map.get(header);
}
public static Node copy_2(Node header){
if (header==null)return null;
Node tail=header;
Node n;
//在原来节点后再添加一个copy节点
while (tail!=null){
n=tail.next;
tail.next=new Node(tail.value);
tail.next.next=n;
tail=n;
}
tail=header;
Node copyTail;
//复制处理rand节点(只对原节点判断)
while (tail!=null){
n=tail.next.next;
copyTail=tail.next;
if (tail.rand!=null)
copyTail.rand=tail.rand.next;
tail=n;
}
Node copyHeader=header.next;//若不提前标记会被回收
tail=header;
//链表分离
while (tail!=null){
n=tail.next.next;
copyTail=tail.next;
if (n!=null)
copyTail.next=n.next;
tail.next=n;
tail=n;
}
return copyHeader;
}
}
class Node{
int value;
Node next;
Node rand;
public Node(int value){
this.value=value;
}
}
三分链表

给定一个只将比该值小的节点放左边,大的放右边
class SEL{
public static Node sEL(Node header,int pivot){
Node head_1=null;
Node tail_1=null;
Node head_2=null;
Node tail_2=null;
Node head_3=null;
Node tail_3=null;
Node nextNode=null;
while (header!=null){
nextNode=header.next;
header.next=null;
if (header.num<pivot){
if (head_1==null){
head_1=header;
tail_1=header;
}else {
tail_1.next=header;
tail_1=tail_1.next;
}
}else if (header.num==pivot){
if (head_2==null){
head_2=header;
tail_2=header;
}else {
tail_2.next=header;
tail_2=tail_2.next;
}
}else {
if (head_3==null){
head_3=header;
tail_3=header;
}else {
tail_3.next=header;
tail_3=tail_3.next;
}
}
header=nextNode;
}
if (tail_1==null){
if (tail_2==null){
return head_3;
}else {
tail_2.next=head_3;
return head_2;
}
}else {
if (tail_2==null){
tail_1.next=head_3;
}else {
tail_1.next=head_2;
tail_2.next=head_3;
}
return head_1;
}
}
}
判断链表是否有环
判断链表是否有环,若有返回第一个入环节点
慢:1 快:2
若慢:1快3:
都入环时相差奇数步,且环节点数量为偶数则永不相交
都入环时相差奇数步说明每次差值减少2步,定在第一轮反超,此时差 环节点个数-1,若该值仍为奇数,那么第二轮也反超,故永不相遇
package Test;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node header=new Node(0);
Node node1=new Node(1);
Node node2=new Node(2);
Node node3=new Node(3);
Node node4=new Node(4);
Node node5=new Node(5);
header.next=node1;
node1.next=node2;
node2.next=node3;
node3.next=node4;
node4.next=node5;
node5.next=node2;
System.out.println(HasCircle.hasCircle(header).num);
}
}
class HasCircle{
public static Node hasCircle(Node header){
if (header==null)return null;
boolean flag=false;
Node slow=header;
Node quick=header;
while (quick.next!=null&&quick.next.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
quick=quick.next.next;
if (slow==quick){//判断是否却有环
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if (!flag)return null;
quick=header;
while (quick!=slow){//相遇时将其中一个指针指向header走相同的步数定在入环节点相遇
quick=quick.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return quick;
}
}
class Node{
int num;
Node next;
public Node(int num){
this.num=num;
}
}
两个链表相交关系
class List{
/*
有环:
1.同环:
- 入环节点相同 返回相交节点
- 入环节点不同 返回其中一个入环节点
2.不同环:
- 返回null
无环:
1.相交:
- 返回相交节点
2.不相交:
- 返回null
*/
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node loop1 = hasCircle(head1);
Node loop2 = hasCircle(head2);
if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {
return noLoop(head1, head2);//无环,判断是否为链式相交或不相交
}
if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);//有环,返回相交节点
}
return null;//一有环,一无环必定不相交
}
private static Node hasCircle(Node header){
if (header==null)return null;
boolean flag=false;
Node slow=header;
Node quick=header;
while (quick.next!=null&&quick.next.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
quick=quick.next.next;
if (slow==quick){//判断是否却有环
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if (!flag)return null;
quick=header;
while (quick!=slow){//相遇时将其中一个指针指向header走相同的步数定在入环节点相遇
quick=quick.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return quick;
}
private static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
//计算链表差值
while (cur1.next != null) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if (cur1 != cur2) {
return null;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
//长的走到和短的长度同位置
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
//判断是否有相同节点,若无就会走到最后返回null
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
private static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
if (loop1 == loop2) {
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != loop2) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
} else {
cur1 = loop1.next;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
if (cur1 == loop2) {
return loop1;//环内相交
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;//两个有环链表环不是同一个
}
}
}
class Node{
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int num){
this.value=num;
}
}
优先队列
持续输出中位数(堆/优先队列)
持续输入一个数,可以在任意时刻输出中位数。
- 构建两个堆,一个大堆,一个小堆,大堆放较小的元素,小堆放较大的元素
- 持续保持两个堆的元素个数差不超过1
- 超过1,将大堆中堆顶元素放进小堆或将小堆堆顶元素放进大堆。
- 这样中位数就一直只和两个堆的堆顶元素相关
class Tree {
private PriorityQueue<Double> little;//存较大数据,取出较小元素
private PriorityQueue<Double> large;//存较小数据,取出较大元素
public Tree() {
little = new PriorityQueue<>();
large = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2, o1));
}
public void add(Double x) {
if (little.size() == 0 && large.size() == 0)
large.add(x);
else {
if (large.peek() < x)little.add(x);
else large.add(x);
if (little.size() - large.size() > 1)
large.add(little.poll());
else if (little.size() - large.size() < -1)
little.add(large.poll());
}
}
public Double getMed(){
if (little.size()-large.size()==0)
return (little.peek()+large.peek())/2;
else if (little.size()-large.size()>0)
return little.peek();
else return large.peek();
}
}
二叉树衍生
前中后横向遍历非递归实现
package Test;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root=new Node(0);
Node node1=new Node(1);
Node node2=new Node(2);
Node node3=new Node(3);
Node node4=new Node(4);
Node node5=new Node(5);
root.left=node1;
root.right=node2;
node1.left=node3;
node1.right=node4;
node4.right=node5;
Tree.pre(root);
System.out.println();
Tree.inOrderUnRecur(root);
System.out.println();
Tree.posOrderUnRecur1(root);
System.out.println();
Tree.posOrderUnRecur2(root);
}
}
class Tree{
//前序遍历
public static void pre(Node root){
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
if (root==null)return;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
Node n=stack.pop();
System.out.print(n.value+" ");
if (n.right!=null){
stack.push(n.right);
}
if (n.left!=null){
stack.push(n.left);
}
}
}
//中序遍历
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head) {
System.out.print("in-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
if (head != null) {//向左搜索压入栈中,向右不入栈
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {//持续搜索右树
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//后序遍历
public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>();
s1.push(head);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
head = s1.pop();
s2.push(head);
if (head.left != null) {
s1.push(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//后序遍历
public static void posOrderUnRecur2(Node h) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (h != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(h);
Node c = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
c = stack.peek();
if (c.left != null && h != c.left && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.left);
} else if (c.right != null && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.right);
} else {
System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " ");
h = c;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//横向遍历
public static void w(Node root){
if (root==null)return;
Deque<Node> deque=new ArrayDeque();
deque.add(root);
while (!deque.isEmpty()){
Node n=deque.poll();
System.out.println(n);
if (n.left!=null){
deque.add(n.left);
}
if (n.right!=null){
deque.add(n.right);
}
}
}
}
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num){
this.value=num;
}
}
计算树每一层的最多节点个数
class Tree{
//基于横向遍历
public static int fun_1(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Deque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque();
HashMap<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
deque.add(root);
int floor=1;//运行的这一层是哪一层
int thisNum=0;//本层节点个数
int maxNum = 0;//每一层最大的值
map.put(root,floor);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node n = deque.poll();
if (map.get(n)==floor){//如果还是这一层
thisNum++;
}else {//如果和上一层不一层了
maxNum=Math.max(maxNum,thisNum);
thisNum=1;//因为已经删除了该层一个元素,所以初始化为1
floor++;//进行下一层
}
if (n.left != null) {
deque.add(n.left);//进入队列
map.put(n.left,floor+1);//记录该元素层数
}
if (n.right != null) {
deque.add(n.right);
map.put(n.right,floor+1);
}
}
return Math.max(thisNum,maxNum);
}
//基于横向遍历
public static int fun_2(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Node thisLastNode=root;//记录遍历节点层的最后一个节点
Node nextLastNode=null;//记录遍历节点下一层最后一个结点
int maxNum=0;
int thisNum=0;//当前层节点个数
Deque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque();
deque.add(root);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node n = deque.poll();
thisNum++;//删除一个就加1
if (n.left != null) {
deque.add(n.left);
nextLastNode=n.left;//更新最后一个节点
}
if (n.right != null) {
deque.add(n.right);
nextLastNode=n.right;//更新最后一个节点
}
if (n==thisLastNode){//删除的借点和该层节点相同说明该层结束
thisLastNode=nextLastNode;//将下一层最后的节点给thisLastNode
nextLastNode=null;//以后动态遍历下一层
maxNum=Math.max(thisNum,maxNum);//记录最大值
thisNum=0;
}
}
return maxNum;
}
}
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num){
this.value=num;
}
}
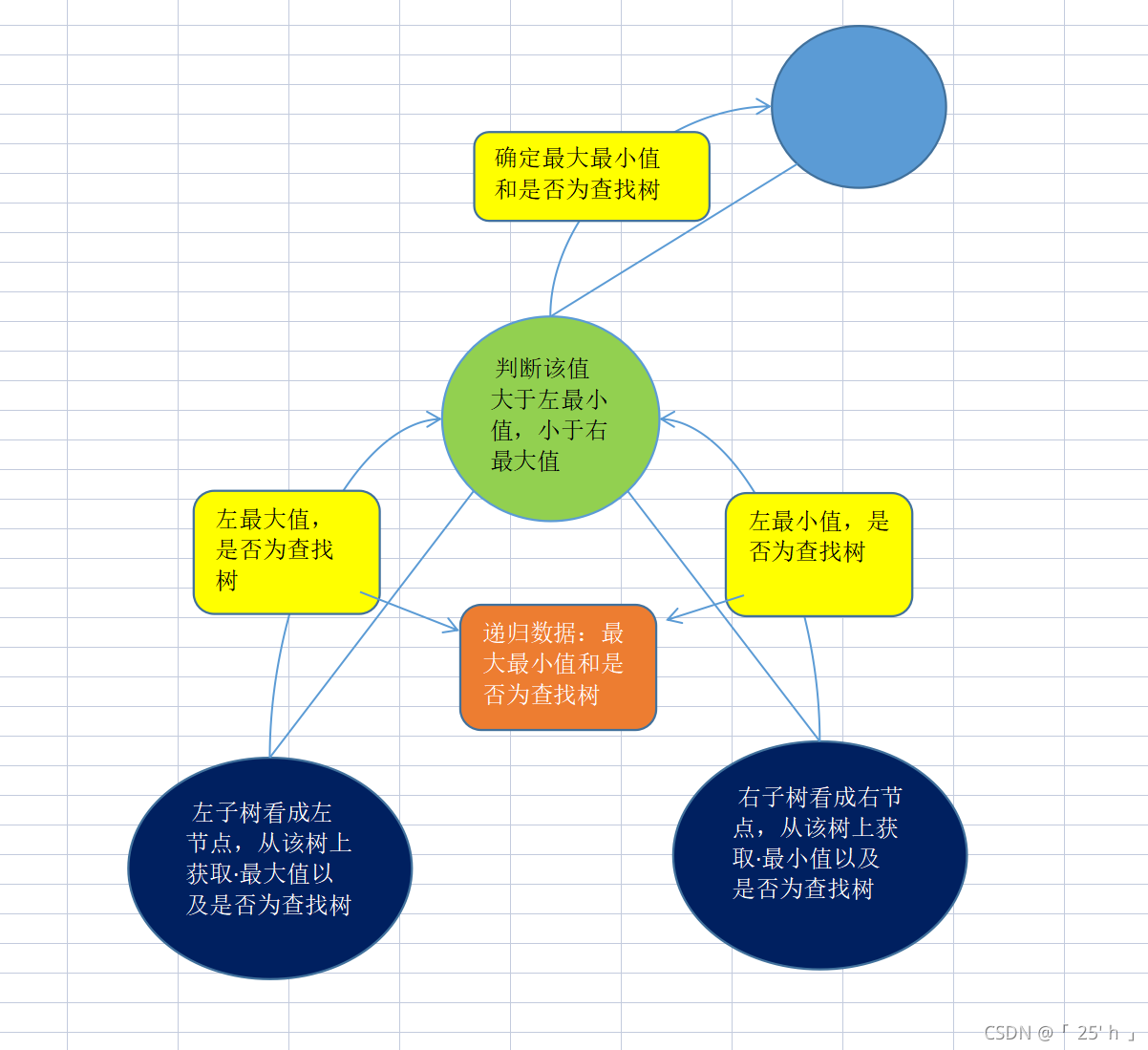
判断是搜索二叉树(套路题)
isBST_2递归套路:
class Tree{
//中序遍历判断
private static int last=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean isBST_1(Node head){
if (head==null){
return true;
}
if (!isBST_1(head.left))return false;
if (last>=head.value)return false;
else last=head.value;
return isBST_1(head.right);
}
//套路递归判断
public static returnType isBST_2(Node head){
if (head==null)return null;
returnType leftType= isBST_2(head.left);
returnType rightType= isBST_2(head.right);
int min=head.value;//初始值
int max=head.value;
boolean flag=true;
//左判断刷新
if (leftType!=null){
if (!leftType.isbst||leftType.max>=head.value)flag=false;
min=Math.min(leftType.min,head.value);
max=Math.max(leftType.max,head.value);
}
//右判断刷新
if (rightType!=null){
if (!rightType.isbst||rightType.min<=head.value)flag=false;
min=Math.min(rightType.min,head.value);
max=Math.max(rightType.max,head.value);
}
return new returnType(min,max,flag);
}
static class returnType{
boolean isbst;
int min;
int max;
private returnType(int min, int max, boolean flag){
this.min=min;
this.max=max;
this.isbst=flag;
}
}
}
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num){
this.value=num;
}
}
判断是完全二叉树(套路题)
class Tree {
public static boolean isCBT(Node head) {
if (head == null) return true;
boolean flag = false;
Deque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<Node>();
deque.add(head);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node node = deque.pop();
if ((node.left == null && node.right != null)//左无节点有有节点
||
(flag && (node.right != null || node.right != null)))//标记后左右存在节点
return false;
if (node.left != null) deque.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) deque.add(node.right);
if (node.left == null || node.right == null) flag = true;//此后不该有子节点,应该放在最后判断,因为判断结果flag不能对此次结果有影响
}
return true;
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num) {
this.value = num;
}
}
判断是满二叉树(套路题)
递归套路:

class Tree {
//方式一
public static boolean isF_1(Node head){
Data data = is_1(head);
return (1<<data.height)-1==data.nodeNum;
}
private static Data is_1(Node head){
if (head==null)return new Data(0,0);
Data lData=is_1(head.left);
Data rData=is_1(head.right);
int num=lData.nodeNum+rData.nodeNum+1;
int he=Math.max(lData.height,rData.height)+1;
return new Data(num,he);
}
//方式二
public static boolean isF_2(Node head){
Data data = is_2(head);
return data != null;
}
private static Data is_2(Node head){
if (head==null)return new Data(0,0);
Data lData=is_2(head.left);
Data rData=is_2(head.right);
if (lData==null||rData==null)
return null;
if (lData.nodeNum!=rData.nodeNum||lData.height!=rData.height)
return null;
int num=lData.nodeNum+rData.nodeNum+1;
int he=lData.height+1;
return new Data(num,he);
}
static class Data{
int nodeNum;
int height;
boolean is;
public Data(int nodeNum,int height){
this.nodeNum=nodeNum;
this.height=height;
}
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num) {
this.value = num;
}
}
判断是平衡树(套路题)
递归套路:

class Tree {
public static Data isAVL(Node head){
if (head==null)return new Data(0,true);
Data lData=isAVL(head.left);
Data rData=isAVL(head.right);
int height=Math.max(lData.height,rData.height)+1;
boolean flag=lData.isAVL&&rData.isAVL&&Math.abs(lData.height-rData.height)<=1;
return new Data(height,flag);
}
static class Data{
int height;
boolean isAVL;
public Data(int height ,boolean is){
this.height=height;
this.isAVL=is;
}
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num) {
this.value = num;
}
}
树节点最远距离(套路题)

递归套路:
- 根据子树最大深度计算出经过当前节点的最长距离
- 向上传递子树和经过当前节点最长距离 的最大值
- 最长距离需要子树深度
- 所以递归数据包括最大距离和最大深度
class U {
public static Data maxLength(Node head){
if (head==null)return new Data(0,0);
Data ld=maxLength(head.left);
Data rd=maxLength(head.right);
int maxLen=Math.max(ld.maxHeight+rd.maxHeight+1,Math.max(ld.maxLen,ld.maxLen));
int maxHeight=Math.max(ld.maxHeight,rd.maxHeight)+1;
return new Data(maxLen,maxHeight);
}
private static class Data{
int maxLen;
int maxHeight;
private Data(int maxLen,int maxHeight){
this.maxLen=maxLen;
this.maxHeight=maxHeight;
}
}
}
最大快乐值(套路题)

递归套路:
- 最大值和每个节点是否去有关,就是取 当前节点不去(0)+子节点去或不去的最大值 和 当前节点去(happy)+子节点不去的最大值
- 每个节点的去和不去都会直接影响父类节点,间接影响祖宗节点。
- 只要递归传递该节点去和不去的最大值信息即可。
class U {
public static Data maxHappy(Node head){
if (head.nexts==null)return new Data(0,head.happy);
int lai=head.happy;
int bu=0;
for (Node node:head.nexts){
Data data = maxHappy(node);
lai+=data.maxBu;//该节点去,子节点不能去
bu+=Math.max(data.maxBu,data.maxLai);//该节点不去,子节点可取可不去
}
return new Data(bu,lai);
}
private static class Data{
int maxBu;
int maxLai;
private Data(int maxBu,int maxLai){
this.maxBu =maxBu;
this.maxLai =maxLai;
}
}
}
class Node {
int happy;
Node[] nexts;
}
查找树中两个节点的最近共父类节点
- 该路径上不存在寻找的o1或o2,就回馈上一次递归null
- 路径上存在o1或o2,返回标记告诉上一次递归存在o1或o2
- 直到在某次递归时判断出左右路径都回馈了有o1或o2,就将该父节点返回
- 将返回的父节点以返回值的方式传给上一次递归直至结束递归。
class Tree {
/**
* @param header 根节点
* @param o1 节点一
* @param o2 节点二
* @return 最近共父节点
*
*/
public static Node ancestor(Node header, Node o1, Node o2) {
if (header == null || o1 == header || o2 == header) return header;
Node lNode = ancestor(header.left, o1, o2);
Node rNode = ancestor(header.right, o1, o2);
//该条件只会成功一次,返回的header就是我们所要找的节点
// 如何将这个节点返回第一次调用这个函数时?
// 由于我们不知道这个父节点是它的父节点的左还是右
// 但是我们知道成功进入该条件后的所有递归中只能出现一边为null,另一边为header节点
// 所以 返回: lNode != null ? lNode : rNode
// 另外这句话也会在找到目标节点前将o1或o2传到上一个递归中,代表着这个路径上存在o1或o2
// 当路径上没有o1或o2时,lNode和rNode均为空,随便返回一个
if (lNode != null && rNode != null)
return header;
return lNode != null ? lNode : rNode;
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int num) {
this.value = num;
}
}
查找后继结点
- 有右节点,右树上的最左节点
- 无右节点,递归寻找节点是父节点左节点的点
- 否则空
class Tree {
public static Node process(Node node){
if (node==null)return null;
if (node.right!=null)return leftLast(node.right);//有右节点
Node parentTail=node.parent;
while (parentTail!=null&&parentTail.left!=node){//递归寻找节点
node=parentTail;
parentTail=parentTail.parent;
}
return parentTail;
}
private static Node leftLast(Node head){//一直寻找左节点
while (head.left!=null)
head=head.left;
return head;
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
Node parent;
public Node(int num) {
this.value = num;
}
}
折纸凹凸问题

上次每个折痕都有两个子折痕,上凹下凸,也就是二叉树节点都有一个凹左节点一个凸右节点。这些折痕的顺序就是二叉树的中序遍历。
class Tree {
/**
* @param N 折N次
*/
public static void pre(int N){
pre(N,true);
}
private static void pre(int num,boolean down){
if (num==0)return;
pre(num-1,true);//true表示凹,false表示凸
System.out.print(down?"down ":"up ");
pre(num-1,false);
}
}
哈夫曼最小代价问题

class Tree {
public static int lessConsumer(int[] arr){
if (arr.length==1)return arr[0];
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();//内部元素为堆结构(优先队列)
for (int i : arr)
queue.add(i);
int sum=0;
while (queue.size()>1){
//构建赫夫曼树
int num1=queue.poll();
int num2=queue.poll();
sum+=(num1+num2);
queue.add(num1+num2);
}
return sum;
}
}
暴力递归
N皇后(位运算)
class E {
public static int num(int num) {
if (num < 1 || num > 32) return 0;
//limit用于限制在所有数据运算过程中保证除后num位的所有位数据均为零,来判断结束和标志结束
int limit = num == 32 ? -1 : (1 << num) - 1;
return process(limit, 0, 0, 0);
}
/**
* @param limit 限制数据在一定的位运算范围内
* @param coLim 该步前所有皇后纵向上已经存在皇后
* @param leftLim 该步前所有皇后在k=-1的方向上对于我们该步皇后存在的限制
* @param rightLim 该步前所有皇后在k=1的方向上对于我们该步皇后存在的限制
* @return 该路径上存在的的情况,只会在成功时返回1
* coLim/leftLim/rightLim三者的限制均是在位上为1的时候表示存在皇后
*/
private static int process(int limit, int coLim, int leftLim, int rightLim) {
if (limit == coLim) return 1;
//(coLim | leftLim | rightLim)结果表示所有位上为1的位置均存在皇后,不能存放。
//~后表示1的地方没有限制,可以存放皇后(但是,在32位的前32-num位上也为1,我们知道这是不合理的,因为不存在那么多的皇后)
//limit& 表示将除num位的值变成0,这样就保证所有为1的元素均为空缺位置。
int pos = limit & (~(coLim | leftLim | rightLim));
int res = 0, mostRightOne;
while (pos != 0) {//pos为0.说明不存在空缺位置
mostRightOne = pos & (~pos + 1);//此时在后num位存在1,就将最右端的1取出。
pos = pos - mostRightOne;//更新pos,将取出的1减掉,表明mostRightOne中1所对应的位存在了,不能放了。
res += process(limit, coLim | mostRightOne // 该mostRightOne位的皇后对于下一皇后纵向上的影响
, (leftLim | mostRightOne) << 1 // mostRightOne对于k=-1方向的影响
, (rightLim | mostRightOne) >> 1); //mostRightOne对于k=1方向的影响
}
return res;
}
}
字符串的全排列

- 我们通常都思路都是将所有字符依次放在最前面,例如ABC,第一位为A,B,C,然后判断第二位,那么我们如何在字符串中标记该字符已经被我们安排在前面了?
- 若我们使用下标的方式,那么在每次选择都会产生一个下标,这样会很乱。
- 于是我们可以通过将欲放在前面的字符就直接放在前面(将字符一次和后面的交换),用一个下标指引我们前面已经定了多少的元素。
- 但是若我们交换后在后续调用时,数据顺序已经打乱,我们可能会造成重复情况,所以我们在每次运行后再将数据交换变成原来位置。
- 但是当数据有重复字符时,会出现重复的全排列,这是我们就要判断交换的字符是否和之前交换的相同,若相同,就不用交换
class PB {
public static List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
public static void process(String string){
char[] chars = string.toCharArray();
process(chars,0);
}
private static void process(char[] chars, int i){
if (i==chars.length){//结果
list.add(new String(chars));
return;
}
boolean[] isVisited=new boolean[26];//默认只有大写字母
for (int j=i;j<chars.length;j++){
if (!isVisited[chars[j]-'A']){//是否重复
isVisited[chars[j]-'A']=true;
swap(chars,i,j);//交换
process(chars,i+1);//递归
swap(chars,i,j);//恢复
}
}
}
private static void swap(char[] chars,int i, int j) {
char c = chars[i];
chars[i]=chars[j];
chars[j]=c;
}
}
纸牌累计分数

class PB {
public static int win(int[] arr){
if (arr.length==0)return 0;
return Math.max(front(arr,0,arr.length-1), end(arr,0,arr.length-1));
}
//先手的人对应的数据
private static int front(int[] arr,int left,int right){
if (left==right)return arr[left];//先手的人,最后还剩一个数据就是这个人的
//取那个值和下一次该我选的时候我的收益最大。
return Math.max(arr[left]+end(arr,left+1,right),arr[right]+end(arr,left,right-1));
}
private static int end(int[] arr, int left, int right){
if (left==right)return 0;
return Math.min(front(arr,left+1,right),+front(arr,left,right-1));
}
}
岛数量问题

class PB {
private static int[][] arr;
private static int N;
private static int M;
public static int process(int[][] arr){
PB.arr=arr;
PB.N=arr.length;
PB.M=arr[0].length;
int res=0;//记录结果
for (int i=0;i<N;i++){
for (int j=0;j<M;j++){
if (arr[i][j]==1){//有1且为被感染
res++;
infect(i,j);//感染
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 感染函数
private static void infect(int i, int j) {
if (i<0||i>=N||j<0||j>=M||arr[i][j]!=1)return;
arr[i][j]=2;
infect(i-1,j);
infect(i+1,j);
infect(i,j-1);
infect(i,j+1);
}
}
返回字符串的所有子字符串(树形)
- 将该问题看成二分类问题,将所有的单个字符元素是否存在看成一个事件,通过对所有的单个字符判读存在情况就可以得出所有子字符串
- 这样可以理解为二叉树的情况,每一层的每个节点下有两个子节点,表示该层对应的字符是否添加进路径中,最后树的所有叶子节点对应的字符串就是所以子字符串
- 我们采用动态生成树的递归方法对树进行动态的遍历。(该树必定为满树)
class PB {
public static List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
private static String s;
public static void childrenString(String string){
s=string;
childrenString("",0);
}
private static void childrenString(String chlidString,int i){
if (i==s.length()){//叶子节点
list.add(chlidString);
return;
}
childrenString(chlidString+s.charAt(i),i+1);//要这个字符
childrenString(chlidString,i+1);//不要这个字符
}
}
数字转化成字母(树形)

class PB {
public static int process(String s,int i){
//若一个不剩或这还剩一个,就返回1(保证剩的不为0),若此时不返回,说明还剩至少两个字符
if (s.length()==i||(s.length()==i+1&&s.charAt(i)!='0'))return 1;
if (s.charAt(i)=='0')return 0;//没有0开头匹配的元素
int res=process(s,i+1);//一个字符的
if (Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i,i+2))<=26)
res+=process(s,i+2);//若满足匹配条件,进行两个字符的
return res;//累加的结果返回就行了
}
}
背包问题(树形)

- 和返回字符串的所有子字符串相似,判断每个物品是否装进了袋子两种选择
- 只需要用递归像树一样遍历所有选择取出最大值即可
- 这样的题可以使用动态规划O(N2),递归O(2^N),关于递归转为动态规划,后续再说。
class PB {
private static int maxBag;
private static int[] weights;
private static int[] values;
public static int process(int[] weights,int[] values,int maxBag){
PB.maxBag=maxBag;
PB.weights=weights;
PB.values=values;
return process(0,0,0);
}
/**
* @param w 此时的权重
* @param v 此时价值
* @param i 当前已经判断到那个物品了
* @return 最大价值
*/
private static int process(int w,int v,int i){
if (w>maxBag)return 0;
if (i==weights.length)return v;
return Math.max(process(w+weights[i],v+values[i],i+1),
process(w,v,i+1));
}
}
贪心算法
最多场会议问题

- 按照结束时间安排
class Progrem {
Time[] times;
public Progrem(Time[] times, int timePoint){
this.times=times;
arrange(timePoint);
}
private void arrange(int timePoint) {
Arrays.sort(times, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.end));
int res=0;
for (Time time : times) {
if (time.start >= timePoint) {//下一个会议开始时间在上一个会议结束后。
res++;//会议数量
timePoint = time.end;//记录该会议结束时间。
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
static class Time{
int start;
int end;
public Time(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
}
投资收益问题

- 两个优先队列
- 一个按count的小根堆P1,另一个按profit的大根堆P2
- 在P1中找能投资的放在P2中,投资P2堆顶元素
- 循环遍历
class Program {
public static int res(int[] counts,int[] profits,int k,int m){
//按照count建堆
PriorityQueue<Node> minCount = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.count));
//按照profit建堆
PriorityQueue<Node> maxProfit = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o2.profit,o1.profit));
//初始化
for (int i=0;i<counts.length;i++)
minCount.add(new Node(counts[i],profits[i]));
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//能承担的放在maxProfit中
while (!minCount.isEmpty()&&minCount.peek().count<m)
maxProfit.add(minCount.poll());
//太穷了,结束
if (maxProfit.isEmpty()) return m;
//投资profit最大的累加
m+=maxProfit.poll().profit;
}
return m;
}
private static class Node{
int count;
int profit;
private Node(int count,int profit){
this.count=count;
this.profit=profit;
}
}
}