总结一下二叉树的四种遍历方式,用递归和迭代,递归代码比较简单,迭代代码相对比较复杂点。
一.前序遍历
(这里以打印出结果为例,还可以用ArrayList,存储子树中的val)
思路
递归:先根节点,再左子树,再右子树。
迭代:需要使用到栈。先压栈root,进入循环(结束循环条件为:栈空),再弹栈用top保留下来打印val,判断top右子树不为空,则压栈,判断top左子树不为空,也压栈(这两个判断顺序不能改变)。拿图直观理解一下。
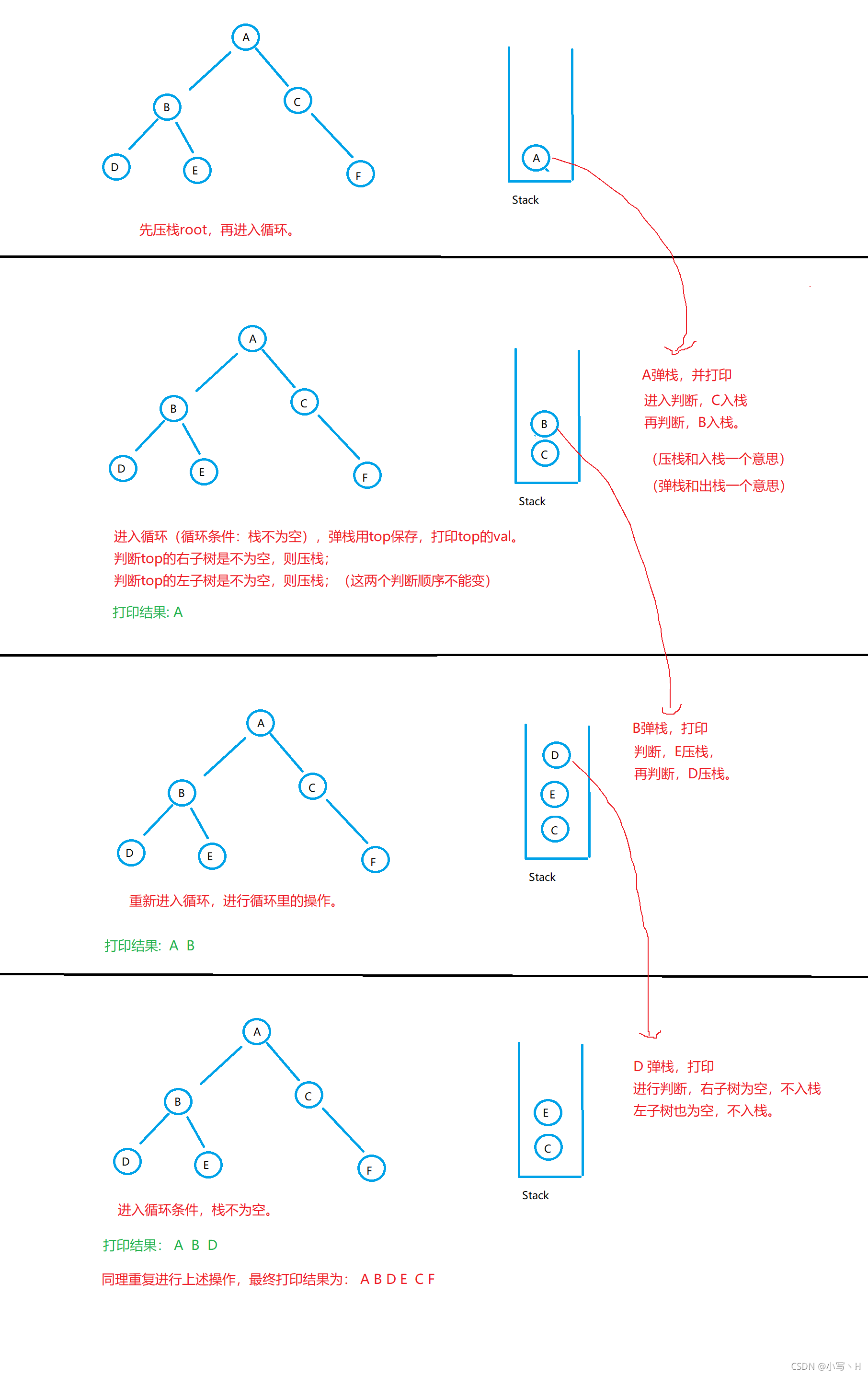
代码
递归
public static void preOrder(Node root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
//根节点
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
//左子树
preOrder(root.left);
//右子树
preOrder(root.right);
}
迭代
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> s=new Stack<>();
//先入栈
s.push(root);
while (!s.empty()){
TreeNode top=s.pop();
System.out.print(top.val+" ");
//先右后左,顺序不能乱
if(top.right!=null){
s.push(top.right);
}
if(top.left!=null){
s.push(top.left);
}
}
}
二.中序遍历
思路
递归:先根左子树,再根节点,再右子树。
迭代:cur=root,进入一个死循环(里面有if判断条件,栈空,则break);
1.再进入一个循环,cur不为空,则入栈,一直向左,入栈,直到左子树为空。
2.判断if,栈空则结束死循环。
3.弹栈,打印。
4.cur=top.right。
重复上述操作
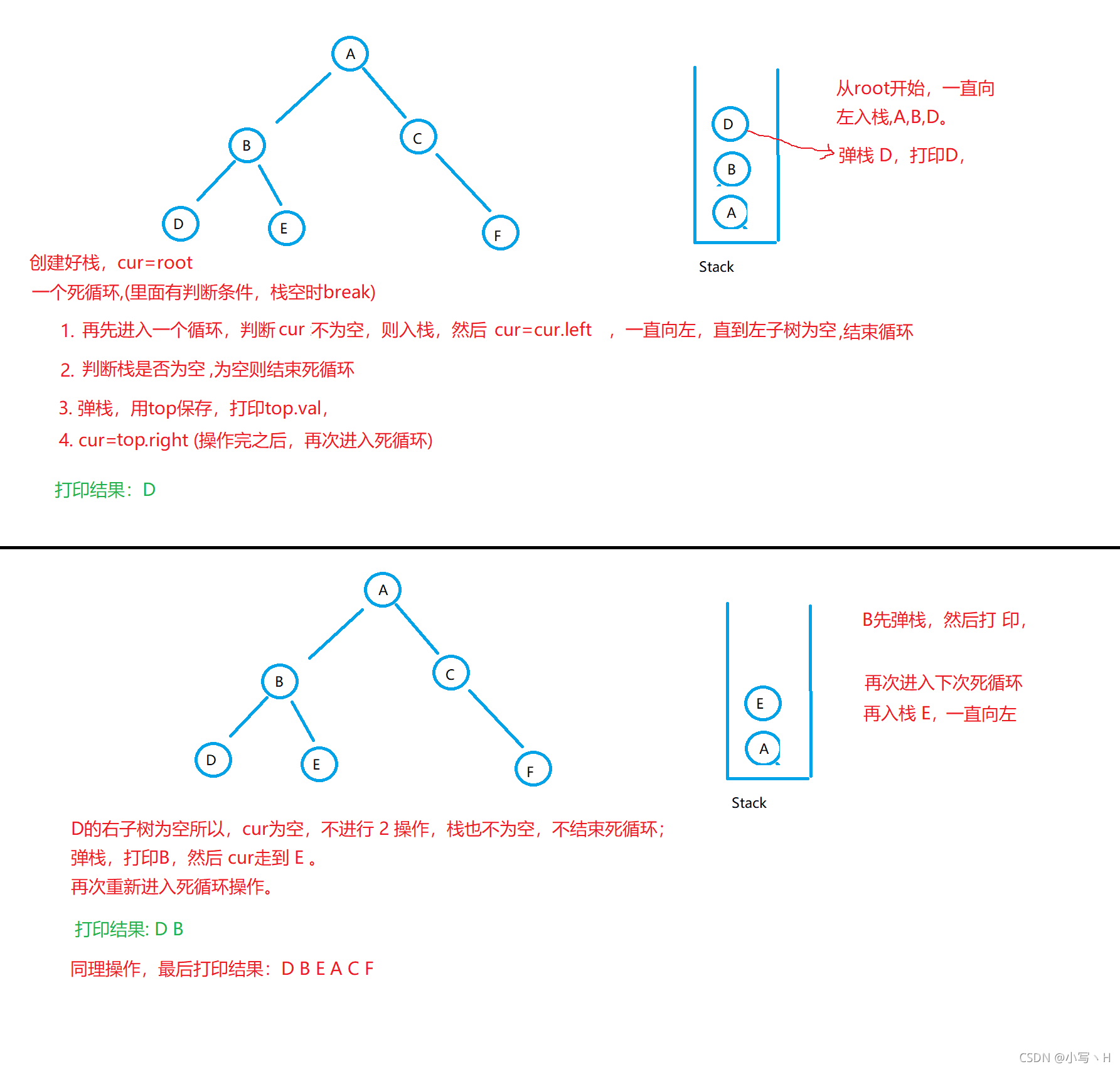
代码
递归
public static void inOrder(Node root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
//左子树
inOrder(root.left);
//根节点
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
//右子树
inOrder(root.right);
}
迭代
public static void inOrder(TreeNode root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> s=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while (true){
//往左找,并且入栈
while (cur!=null){
s.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
//栈为空,遍历就结束
if(s.empty()){
break;
}
//取栈顶元素访问
TreeNode top=s.pop();
System.out.print(top.val+" ");
//从当前节点右子树出发重复上面操作
cur=top.right;
}
}
三.后序遍历
思路
递归:先根左子树,再根右子树,再根节点。
迭代:后序的思路和中序差不多,有一点区别在于,
取栈顶元素的时候此时是peek(),要看栈顶元素,是否有右子树或者右子树是否已经被访问过了。当没有右子树,或者已经访问过,则直接弹栈打印。
其余操作和中序一样,看代码就可以理解。
代码
递归
public static void postOrder(Node root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
//左子树
postOrder(root.left);
//右子树
postOrder(root.right);
//根节点
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}
迭代
public static void postOrder(TreeNode root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> s=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode prev=null;
while (true){
//往左找,并且入栈
while (cur!=null){
s.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
//栈为空,遍历就结束
if(s.empty()){
break;
}
//取出栈顶元素来看看能不能访问
TreeNode top=s.peek();
//栈顶元素右子树为空,或者已经被访问过了
if(top.right==null||top.right==prev){
System.out.println(top.val+" ");
s.pop();
//保持好,prve为已经遍历完的最后一个元素(这个细节很重要哦)用来判断是否已经访问过了
prev=top;
}else {
cur=top.right;
}
}
}
四.层序遍历
思路
递归:以力扣的102题为例。
迭代:用队列来操作。先入队root,进入循环(结束条件,队列为空)。
1.cur保存出队元素,并打印val。
2.cur.left不为空,则入队。
3.cur.right 不为空,则入队。
重新操作循环。直到队列为空,结束循环。
代码
递归
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<>();
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return result;
}
helper(root,0,result);
return result;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, int level,List<List<Integer>> result) {
//当访问的该行没有在result中对应的时候,就加入一行
if(level==result.size()){
result.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
//get访问到行,add添加元素val
result.get(level).add(root.val);
//访问左边
if(root.left!=null){
helper(root.left,level+1,result);
}
//访问右边
if(root.right!=null){
helper(root.right,level+1,result);
}
}
迭代
public static void levelOrder(Node root){
//根节点为空,直接结束
if(root==null){
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Node cur=queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
//判断左子树
if(cur.left!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
//判断右子树
if(cur.right!=null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}