?
数据结构与算法
算法面试题实例
1、字符串匹配问题
- 暴力匹配
- KMP算法(部分匹配表)
2、汉诺塔问题
- 分治算法
3、八皇后问题
- 回溯算法
4、马踏棋盘算法
- 图的深度优先遍历算法(DFS)+贪心算法优化
线性结构和非线性结构
数据结构包括:线性结构和非线性结构
线性结构的存储结构:线性存储结构和链式存储结构
线性结构:
数组、队列、链表、栈
非线性结构:
二维数组、多维数组、广义表、树结构、图结构
稀疏数组和队列
1、稀疏数组:用来缩小程序规模(特殊的数组——>稀疏数组 )
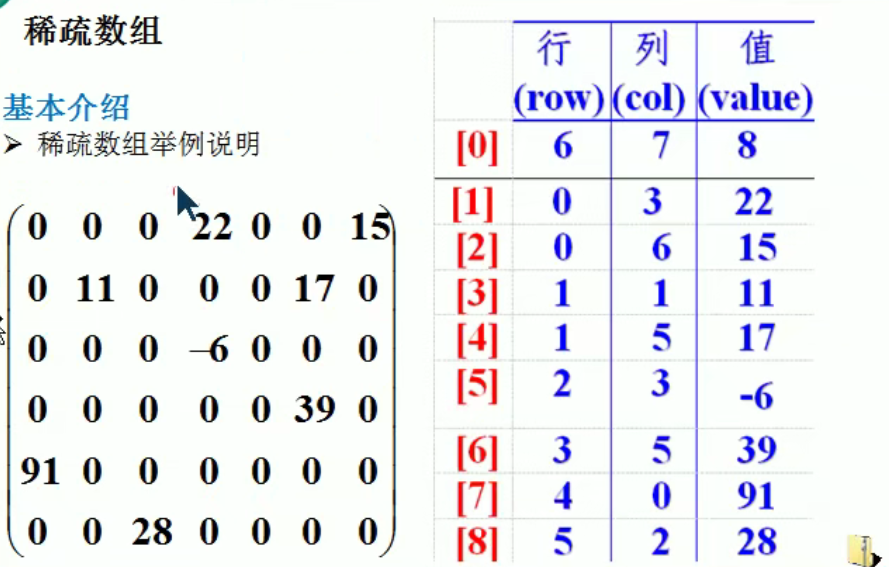
package com.zeng.sparsearray;
public class sparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int chessArr1[][] = new int[11][11];
chessArr1[1][2] = 1;
chessArr1[2][3] = 2;
chessArr1[3][5] = 3;
int sum = 0;
for (int[] row : chessArr1){
for (int data : row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
if(data != 0){
sum++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("————————————————————————");
int chessArr2[][] = new int[sum+1][3];
chessArr2[0][0] = 11;
chessArr2[0][1] = 11;
chessArr2[0][2] = sum;
int count = 1;
// chessArr2[1][0] = 1;
// chessArr2[1][1] = 2;
// chessArr2[1][2] = 1;
// chessArr2[2][0] = 2;
// chessArr2[2][1] = 3;
// chessArr2[2][2] = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (chessArr1[i][j] != 0){
chessArr2[count][0] = i;
chessArr2[count][1] = j;
chessArr2[count][2] = chessArr1[i][j];
count++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("row col val");
// for (int[] row : chessArr2){
// for (int data : row){
// System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
for (int i = 0; i < chessArr2.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t\n",chessArr2[i][0],chessArr2[i][1],chessArr2[i][2]);
}
System.out.println("——————————————————————————");
int chessArr3[][] = new int[11][11];
// for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
// for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
// chessArr3[i][j] = 0;
// }
// }
for (int i = 1; i < sum+1; i++) {
chessArr3[chessArr2[i][0]][chessArr2[i][1]] = chessArr2[i][2];
}
for (int[] row : chessArr1){
for (int data : row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
if(data != 0){
sum++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
课后习题:将二维数组转换成稀疏数组存储到map.data文件中,再将稀疏数组拿出转换成二维数组。(熟练文件输入输出)
\\主要步骤
File file = new File("D:\\数据结构与算法\\data\\map.data");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter write = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "UTF-8");
if (i == chessArr2.length - 1) {
write.append(chessArr2[i][0] + "," + chessArr2[i][1] + "," + chessArr2[i][2]);
} else {
write.append(chessArr2[i][0] + "," + chessArr2[i][1] + "," + chessArr2[i][2] + ",");
}
write.close();
fos.close();
while (reader.ready()) {
sb.append((char) reader.read());// 转成char加到StringBuffer对象中
}
reader.close();// 关闭读取流
fis.close();// 关闭输入流,释放系统资源
String[] str = sb.toString().split(",");
2、队列(先进先出 front rear 增加数据rear++ 取出数据front++ front和rear都是脚标,用来标记位置)
package com.zeng.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue01 queue = new ArrayQueue01(3);
char key = ' ';
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while(loop){
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列中取出");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头数据");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出系统");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key){
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("请输入要添加的数:");
queue.addQueue(scanner.nextInt());
break;
case 'g':
try {
queue.getQueue2();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int i = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列的头数据是:%d\n",i);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
class ArrayQueue01{
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public ArrayQueue01(int arrayMaxSize){
maxSize = arrayMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return rear == maxSize - 1;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rear == front;
}
public void addQueue(int n){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("队列满,不能加数据了");
return;
}
rear++;
arr[rear] = n;
}
public int getQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
front++;
return arr[front];
}
//这个是自己加的代码,因为用getQueue从队列中取出后数据还会在队列中,所以添加这个方法
public void getQueue2(){
System.out.printf("取出的数据是:%d\n",getQueue());
if (!isEmpty()){
arr[front] = 0;
}
}
public void showQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列空,没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d] = %d\n",i,arr[i]);
}
}
//显示队列的头数据
public int headQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,没有数据");
}
return arr[front+1];
}
}
这个代码应该还要优化,因为取出一个后本应该继续补上,但是它不能,所以需要改进成环形队列
3、环形队列

方法一:有效数据为maxSize-1
package com.zeng.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CircleArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleArrayQueue queue = new CircleArrayQueue(4);
char key = ' ';
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while(loop){
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列中取出");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头数据");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出系统");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key){
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("请输入要添加的数:");
queue.addQueue(scanner.nextInt());
break;
case 'g':
try {
System.out.printf("取出的数据是:%d\n",queue.getQueue());
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int i = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列的头数据是:%d\n",i);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
class CircleArrayQueue{
private int maxSize;
private int front;//默认为零
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public CircleArrayQueue(int arrayMaxSize){
maxSize = arrayMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
//约定最后一个有效位置rear后一个的位置为空,但是存在
public boolean isFull(){
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rear == front;
}
public void addQueue(int n){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("队列满,不能加数据了");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
public int getQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
public void showQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列空,没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d] = %d\n",i % maxSize,arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
//有效数的个数
public int size(){
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
//显示队列的头数据
public int headQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,没有数据");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
方法二:有效数据为maxSize
链表
栈

前缀、中缀、后缀(逆波兰表达式)表达式
后缀表达式(适合计算机计算)


递归

迷宫问题
八皇后问题(回溯算法)
排序算法
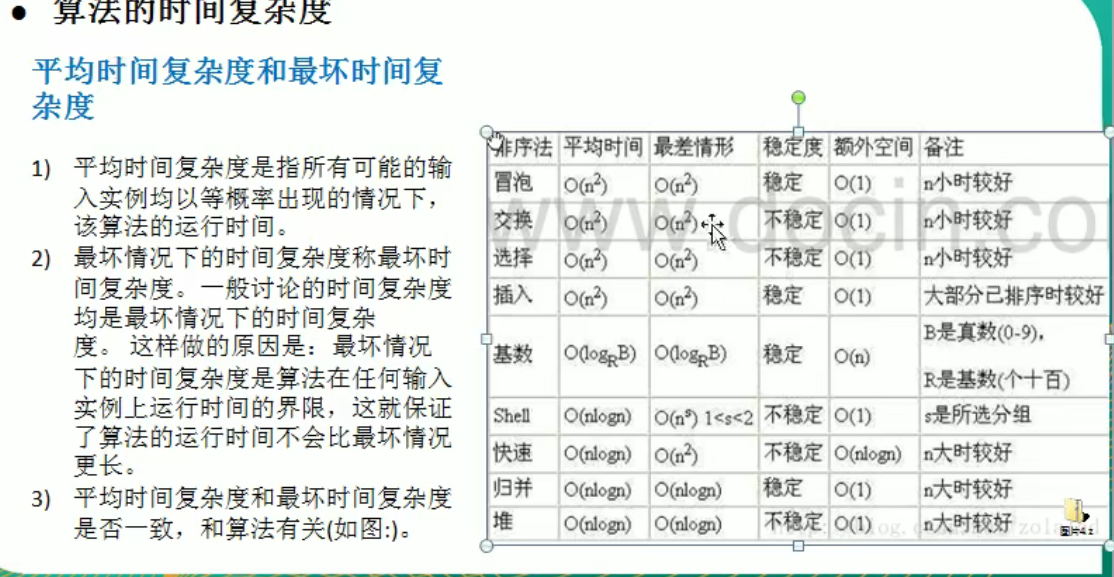
1、内部排序(使用内存)
-
插入
- 直接插入(假设第一个数为有序的,从第二个数开始,逐一将每个数插入到有序数组中)
- 希尔排序(缩小增量排序,就是在直接插入排序的数组上进行分组)(交换法、移动法(效率高))
-
选择
-
简单选择排序(整个数组循环遍历找出最小的排进有序数组中)
-
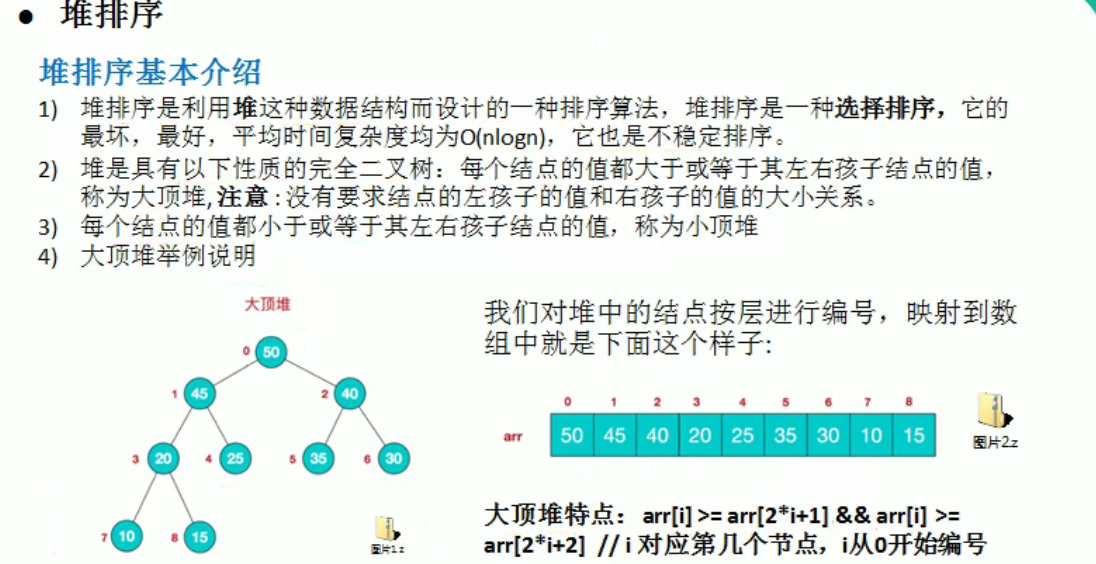
堆排序(树结构)
//将无序序列构件成一个堆 //将堆顶元素与末尾元素交换,将最大元素"沉"到数组末端; //重新调整结构,使其满足堆定义,然后继续交换堆顶元素与当前末尾元素,反复执行调整+交换步骤,直到整个序列有序。
-
-
交换
- 冒泡排序
- 快速排序(找一个值当作中间值,比它小的放一边,比它大的放一边)
-
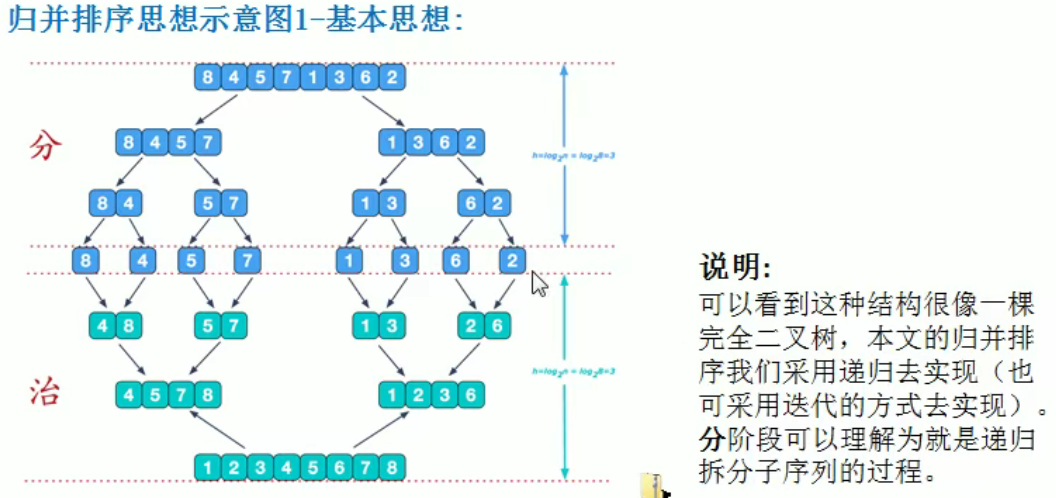
归并(分治策略)
-
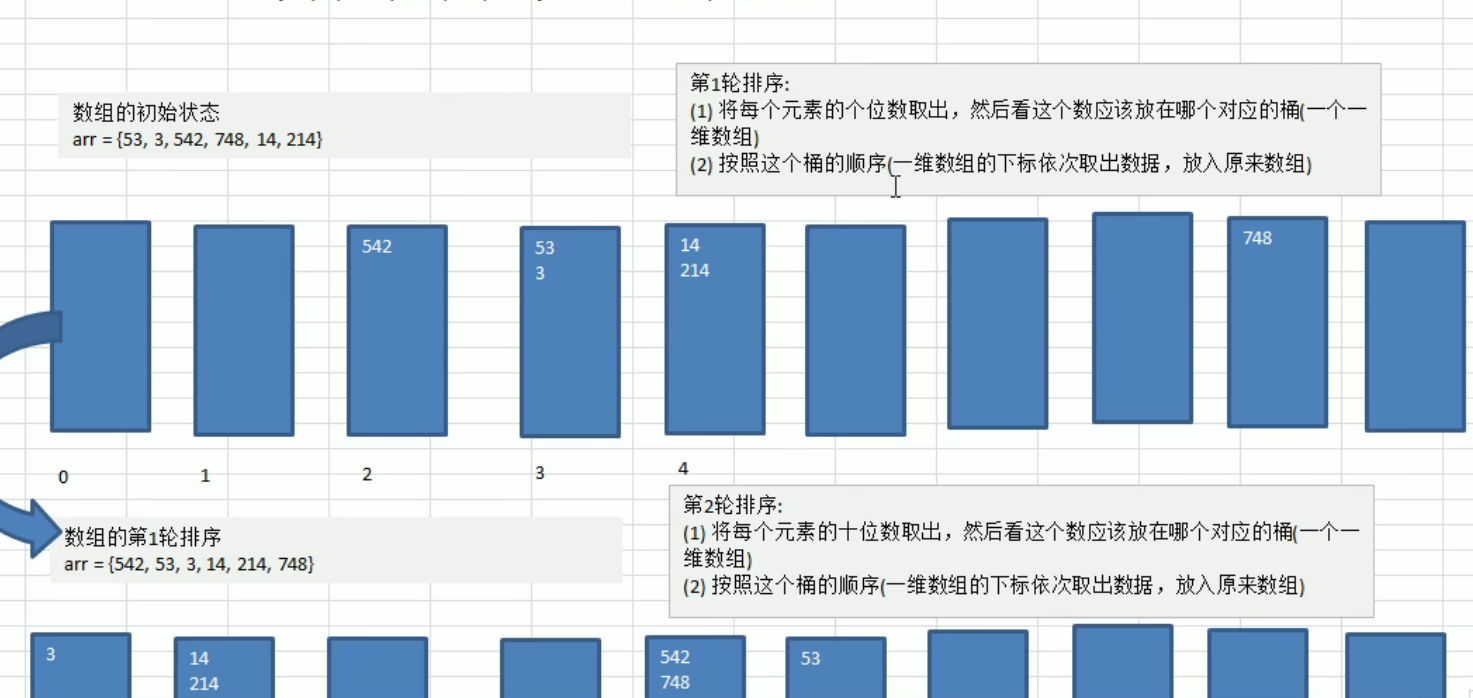
基数(桶排序的扩展)(空间换时间的经典算法)
2、外部排序(使用内存和外存结合)
查找算法
-
顺序(线性)查找
-
二分查找(要在有序数组中)/折半查找
-
插值查找(其实是二分查找的改良版)
( int mid = left + (right - left) * (findVal - arr[left]) / (arr[right] - arr[left]) )
-
斐波那契查找(有序数组)(黄金分割点查找 )(难懂!!)
( mid=low+F(k-1)-1 )
import java.util.Arrays; /** * @program: text * @description: 斐波那契查找 * @author: min * @create: 2019-08-06 15:30 **/ public class FibonacciSearch { public static int maxSize = 20; public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 8, 10, 89, 1000, 1234}; System.out.println("index=" + fibSearch(arr, 89));// 0 } //因为后面我们 mid=low+F(k-1)-1,需要使用到斐波那契数列,因此我们需要先获取到一个斐波那契数列 //非递归方法得到一个斐波那契数列 public static int[] fib() { int[] f = new int[maxSize]; f[0] = 1; f[1] = 1; for (int i = 2; i < maxSize; i++) { f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]; } return f; } //编写斐波那契查找算法 //使用非递归的方式编写算法 /** * @param a 数组 * @param key 我们需要查找的关键码(值) * @return 返回对应的下标,如果没有-1 */ public static int fibSearch(int[] a, int key) { int low = 0; int high = a.length - 1; int k = 0; //表示斐波那契分割数值的下标 int mid = 0; //存放 mid 值 int f[] = fib(); //获取到斐波那契数列 //获取到斐波那契分割数值的下标 while (high > f[k] - 1) { k++; } // 因为 f[k] 值 可能大于 a 的 长度,因此我们需要使用 Arrays 类,构造一个新的数组,并指向 temp[] // 不足的部分会使用 0 填充 int[] temp = Arrays.copyOf(a, f[k]); //实际上需求使用 a 数组最后的数填充 temp //举例: //temp = {1,8, 10, 89, 1000, 1234, 0, 0} => {1,8, 10, 89, 1000, 1234, 1234, 1234,} for (int i = high + 1; i < temp.length; i++) { temp[i] = a[high]; } // 使用 while 来循环处理,找到我们的数 key while (low <= high) { // 只要这个条件满足,就可以找 mid = low + f[k - 1] - 1; if(key < temp[mid]) { //我们应该继续向数组的前面查找(左边) high = mid - 1; //为甚是 k-- //说明 //1. 全部元素 = 前面的元素 + 后边元素 //2. f[k] = f[k-1] + f[k-2] //因为 前面有 f[k-1]个元素,所以可以继续拆分 f[k-1] = f[k-2] + f[k-3] //即 在 f[k-1] 的前面继续查找 k-- //即下次循环 mid = f[k-1-1]-1 k--; }else if ( key > temp[mid]) { // 我们应该继续向数组的后面查找(右边) low = mid + 1; //为什么是 k -=2 //说明(结合下图看,减2是因为后半段本来就是f[k-2]) //1. 全部元素 = 前面的元素 + 后边元素 //2. f[k] = f[k-1] + f[k-2] (结合下图看) //3. 因为后面我们有 f[k-2] 所以可以继续拆分 f[k-1] = f[k-3] + f[k-4] //4. 即在 f[k-2] 的前面进行查找 k -=2 //5. 即下次循环 mid=f[k-1-2]-1 k -= 2; }else { //找到 //需要确定,返回的是哪个下标 if (mid <= high) { return mid; } else { return high; } } } return -1; } }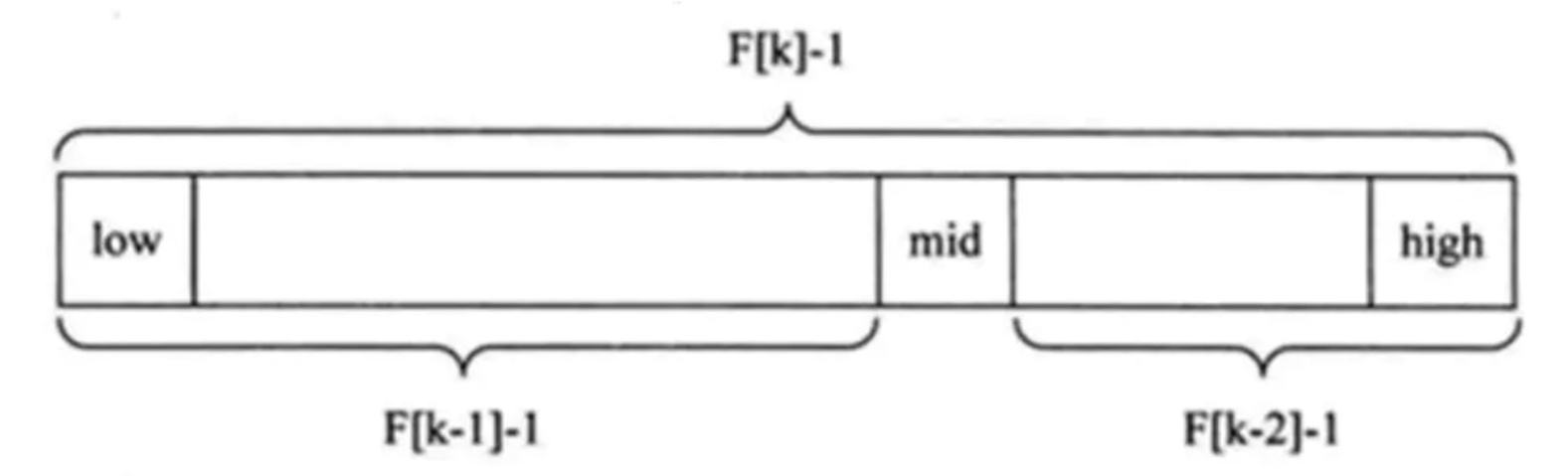
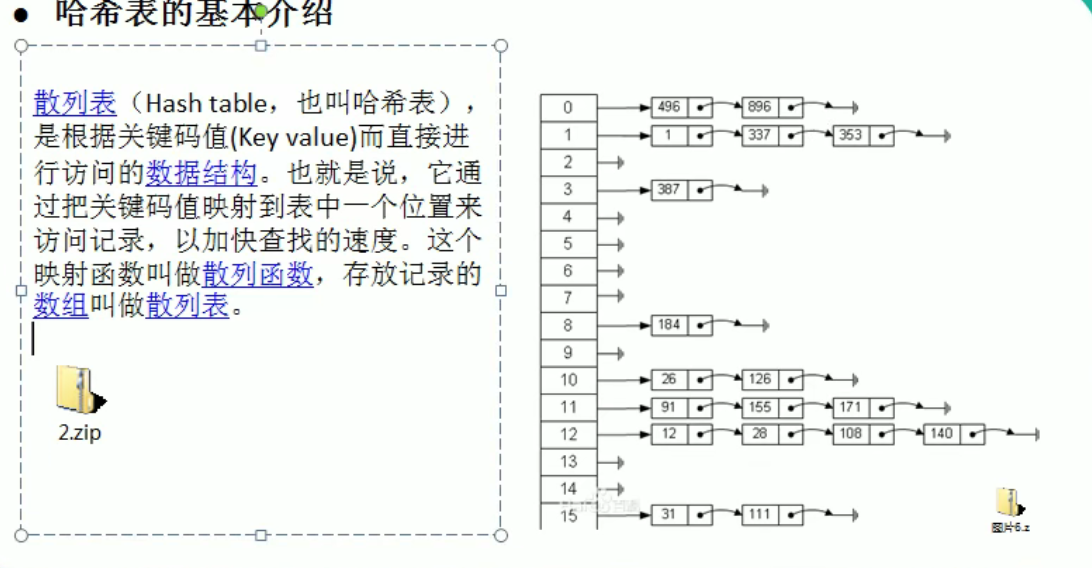
哈希表(散列)
不使用数据库,尽量节省内存,速度越快越好
二叉树



前序遍历
中序遍历
后序遍历




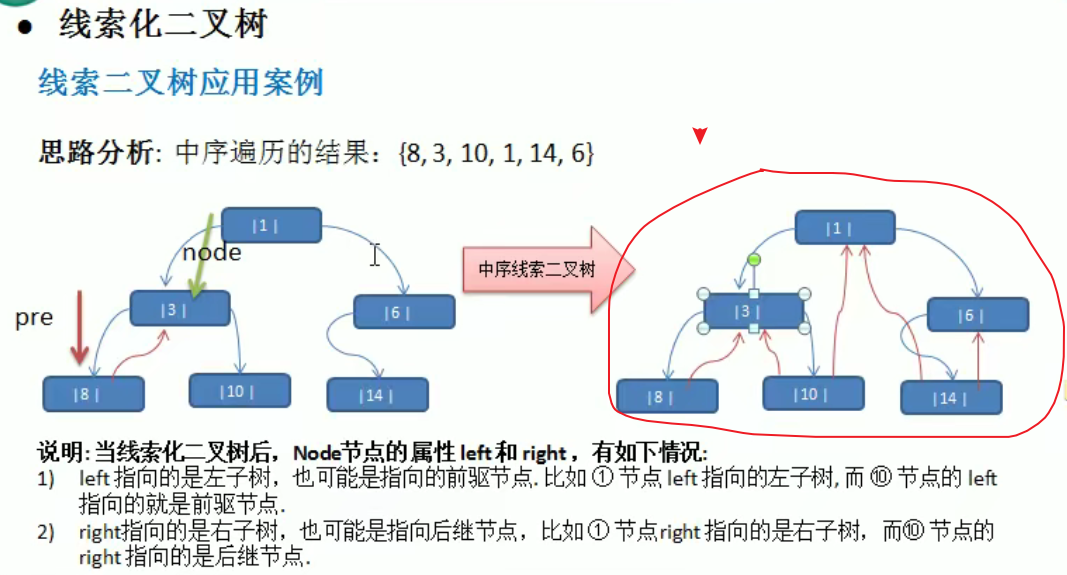
线索化二叉树是要看 用的是先序、中序、后序遍历
哈夫曼树(赫夫曼树HuffmanTree)


赫夫曼编码

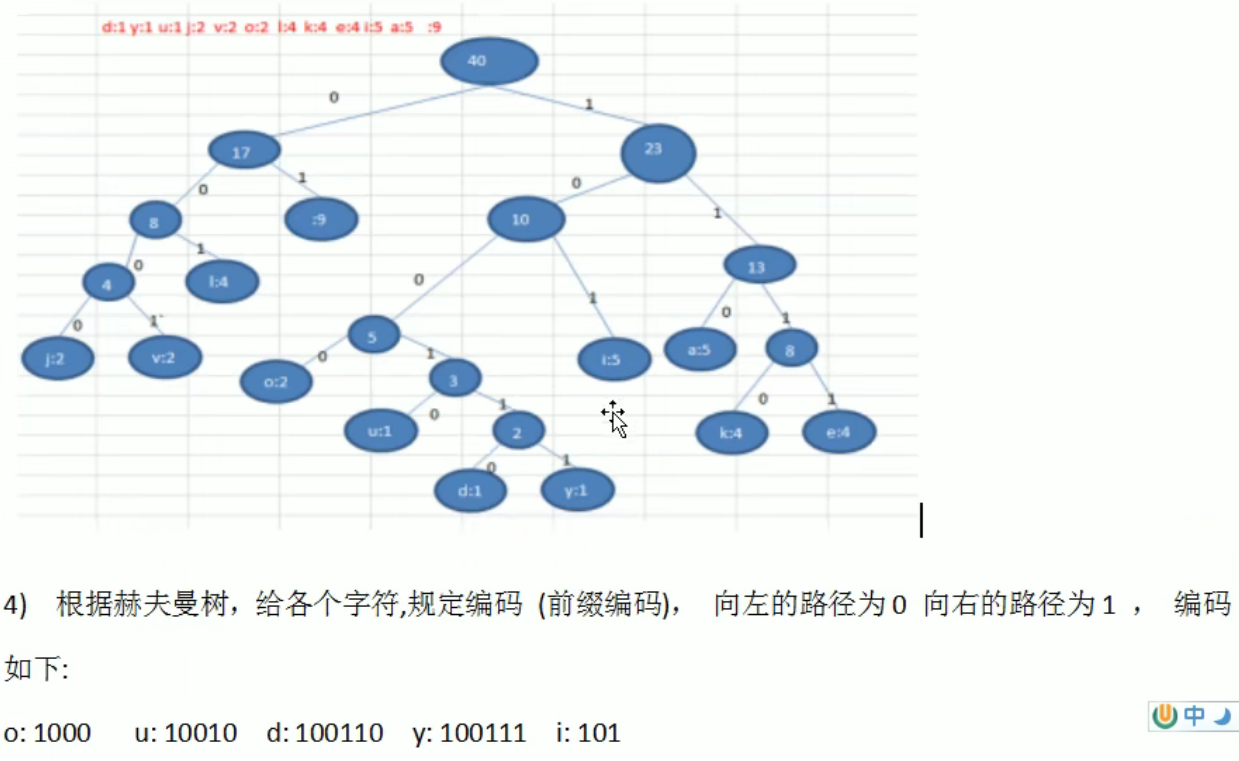
赫夫曼树的不同构建方式会产生不同的赫夫曼树,但它们的赫夫曼编码的长度是一样的

二叉排序树

重难点:二叉排序树的删除
- 删除叶子结点
- 删除只有一个子树的结点
- 删除有两颗子树的结点
平衡二叉树(AVL树)

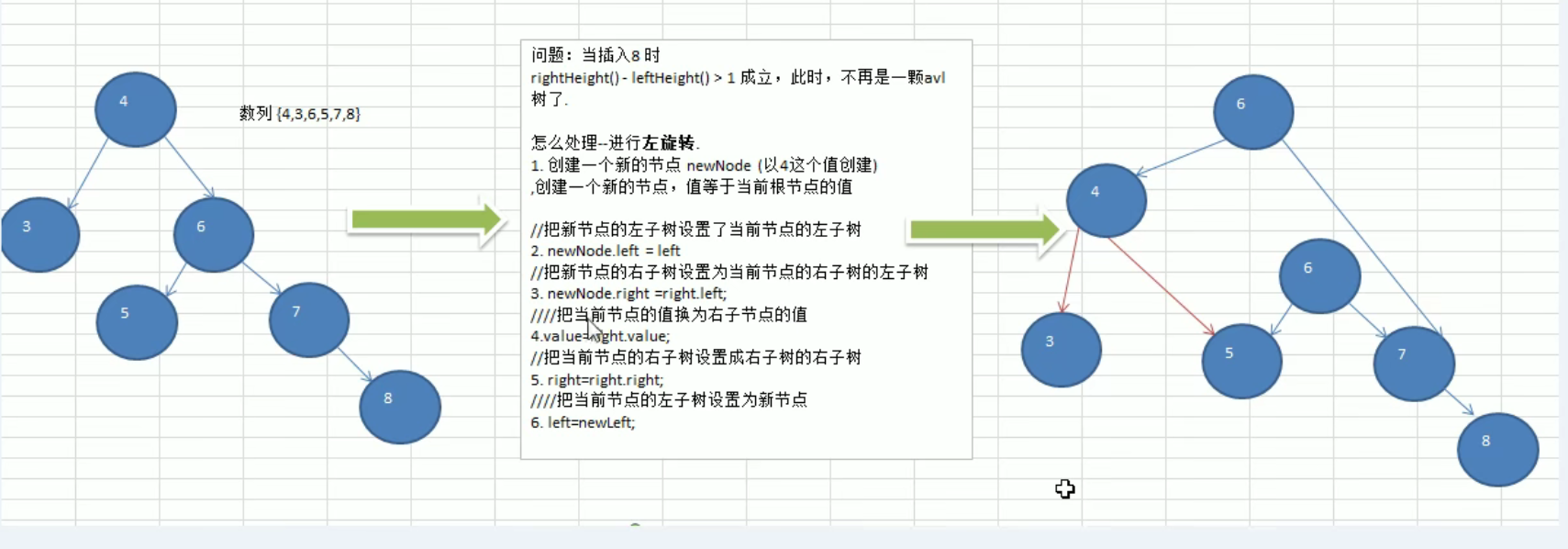
(第四步的意思是把当前节点的值换为6,第五步的意思是把当前的右子树设置成之前4的右子树的右子树。(它其实就是指针的变化))

多叉树(简讲)
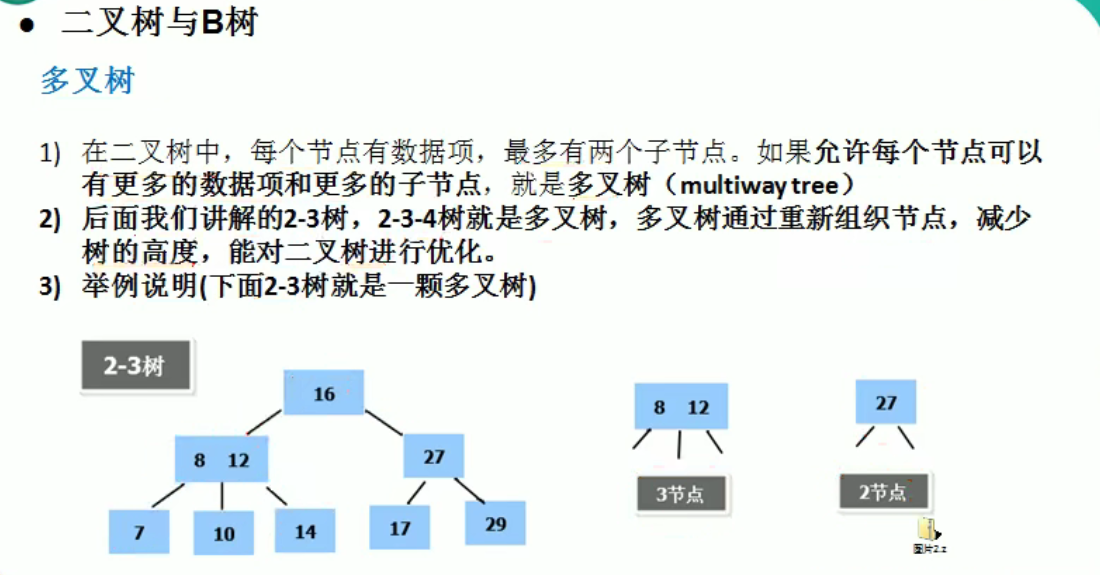

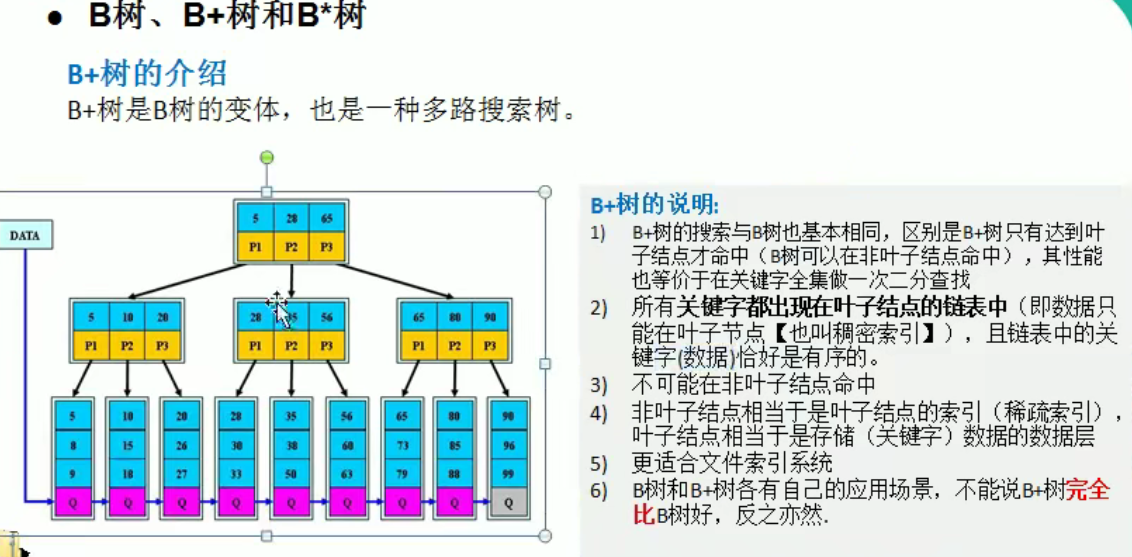
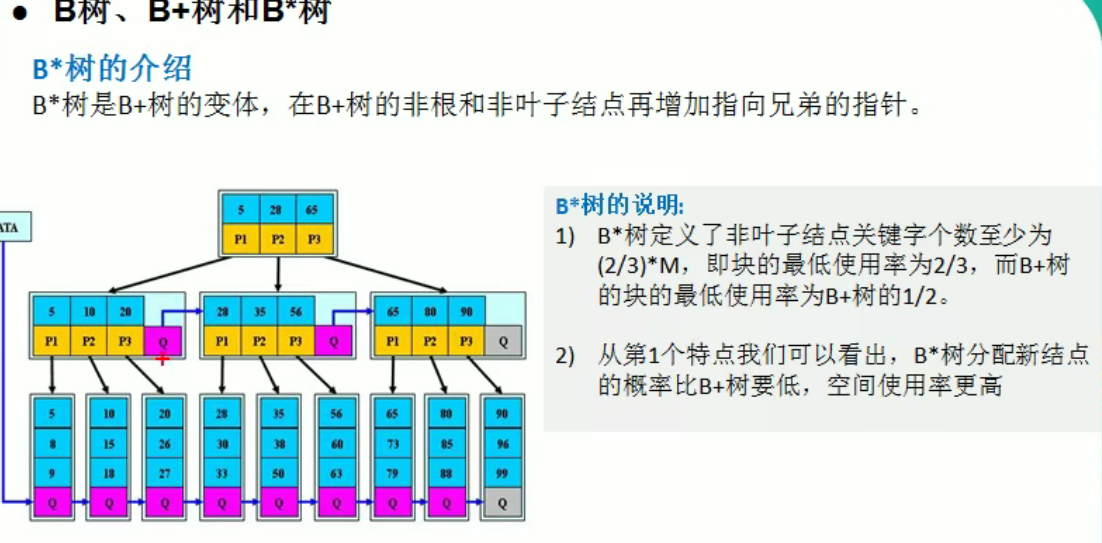
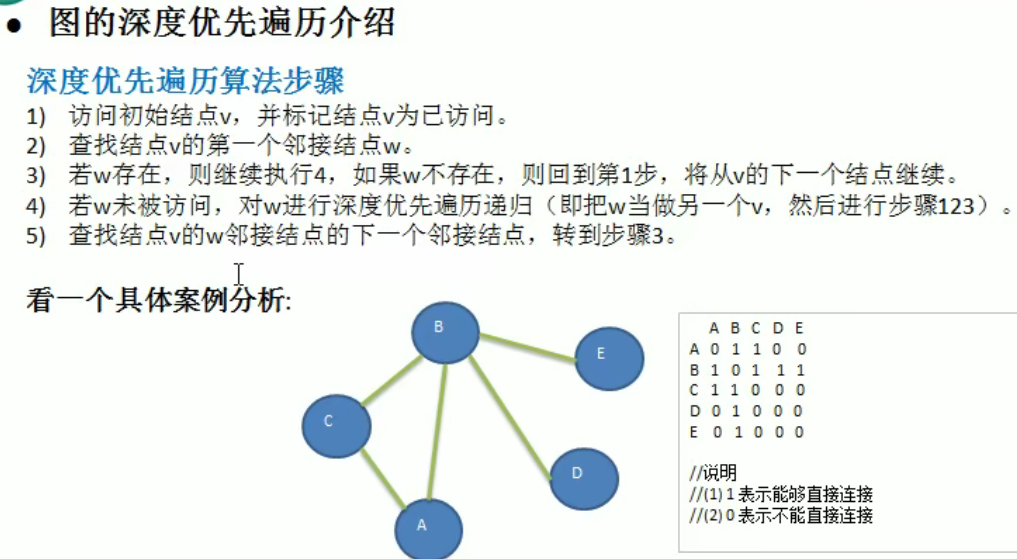
图


程序员常用的十种算法
二分查找算法(非递归)
分治算法


动态规划算法

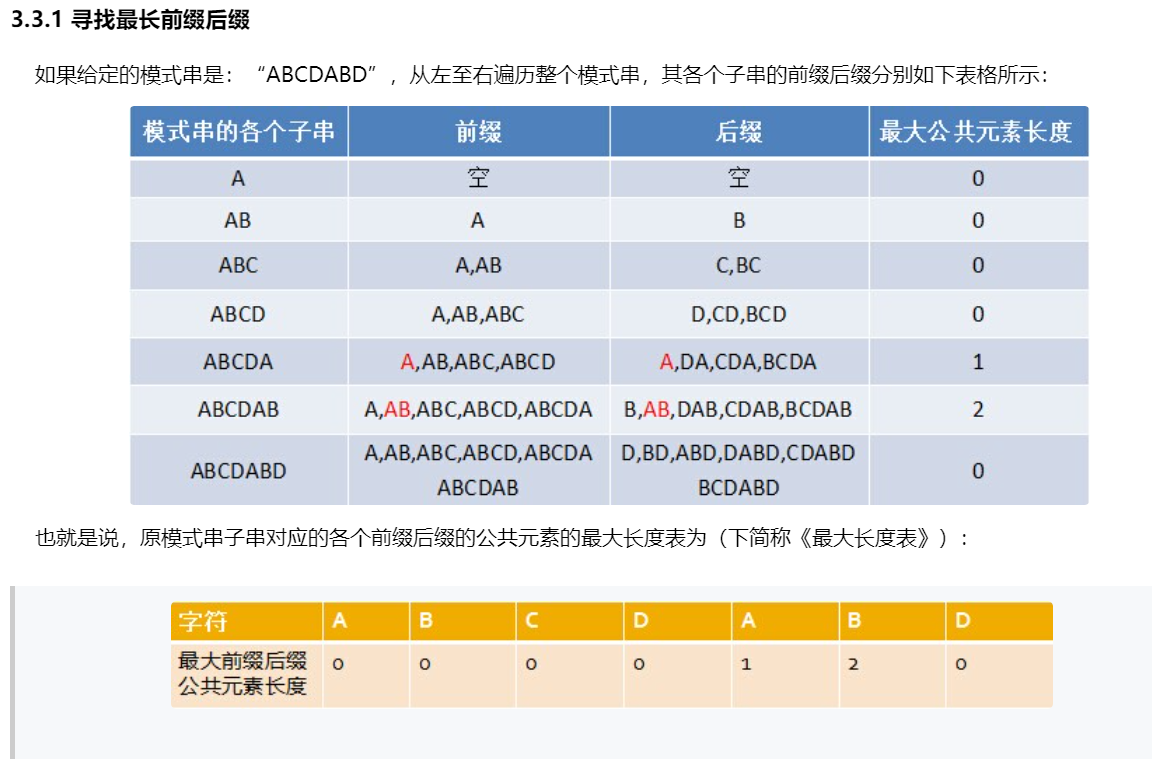
KMP算法(难)
部分匹配值(理解这个对理解kmp算法有帮助)




贪心算法
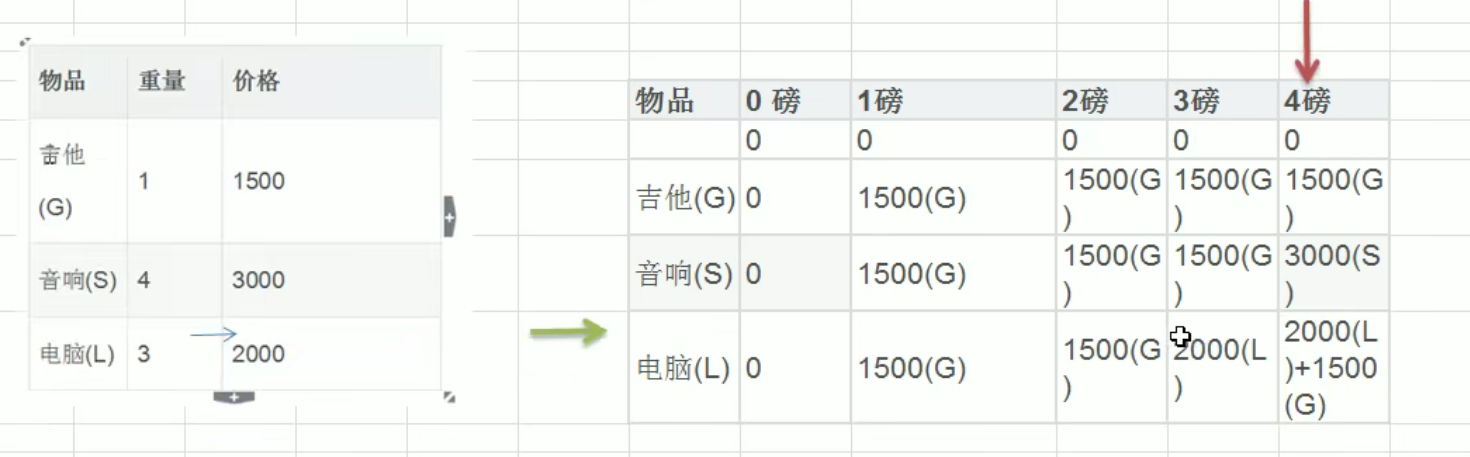
解决集合覆盖问题

代码里面有五个城市组,通过代码筛选能发现只有第四组是完全重复的,所以selects里面没有它

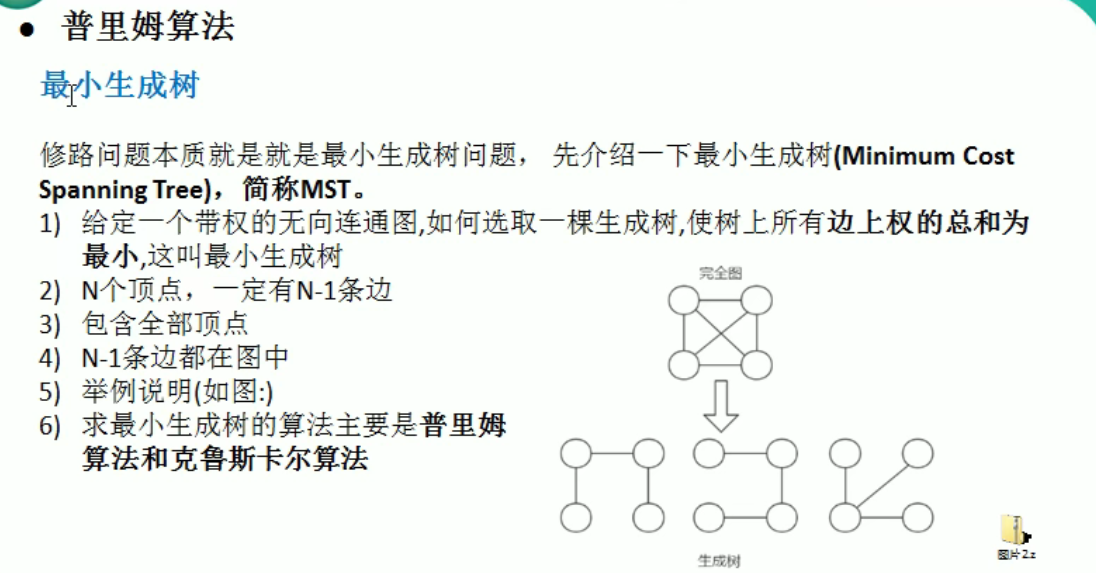
普利姆算法


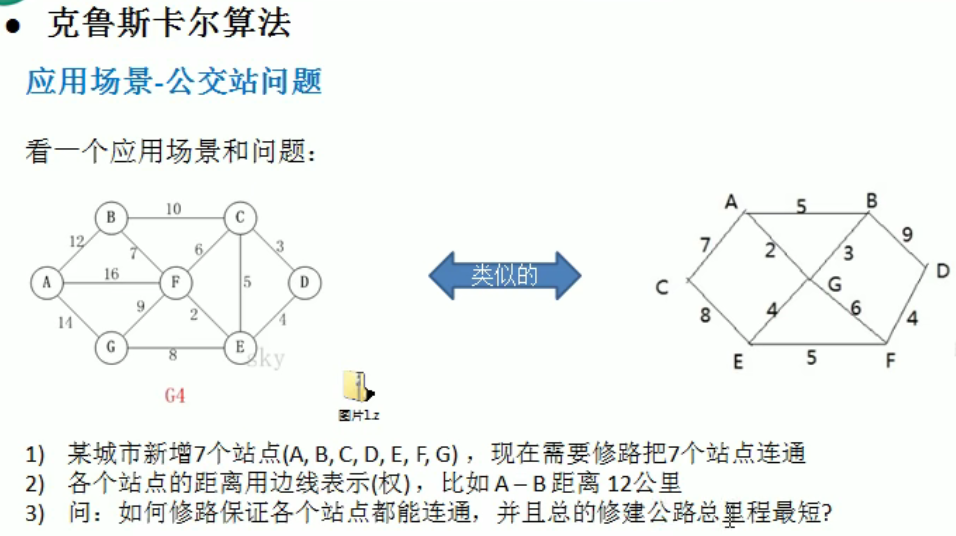
克鲁斯卡尔算法

加入的边的两个顶点不能都指向同一个重点,否则将构成回路
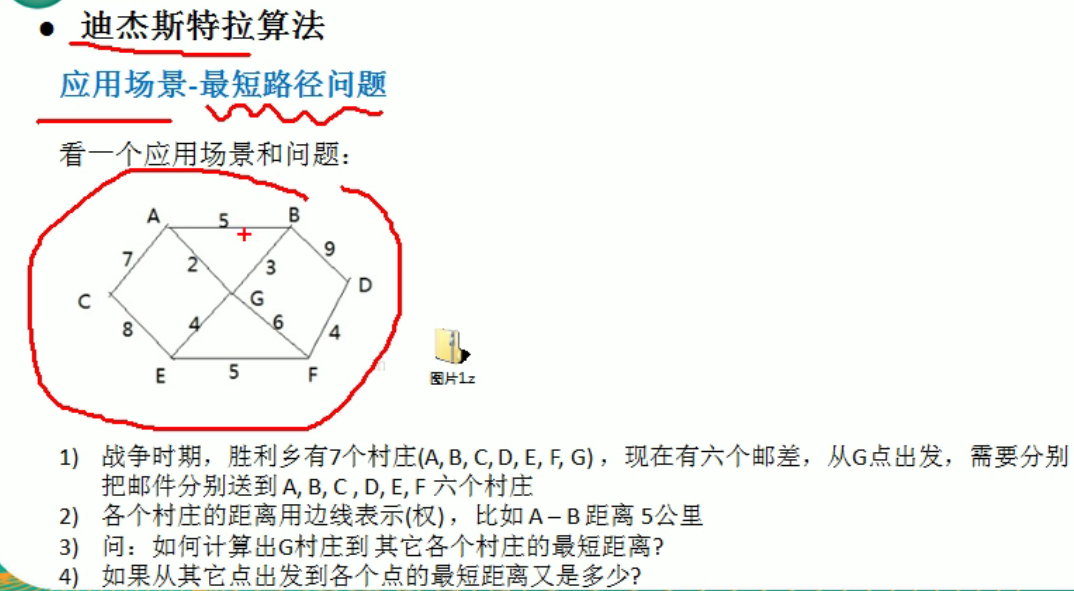
迪杰斯特拉算法
底层运用到了广度优先算法

弗洛伊德算法


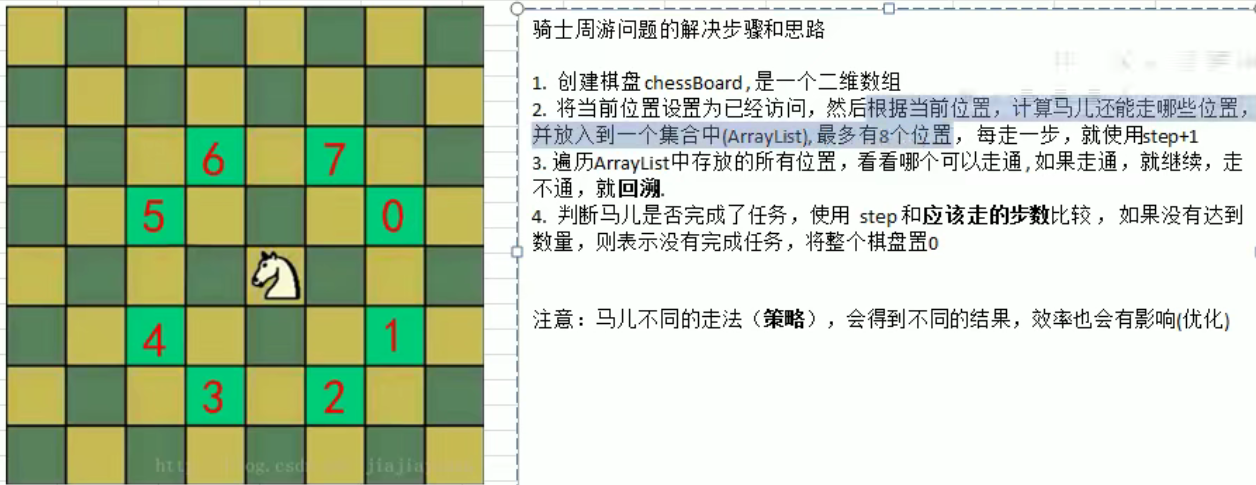
马踏棋盘算法
-
普通方法
-
贪心算法优化
(我们需要对ps中所有point的下一步的所有集合的数目,进行非递减排序)

启发式搜索
其代表算法为:贪婪最佳优先搜索(Greedy best-first search)和A ?搜索。
- 贪婪最佳优先搜索不是最优的。
- 启发函数代价最小化这一目标会对错误的起点比较敏感。
- 贪婪最佳优先搜索也是不完备的。所谓不完备指的是它可能沿着一条无限的路径走下去而不回来做其他的选择尝试,因此无法找到最佳路径。
- 在最坏的情况下,贪婪最佳优先搜索的时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是 O(b^{m})(这个就理解成计算机要循环迭代多少次吧),其中b是节点的分支因子数目、m是搜索空间的最大深度。
A* 算法
当估价函数满足一定条件,算法一定能找到最优解。估价函数满足一定条件的算法称为A*算法。
在最短路径中,我们的 g(x) 就是到 x 点的权值,h(x) 就是 x 点到目标结点的最短路或直线距离。
它的限制条件是 F(x) = g(x) + h(x) 。 代价函数g(x) >0 ;h(x) 的值不大于x到目标的实际代价 h*(x) 。即定义的 h(x) 是可纳的,是乐观的。
不同的估价函数对算法的效率可能产生极大的影响。尤其是 h(x) 的选定,比如在接下来的八数码问题中,我们选择了曼哈顿距离之和作为 h(x) ,你也可以选择相差的格子作为 h(x),只不过搜索的次数会不同。当 h(x) 越接近 h*(x) ,那么扩展的结点越少!
(我们需要对ps中所有point的下一步的所有集合的数目,进行非递减排序)
[外链图片转存中…(img-2cbx77gZ-1634308180276)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-Qmzf2Noq-1634308180277)]
启发式搜索
其代表算法为:贪婪最佳优先搜索(Greedy best-first search)和A ?搜索。
- 贪婪最佳优先搜索不是最优的。
- 启发函数代价最小化这一目标会对错误的起点比较敏感。
- 贪婪最佳优先搜索也是不完备的。所谓不完备指的是它可能沿着一条无限的路径走下去而不回来做其他的选择尝试,因此无法找到最佳路径。
- 在最坏的情况下,贪婪最佳优先搜索的时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是 O(b^{m})(这个就理解成计算机要循环迭代多少次吧),其中b是节点的分支因子数目、m是搜索空间的最大深度。
A* 算法
当估价函数满足一定条件,算法一定能找到最优解。估价函数满足一定条件的算法称为A*算法。
在最短路径中,我们的 g(x) 就是到 x 点的权值,h(x) 就是 x 点到目标结点的最短路或直线距离。
它的限制条件是 F(x) = g(x) + h(x) 。 代价函数g(x) >0 ;h(x) 的值不大于x到目标的实际代价 h*(x) 。即定义的 h(x) 是可纳的,是乐观的。
不同的估价函数对算法的效率可能产生极大的影响。尤其是 h(x) 的选定,比如在接下来的八数码问题中,我们选择了曼哈顿距离之和作为 h(x) ,你也可以选择相差的格子作为 h(x),只不过搜索的次数会不同。当 h(x) 越接近 h*(x) ,那么扩展的结点越少!