题目:
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
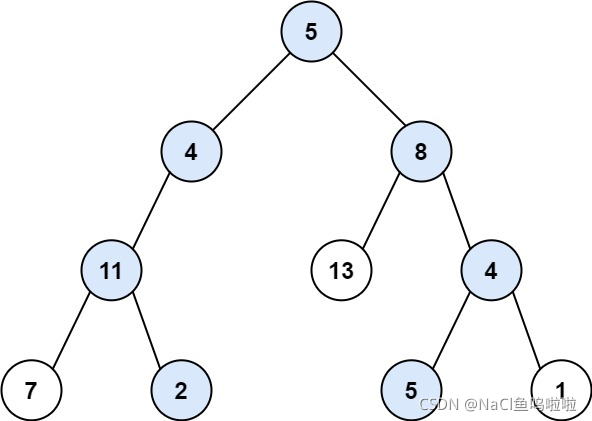
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路一:递归实现DFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int** ret; //用来保存所有路径
int retSize; //用于保存路径的数量
int* retColumnSize; //用来保存某一路径的长度
int* path; //用于保存一条路径上所有节点的值
int pathSize; //用于保存一条路径上的节点个数
void DFS(struct TreeNode* node, int targetSum)
{
if(node == NULL)
return;
path[pathSize] = node->val;
pathSize++;
targetSum = targetSum - node->val;
if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL && targetSum == 0)
{
//需要把path添加到ret[retSize]里
int* temp = (int*)malloc(pathSize * sizeof(int));
memcpy(temp,path,pathSize * sizeof(int));
ret[retSize] = temp;
retColumnSize[retSize] = pathSize;
retSize++;
}
DFS(node->left,targetSum);
DFS(node->right,targetSum);
pathSize--;
}
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
ret = (int **)malloc(5001 * sizeof(int*));
path = (int *)malloc(5001 * sizeof(int));
retColumnSize = (int *)malloc(5001 * sizeof(int));
retSize = 0;
pathSize = 0;
DFS(root,targetSum);
*returnSize = retSize;
*returnColumnSizes = retColumnSize;
return ret;
}
分析:
重点在于如何保存数据,请看全局变量的声明及注释:
int** ret; //用来保存所有路径
int retSize; //用于保存路径的数量
int* retColumnSize; //用来保存某一路径的长度
int* path; //用于保存一条路径上所有节点的值
int pathSize; //用于保存一条路径上的节点个数
思路二:广度优先遍历
int** ret;
int retSize;
int* retColSize;
int* path;
int pathSize;
typedef struct {
struct TreeNode* key;
struct TreeNode* val;
UT_hash_handle hh;
} hashTable;
hashTable* parent;
void insertHashTable(struct TreeNode* x, struct TreeNode* y) {
hashTable* rec = malloc(sizeof(hashTable));
rec->key = x;
rec->val = y;
HASH_ADD_PTR(parent, key, rec);
}
struct TreeNode* queryHashTable(struct TreeNode* x) {
hashTable* rec;
HASH_FIND_PTR(parent, &x, rec);
return rec->val;
}
void getPath(struct TreeNode* node) {
int* tmp = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
int tmpSize = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
tmp[tmpSize++] = node->val;
node = queryHashTable(node);
}
for (int i = 0; i < tmpSize / 2; i++) {
int t = tmp[i];
tmp[i] = tmp[tmpSize - 1 - i], tmp[tmpSize - 1 - i] = t;
}
ret[retSize] = tmp;
retColSize[retSize++] = tmpSize;
}
int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
ret = malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2001);
retColSize = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
path = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
retSize = pathSize = 0;
parent = NULL;
insertHashTable(root, NULL);
if (root == NULL) {
*returnColumnSizes = retColSize;
*returnSize = retSize;
return ret;
}
struct TreeNode* que_node[10001];
int que_sum[10001];
int left = 0, right = 0;
que_node[right] = root;
que_sum[right++] = 0;
while (left < right) {
struct TreeNode* node = que_node[left];
int rec = que_sum[left++] + node->val;
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {
if (rec == targetSum) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node->left != NULL) {
insertHashTable(node->left, node);
que_node[right] = node->left;
que_sum[right++] = rec;
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
insertHashTable(node->right, node);
que_node[right] = node->right;
que_sum[right++] = rec;
}
}
}
*returnColumnSizes = retColSize;
*returnSize = retSize;
return ret;
}
/*
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/solution/lu-jing-zong-he-ii-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
*/
分析:使用了哈希表,用了一个新的数据结构,比较麻烦,就没有自己实现。