
目录
1. 基础知识
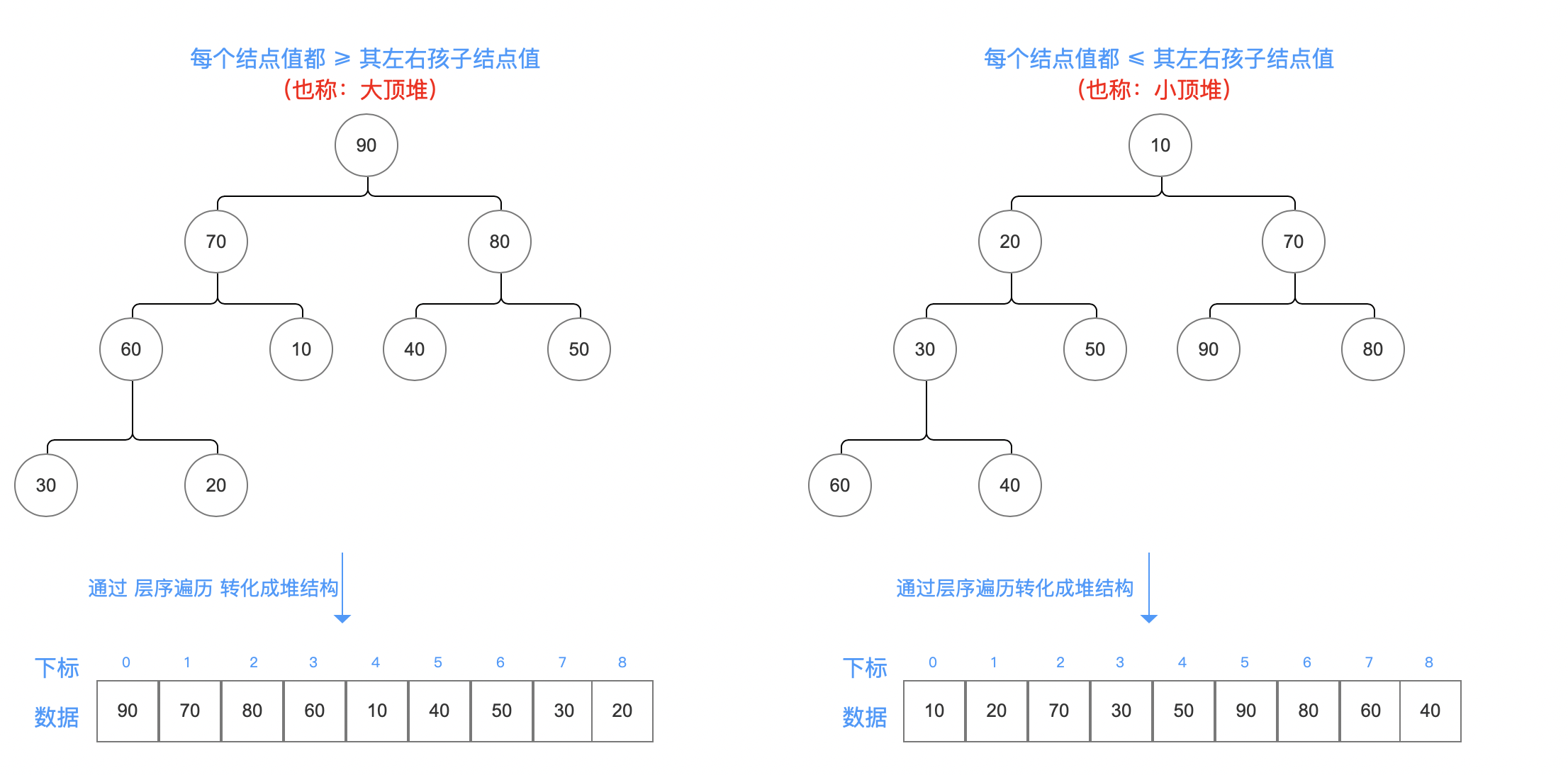
堆的定义 = 具有下列性质的完全二叉树:
2. 简介
利用堆(大 / 小顶堆) 进行排序 的方法
- 充分利用了完全二叉树深度 =
[log2n] + 1的特性- 是 简单选择排序 的优化 & 改进
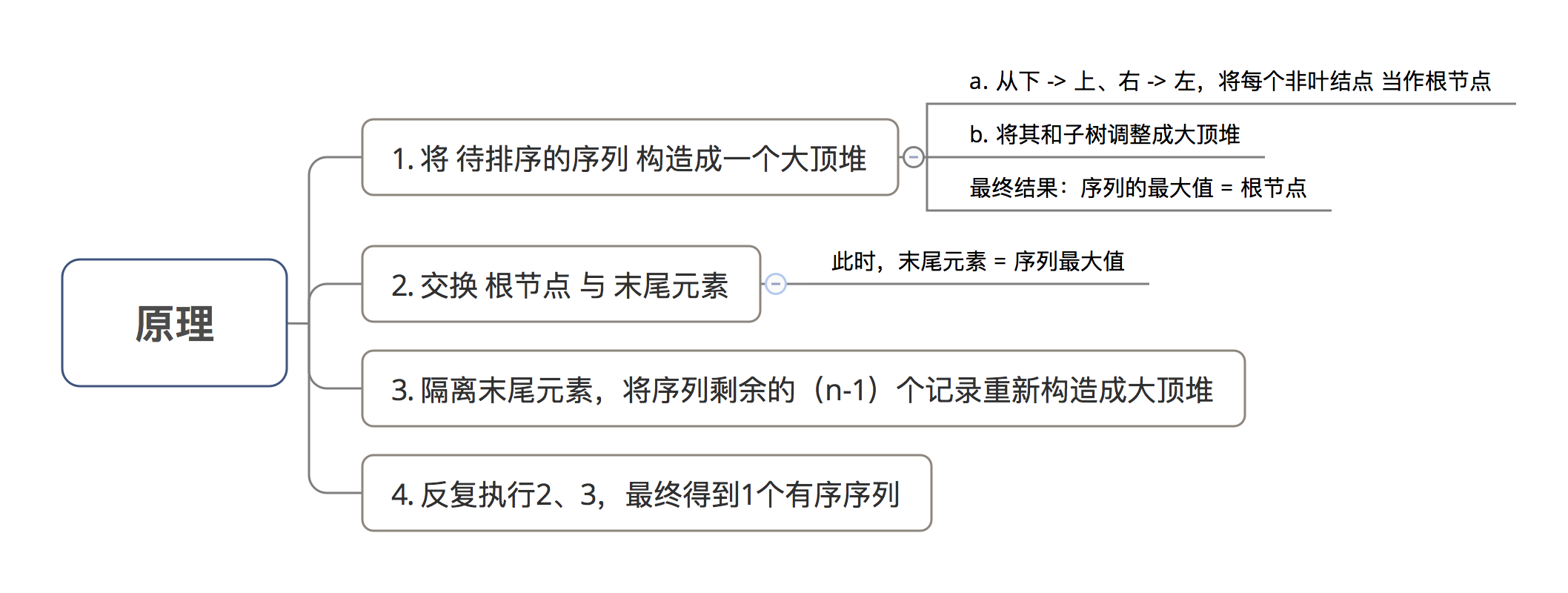
3. 算法原理
4. 算法示意图
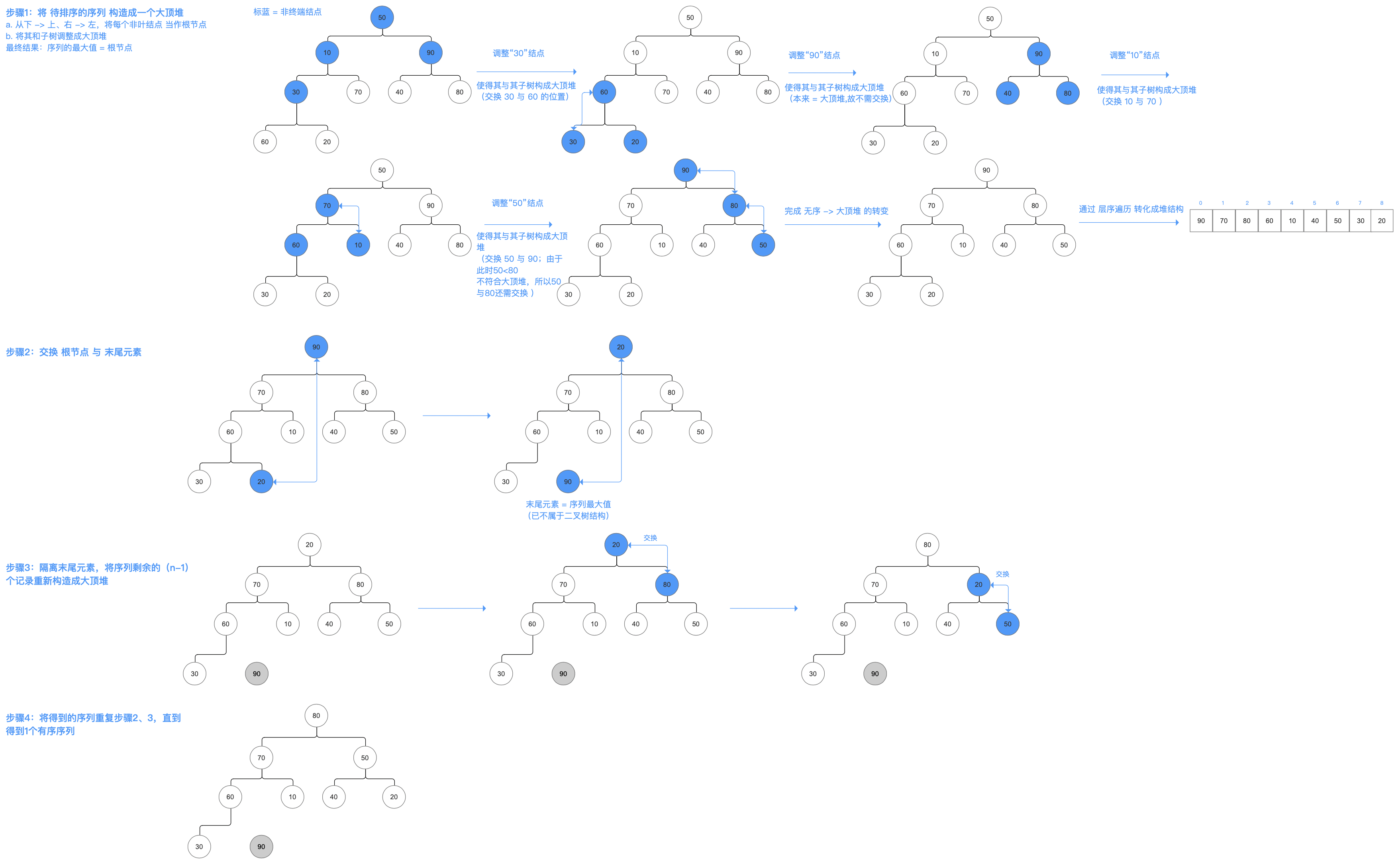
初始状态 & 算法目标
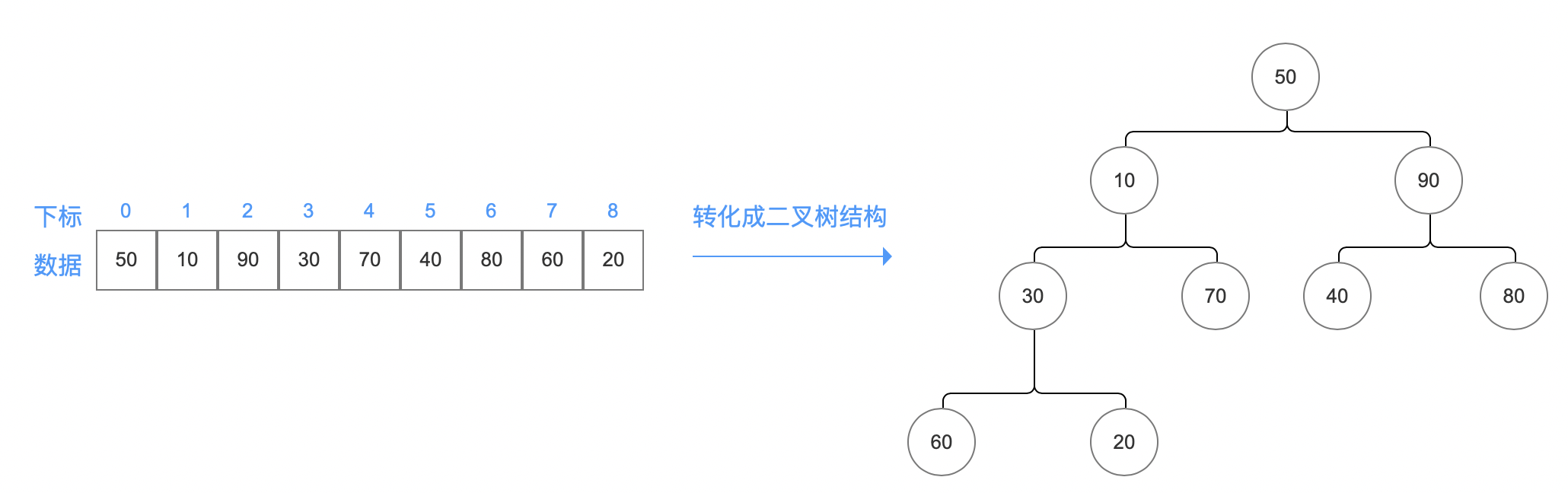
具体算法
5. 算法实现
- 具体请看注释
public class HeapSort {
/**
* 执行 堆排序 算法
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义待排序数列
int[] src = new int[]{ 50, 10, 90, 30, 70, 40, 80, 60, 20 };
// 输出结果
heapSort(src);
}
/**
* 堆排序算法
*/
private static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
// 步骤1:将待排序的序列构建成一个大顶堆
for (int i = arr.length / 2; i >= 0; i--){
// i = i / 2 :求出非终端结点(即,具备孩子的结点)
// 逐渐递减: i = 4-3-2-1
heapAdjust(arr, i, arr.length);
}
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// 步骤2:交换 根节点 与 末尾元素
swap(arr, 0, i);
// 步骤3:将序列剩余的(n-1)个记录重新构造成大顶堆
heapAdjust(arr, 0, i);
// 循环步骤2 、3,直到整个序列有序
}
// 输出排序后的序列
for(int a =0;a<arr.length;a++)
System.out.println(arr[a]);
}
/**
* 构建堆的过程
* 参数说明:
* @param arr = 需排序的数组
* @param i = 需要构建堆的根节点的序号
* @param n = 数组的长度
*/
private static void heapAdjust(int[] arr, int i, int n) {
int child;
int father;
for (father = arr[i]; leftChild(i) < n; i = child) {
child = leftChild(i);
// 若左子树<右子树,则比较右子树和父节点
if (child != n - 1 && arr[child] < arr[child + 1]) {
child++; // 序号增1,指向右子树
}
// 若父节点<孩子结点,则需要交换
if (father < arr[child]) {
arr[i] = arr[child];
} else {
// 大顶堆结构未被破坏,不需要调整
break;
}
}
arr[i] = father;
}
// 获取左孩子结点 位置
private static int leftChild(int i) {
return 2 * i + 1;
}
// 交换元素位置
private static void swap(int[] arr, int index1, int index2) {
int tmp = arr[index1];
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
arr[index2] = tmp;
}
}
- 测试结果
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Demo地址:Carson_Ho的Github地址:堆排序
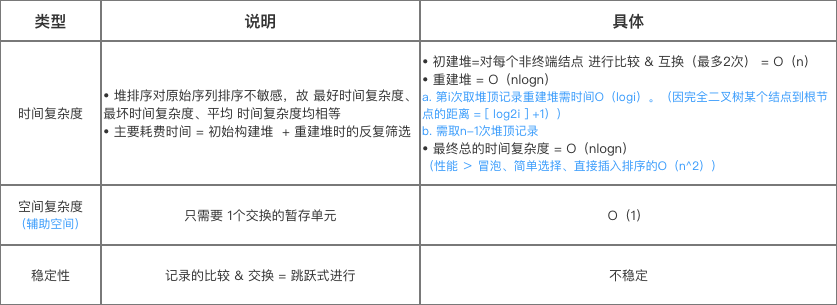
6. 性能分析
以下将分析算法的性能:时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
7. 应用场景
不适合待排序序列个数较少的情况
原因 = 初始构建堆的比较次数较多
8. 总结
- 本文全面讲解了数据结构中的排序算法:堆排序
- Carson带你学数据结构系列文章:
Carson带你学数据:线性表-数组、链表
Carson带你学数据:特殊的线性表-栈、队列
Carson带你学数据:串
Carson带你学数据:树
Carson带你学数据:二叉树
Carson带你学数据:图
Carson带你学数据:查找
欢迎关注Carson_Ho的CSDN博客 !
博客链接:https://carsonho.blog.csdn.net/
