图染色问题解决示例(GCP)
引言
图着色问题(Graph Coloring Problem, GCP)又称着色问题,是最著名的NP-完全问题之一。这个问题是启发式与元启发式算法课上的一个题目,其本质上也是一个求最优解的过程,解决方案有很多,当节点数数较少时其实使用暴力检索比较容易理解,但是多的时候就需要用特别的方法来做了,这里作业的要求是使用DSJC500.5.col文件,也就是500个顶点的图,这个文件的最优解是47个,但是我解不出来,目前最好战绩就是48,而且应该是运气成分,这里介绍3种课上的方法,分别如下:
DSATUR
Tabu
Simulated Annealing
1.问题基本描述
emmmm,这个问题是需要求一个最优解,使得最少的颜色在整个图中染色后没有冲突边。一般在求最优解的过程中往往需要涉及到解决跳出局部最优的难点,在下边3种方法中,是禁忌搜索算法和模拟退火算法直接需要改进下山这个过程会出现的局部最优,具体的设计过程会在下边介绍
2.三种方法的实现
2.1DSATUR
通过选择所有节点的度来对它进行已有颜色的染色来开始染色,接下来的过程度需要不断判断节点的饱和度,饱和度越高(周围邻居所染颜色的个数)的节点优先级越高,如果已有颜色满足不了就增加一种颜色,最终直到所有节点都被染色——这里有个问题就是饱和度计算的问题,以下第一种方法是没有实时更新饱和度的,但是可以实时更新饱和度
2.1.1主要过程流程
2.1.2主要数据结构
int **graph=NULL; 邻接矩阵
int *colored=NULL; 颜色数组
2.1.3完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
//创建表示图的数组
int **graph=NULL;
int *colored=NULL;
int colors=1;
int num=0;
int getNodeGrade(int index); //获取节点的度
int getMaxGradeNode(); //获取具有更高级别的非着色节点
bool isColored(int index); //检查节点是否着色
void setColor(int index); //着色
int getSaturation(int index);//获取节点饱和度
int getMaxSaturation();//最大饱和度点的索引
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
//这里是打开一个文件,我把那个col文件改成了txt为了方便读,冗余的信息也删掉了
if((fp = fopen ("graphs/temp.txt", "r" ))==NULL){
printf("没文件啊\n");
return 0;
}
//读数据
fscanf(fp, "%d" ,&num);
colored= (int*)malloc(num*sizeof(int*));
graph = (int**)malloc(num*sizeof(int*));
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
graph[i] = (int*)malloc(num*sizeof(int));
// 邻接矩阵初始化,没啥
for(int j=0;j<num;j++){
graph[i][j]=0;
}
colored[i]=0;
}
int a,b;
//矩阵那个赋值,然后这里是0起始,所以减一
while(feof(fp)==0){
fscanf(fp,"%d %d",&a,&b);
graph[a-1][b-1]=1;
graph[b-1][a-1]=1;
}
//纯粹看看数据对不对
/*for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < num; ++j)
printf("%d ",graph[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}*/
clock_t ti, tf;
ti = clock();
//Algorithm DSatur
//1. 选择初始节点(度较高的节点)
int actNode=getMaxGradeNode();
//2. 为节点指定颜色
setColor(actNode);
//printf("curNode: %d Color: %d\n",actNode,colored[actNode]);
int visited=1;
//3. 迭代到全部着色
while (visited<num) {
/*
4. 选择非着色节点中最大饱和度的节点
*/
actNode=getMaxSaturation();
//5.指定颜色赋值
setColor(actNode);
//6.标记
visited++;
}
tf = clock();
printf("最小颜色数: %d\n",colors);
double time = (double)(tf - ti) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("\ntime: %lf s\n",time);
free(fp);
free(graph);
free(colored);
return 0;
}
int getNodeGrade(int index){
int grade=0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(graph[index][i]!=0)
grade++;
}
return grade;
}
bool isColored(int index){
if(colored[index]!=0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//获取具有更高级别的非着色节点
int getMaxGradeNode(){
int max=0; int index=0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
int aux=getNodeGrade(i);
if(!isColored(i)&&aux>max){
max=aux;
index=i;
}
}
return index;
}
//着色
void setColor(int index){
bool flag=true;
int colorIndex=1;
while(flag){
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(graph[index][i]==1 && colored[i]==colorIndex) //检查当前节点和邻居节点的颜色
count++;//邻居的出颜色现一个已有颜色就加一
}
if(count==0){
flag=false;//该节点的邻居都没有染色
}else{
colorIndex++;
}
}
colored[index]=colorIndex;
if(colorIndex>colors)
colors=colorIndex;
}
//获取节点饱和度
int getSaturation(int index){
int count=0;
for(int i=1;i<=colors;i++){
for(int j=0;j<num;j++){
if(graph[index][j]==1 && colored[j]==i){ //i和j相连,j点染色为i
count++;//饱和度增加
j=num;
}
}
}
return count;
}
//最大饱和度点的索引
int getMaxSaturation(){
int maxSat=0; int index=0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(colored[i]==0){
int aux=getSaturation(i);
if(aux > maxSat){
maxSat=aux;
index=i;
}else if(aux==maxSat){
if(getNodeGrade(i)>getNodeGrade(index))
index=i;
}
}
}
return index;
}
2.1.4结果展示
这里的结果是用云主机跑的,有亿点点拉胯
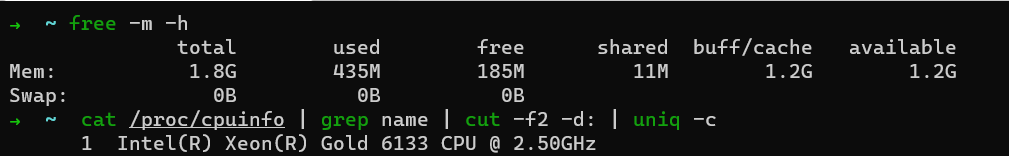
最小颜色数: 65
time: 9.251990 s
2.1.5实时计算饱和度的方法
这里就简单说一下啦,基本思路和上边的一样,就是上边各点染色的优先级一直是根据起始时的饱和度,这个是实时更新饱和度,过程就是参考老师的课件,下边直接上代码。

class Ds {
public:
int **graph=nullptr;
int *colored=nullptr;
int *degree=nullptr;
int *saturation=nullptr;
int isColor[500] = {0};
int colors=1;
int n=0;
void DegreeMinusOne(int Node) const;
void SaturationPlusOne(int Node) const;
void setColor(int Node);
int MaxSaturationNode();
};
主函数
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
//选定初始节点即度最高的节点
int Initialnode;
int max=0; int Node=0;
for(int i=0;i<dsatur->n;i++)
{
int nd=dsatur->degree[i];
if(nd>max)
{
max=nd;
Node=i;
}
}
Initialnode=Node;
dsatur->setColor(Initialnode);
dsatur->DegreeMinusOne(Node);//饱和度更新
dsatur->SaturationPlusOne(Node);
int Dyed=1;
//迭代直到每个节点都有颜色
while (Dyed++<dsatur->n)
{
int MaxNode=0;
MaxNode=dsatur->MaxSaturationNode();
//为上述操作最终得到的节点染色
dsatur->setColor(MaxNode);
dsatur->DegreeMinusOne(Node);
dsatur->SaturationPlusOne(Node);
}
end = clock();
printf("color is %d\n",dsatur->colors);
double sec = (double)(end-start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("\ntime is %lf s\n",sec);
free(dsatur->graph);
free(dsatur->colored);
delete dsatur;
return 0;
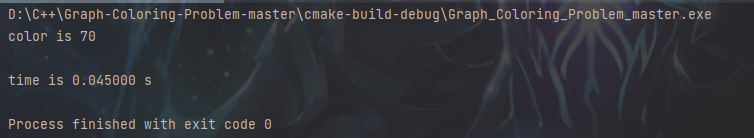
结果好快啊,麻蛋真的快,模拟退火的时候70种颜色要2s左右,这个可以说颜色多的情况下碾压其他的算法。
2.2禁忌搜索
下山法改进,开始给所有节点随机染色,然后每次改变一个节点的颜色,主要还是通过不断计算改变后的冲突边变化量,然后选择接下来如何改变哪个节点的颜色(这里主要是贪心——每次选择最好的那个(冲突边变化量可正可负),如果有相等解就随机选取,所有可执行的解需要不在禁忌期内),新颜色为非原色的其他颜色,同时给一些在迭代过程中得到的临时解设置禁忌期,禁忌期内该解不能再次到达。
2.2.1主要过程流程
2.2.2主要数据结构
Ne 节点个数
N_C 颜色数
class Tabu_k 禁忌搜索结构 {
array<int,Ne> sol{};//
保存每个点的颜色
array<int,Ne>num_adj{}; //保存邻点个数
array<array<int,N_C>,Ne> adj_color_table{};//领域颜色表
array<array<int,N_C>,Ne> tabutenure{};//禁忌表
array<array<int,Ne-1>,Ne> Nb{};//邻接表,顶点数*(顶点数-1),保存邻点有哪些
array<array<bool,Ne>,Ne> Adj{};//邻接矩阵,相邻则为true
array<array<int,2>,Ne*(N_C-1)> equ_delt{};//保存相等的解
explicit Tabu_K(const string& strFile);
构造函数,读取文件的同时初始化基本的数据结构
~Tabu_K();释放掉使用的一些数据
void Initialize(const string& fileName);读取文件并将值赋给对应的数据结构
void FindMove();寻找解
void MakeMove();执行改变某个指定点的颜色的操作
void DeleteArray();释放数组
}
2.2.3完整代码
//
// Created by Administrator on 2021/10/30.
//
#include<iostream>
#include<time.h>
#include<string>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<fstream>
#include<array>
#define N_C 49
#define Ne 500
using namespace std;
class Tabu_K {
public:
string str;
int N{}, K{};//暂时无用
int f{}, best_f{};//冲突数
int delt{};//此次迭代的最优解
int equ_count = 0;//记录相等解的个数
int iter=0;//迭代次数
int sel_vertex{}, sel_color{};// move的点和颜色
array<int,Ne> sol{};//保存每个点的颜色
array<int,Ne>num_adj{}; //保存邻点个数
array<array<int,N_C>,Ne> adj_color_table{};//领域颜色表
array<array<int,N_C>,Ne> tabutenure{};//禁忌表
array<array<int,Ne-1>,Ne> Nb{};//邻接表,顶点数*(顶点数-1),保存邻点有哪些
array<array<bool,Ne>,Ne> Adj{};//邻接矩阵,相邻则为true
array<array<int,2>,Ne*(N_C-1)> equ_delt{};//保存相等的解
explicit Tabu_K(const string& strFile);
~Tabu_K();
void Initialize(const string& fileName);
void FindMove();
void MakeMove();
void DeleteArray();
};
/*
*释放数组的模板函数
*/
template<class T>
bool freeArray(T &a){
a.fill(0);
return true;
}
/*
*
*/
void Tabu_K::Initialize(const string& fileName)
{
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open(fileName);
string tmp;
if(!ifs.is_open()){
cout<<"failed"<<endl;
return ;
}
while (!ifs.eof())
{
if (tmp=="edge")
{
ifs >> N;
v = new Vertex[nVertex]; //初始化nV个顶点
for(auto &it:Adj){
it.fill(false);
}
}
if (tmp=="e")
{
int m, n;
ifs >> m >> n;
Adj[m - 1][n - 1] = true;//对称形成邻接矩阵
Adj[n - 1][m - 1] = true;
}
ifs >> tmp;
}
cout<<"file ready"<<endl;
ifs.close();
//开辟equ_delt,最多有N*(K-1)个解.即每个顶点可以产生K-1个delt
//[i][0]存第i个解的顶点,[i][1]存第i个解的newcolor
for(auto &it:equ_delt) freeArray(it);
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) sol[i] = rand() % K; //给每个点随机着色
for(auto &it:adj_color_table) freeArray(it);
//初始化adj_color_table
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
if (Adj[i][j]) //点i和点j相邻 ,更新邻居边不同颜色的冲突边数
{
adj_color_table[i][sol[j]]++; //点i为sol[j]颜色的邻居加1
adj_color_table[j][sol[i]]++; //点j为sol[i]颜色的邻居加1
if (sol[i] == sol[j]) //判断两个点的颜色是否相同
{
f++; //两点颜色相等,则冲突数加一
}
}
}
}
best_f = f; //初始化最优f
cout<<"初始化最优解(冲突边数)"<<best_f<<endl;
//初始化tabutenure
for(auto &it:tabutenure) freeArray(it);
//初始化NbID为N*(N-1)数组和num_adj
freeArray(num_adj);
for(auto &it:Nb) freeArray(it);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (Adj[i][j]) {
int tmp_t = num_adj[i];
num_adj[i]++;
Nb[i][tmp_t] = j;
}
}
for(auto &it:Adj){
it.fill(false);
}
}
/*
* 读取文件和初始化
*/
void Tabu_K::FindMove() {
delt = 10000;//初始为最大整数
int tmp_delt;
int c_color;//当前结点颜色
array<int,N_C>h_tabu{},h_color{};//禁忌表行首指针,邻接颜色表行首指针
h_color.fill(0);//初始化
int c_color_table;//当前结点邻接颜色表的值
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
c_color = sol[i];
h_color = adj_color_table[i]; //当前节点i所有不同颜色邻居的个数
c_color_table = h_color[c_color];//即adj_color_table[i][sol[i]]的值 -> i节点颜色为sol[i]的邻居的个数
if (c_color_table > 0) { //颜色表此处的值不为0
h_tabu = tabutenure[i]; //i节点的禁忌表元素
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++) {
if (c_color != j) { //如果颜色不相同
tmp_delt = h_color[j] - c_color_table; //这里的意思就是判断如果将节点i的颜色转换为颜色j时的冲突节点数变化量,因为原本的c_color_table记录的就是当前节点相同颜色
//邻居的个数,那冲突边就是c_color_table,如果换成其他邻居的颜色,冲突边就变为新颜色的同颜色邻居个数,如果新的冲突边小于
//原来的,就相当于变换颜色可以实现减少冲突边的效果,那就将减少的量记录为delt,且一直记录减少量最多的(负值,因此取最小)
if (tmp_delt <= delt && (iter > h_tabu[j] || (tmp_delt + f) < best_f)) {
/*这里的三个条件a&&(b||c)
* a条件的含义是当前改变颜色的操作需要是使冲突边数减少最多的解或者增加最少的解
* b条件是指将i节点的颜色改变为j的这种方式是否符合禁忌表的规则,禁忌表的初始化为0,但在第一次实际赋值时的初值是迭代次数,所以相当于禁忌表中的所有禁忌期都含有
* 一个大小为iter的偏置,只有大于这个偏置才相当于禁忌期为0,否则这种方式就在禁忌期内
* c条件的含义是当前颜色改变方式产生的冲突边减少量
*/
if (tmp_delt < delt) {//当前解小于本次迭代最优解,则重新开始保存解
equ_count = 0;
delt = tmp_delt;
}
//这里保存解的时候其实就是贪心,每次只保留效果最好的解,但是冲突边减少量最多的解不一定只有一个,所以在后边选择解的时候还是要随机选出一个解,上边的代码是对这个
//判断语句的深入选择,因为开始的a条件是小于等于,小于时equ_count最大为1,但是出现等于情况时equ_count就会大于1
equ_delt[equ_count][0] = i;
equ_delt[equ_count][1] = j;
equ_count++;//end of another way
}
}
}
}
}
int tmp = rand() % equ_count;//有多个解时,随机选择
sel_vertex = equ_delt[tmp][0];
sel_color = equ_delt[tmp][1];
}
/*
* 更新禁忌表和颜色表
*/
void Tabu_K::MakeMove() {
f = delt + f;
if (f < best_f) best_f = f;
int old_color = sol[sel_vertex];
sol[sel_vertex] = sel_color; //更新颜色
tabutenure[sel_vertex][old_color] = iter + f + 0.6*(rand() % 10);//更新禁忌表,是否最后要+1??
//还要有数组存下每个顶点的邻边,以及邻边的数量
array<int,Ne-1> h_NbID = Nb[sel_vertex];
int num_edge = num_adj[sel_vertex];
int tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < num_edge; i++) {//更新邻接颜色表
tmp = h_NbID[i];//等于nbID[sel_vertex][i]
adj_color_table[tmp][old_color]--;
adj_color_table[tmp][sel_color]++;
}
}
/*
* 释放所使用的数组
*/
void Tabu_K::DeleteArray() {
for(auto &it:adj_color_table) freeArray(it);
freeArray(sol);
for(auto &it:tabutenure) freeArray(it);
freeArray(num_adj);
for(auto &it:equ_delt) freeArray(it);
for(auto &it:Nb) freeArray(it);
}
Tabu_K::~Tabu_K() {
DeleteArray();
}
Tabu_K::Tabu_K(const string& strFile) {
//this->str.assign(strFile) ;
N = Ne;
K = N_C;
Initialize(strFile);
}
int main()
{
int result_count = 10;//自动计算10次
while (result_count) {
auto *tabu = new Tabu_K("DSJC500.5.col");
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
while (tabu->f)
{
tabu->FindMove();
tabu->MakeMove();
tabu->iter++;
}
end = clock();
cout << "iter=" << tabu->iter << "\t time=" << (end - start) << endl;
delete tabu;
result_count--;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.2.4结果展示
20次求解 49 色结果
| 序号 | 迭代次数 | 时间 (ms) | 冲突边数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 180740459 | 1182286 | 1285 |
| 2 | 8342196 | 61655 | 1339 |
| 3 | 59054099 | 386090 | 1212 |
| 4 | 83381554 | 552100 | 1277 |
| 5 | 5726737 | 41573 | 1264 |
| 6 | 147159162 | 955887 | 1307 |
| 7 | 50415504 | 317707 | 1249 |
| 8 | 27704993 | 176346 | 1299 |
| 9 | 8904240 | 313034 | 1287 |
| 10 | 104238364 | 732617 | 1246 |
| 11 | 180740459 | 281765 | 1296 |
| 12 | 7264308 | 8904240 | 1282 |
| 13 | 11328920 | 365319 | 1168 |
| 14 | 40465218 | 1255711 | 1302 |
| 15 | 10166362 | 321141 | 1257 |
| 16 | 153975124 | 5270507 | 1229 |
| 17 | 36504657 | 1175427 | 1286 |
| 18 | 1411578 | 43343 | 1280 |
| 19 | 49998945 | 1612699 | 1231 |
| 20 | 6471590 | 196046 | 1278 |

这里的话是展示了20次的结果,为了方便其实是跑了两个10次,结果还是比较明显的,第一批的十次迭代超过5000w次的不在少数,共有6次,而第二批却只有1次,并且第二批跑出了一个相当优秀的成果,1280条冲突边却只花了不到43s就结束了染色。
总的成功率为65%,平均迭代次数为58385946,平均迭代时间为1207274ms,约为20分钟.
但是总得来看以迭代次数评定成功与否也有很大缺陷,比如第9次和第11次,对于第九次
虽然迭代次数较多,但时间却较短,因此时间较长应该也不应该计为成功,反而迭代次数超过标准不多的如果时间较短的应该也计为成功
2.3模拟退火
模拟退火基本的思想是温度越高时,求解时的随机性就越高,相当于给上山的可能性越大,而这个过程中就可能跳出了局部最优解,但是在温度降到一定程度时,基本就退化成了下山,除此外,我针对这个问题进行了一些简单的优化,比如适度调整某个温度时的steps,还有在解降到一定程度时,多次的迭代可能会长时间处于一个解,手动给它一个随机解使其跳出当前状态,对于颜色数较少时的求解有一定的提升效果,但是迭代次数相当大,只是有了一定的成功率,比最基本的模拟退火效果好。
这里的实现过程是基于前边的禁忌搜索完成的,因此代码可以说有点乱七八糟的
2.3.1主要过程流程
关键过程MainLoop伪代码
while(steps--) {
random_node = i; //随机选取一个点
random_color = j; //随机选取一个新颜色
if color[i]!=j
then
tmp_delt = δ(i,j); //计算i点变为新颜色的代价
probably = rand() % 1000 /1000; //随机生成一个概率
if tmp_delt<0 or probably < exp(-tmp_delt/T*α)
then
select node = random_node, new_color = random_color;
fi
fi
MakeMove();
}
2.3.2主要数据结构
#define Ne 500
#define K_c 50
array<bool,Ne> is_c{false}; 用于标记判断在初始化解是否每种颜色都被用到了
模拟退火类结构class SA {
array<int,Ne> sol{};
每个点的颜色
array<int,Ne> num_adj{};邻点个数
array<array<int,K_c>,Ne> adj_color_table{};//领域颜色表
array<array<bool,Ne>,Ne>Adj;邻接矩阵
array<array<int,Ne-1>,Ne> Nb{};//邻接表,顶点数*(顶点数-1),保存邻点有哪些
SA(const string& fileName);
~SA();
void MainLoop();主循环
void Cool(int num);冷却方式
void RandomReset();随机新解
void MakeMove();改变颜色重新计算冲突边
void DeleteArray();释放数组
int getConflict(int);获取节点的当前冲突边数
}
2.3.3完整代码
//
// Created by Administrator on 2021/10/31.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <array>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "tmp.cpp"
using namespace std;
#define Ne 500
#define K_c 48
array<bool,Ne> is_c{false};
class SA{
public:
int N{}, K{};
int iter{};
int flag = 0;//判断是否经过steps增加的步骤
double temp = 10.0;
double min_temp = 0.0000000000001;
double rate = 0.99;
int steps = 10000;//这里考虑一下如何随着温度的降低调整一下,
// 一开始可以小一点,理论上应该是温度越低步长越小,那就应该多探索几次
int f=0,best_f=0;
int sel_vertex{}, sel_color{};// move
int delt{};//此次迭代的最优解
array<int,Ne> sol{};
array<int,Ne> num_adj{};
array<array<int,K_c>,Ne> adj_color_table{};//领域颜色表
array<array<bool,Ne>,Ne>Adj;
array<array<int,Ne-1>,Ne> Nb{};//邻接表,顶点数*(顶点数-1),保存邻点有哪些
SA(const string& fileName);
~SA();
void MainLoop();
void Cool(int num);
void RandomReset();
void MakeMove();
void DeleteArray();
int getConflict(int);
private:
double alpha = 0.01;
};
SA::~SA() {
DeleteArray();
cout<<"end"<<endl;
}
SA::SA(const string& fileName) {
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open(fileName);
cout<<"init"<<endl;
srand(time(NULL));
string _tmp;
if(!ifs.is_open()){
cout<<"failed"<<endl;
return ;
}
while(!ifs.eof()){
if (_tmp=="edge"){
ifs >> N;
for(auto &it:Adj) it.fill(false);
}
if(_tmp=="e") {
int m,n;
ifs >> m >> n;
Adj[m - 1][n - 1] = true;//对称形成邻接矩阵
Adj[n - 1][m - 1] = true;
}
ifs >> _tmp;
}
ifs.close();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
sol[i] = rand() % K_c;
is_c[i] = true;
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
if(!is_c[i])
cout<<"failed color"<<endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
if (Adj[i][j]) //点i和点j相邻 ,更新邻居边不同颜色的冲突边数
{
adj_color_table[i][sol[j]]++; //点i为sol[j]颜色的邻居加1
adj_color_table[j][sol[i]]++; //点j为sol[i]颜色的邻居加1
if (sol[i] == sol[j]) //判断两个点的颜色是否相同
{
f++; //两点颜色相等,则冲突数加一
//cout<<f<<endl;
}
}
}
}
best_f = f; //初始化最优f
cout<<"初始化最优解(冲突边数)"<<best_f<<endl;
//初始化NbID为N*(N-1)数组和num_adj
freeArray(num_adj);
for(auto &it:Nb) freeArray(it);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (Adj[i][j]) {
int tmp_t = num_adj[i];
num_adj[i]++;
Nb[i][tmp_t] = j;
}
}
for(auto &it:Adj){
it.fill(false);
}
}
void SA::MainLoop() {
if(f<50&&flag==0) steps = 100000;
for(int it=0;it<steps; it++) {
//NextNe();
delt = 0;//初始为最大整数
int tmp_delt = 0;
int c_color = 0;//当前结点颜色
array<int,K_c>h_tabu{},h_color{};
h_color.fill(0);//初始化
int c_color_table = 0;//当前结点邻接颜色表的值
int i = rand() % Ne;
c_color = sol[i];
h_color = adj_color_table[i]; //当前节点i所有不同颜色邻居的个数
c_color_table = h_color[c_color];//即adj_color_table[i][sol[i]]的值 -> i节点颜色为sol[i]的邻居的个数
if (c_color_table > 0) { //颜色表此处的值不为0
int j = rand() % K_c;
if (c_color != j) { //如果颜色不相同
tmp_delt = h_color[j] - c_color_table;
double gailv = rand()%1000 /1000;
//std::default_random_engine e((unsigned int)time(0));
//double gailv = 0.7;
if (tmp_delt < 0|| (exp(-tmp_delt/temp*10) >gailv)) {
//if(f<50) steps*=10;
sel_vertex = i;
sel_color = j;
delt = tmp_delt;
}
}
}
// if(temp<min_temp) break;
f = delt + f;
if (f < best_f) best_f = f;
/*int old_color = sol[sel_vertex];
sol[sel_vertex] = sel_color; //更新颜色
//还要有数组存下每个顶点的邻边,以及邻边的数量
array<int,Ne-1> h_NbID = Nb[sel_vertex];
int num_edge = num_adj[sel_vertex];
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_edge; i++) {//更新邻接颜色表
tmp = h_NbID[i];//等于nbID[sel_vertex][i]
adj_color_table[tmp][old_color]--;
adj_color_table[tmp][sel_color]++;
}*/
MakeMove();
}
//cout<<temp<<endl;
}
void SA::Cool(int num) {
switch (num) {
case 0:
temp = temp - alpha;
break;
case 1:
temp = temp * rate;
break;
case 2:
temp = temp/(1+alpha*temp);
default:
temp = temp * (1/log(1/num+2));
break;
}
}
void SA::MakeMove() {
int old_color = sol[sel_vertex];
sol[sel_vertex] = sel_color; //更新颜色
//还要有数组存下每个顶点的邻边,以及邻边的数量
array<int,Ne-1> h_NbID = Nb[sel_vertex];
int num_edge = num_adj[sel_vertex];
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_edge; i++) {//更新邻接颜色表
tmp = h_NbID[i];//等于nbID[sel_vertex][i]
adj_color_table[tmp][old_color]--;
adj_color_table[tmp][sel_color]++;
}
}
void SA::RandomReset() {
int c_color = 0;
int c_node = 0;
int max_f = 0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
int c_f = getConflict(i);
if (c_f>max_f) {
max_f = c_f;
c_node = i;
c_color = sol[i];
}
}
while(true) {
int j = rand() % K_c;
if(c_color!=j){
sel_vertex = c_node;
sel_color = j;
break;
}
}
//int tmp_f = getConflict(sel_vertex);
int tmp_delt = adj_color_table[c_node][sol[sel_color]]-adj_color_table[c_node][sol[c_node]];
MakeMove();
f+=tmp_delt;
//int tmp_f1 = getConflict(sel_vertex);
//f = f+ tmp_f - tmp_f1;
//cout<<c_node<<":"<< tmp_f<<" "<<tmp_f1<<endl;
//cout<<tmp_f<<" "<<tmp_f1<<endl;
//system("pause");
}
int SA::getConflict(int node) {
int tmp_f = 0;
for(int j=0;j<Ne;j++) {
if(Nb[node][j]){
if(sol[node]==sol[j]){
tmp_f++;
}
}
}
return tmp_f;
}
void SA::DeleteArray() {
for(auto &it:Nb) freeArray(it);
for(auto &it:adj_color_table) freeArray(it);
freeArray(num_adj);
freeArray(sol);
}
int main()
{
int result_count = 10;//自动计算10次
while (result_count) {
auto *Si = new SA("DSJC500.5.col");
clock_t start, end;
start = clock();
Si->steps = 10000;
Si->flag = 0;
int count = 0;
int last_f = 0;
while (Si->f)
{
Si->MainLoop();
if(Si->f==last_f)
count++;
if(count>=50) {
count = 0;
last_f = 0;
Si->RandomReset();
//cout<<"Reset"<<endl;
}
Si->Cool(1);
Si->iter+=Si->steps;
//cout<<Si->iter<<":"<<Si->f<<endl;
last_f = Si->f;
if(Si->temp<Si->min_temp) break;
if(Si->f<=0) {
cout<<"succ"<<endl;
break;
}
}
end = clock();
//cout<<Si->f<<endl;
cout << "iter=" << Si->iter << "\t time=" << (end - start) << endl;
result_count--;
//cout<<Si->getConflict(18)<<endl;
//result_count--;
delete Si;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.3.4结果展示
20次求解 50 色结果
| 序号 | 迭代次数(万次) | 时间 (ms) | 冲突边数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24817 | 1051772 | 1223 |
| 2 | 25636 | 1039370 | 1253 |
| 3 | 24646 | 990623 | 1260 |
| 4 | 11649 | 477575 | 1310 |
| 5 | 25249 | 41573 | 1264 |
| 6 | 25519 | 1020825 | 1252 |
| 7 | 25375 | 1043661 | 1273 |
| 8 | 25438 | 1038499 | 1207 |
| 9 | 12073 | 495113 | 1298 |
| 10 | 16382 | 685993 | 1311 |
| 11 | 25402 | 1051110 | 1260 |
| 12 | 25375 | 1041686 | 1251 |
| 13 | 25330 | 1057325 | 1278 |
| 14 | 25375 | 1045820 | 1240 |
| 15 | 24501 | 1006028 | 1277 |
| 16 | 24673 | 1035971 | 1273 |
| 17 | 25438 | 1069528 | 1265 |
| 18 | 16035 | 655775 | 1260 |
| 19 | 25555 | 1080123 | 1253 |
| 20 | 24349 | 1011071 | 1230 |
这里需要注明一下其中有些地方的基本参数
double temp = 10.0; //起始温度
double min_temp = 0.0000000000001; //最低温度
double rate = 0.99; //几何下降的倍率
int steps = 10000;// 初始的周期
if(f<50&&flag==0) steps = 100000; //冲突边小于50后,steps扩大10倍
double gailv = 0.7;
//这个概率可以替换随机生成的,0.7到0.8之间会使最优解下降的比较慢,太大了很容易陷入局部最优解,在颜色数较多时不太影响,太多了就影响比较明显了,不过最后没有使用这个概率。
if (tmp_delt < 0|| (exp(-tmp_delt/temp*10) >gailv)) 这里的10对应伪代码里的α,也是用于调节起始最优解下降速度的参数,为了方便就以10的倍数调了,开始设置温度为1,这里就是100,但是后来发现如果温度是从1开始下降的话,这里的计算可能保持一个比较稳定的范围,于是把温度从1调到了10,然后对应的α也调成了10

总的成功率为25%,平均迭代次数为22940w次,平均迭代时间为896972ms,约为15分钟
这里列举一下48色的成功例子,但是成功率很低,大概试了二十多次才成功一次,49次没怎么试,应该成功率不会太高,但是整体速度是快于禁忌搜索的,只能说各有利弊吧
1309
succ
iter=153870000
time=621164
总结
这次作业历时还是比较久的,中间最折磨的是迭代时间比较久,还好在git上提交了历史代码,两台电脑一起跑,参数一起调,然后加上在云主机上也调,相当于三台电脑一起搞,笑死个yin。
这个图染色问题目前还有其他算法,了解到的是基于遗传算法的一些算法,
暂时就不搞了,有时间再深入学吧。