一、简介
首先对病灶图片进行gabor小波纹理特征提取,然后输入进经PSO优化的svm进行训练与测试分类
二、部分源代码
%% 清空环境变量以及加载数据
clc
clear
close all
warning off
format long
format compact
%% 网络结构建立
%读取数据
load img_tz %纹理特征
%%
%由于特征维数过高,每个gabbor特征有1440维,不利于训练网络,因此我们用PCA进行降维
[pca1,pca2,pca3]=pca(input);
proportion=0;
i=1;
while(proportion < 95)
proportion = proportion + pca3(i);
i = i+1;
end
input=pca2(:,1:10);
%随机提取训练样本,预测样本
rand('seed',0)
[m n]=sort(rand(1,size(input,1)));
m=150;
train_wine=input(n(1:m),:);
train_wine_labels=output(n(1:m),:);
test_wine=input(n(m+1:end),:);
test_wine_labels=output(n(m+1:end),:);
%%
%%%%% 选择最佳的SVM参数c&g-利用粒子群算法进行选择
% 粒子群参数初始化
pso_option = struct('c1',0.9,'c2',0.9,...
'maxgen',200,'sizepop',50, ...
'k',0.6,'wV',0.8,'wP',0.8, ...
'popcmax',10^2,'popcmin',10^(-2),...
'popgmax',10^2,'popgmin',10^(-2));
%%
[bestacc,bestc,bestg,trace] = psoSVMcgForClass(train_wine_labels,train_wine,test_wine_labels,test_wine,pso_option);
GlobalParams=[bestc bestg];
img3= double(imresize(img2,[48 48],'bilinear')); %采用'bilinear':采用双线性插值算法扩展为48*48
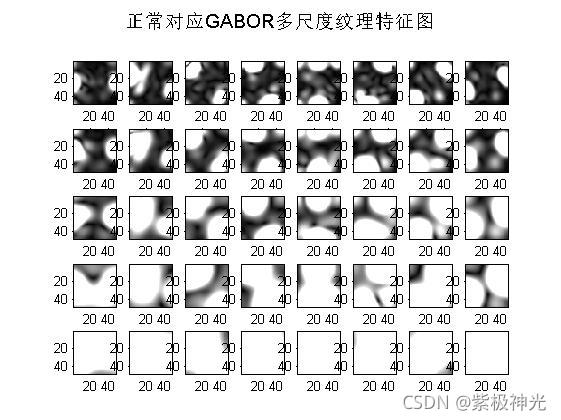
H2 = filter_image_with_Gabor_bank1(img3,filter_bank,64);%%提取gabor纹理特征
suptitle('正常对应GABOR多尺度纹理特征图');
data_matrix1=[data_matrix1 H2];%将提取的特征放进data_matrix1中
disp(sprintf('完成正常文件夹中第%i图的gabor特征提取',i));
end
tz_image1=data_matrix1';
%%
class1path=dir('溃疡');
data_matrix1=[];
for i=1%:length(class1path)-2
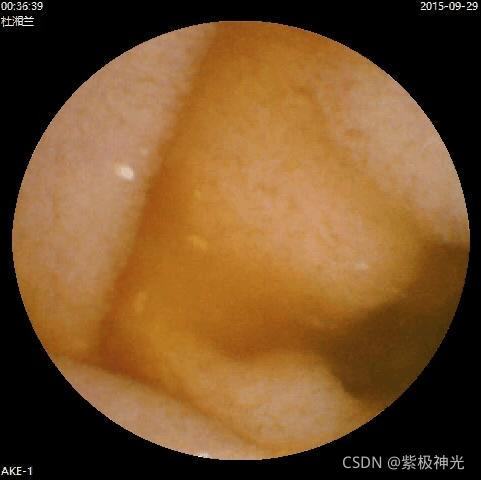
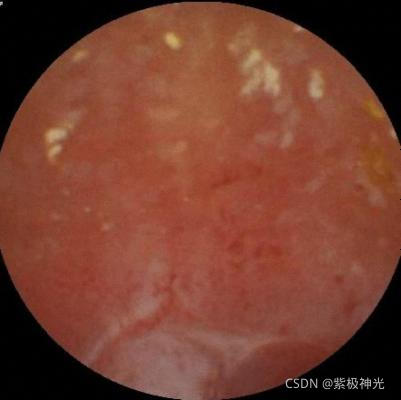
imgpath=['溃疡\' class1path(i+2).name];%煤炭的路径
img1=imread(imgpath);%读取图片
figure;imshow(img1);title('溃疡原始图片')
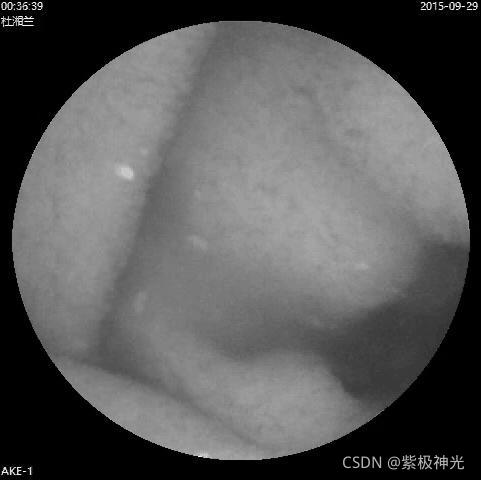
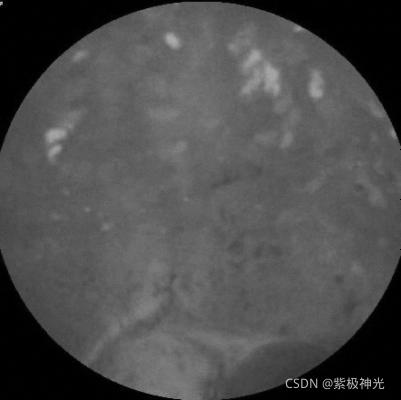
img2=rgb2gray(img1);%灰度化
figure;imshow(img2);title('溃疡原始图片灰度图')
img3= double(imresize(img2,[48 48],'bilinear')); %采用'bilinear':采用双线性插值算法扩展为48*48
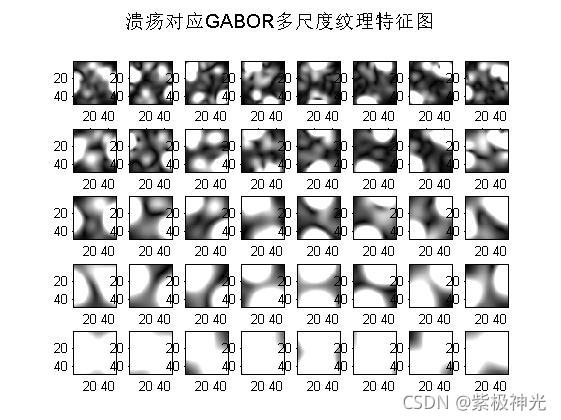
H2 = filter_image_with_Gabor_bank1(img3,filter_bank,64);%%提取gabor纹理特征
data_matrix1=[data_matrix1 H2];%将提取的特征放进data_matrix1中
suptitle('溃疡对应GABOR多尺度纹理特征图');
disp(sprintf('完成溃疡文件夹中第%i图的gabor特征提取',i));
end
tz_image2=data_matrix1';
%% 保存结果 以及对应标签 其中正常设为第一类 溃疡设为第二类
input=[tz_image1;tz_image2];
output=[ones(1,size(tz_image1,1)) 2*ones(1,size(tz_image2,1))]';
function [bestCVaccuarcy,bestc,bestg,trace] = psoSVMcgForClass(train_wine_labels,train_wine,test_wine_labels,test_wine,pso_option)
if nargin == 4
pso_option = struct('c1',0.9,'c2',0.9,'maxgen',100,'sizepop',10, ...
'k',0.6,'wV',0.8,'wP',0.8,'v',5, ...
'popcmax',10^2,'popcmin',10^(-2),'popgmax',10^2,'popgmin',10^(-2));
end
% c1:初始为1.5,pso参数局部搜索能力
% c2:初始为1.7,pso参数全局搜索能力
% maxgen:初始为200,最大进化数量
% sizepop:初始为20,种群最大数量
% k:初始为0.6(k belongs to [0.1,1.0]),速率和x的关系(V = kX)
% wV:初始为1(wV best belongs to [0.8,1.2]),速率更新公式中速度前面的弹性系数
% wP:初始为1,种群更新公式中速度前面的弹性系数
% v:初始为3,SVM Cross Validation参数
% popcmax:初始为100,SVM 参数c的变化的最大值.
% popcmin:初始为0.1,SVM 参数c的变化的最小值.
% popgmax:初始为1000,SVM 参数g的变化的最大值.
% popgmin:初始为0.01,SVM 参数c的变化的最小值.
Vcmax = pso_option.k*pso_option.popcmax;
Vcmin = -Vcmax ;
Vgmax = pso_option.k*pso_option.popgmax;
Vgmin = -Vgmax ;
eps = 10^(-3);
% 产生初始粒子和速度
for i=1:pso_option.sizepop
% 随机产生种群和速度
pop(i,1) = (pso_option.popcmax-pso_option.popcmin)*rand+pso_option.popcmin;
pop(i,2) = (pso_option.popgmax-pso_option.popgmin)*rand+pso_option.popgmin;
V(i,1)=Vcmax*rands(1,1);
V(i,2)=Vgmax*rands(1,1);
% 计算初始适应度
fitness(i) =fun(pop(i,:),train_wine_labels,train_wine,test_wine_labels,test_wine)
end
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.