二叉树 概念
二叉树要么是空树,要么是非空树,即由根结点、根结点的左子树和根结点的右子树组成。
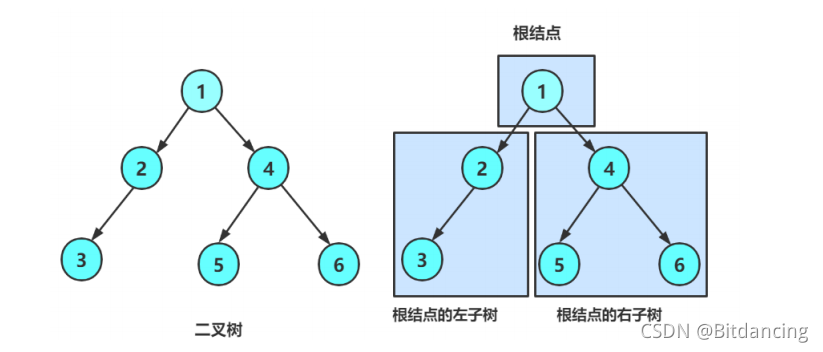
可以看出二叉树是递归定义的,后序操作都是基于这个结论实现的。
前序(先序)遍历
按照 根结点-左子树-右子树 的顺序遍历树。
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
对于上图二叉树,前序遍历的结果是
(下一行是程序运行结果)

中序遍历
按照 左子树-根结点-右子树 的顺序遍历树。
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}

后序遍历
按照 左子树-右子树-根结点 的顺序遍历树。
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}

层序遍历
借助队列实现层序遍历。
1、空树:直接返回
2、树不为空时,把根结点入队列。每次结点出队列,就把这个结点的左右孩子带进队列中。
// 层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
// 使用队列
// 树空,直接返回
// 树不为空,根结点入队列
// 每次结点出队列,把左右孩子带进队列里
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
// 非空树
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
// 保存队头元素
QDataType front = QueueFront(&q);
// 出队头
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%c ", front->data);
// 孩子结点入队
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}

二叉树结点个数
二叉树结点个数 = 根结点个数+左右子树结点总数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
二叉树叶子节点个数
叶子节点左右孩子都是NULL。
二叉树叶子节点 = 左子树叶子节点 + 右子树叶子节点
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
// 左子树叶子节点+右子树叶子结点
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
二叉树第k层结点个数
二叉树第k层结点个数等于左右子树第k-1层结点个数。
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
// root不为空,k不等于1,第k层存在在子树中
// 统计左右子树第k-1层结点个数
return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) +
BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
二叉树深度/高度
二叉树深度/高度是左右子树最大高度加一。
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
// 非空树,左右子树最大高度+1
int leftDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);
return fmax(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
// return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;
}
二叉树查找值为x的节点
先判断根结点是不是值为x的结点,如果不是,去左右子树中查找。
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
// 根结点判断,不是,进入左右子树查找
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* leftret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (leftret)
return leftret;
BTNode* rightret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (rightret)
return rightret;
return NULL;
}
判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
首先要分析得出完全二叉树和一般二叉树的区别。本题基于层序遍历的知识更好理解。
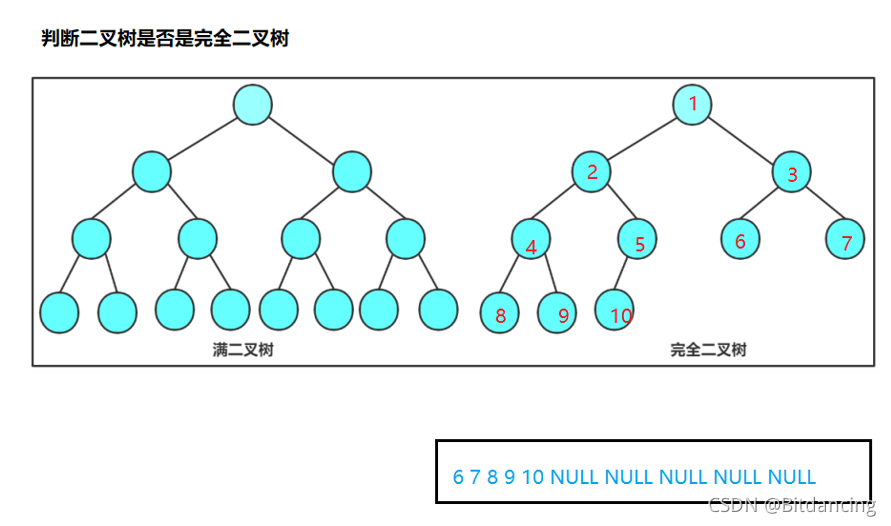
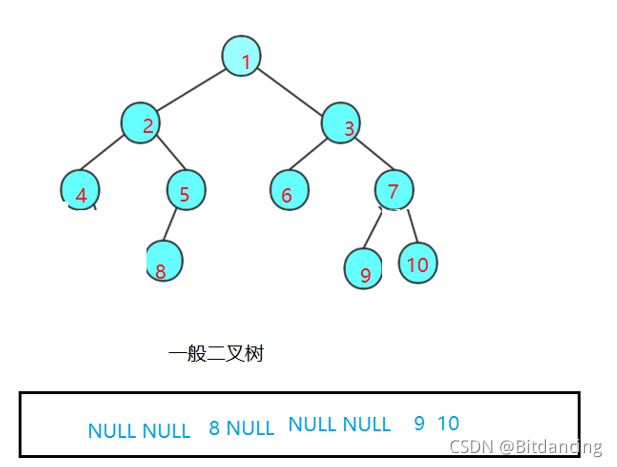
可以得出,完全二叉树在找到NULL时,后面没有元素。
一般二叉树在找到NULL后,后面还会有元素。
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
// 根结点入队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
// 队列非空
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
// 获得队顶元素
QDataType tmp = QueueFront(&q);
// 队顶出队
QueuePop(&q);
// 如果tmp是NULL,跳出进行判断
if (tmp == NULL)
{
break;
}
else
{
// tmp 非空
// 带入孩子结点
QueuePush(&q, tmp->left);
QueuePush(&q, tmp->right);
}
}
// 遇到NULL,检查队列剩下的结点
// 全是NULL,完全二叉树
// 存在非空,不是完全二叉树
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
// 依次取队头元素进行判断
QDataType front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
二叉树销毁
后序遍历进行销毁。使用前序遍历销毁还要保留root结点,用后序遍历更加遍历。
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// 后序销毁
BinaryTreeDestory(root->left);
BinaryTreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}