什么是链表?
链表是一种常见的基础数据结构,结构体指针在这里得到了充分的利用。链表可以动态的进行存储分配,也就是说,链表是一个功能极为强大的数组,他可以在节点中定义多种数据类型,还可以根据需要随意增添,删除,插入节点。链表都有一个头指针,一般以head来表示,存放的是一个地址。链表中的节点分为两类,头结点和一般节点,头结点是没有数据域的。链表中每个节点都分为两部分,一个数据域,一个是指针域。说到这里你应该就明白了,链表就如同车链子一样,head指向第一个元素:第一个元素又指向第二个元素;……,直到最后一个元素,该元素不再指向其它元素,它称为“表尾”,它的地址部分放一个“NULL”(表示“空地址”),链表到此结束。
作为有强大功能的链表,对他的操作当然有许多,比如:链表的创建,修改,删除,插入,输出,排序,反序,清空链表的元素,求链表的长度等等。
链表和数组作为算法中的两个基本数据结构,在程序设计过程中经常用到。尽管两种结构都可以用来存储一系列的数据,但又各有各的特点。
数组的优势,在于可以方便的遍历查找需要的数据。在查询数组指定位置(如查询数组中的第4个数据)的操作中,只需要进行1次操作即可,时间复杂度为O(1)。但是,这种时间上的便利性,是因为数组在内存中占用了连续的空间,在进行类似的查找或者遍历时,本质是指针在内存中的定向偏移。然而,当需要对数组成员进行添加和删除的操作时,数组内完成这类操作的时间复杂度则变成了O(n)。
链表的特性,使其在某些操作上比数组更加高效。例如当进行插入和删除操作时,链表操作的时间复杂度仅为O(1)。另外,因为链表在内存中不是连续存储的,所以可以充分利用内存中的碎片空间。除此之外,链表还是很多算法的基础,最常见的哈希表就是基于链表来实现的。基于以上原因,我们可以看到,链表在程序设计过程中是非常重要的。本文总结了我们在学习链表的过程中碰到的问题和体会思考。
接下来,我们将对链表进行介绍,用C语言分别实现:链表的初始化、创建、元素的插入和删除、链表的遍历、元素的查询、链表的删除、链表的逆序以及判断链表是否有环等这些常用操作。并附上在Visual Studio 2013 中可以运行的代码供学习者参考。
可能有些人还对其概念不是很了解。简单来说,我们可以将一条链表想象成环环相扣的结点,就如平常所见到的锁链一样。链表内包含很多结点(当然也可以包含零个结点)。其中每个结点的数据空间一般会包含一个数据结构(用于存放各种类型的数据)以及一个指针,该指针一般称为next,用来指向下一个结点的位置。由于下一个结点也是链表类型,所以next的指针也要定义为链表类型。
以下是代码部分,完整源代码在后面,需要自取,标注出处,侵权必究
先放各个功能的实现
动态申请一个节点,存储值为x
//动态申请一个节点,存储值为x
SLNode* BuySListNode(DataType x)
{
SLNode* node = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (NULL == node)
{
assert(0);
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
单链表打印
void SListPrint(SLNode* plist)
{
SLNode* cur = plist;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d--->", cur->data);
// cur++; // cur指向的是链表中的节点,而链表在物理内存上不一定连续
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
单链表尾插
链表区别于顺序表,它是用一块内存申请一块,所以不需要担心容量问题,插入时不用检测容量,但是需要注意是否链表为空
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pplist, DataType x)
{
assert(pplist); // 链表是否存在
// 1. 链表为空
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = BuySListNode(x);
return;
}
else
{
// 2. 链表不为空
// a. 找当前链表中最后一个节点
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
// b. 插入新节点
cur->next = BuySListNode(x);
}
}
单链表的头插
链表中节点为什么传二级指针?
我们在函数中需要一级指针的解引用就可以取到并操作到链表节点本身去修改它中间储存的值 但是我们想要操作原链表的节点地址,因为链表的特殊性需要保存下一个节点的地址并在一些功能中修改地址 所以二级指针是为了可以操作节点的地址,比如头插就需要改变首节点next中存放的地址.
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pplist, DataType x)
{
assert(pplist);
//创建一个指针变量newnode,指向新创建的节点
SLNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
//将新节点中的next放上原链表首节点的地址
newnode->next = *pplist;
//将新节点地址newnode赋值给首节点地址*pplist,newnode是新节点的地址
*pplist = newnode;
}
单链表的尾删
尾删注意不仅需要判断是否一开始就是空链表,还需要判断链表中是否只有一个节点,也就是删完之后就是空链表了,删节点需要free,不能忘,不然内存泄露啦!!!
思考这里为什么用结构体类型指针?
指针类型必须和指向的东西类型一致
如果用int的指针 首先语法这块是不通过的
其次假设可以 那int的指针只会将节点当成一个int类型的变量来访问 那next这些就拿不到了
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
if (NULL == *pplist)
{
//空链表
return;
}
else if (NULL==(*pplist)->next)
{
//判断是否只有一个节点
*pplist = NULL;
free(*pplist);
}
else
{
//用循环找到最后一个节点,但需要上一个节点的next指向NULL,需要保存上一个节点
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
SLNode* prev = NULL;
while (cur->next)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//执行尾删
prev->next = NULL;
//删掉的节点要记得释放空间,避免内存泄露
free(cur);
}
}
单链表头删
思路是第一个节点指向next,释放第一个节点
思考取next这个操作用*pplist可以吗?
取next这个操作用pplist是不可以的,也就是说不能写做pplist->next,因为next是节点中保存的一个指针变量,要取只能从节点中取,所以只能创建一个结构体类型节点才能访问next
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
//删除操作要判断链表是否为空
if (NULL == *pplist)
{
return;
}
else
{
SLNode* nodedel = *pplist;
*pplist = nodedel->next;
free(nodedel);
}
}
单链表查找
没什么好说的,写个查找代码就好了,找到了返回当前节点地址
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* plist, DataType x)
{
assert(plist);
if (NULL == plist)
{
return NULL;
}
SLNode* cur = plist;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
单链表在pos位置之后插入x
思考为什么不在pos位置之前插入?
因为单链表无法获取前一个节点的地址
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, DataType x)
{
//检测pos位置是否合理
if (pos == NULL)
{
return;
}
//创建新节点
SLNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
单链表删除pos位置之后的值
思考为什么不删除pos位置?
因为删除操作需要更改前一个节点的指针,单链表无法获取前一个节点,如果删除将造成链表丢失
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
//检测pos位置是否合理
if (pos == NULL||pos->next==NULL)
{
return;
}
SLNode* nodedel = pos->next;
pos->next = nodedel->next;
free(nodedel);
}
链表逆置
递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归递归
void SListReversePrint(SLNode* plist)
{
if (NULL != plist)
{
SListReversePrint(plist->next);
printf("%d---> ", plist->data);
}
}
销毁
不销毁=内存泄漏
void SListDestroy(SLNode** plist)
{
assert(plist);
SLNode* cur = *plist;
while (cur)
{
*plist = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = *plist;
}
*plist = NULL;
}
结束,下面是完整代码,分为三个文件
头文件
#pragma once
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
DataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLNode;
// 动态申请一个节点
SLNode* BuySListNode(DataType x);
// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SLNode* plist);
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pplist, DataType x);
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pplist, DataType x);
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pplist);
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pplist);
// 单链表查找
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* plist, DataType x);
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, DataType x);
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos);
void SListDestroy(SLNode** plist);
//
void TestSList();
main代码
#include"SList.h"
int main()
{
TestSList();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
源代码
#include"SList.h"
//动态申请一个节点,存储值为x
SLNode* BuySListNode(DataType x)
{
SLNode* node = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (NULL == node)
{
assert(0);
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SLNode* plist)
{
SLNode* cur = plist;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d--->", cur->data);
// cur++; // cur指向的是链表中的节点,而链表在物理内存上不一定连续
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pplist, DataType x)
{
assert(pplist); // 链表是否存在
// 1. 链表为空
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = BuySListNode(x);
return;
}
else
{
// 2. 链表不为空
// a. 找当前链表中最后一个节点
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
// b. 插入新节点
cur->next = BuySListNode(x);
}
}
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pplist, DataType x)
{
assert(pplist);
//创建一个指针变量newnode,指向新创建的节点
SLNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
//这里说一下链表中首节点为什么传二级指针
//我们在函数中需要一级指针的解引用就可以取到并操作到链表节点本身去修改它中间储存的值
//但是我们想要操作原链表的节点地址,因为链表的特殊性需要保存下一个节点的地址并在一些功能中修改地址
//所以二级指针是为了可以操作节点的地址,比如头插就需要改变首节点next中存放的地址
//将新节点中的next放上原链表首节点的地址
newnode->next = *pplist;
//将新节点地址newnode赋值给首节点地址*pplist,newnode是新节点的地址
*pplist = newnode;
}
// 单链表的尾删
//要注意删除操作需要先判断有没有要删的这个元素,这里要判断链表是否为空
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
if (NULL == *pplist)
{
//空链表
return;
}
else if (NULL==(*pplist)->next)
{
//判断是否只有一个节点
*pplist = NULL;
free(*pplist);
}
else
{
//用循环找到最后一个节点,但需要上一个节点的next指向NULL,需要保存上一个节点
//思考这里为什么用结构体类型指针
//指针类型必须和指向的东西类型一致
//如果用int*的指针 首先语法这块是不通过的
//其次假设可以 那int*的指针只会将节点当成一个int类型的变量来访问 那next这些就拿不到了
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
SLNode* prev = NULL;
while (cur->next)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//执行尾删
prev->next = NULL;
//删掉的节点要记得释放空间,避免内存泄露
free(cur);
}
}
// 单链表头删
//第一个节点指向next,释放第一个节点
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
//删除操作要判断链表是否为空
if (NULL == *pplist)
{
return;
}
else
{
SLNode* nodedel = *pplist;
//取next这个操作*pplist是不可以的,所以只能创建一个结构体类型节点才能访问next
*pplist = nodedel->next;
free(nodedel);
}
}
// 单链表查找
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* plist, DataType x)
{
assert(plist);
if (NULL == plist)
{
return NULL;
}
SLNode* cur = plist;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, DataType x)
{
//检测pos位置是否合理
if (pos == NULL)
{
return;
}
//创建新节点
SLNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
// 为什么不在pos位置之前插入?
//因为单链表无法获取前一个节点的地址
// 为什么不删除pos位置?
//因为删除操作需要更改前一个节点的指针,单链表无法获取前一个节点,如果删除将造成链表丢失
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
//检测pos位置是否合理
if (pos == NULL||pos->next==NULL)
{
return;
}
SLNode* nodedel = pos->next;
pos->next = nodedel->next;
free(nodedel);
}
// 1--->2--->3--->4--->NULL
//递归实现
void SListReversePrint(SLNode* plist)
{
if (NULL != plist)
{
SListReversePrint(plist->next);
printf("%d---> ", plist->data);
}
}
//销毁
void SListDestroy(SLNode** plist)
{
assert(plist);
SLNode* cur = *plist;
while (cur)
{
*plist = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = *plist;
}
*plist = NULL;
}
/
void TestSList()
{
SLNode* plist = NULL;//这里的变量plist是一级指针
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);//尾插
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);//尾插
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);//尾插
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);//尾插
SListPushBack(&plist, 5);//尾插
SListPrint(plist);//打印,预期效果12345
SListPushFront(&plist, 0);//头插
SListPrint(plist);//打印,预期效果012345
SListPopBack(&plist);//尾删
SListPrint(plist);//打印,预期效果01234
SListPopFront(&plist);//头删
SListPrint(plist);//打印,预期效果1234
SListInsertAfter(SListFind(plist, 1), 999);//pos后加x,在1的位置后加999
SListPrint(plist);//打印,预期效果1 999 2 3 4
SListEraseAfter(SListFind(plist, 1));//pos后删x,删除1后的一个x
SListPrint(plist);//打印,预期效果1 2 3 4
SListReversePrint(plist);//逆序打印链表,预期效果4321
SListDestroy(&plist);
}
好,终于写完了,咱们来运行一下
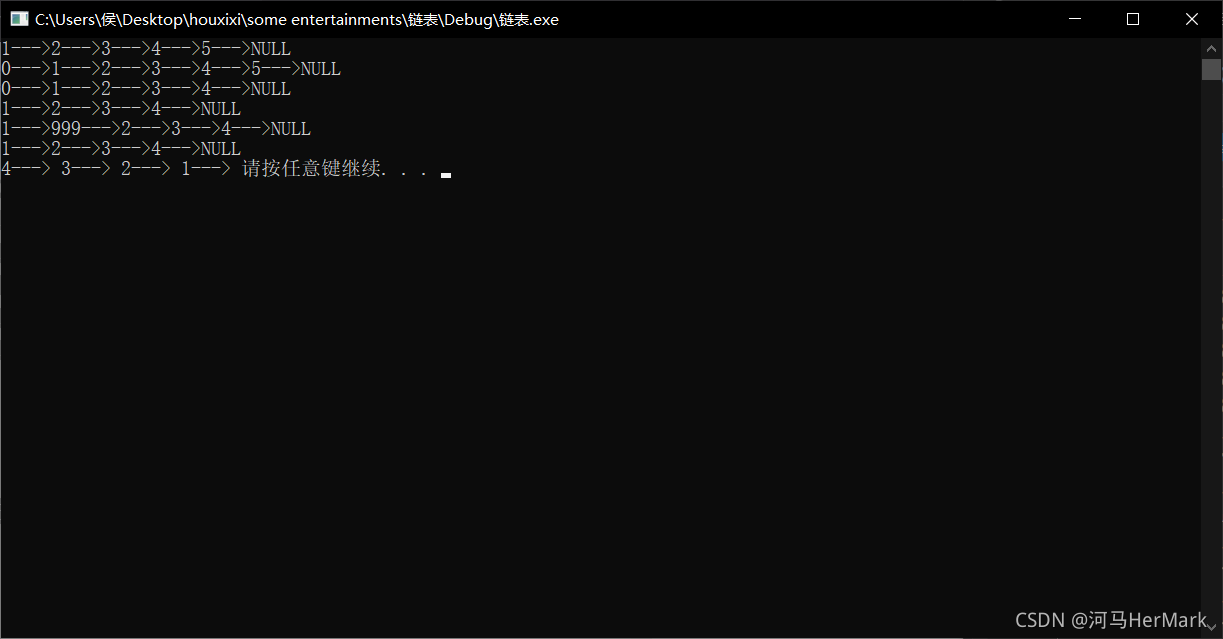
非常完美!没有问题!!!