文章目录
List
1. 预备知识-泛型(Generic)
1.1 泛型的引入
问题:我们之前实现过的顺序表,只能保存 int类型的元素,如果现在需要保存 指向 Person类型对象的引用的顺序表,请问应该如何解决?如果又需要保存指向 Book 对象类型的引用呢?
回答:
对象类型的引用呢?
- 首先,我们在学习多态过程中已知一个前提,基类的引用可以指向子类的对象。
- 其次,我们也已知Object是 java 中所有类的祖先类。
那么,要解决上述问题,我们很自然的想到一个解决办法,将我们的顺序表的元素类型定义成 Object类型,这样我们的Object类型的引用可以指向Person类型的对象或者指向Book类型的对象了。
之前的实现的ArrayList:
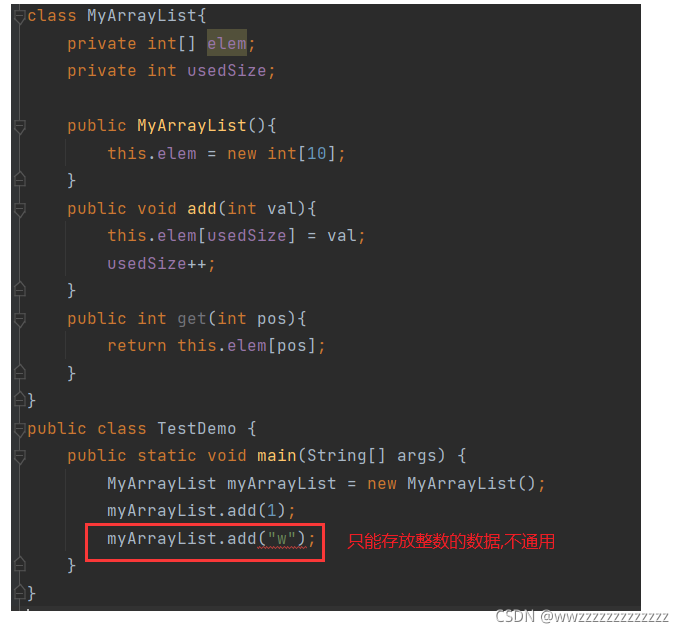
改成Object之后:
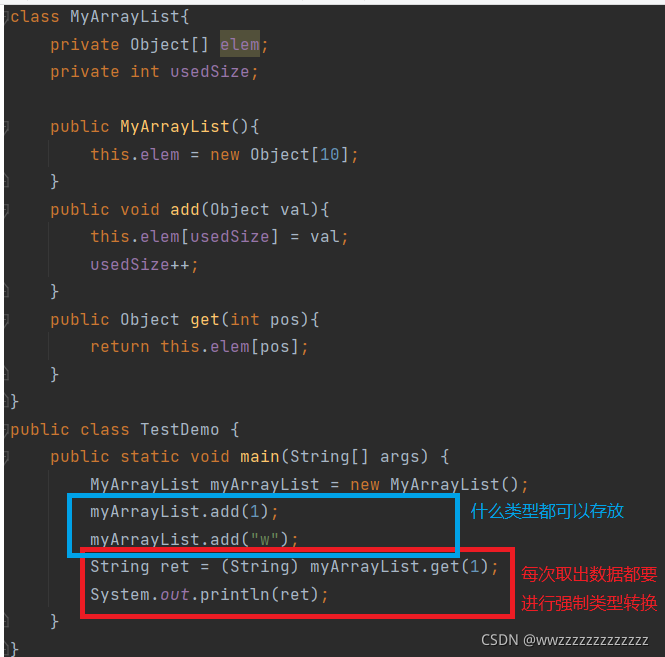
问题:
- 能不能指定这个顺序表的类型?
- 指定类型之后,是不是只能存放指定的数据类型?
- 取出数据,能不能不进行强制类型转换?
于是就有了泛型
1.2 泛型类的简单演示
// 1. 尖括号 <> 是泛型的标志
// 2. E 是类型变量(Type Variable),变量名一般要大写
// 3. E 在定义时是形参,代表的意思是 MyArrayList 最终传入的类型,但现在还不知道
class MyArrayList<E>{
private E[] elem;
private int usedSize;
public MyArrayList(){
this.elem = (E[]) new Object[10];
}
public void add(E val){
this.elem[usedSize] = val;
usedSize++;
}
public E get(int pos){
return this.elem[pos];
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList<String> myArrayList = new MyArrayList<>();
MyArrayList<Integer> myArrayList1 = new MyArrayList<>();
MyArrayList<Boolean> myArrayList2 = new MyArrayList<>();
}
}
1.3 泛型的意义
1. 自动对类型进行检查
2. 自动对类型进行强制类型的转换
3. 泛型中尖括号当中的内容 不参与类型的组成
1.4 泛型是怎么编译的?
泛型是编译时期的一种机制,擦除机制
1.5 泛型总结
1. 泛型是为了解决某些容器、算法等代码的通用性而引入,并且能在编译期间做类型检查。
2. 泛型利用的是 Object 是所有类的祖先类,并且父类的引用可以指向子类对象的特定而工作。
3. 泛型是一种编译期间的机制,即 MyArrayList 和 MyArrayList 在运行期间是一个类型。
4. 泛型是 java 中的一种合法语法,标志就是尖括号 <>
2 . 包装类
2.1 基本数据类型和包装类直接的对应关系
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
2.2 包装类的使用,装箱(boxing)和拆箱(unboxing)
- 装箱 装包 : 把简单类型 ========> 包装类类型
- 拆箱 拆包 : 把包装类类型 =========> 简单数据类类型的数据
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 123;//装箱 装包[隐式的]
int b = a;//拆箱 拆包[隐式的]
System.out.println("====================");
//装箱 装包[显式的]
Integer a2 = Integer.valueOf(123);
Integer a3 = new Integer(123)
//拆箱 拆包[显式的]
int b2 = a2.intValue();
double d = a3.doubleValue();
}
3 . ArrayList简介
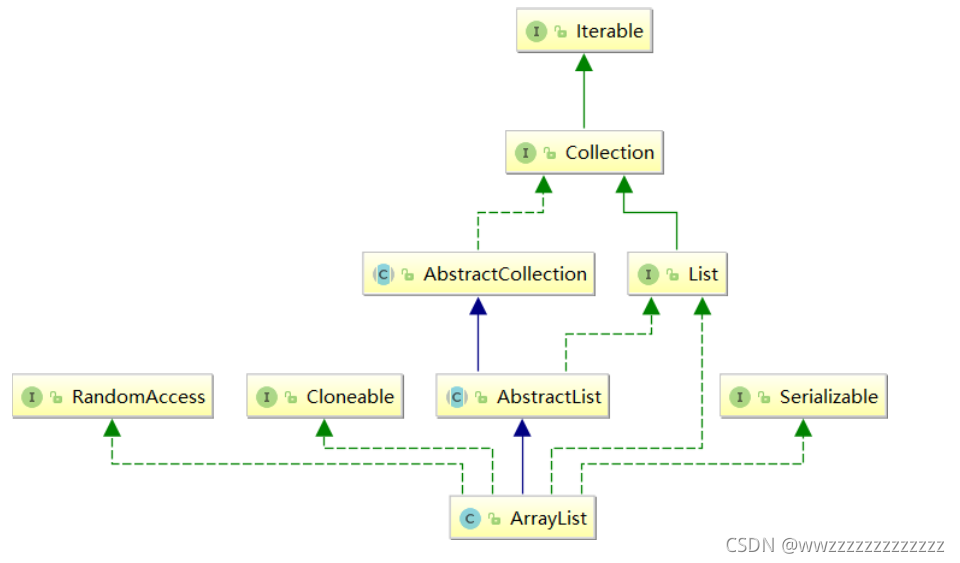
【说明】
1.ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问2.ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
3.ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
4.和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
5.ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
4 . ArrayList使用
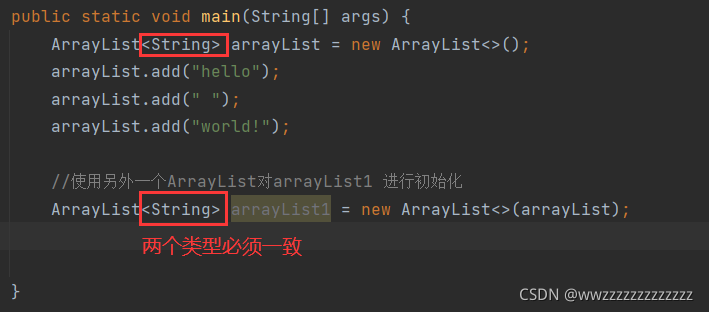
4.1 ArrayList的构造
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | 无参构造 |
| ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) | 利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList |
| ArrayList(int initialCapacity) | 指定顺序表初始容量 |
4.2 ArrayList的遍历
有三种遍历方式:for循环,foreach,迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("hello");
arrayList.add("+");
arrayList.add("world!");
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("======1.for循环======");
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(arrayList.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======2.foreach======");
for (String s:arrayList) {
System.out.print(s+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======3.使用迭代器的方法======");
Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======4.迭代器List相关打印======");
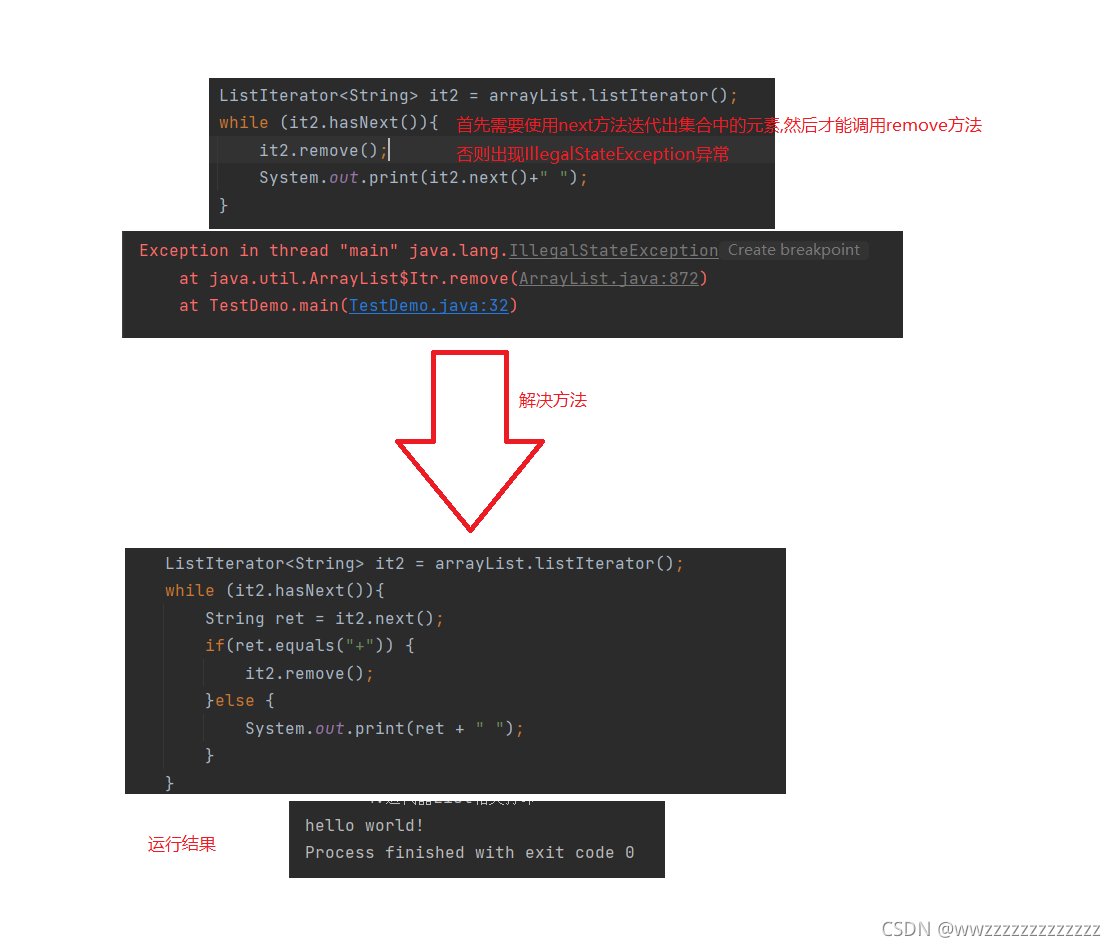
ListIterator<String> it2 = arrayList.listIterator();
while (it2.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it2.next()+" ");
}
4.2.1 迭代器 Iterator ListIterator
4.3 ArrayList常见操作
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
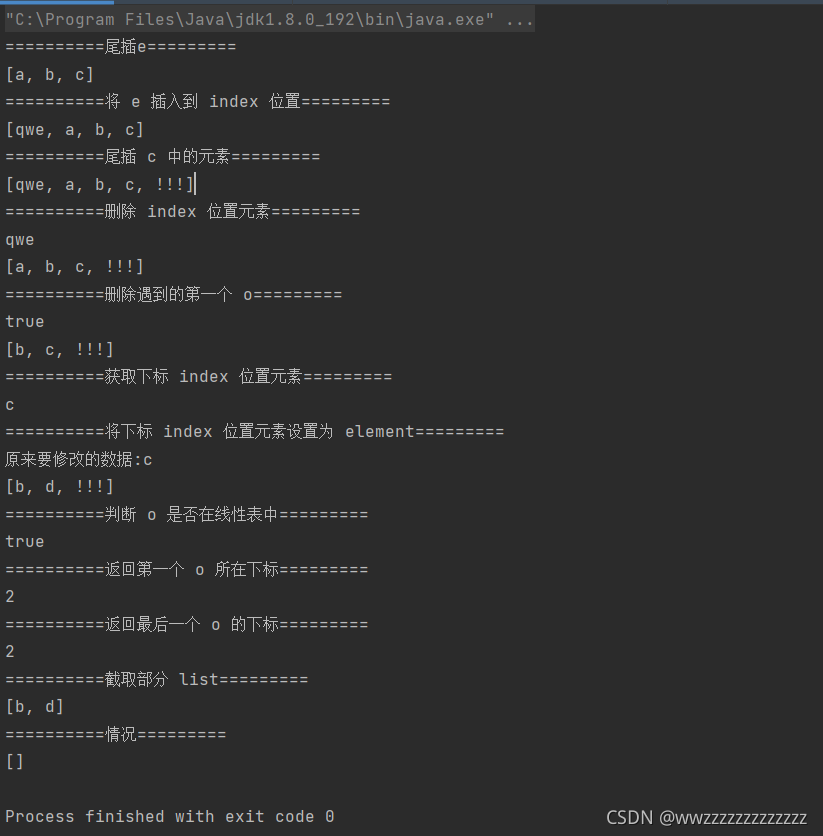
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("==========尾插e=========");
arrayList.add("a");
arrayList.add("b");
arrayList.add("c");
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("==========将 e 插入到 index 位置=========");
arrayList.add(0,"qwe");
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("==========尾插 c 中的元素=========");
ArrayList<String> arrayList1 = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList1.add("!!!");
arrayList.addAll(arrayList1);
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("==========删除 index 位置元素=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.remove(0));
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("==========删除遇到的第一个 o=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.remove("a"));
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("==========获取下标 index 位置元素=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.get(1));
System.out.println("==========将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element=========");
System.out.println("原来要修改的数据:"+arrayList.set(1,"d"));
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println("==========判断 o 是否在线性表中=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.contains("!!!"));
System.out.println("==========返回第一个 o 所在下标=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf("!!!"));
System.out.println("==========返回最后一个 o 的下标=========");
System.out.println(arrayList.lastIndexOf("!!!"));
System.out.println("==========截取部分 list=========");
List<String> sub = arrayList.subList(0,2);//左闭右开
System.out.println(sub);
System.out.println("==========情况=========");
arrayList.clear();
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
运行结果:
4.4 ArrayList的扩容机制

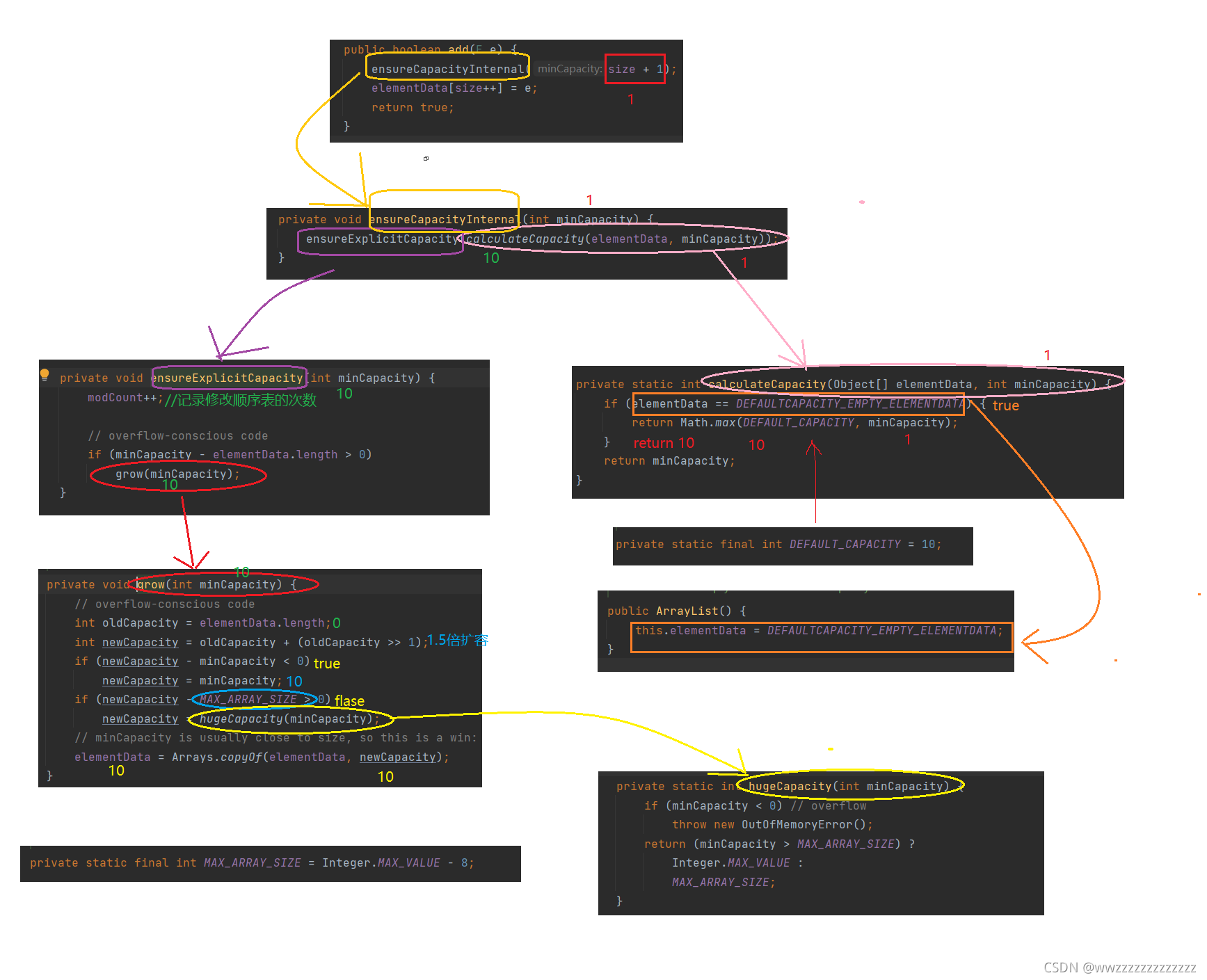
结论:
如果ArrayList调用无参的构造方法new ArrayList() , 那么顺序表的大小是0.当第一次add的时候, 整个顺序表才变为了10;
当这10个放满之后,才开始扩容,以1.5倍的方式扩容.
如果调用的是给定容量的构造方法new ArrayList(13) , 那么顺序表的大小就是给定容量的大小,如果放满了,还是以1.5倍进行扩容.
5 . ArrayList的使用示例
5.1 ArrayList可以放自定义的数据类型
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Student{
private String name;
private String classes;
private double score;
public Student(String name, String classes, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.classes = classes;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClasses() {
return classes;
}
public void setClasses(String classes) {
this.classes = classes;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", classes='" + classes + '\'' +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
public class TestDemo10 {
public static void main1(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("niubi","102-1",98.9));
students.add(new Student("21e","123",22.2));
students.add(new Student("qwq","wqqe",455.4));
System.out.println(students);
}
}
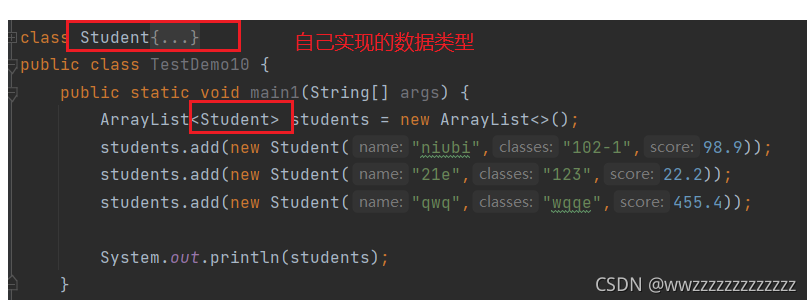
运行结果:

5.2 ArrayList可以对数据进行排序
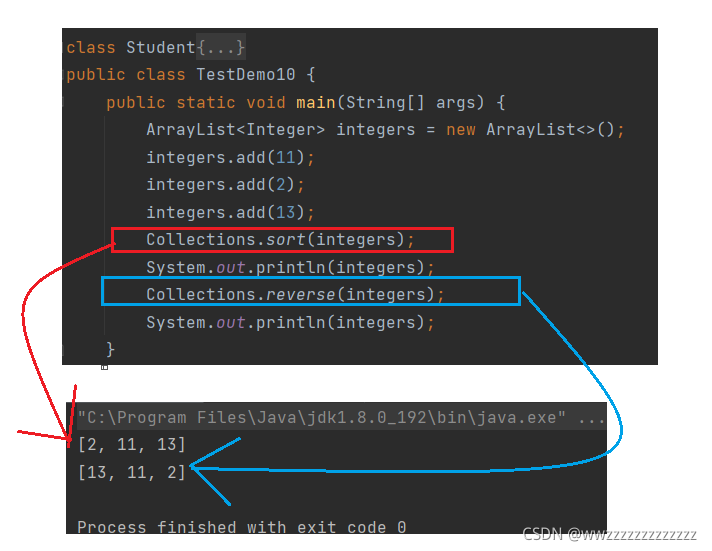
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>();
integers.add(11);
integers.add(2);
integers.add(13);
Collections.sort(integers);
System.out.println(integers);
}
运行结果:
5.3 删除第一个字符串当中的第二个字符串中的字符
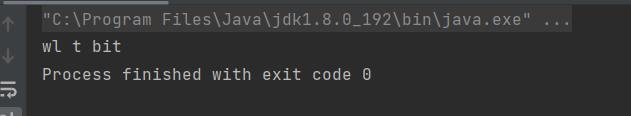
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "welcome to bit";
String str2 = "come";
ArrayList<Character> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
char ch = str1.charAt(i);
if(!str2.contains(ch+"")){
list1.add(ch);
}
}
for (char ch : list1 ) {
System.out.print(ch);
}
}
运行结果:
5.4 ArrayList实现的简易扑克牌
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
class Card{
private int rank;
private String suit;
public Card(int rank, String suit) {
this.rank = rank;
this.suit = suit;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(int rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
public String getSuit() {
return suit;
}
public void setSuit(String suit) {
this.suit = suit;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" + suit + "->" +rank + "}";
}
}
public class Test {
private static final String[] suits = {"?","?","?","?"};
/**
* 构造一副牌
* @return
*/
public static List<Card> buyCard(){
ArrayList<Card> cards = new ArrayList<>();
//四种花色
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//每个花色13张牌
for (int j = 0; j < 13; j++) {
/*String suit = suits[i];//花色
int rank = j ;//牌数
Card card = new Card(rank,suit);//得到一张牌card
cards.add(card);*/
cards.add(new Card(j,suits[i]));//优化后的代码
}
}
return cards;
}
private static void swap(List<Card> cards,int i,int j){
Card tmp = cards.get(i);
cards.set(i,cards.get(j));
cards.set(j,tmp);
}
/**
* 洗牌
* @param cards
*/
public static void shuffle(List<Card> cards){
int size = cards.size();
for (int i = size - 1; i > 0; i--) {
Random random = new Random();
int rand = random.nextInt(i);
swap(cards,i,rand);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Card> cards = buyCard();
System.out.println("刚开始的牌:"+cards);
shuffle(cards);
System.out.println("洗过后的牌:"+cards);
ArrayList<List<Card>> hand = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand3 = new ArrayList<>();
hand.add(hand1);
hand.add(hand2);
hand.add(hand3);
//每个人,轮流揭牌
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cards.remove(0);//拿一张牌 少一张牌 remov去掉
hand.get(j).add(card);
}
}
System.out.println("第1个人的牌: "+hand1);
System.out.println("第2个人的牌: "+hand2);
System.out.println("第3个人的牌: "+hand3);
System.out.println("剩余的排: "+cards);
}
}
6 . ArrayList的模拟实现
package demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
class MyArrayList<E> {
private Object[] elem;//数组
private int usedSize;//代表有效数据个数
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public MyArrayList(int capacity) {
//对参数进行一个判断
if (capacity > 0) {
this.elem = new Object[capacity];
} else if (capacity == 0) {
this.elem = new Object[0];
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("不能为负数!");
}
}
/**
* 尾插 e
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//缺点一个真正的容量.扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(usedSize + 1);
elem[usedSize] = e;
usedSize++;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//计算出需要的容量
int capacity = calculateCapacity(elem, minCapacity);
//拿着计算出的容量,去判断是否扩容,需要扩容就扩容
ensureExplicitCapacity(capacity);
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elem, int minCapacity) {
//1.是否elem数组分配过大小
if (elem == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(10, minCapacity);
}
//2.分配过 就返回+1的值
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity - elem.length > 0) {
//扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elem.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//1.5倍扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
//说明需要的容量非常大
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
/**
* 将 e 插入到 index 位置
*
* @param index
* @param e
*/
public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(usedSize + 1);
copy(index, e);
usedSize++;
}
private void copy(int index, E e) {
for (int i = usedSize - 1; i >= index; i--) {
elem[i + 1] = elem[i];
}
elem[index] = e;
}
/**
* 判断index位置是否合法
*
* @param index
*/
public void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index位置不合法无法插入");
}
}
/**
* 获取顺序表的大小
*
* @return
*/
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
/**
* 获取o第一次出现的位置
*
* @param o
* @return
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (null == o) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i].equals(o)) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 删出第一次出现的e
*
* @param o
* @return
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int index = indexOf(o);
if (index == -1) {
return false;
}
remove(index);
return true;
}
/**
* 删除index位置上元素
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
E e = (E) elem[index];
// 将index之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; ++i) {
elem[i] = elem[i + 1];
}
elem[usedSize] = null;
usedSize--;
return e;
}
/**
* 获取index位置上的元素
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return (E) elem[index];
}
/**
* 将index位置上元素设置为e
*
* @param index
* @param e
* @return
*/
public E set(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
elem[index] = e;
return e;
}
/**
* 清空
*/
public void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
elem[i] = null;
}
usedSize = 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String s = "[";
if (usedSize > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
s += elem[i];
s += ", ";
}
s += elem[usedSize - 1];
}
s += "]";
return s;
}
}
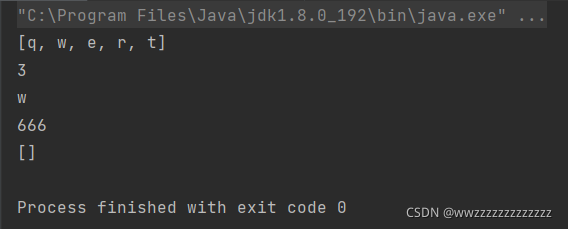
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList<String> list = new MyArrayList<>();
list.add("q");
list.add("w");
list.add("e");
list.add("r");
list.add("t");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.indexOf("r"));
System.out.println(list.get(1));
System.out.println(list.set(5, "666"));
list.clear();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
运行结果:
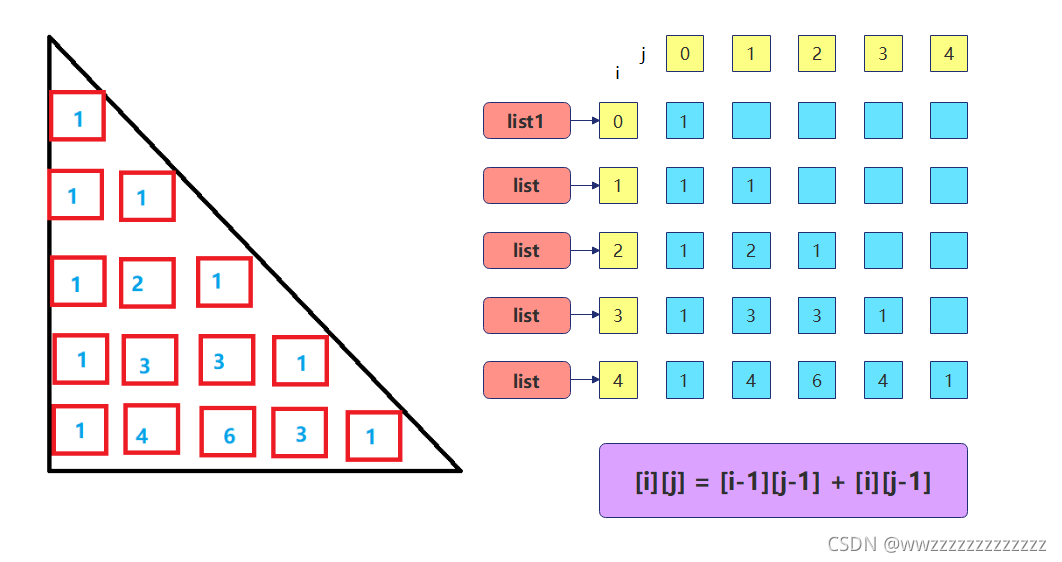
7 . 解决杨辉三角题
LeetCode 118:杨辉三角
描述:
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。


解题思路:
1.第一行永远为1,提前让第一行为1.
2.从第二行开始,首尾都是1,中间的是由上一层该位置和前一个位置的和组成
3.杨辉三角每一层数的个数和层数相同
画图解析:
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
//第一行 永远为1的情况:
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(1);
ret.add(list1);
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);//每一行的开头
//中间情况
List<Integer> preRows = ret.get(i-1);//上一行
for (int j = 1; j < i ; j++) {
int num1 = preRows.get(i) + preRows.get(j-1);
list.add(num1);
}
list.add(1);//每一行的末尾
ret.add(list);//将这一行放入list
}
return ret;
}