📢博客主页:🏀敲代码的布莱恩特🏀
📢欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ?留言 📝 欢迎讨论!👏
📢本文由 【敲代码的布莱恩特】 原创,首发于 CSDN🙉🙉🙉
📢由于博主是在学小白一枚,难免会有错误,有任何问题欢迎评论区留言指出,感激不尽!?
📖精品专栏(不定时更新)【JavaSE】 【Java数据结构】【LeetCode】

【Java数据结构】二叉树进阶——非递归实现前中后序遍历二叉树+进阶大厂面试题
🗽非递归实现遍历二叉树(深入理解二叉树)
- 代码每行都有注释,可以一步一步的画着图走一走,多走几遍,理解会上一个档次!
- 前序遍历和中序遍历都用到栈,代码可以说一模一样,只不过打印节点的时机不一样
?非递归前序遍历
// 非递归实现前序遍历
public void FDG_reOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) {//先判断根节点是否空
return;//第一个根节点如果空的话,就直接返回了
}
TreeNode cur = root;//设置临时节点cur,通过这个节点来遍历整棵树
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();//创建一个栈
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {//外循环,先写内循环采写外循环,只要栈不为空,说明还没遍历完成
while (cur != null) {//内循环
stack.push(cur);//将当前cur节点入栈
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");//打印cur节点,前序遍历是在入栈后打印
cur = cur.left;//cur走到原节点的左孩子节点
}
//当左子树走完,cur.left肯定会走到空节点,这时候就要走右子树了
TreeNode top = stack.pop();//弹出栈顶节点,注意是弹出,不然会影响后遍历上一个节点的右孩子节点
cur = top.right;//cur走到上一个节点的右孩子节点
}
//栈空了,说明遍历完了所有节点
System.out.println();
}
?非递归中序遍历
// 非递归实现中序遍历
public void FDG_inOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {//先判断根节点是否空
return;//第一个根节点如果空的话,就直接返回了
}
TreeNode cur = root;//设置临时节点cur,通过这个节点来遍历整棵树
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();//创建一个栈
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {//外循环,先写内循环采写外循环,只要栈不为空,说明还没遍历完成
while (cur != null) {//内循环
stack.push(cur);//将当前cur节点入栈,但不打印,需要用它来找左右孩子节点
cur = cur.left;//cur走到原节点的左孩子节点
}
//当左子树走完,cur.left肯定会走到空节点,这时候就要走右子树了
TreeNode top = stack.pop();//弹出栈顶节点,注意是弹出,不然会影响后遍历上一个节点的右孩子节点
System.out.print(top.value+" ");//打印cur节点,中序遍历是在节点出栈后打印
cur = top.right;//cur走到上一个节点的右孩子节点
}
//栈空了,说明遍历完了所有节点
System.out.println();
}
?非递归后序遍历
//非递归后续遍历
public void postOrderTraversalNor(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;//第一个根节点如果空的话,就直接返回了
TreeNode cur = root;//设置临时节点cur,通过这个节点来遍历整棵树
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();//创建一个栈
TreeNode pre = null;//用来指定 上一个被打印的元素
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {//外循环,只要栈不为空,说明还没遍历完成
while (cur != null) {//内循环
stack.push(cur);//将当前cur节点入栈,但不打印,需要用它来找左右孩子节点
cur = cur.left;//cur走到原节点的左孩子节点
}
cur = stack.peek();//查看栈顶节点
if (cur.right == null || cur.right == pre) {//如果栈顶节点的右节点为空,或者已经遍历过了
TreeNode popNode = stack.pop();//弹出栈顶节点并打印
System.out.print(popNode.value + " ");
pre = cur;//用pre将遍历(打印)过的节点记录下来
cur = null;//cur要置空,不然就又来一遍了,置空后可以继续查看下一个栈顶节点而不进入内循环
} else {//若栈顶节点右节点不为空
cur = cur.right;//则遍历这个右节点
}
}
System.out.println();
}
🗽大厂OJ面试题
🎄1. 二叉树的构建及遍历
题目:
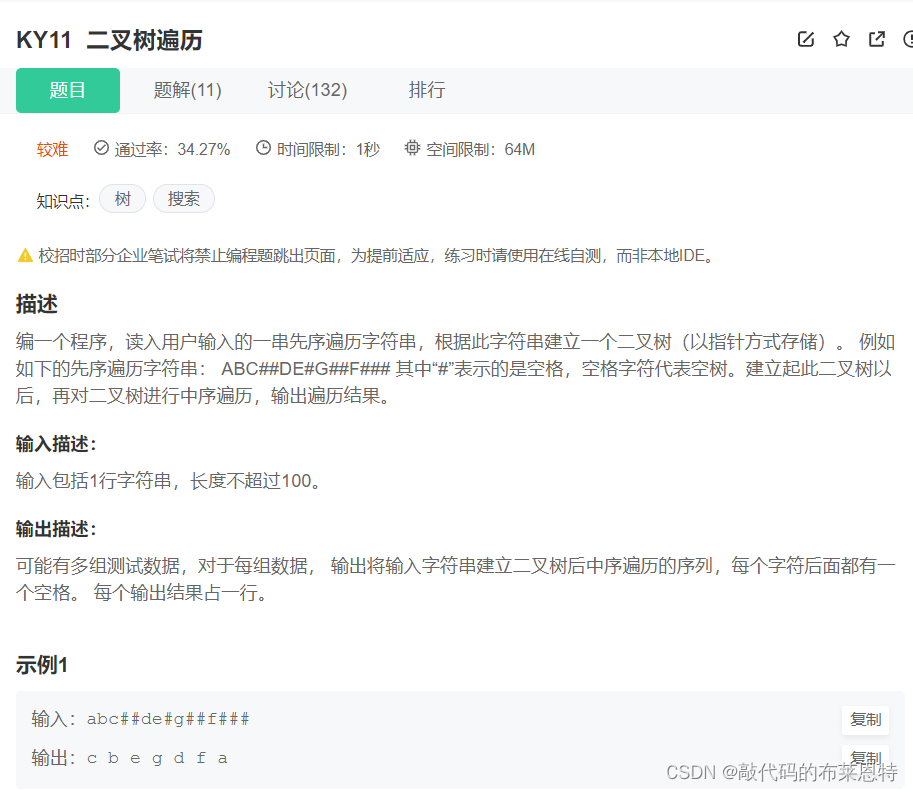
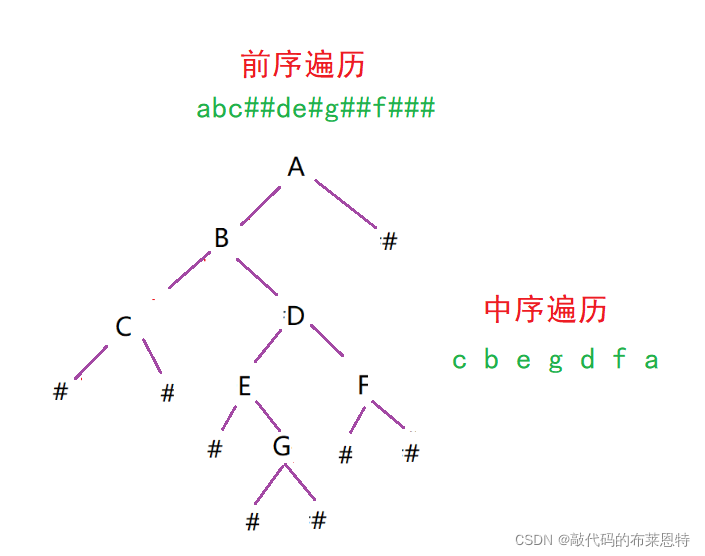
思路:
- 本题思路很简单,就是遍历字符串,因为这是根据前序遍历搞出来的字符串
- 所以构建二叉树,也要根据这个 根->左节点->右节点 的顺序来构建
实现代码:
import java.util.*;
//题目啥也没给,节点类也要自己定义一下
class TreeNode{
char value;//节点有值
TreeNode left;//有左孩子节点
TreeNode right;//有右孩子节点
public TreeNode(char value){//构造函数,用于给节点赋值
this.value = value;
}
}
public class Main{
//主函数,用于输入字符串,主要在creatTree方法里来实现
public static void main(String[]args){
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scn.nextLine();
TreeNode root = creatTree(str);
inOrderTraveled(root);
}
public static int i = 0;//i用于记录字符串中字符的下标
//因为构建过程是递归的,不能用局部变量,所以要在外部设置成静态的
public static TreeNode creatTree(String str){
if(str==null){//如果字符串为空
return null;//直接返回null
}
//字符串不为空,就进行构构建二叉树的过程
TreeNode root = null;//先创建一个根节点,指向空,这样做是为了初始化
if(str.charAt(i)!='#'){//依次读取字符串中的字符,不为 # 就进行二叉树构造
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));//将读取的字符给节点实例化
i++;//当前读取的字符被用过之后,字符串下标要往后走一位
root.left = creatTree(str);//递归构建左树
root.right = creatTree(str);//递归构建右树
}else{//读取到的字符是 # ,代表空节点,不用构建
i++;//字符串下标往后走一位
}
return root;//最后返回根节点即可
}
//对构建好的二叉树进行中序遍历,用递归实现就好了
public static void inOrderTraveled(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
inOrderTraveled(root.left);
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
inOrderTraveled(root.right);
}
}
🎄2. 二叉树的分层遍历
题目:
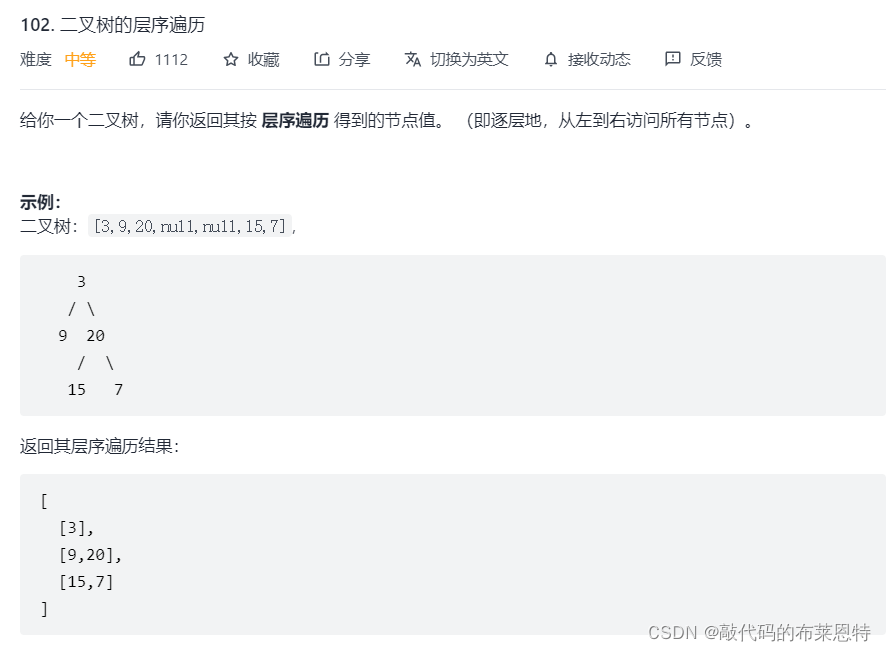
思路:
-
层序遍历就是一层一层的遍历节点
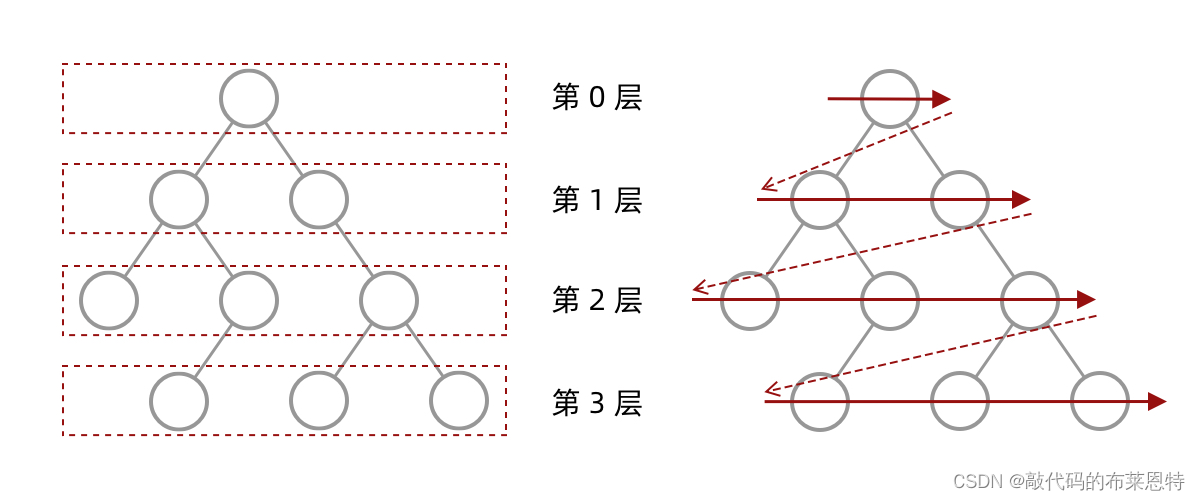
-
这题还有一个要求就是,输出的时候将一层的节点放在一行,下一层的节点放在下一行,这就需要用到一个
二维数组来储存每一层的节点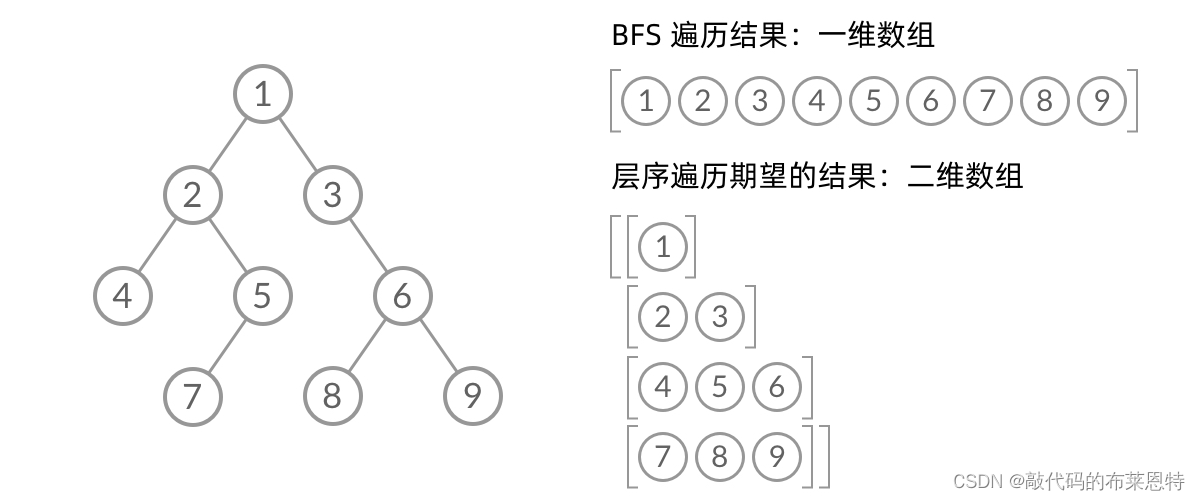
-
我们先来观察一下 层序遍历的过程中,结点进队列和出队列的过程: 请看图

-
可是如何知道当前访问到的节点是哪一层的呢? 截取 BFS 遍历过程中的某个时刻:
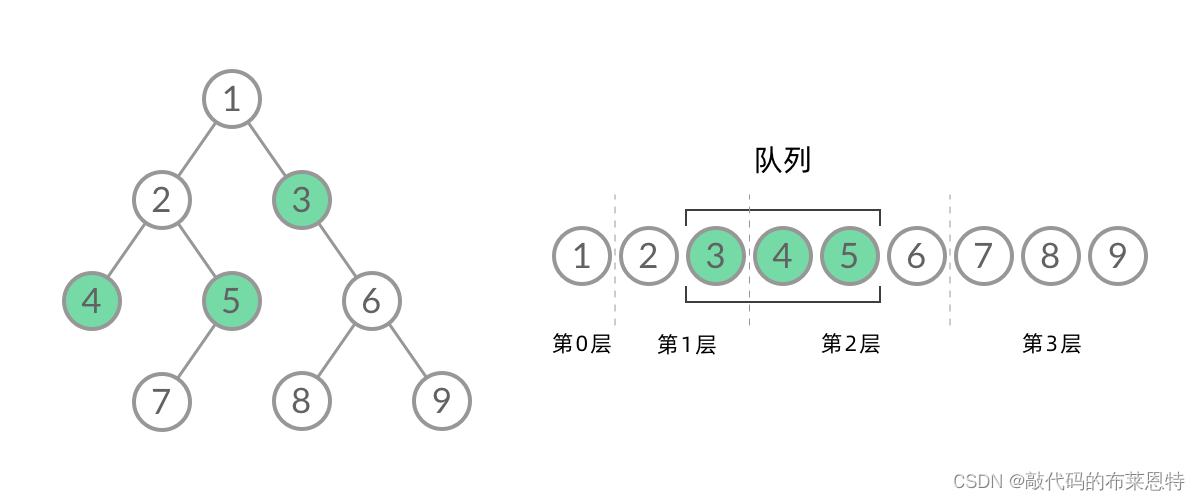
可以看到,此时队列中的结点是 3、4、5,分别来自第 1 层和第 2 层。这个时候,第 1 层的结点还没出完,第 2 层的结点就进来了,而且两层的结点在队列中紧挨在一起,我们无法区分队列中的结点来自哪一层。
因此,我们在每一层遍历开始前,先记录队列中的结点数量 n(也就是这一层的结点数量),然后一口气处理完这一层的 n 个结点。
实现代码:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//建立一个二维数组来记录每一层的情况
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();//用队列实现层序遍历
if (root==null){
return list;
}
queue.offer(root);//根节点先入队
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int n = queue.size();//记录每一层有多少个节点,循环n次
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList();//每一层用一个数组记录
for(int i = 0 ; i<n ; i++){//弹出当前层里的节点,
// 变量 i 无实际意义,只是为了循环 n 次
TreeNode top = queue.poll();//弹出队头节点
level.add(top.val);//将弹出的节点加入它所在的那一层
//弹出的时候不要忘了将弹出节点的孩子节点入队
if (top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if (top.right != null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
}
}
list.add(level);//将每一层添加到二维数组中
}
return list;//最后返回二维数组即为所求
}
}
🎄3. 给定一个二叉树,找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先
题目:

思路:
-
祖先的定义: 若节点 p 在节点 root 的左(右)子树中,或 p = root ,则称 root 是 p 的祖先。
-
根据以上定义,若 root 是 p,q 的 最近公共祖先 ,则只可能为以下情况之一:
①p 和 q 在 root的子树中,且分列 root 的 异侧(即分别在左、右子树中);
②p = root ,且 q 在 root 的左或右子树中;
③q = root ,且 p 在 root 的左或右子树中;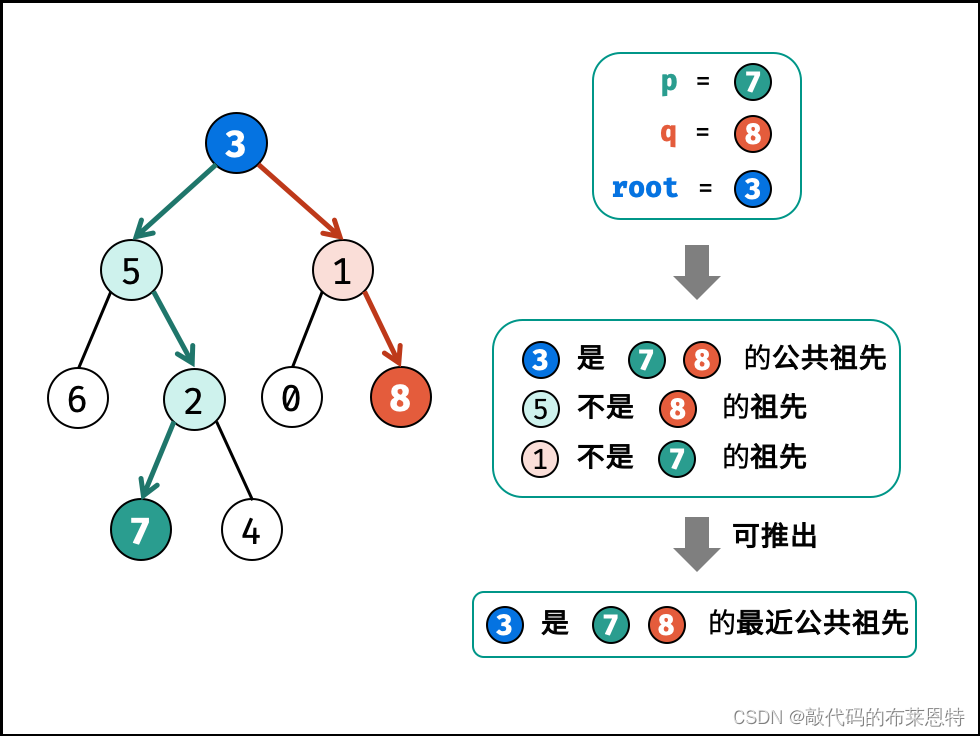
考虑通过递归对二叉树进行先序遍历,当遇到节点 p 或 q 时返回。从底至顶回溯,当节点 p,q 在节点 root的异侧时,节点 root 即为最近公共祖先,则向上返回 root 。

实现代码:
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null) return null;//根节点空的话,直接返回null,无公共祖先
if(root==p || root == q) return root;//如果q或者p就是根节点,那直接返回,此时他们就是最近公共祖先
//一开始的根节点不是祖先就往下遍历左右子树
//递归左树找目标点q和p,找到的话会返回找到的节点,没找到则返回空
TreeNode leftTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
//递归右树找目标点q和p,找到的话会返回找到的节点,没找到则返回空
TreeNode rightTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
//如果两边都找到了目标点(q/p)那么当前这个节点就是最近祖先
if(leftTree!=null && rightTree!=null){
return root;
}
//代码走到这里说明有一个为空(没找到目标点)
//只有左边找到了目标点(q/p),那当前根节点的左节点就是最近祖先
if(leftTree!=null){
return leftTree;
}
//只有右边找到了目标点(q/p),那当前根节点的右节点就是最近祖先
if(rightTree!=null){
return rightTree;
}
//没有找到目标点q或者p
return null;
}
}
🎄4. 二叉树搜索树转换成排序双向链表
题目:
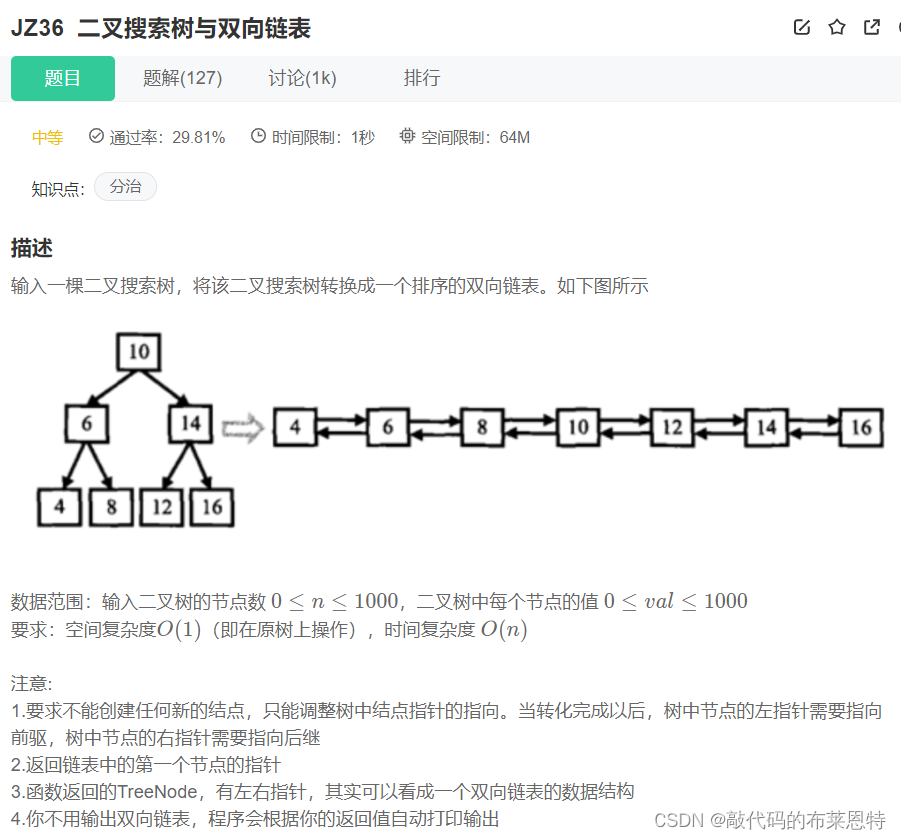
思路:
- 已知将二叉搜索树进行中序遍历可以得到
由小到大的顺序排列,因此本题最直接的想法就是进行中序遍历。 - 根据题目的要求1,不能创建新的结点,所以我们
设置一个pre用于指向前驱节点
例如root为指向10的时候,preNode指向8,如图所示: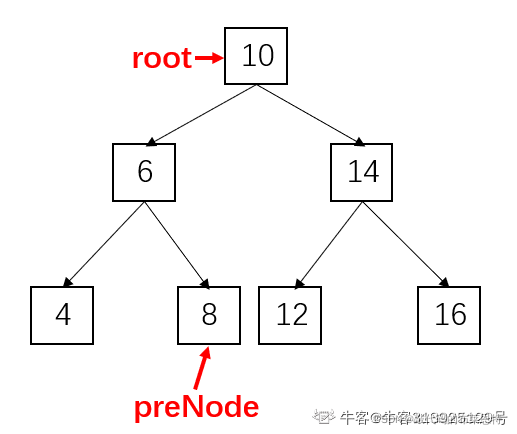
实现代码:
public class Solution {
public TreeNode pre = null;//因为是要递归,所以pre要设在外部
public void ConvertChild(TreeNode pcur) {
if(pcur==null){
return;
}
ConvertChild(pcur.left);//因为是中序遍历,所以先递归左节点
//处理根节点
//关键点
pcur.left=pre;//当前节点的左指针指向前驱节点
if(pre!=null){//如果前驱节点非空
pre.right=pcur;//前驱节点右指针指向当前节点
}
pre=pcur;//pre走到当前节点,也就是当前节点成为下一个节点的前驱节点
//三行代码,关键点
ConvertChild(pcur.right);//递归左节点
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null) return null;
ConvertChild(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head = pRootOfTree;
while(head.left!=null){
head=head.left;
}
return head;
}
}
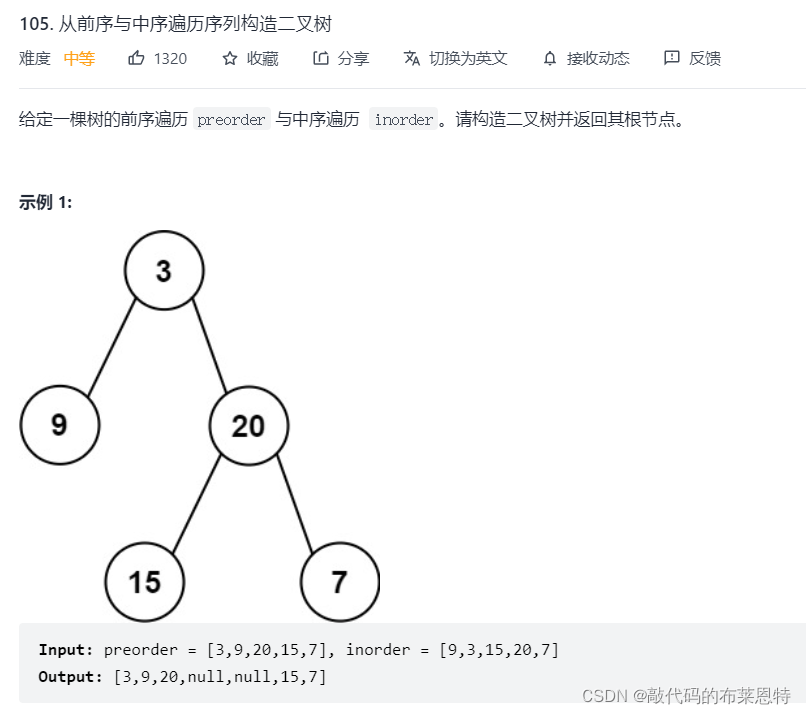
🎄5. 根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树
题目:
思路:
-
所以我们只需要根据先序遍历得到根节点,然后在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置,它的左边就是左子树的节点,右边就是右子树的节点。
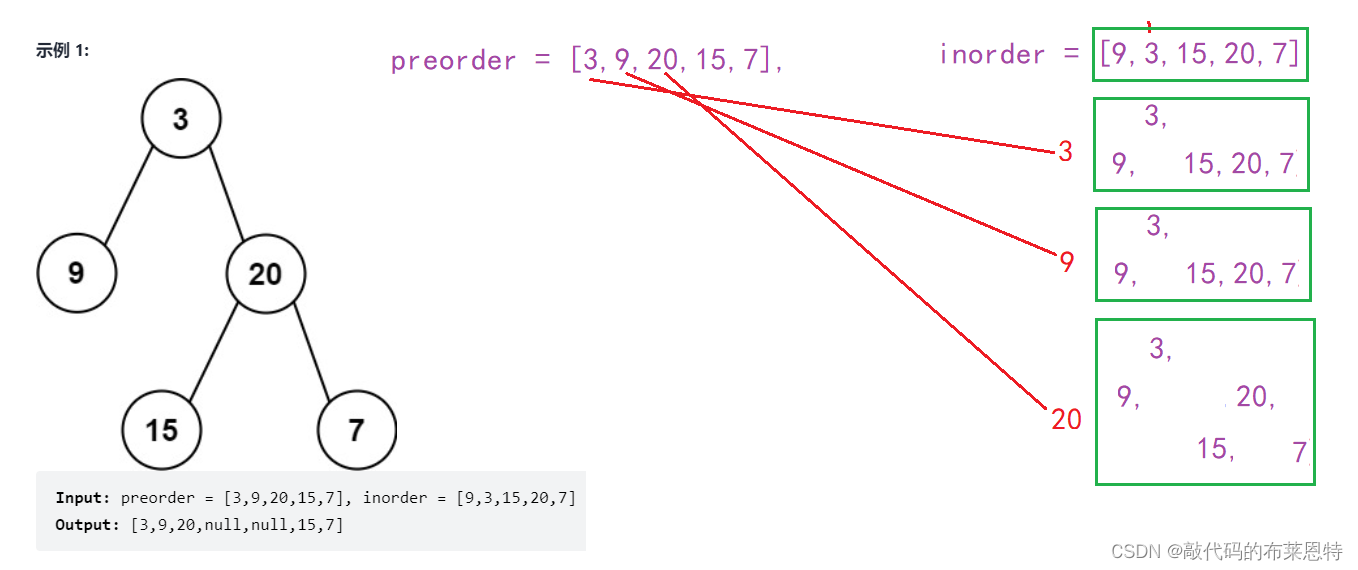
-
递归生成左子树和右子树

实现代码:
class Solution {
public int preindex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;//左树 或者 右树 为空
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preindex]);
//找根节点在中序遍历的数组中的结果
int rootIndex = findRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preindex]);
preindex++;
//构建 左树
root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
//构建 右树
root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
return root;
}
//就是一个数组当中的查找代码
public int findRootIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key) {
for(int i = inbegin;i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null) return null;
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
}
🎄6. 根据一棵树的中序遍历和后序遍历构造二叉树
题目:
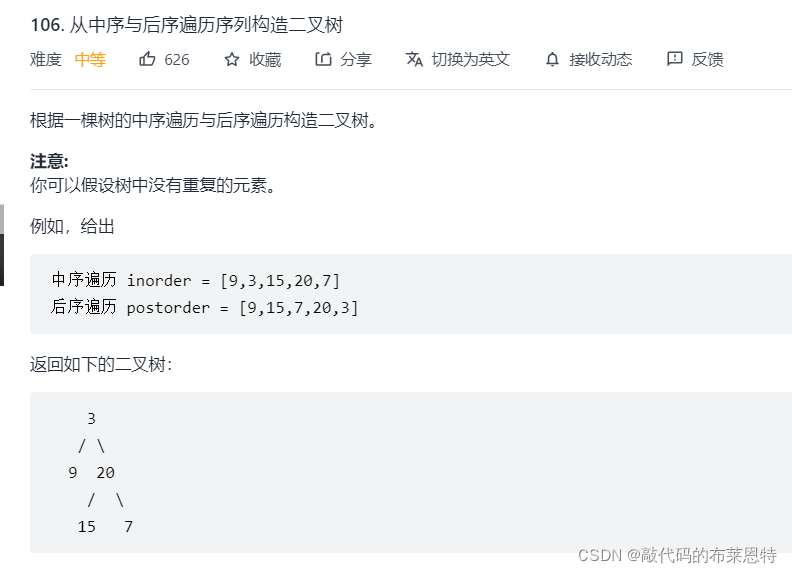
思路:
- 和上题几乎一样,只需要
几处小改动 - 因为是给的是
后续遍历,所以构建的时候,读取后续遍历数组要从后往前读取,并且构建的时候是根->右->左
实现代码:
class Solution {
public int postindex = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] postorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;//左树 或者 右树 为空
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postindex]);
//找根节点在中序遍历的数组中的结果
int rootIndex = findRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postindex]);
postindex--;//从后往前
//构建右树
root.right = buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
//构建左树
root.left = buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
return root;
}
//就是一个数组当中的查找代码
public int findRootIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key) {
for(int i = inbegin;i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
postindex = postorder.length-1;//将后序遍历数组的下标设为长度-1,即最后一个位置,好让其从后往前遍历数组
if(postorder == null || inorder == null) return null;
return buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
}
🎄7. 二叉树创建字符串
题目:

思路:
- 我们可以使用递归的方法得到二叉树的前序遍历。在递归时,根据题目描述,我们需要加上额外的括号,会有以下 4 种情况:
① 如果当前节点有两个孩子,那我们在递归时,需要在两个孩子的结果外都加上一层括号;
②如果当前节点没有孩子,那我们不需要在节点后面加上任何括号;
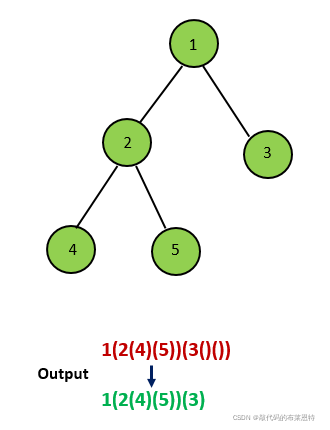
③如果当前节点只有左孩子,那我们在递归时,只需要在左孩子的结果外加上一层括号,而不需要给右孩子加上任何括号;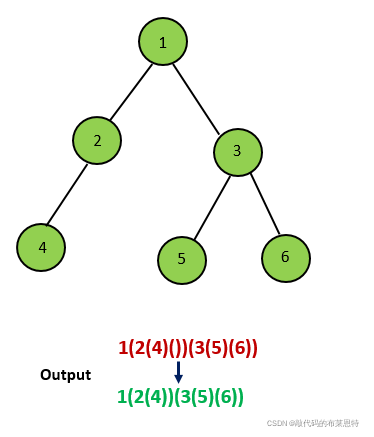
④如果当前节点只有右孩子,那我们在递归时,需要先加上一层空的括号 () 表示左孩子为空,再对右孩子进行递归,并在结果外加上一层括号。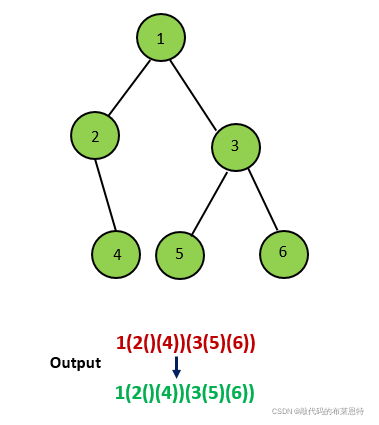
考虑完上面的 4 种情况,我们就可以得到最终的字符串。
实现代码:
class Solution {
public void tree2strChild(TreeNode root,StringBuilder sb) {
if(root == null) return ;
sb.append(root.val);//前序遍历,先将根节点加入可变字符串
if(root.left==null){//左树为空,还得考虑右树的情况
if(root.right==null){//如果右树为空,说明当前根节点没有孩子
//直接返回,因为题目要求把不必要的()省略
return;
}else{//右树不为空,加(),这里还在左树,这个()是表示左子树为空
//因为右树不为空,所有不能省略
sb.append("()");
}
}else{//左树不为空,先加(,然后继续遍历左树,再加)
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(root.left,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
//左树遍历完要遍历右树了
if(root.right==null){//如果右树为空
return;//直接返回,因为省略()不会影响字符串与树的映射关系
}else{//否则,先加(,然后继续遍历右树,再加)
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(root.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
}
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
tree2strChild(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
}
🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙
????????原创不易,如有错误,欢迎评论区留言指出,感激不尽?
???????????????????????如果觉得内容不错,给个三连不过分吧~ ?????? ?
????????????????????????????????????看到会回访~ ??????????????? ???????????????????? ?
🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙🌙