武汉大学 遥感院 数据结构实习
实习内容

1.CSV格式数据文件的读写
1)CSV文件格式:
cities.csv与routes.csv文件如下:
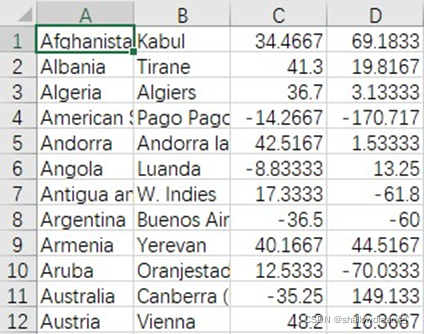
其中,第一列为国家名,第二列为城市名,第三列为城市所在纬度,第四列为城市所在经度。
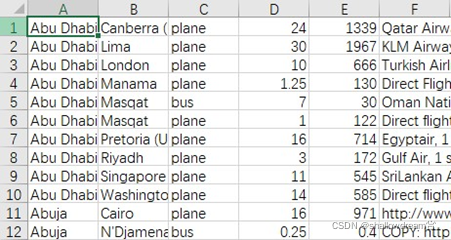
其中,第一列为出发城市,第二列为目的城市,第三列为交通方式,含飞机、火车、巴士三种,第四列为路程时间,第五列为路程费用,第六列为附加信息。
2)问题分析及数据结构:
针对该问题,首先需要建立世界城市网络模型,并且由于城市间往返交通属性不同,且同意线路可能具有多种方式,因此,可以使用带权有向图的模型来解决。其中,顶点即为城市,边(弧)即为两城市之间的交通线路。
由于城市数量较大,采用邻接矩阵的方法存储会消耗过多的内存,故在此采用邻接表的方式进行存储。
第一个结构体定义了城市信息,并重命名为CITIES,包含国家cNation,cCity,dLongitude, dLatitude。
typedef struct CITIES {
char cNation[64];
char cCity[64];
double dLongitude;
double dLatitude;
}CITIES;
第二个结构体定义了路径上的信息,并重命名为ROUTES,包含交通方式cTripMode,所需时间dTime,所需费用dCost 以及附加信息InfoType,城市起点以及终点cStartCity与cEndCity。
typedef struct ROUTES {
char cStartCity[64];
char cEndCity[64];
double dTime;
char cTripMode[16];
double dCost;
char InfoType[1024];
}ROUTES;
第三个结构体定义了边节点的信息,并重命名为
ArcNode,包含邻接的顶点nAdjvex,下一个邻接边指针 nextarc,路径信息结构体Information。
typedef struct ArcNode {
int nAdjvex;
struct ArcNode* nextArc;
ROUTES Information;
}ArcNode;
第四个结构体定义了顶点节点(头节点)的信息,并重命名为VNode以及一个顶点向量AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]。其中包含了顶点信息City,该顶点指向的第一个边节点 firstarc。
typedef struct VNode {
CITIES City;
ArcNode* Firstarc;
}AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
最后,给出图的定义,命名为ALGraph,其中包含该图的顶点向量vertices,顶点个数nVexnum,边个数nArcnum。
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices;
int nVexnum, nArcnum;
int Kind;
bool bFinal[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
}ALGraph;
3)创建城市链表
首先,先建立城市信息数组,由于城市个数不确定,且城市数量较大,采用数组表示法并不方便,而对于STL中的vector模板可较方便的存储未知数目的元素信息,因此,本算法中采取vector存储的方式存储城市信息。
同时注意到,csv文件本质上为逗号分隔值得文件,即两列信息中间以逗号进行分隔,故考虑采用 strtok()函数进行取值。
CITIES* CreateCitiesArray(FILE* Fp) {//该函数用于制作城市表,从city.csv中读取城市信息
if (SuccessfulOpen(Fp)) {
cout << "failed to open file for reading" << endl;
return NULL;
}
int nLine = FindLinesInCSV(Fp);
char* pcLine=NULL;
char* cFinal = NULL;
struct CITIES* pCity = new CITIES[nLine];
char cLine[256] = {0};
fseek(Fp, 0, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < nLine; j++) {
pcLine = fgets(cLine, 256, Fp);
cFinal = strtok(pcLine, ",");
while (cFinal != NULL) {
strcpy(pCity[j].cNation, cFinal);//国家
cFinal = strtok(NULL, ",");
strcpy(pCity[j].cCity, cFinal);//首都
cFinal = strtok(NULL, ",");
pCity[j].dLatitude = atof(cFinal);//纬度
cFinal = strtok(NULL, ",");
pCity[j].dLongitude = atof(cFinal);//经度
cFinal = strtok(NULL, ",");
}
}
return pCity;
}
建立好城市信息表后,将城市之间的交通信息以带权有向图的方式存入G中。由于route.csv文件中给出的是具体的城市名,不便于在图G中存储信息,故先创建一个函数SearchCity()读取某城市在城市表city中的下标,从而将图中的城市信息与city中的城市信息相对应。
int SearchCitiesSerialNumber(char* Temp, CITIES* pCity, FILE* Fp) {
fseek(Fp, 0, 0);//将文件指针重新指向文件开头
int nLine = FindLinesInCSV(Fp);//得到文件中共有几行数据
for (int i = 0; i < nLine; i++) {
if (!strcmp(pCity[i].cCity, Temp))return i;
}
return -1;
}
2.创建图
此时根据边信息创建网图G。同样,由于routes.csv文件也是逗号分隔值文件,故采用strtok()获取值。
void CreateGraph(ALGraph& G, CITIES* pCity,FILE*pCitiesFile,FILE*pRoutesFile) {
G.nVexnum = FindLinesInCSV(pCitiesFile);//得到城市的个数即为图顶点的个数
G.nArcnum = 0;//将图的边的个数初始化为0
for (int i = 0; i < G.nVexnum; i++) {
G.vertices[i].City = pCity[i];//将城市的信息传给图
G.vertices[i].Firstarc = NULL;//将头节点初始化为NULL
}
if (SuccessfulOpen(pRoutesFile)) {
cout << "Filed to open this File" << endl;
return;
}
char* pcRecord = NULL;
char* pcLine = NULL;
char cBuffer[1024];//缓冲区域
int nLine = FindLinesInCSV(pRoutesFile);//得到边的个数
fseek(pRoutesFile, 0, 0);//将文件指针重新指向文件头
for (int j = 0; j < nLine; j++) {//依次向图中录入信息
pcLine = fgets(cBuffer, 1024, pRoutesFile);
pcRecord = strtok(cBuffer, ",");
int nStrat, nEnd;
ArcNode* pArc = new ArcNode();
pArc->nextArc = NULL;
char cTemp[1024];
strcpy(cTemp, pcRecord);
nStrat = SearchCitiesSerialNumber(cTemp, pCity, pCitiesFile);
pcRecord = strtok(NULL, ",");
strcpy(cTemp, pcRecord);
nEnd = SearchCitiesSerialNumber(cTemp, pCity, pCitiesFile);
pArc->nAdjvex = nEnd;
pcRecord = strtok(NULL, ",");
strcpy(cTemp, pcRecord);
strcpy(pArc->Information.cTripMode, cTemp);
pcRecord = strtok(NULL, ",");
strcpy(cTemp, pcRecord);
pArc->Information.dTime = atof(cTemp);
pcRecord = strtok(NULL, ",");
strcpy(cTemp, pcRecord);
pArc->Information.dCost = atof(cTemp);
pcRecord = strtok(NULL, "\n");
strcpy(cTemp, pcRecord);
strcpy(pArc->Information.InfoType, cTemp);
pcRecord = strtok(NULL, "\n");
if (G.vertices[nStrat].Firstarc == NULL) G.vertices[nStrat].Firstarc = pArc;
else {//创建邻接表
ArcNode* pTemp = G.vertices[nStrat].Firstarc;
while (pTemp->nextArc)
pTemp = pTemp->nextArc;
pTemp->nextArc = pArc;
G.nArcnum++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_VERTEX_NUM; i++) {
G.bFinal[i] = false;
}
return;
}
3.寻找最短路径
1)Dijkstra算法寻找最短路径
首先引入辅助变量D,其每个分量D[i]表示当前所找到的由起点v0到其他顶点vi的最短路径长度。
在本例中,其定义为:
typedef double dShortPath[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
值得注意的是,D的值是在不断更新并且逼近最终结果的,过程中并不一定等于最短路径。
D[i]的初始状态为从v0到vi弧的权值,如果该两顶点间无弧,则D[i] = ∞。
此时,长度为D[j] = Min{D|vi∈v}的路径就是从 v0出发到vj的长度最短的一条路径,此路径为(v,vj)。下一条长度次短的是从v0到下一个顶点的最短路径所对应的顶点,且这条最短路径长度仅次于从v0 到vj的最短路径长度。
假设该路径次短路径的终点为vk,则该路径只可能为(v0,vk)或者(v0,vj,vk)。
根据以上算法过程可以证明,假设S为已求得从 v0出发的最短路径长度的顶点的集合,则下一条终点为v的次短路径,其路径要么是弧(v0,v),要么是从v0出发只经过S中的若干顶点最后到达v,则该最短路径长度D[j] = Min{D[i]|vi∈v-S},其中D[i]是弧(v,vi)
的权值或Dk和弧(vk,vi)权值之和的较小值。由于需要记录最短路径,故建立一个数组,在每次求得最短路径值时,保存上一个顶点的下标值。若
无上一个顶点,即为起点或不经过该点,则保存为-1。
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 199
typedef double dShortPath[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int nPath[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
2)算法实现
由于两个城市间的交通线路权值有多样性包括时间time和费用money,且两个城市间交通方式的多样性,例如飞机plane和火车train均能到达,则必然有最优路径的选择,故创建一个函数GetWeight(),根据用户不同的需求,返回不同的权值。
double GetWeight(ALGraph G, int nStart, int nEnd, char cKind) {
double dMin = INFINITY*1.0;
if (cKind == 'T') {
ArcNode* pT = G.vertices[nStart].Firstarc;
for (; pT != NULL; pT = pT->nextArc) {
if (pT->nAdjvex == nEnd) {
if (pT->Information.dTime < dMin) dMin = pT->Information.dTime;
}
}
return dMin;
}
if (cKind == 'M') {
ArcNode* pM = G.vertices[nStart].Firstarc;
for (; pM != NULL; pM = pM->nextArc) {
if (pM->nAdjvex == nEnd) {
if (pM->Information.dCost < dMin) dMin = pM->Information.dCost;
}
}
return dMin;
}
}
在此基础之上,进行迪杰斯特拉算法。代码如下:
void ObtainOptimalPath(ALGraph G,int nStart,dShortPath &dSP,char cKind) {
double dMin;
int nVex;
cout << G.vertices[nStart].City.cCity << "-->";
for (nVex = 0; nVex < G.nVexnum; nVex++) {//初始化各项的值
G.bFinal[nVex] = false;
dSP[nVex] = GetWeight(G, nStart, nVex, cKind);
nPath[nVex] = -1;
}
dSP[nStart] = 0;
G.bFinal[nStart] = true;
for (int k = 1; k < G.nVexnum; k++) {
dMin = INFINITY;//当前所知离v0顶点的最近距离
for (int j = 0; j < G.nVexnum; j++) {
if (!G.bFinal[j] && dSP[j] < dMin) {//w顶点离v0顶点更近
nVex = j;
dMin = dSP[j];
}
}
G.bFinal[nVex] = true;//离v0顶点最近的v的final[v]置为1
for (int j = 0; j < G.nVexnum; j++) {//更新当前最短路径及距离
if (!G.bFinal[j] && (dMin + GetWeight(G, nVex, j, cKind) < dSP[j])) {
dSP[j] = dMin + GetWeight(G, nVex, j, cKind);
nPath[j] = nVex;//记录到达w路径的上一个顶点v值
}
}
}
return;
}
4.递归遍历图
递归深度优先遍历图:
简述算法过程
1、任选一顶点作始点 v ,访问该顶点
2、沿深度方向,依次遍历 v 的未访问邻接点——直到本次遍历结束
3、一次遍历完时,若有未访问顶点:任选一个未访问顶点作起始点,GOTO第二步
void DFS_AL(ALGraph &G, int v) {//深度优先搜索
cout << G.vertices[v].City.cCity;
if (!G.bFinal[v]) cout << "-->";
G.bFinal[v] = true;
ArcNode* p;
p = G.vertices[v].Firstarc;
while (p != NULL) { //遍历节点的所有相邻点
int w = p->nAdjvex;
if (!G.bFinal[w])
DFS_AL(G, w);//递归遍历
p = p->nextArc;
}
}
输出路径:
void GetArc(ALGraph G, int w1, int w2, ArcNode& Arc) {
ArcNode* pT = G.vertices[w1].Firstarc;
for (; pT != NULL; pT = pT->nextArc) {
if (pT->nAdjvex == w2) {
Arc = *pT;
cout << G.vertices[w2].City.cCity<<"--->";
}
}
}
5.可视化输出
可视化输出用到html语言
根据htm文件格式,可以格式化输出htm文件,以
可视化的输出最短路径。
由上述分析可知,Path[]中存储的是每个节点在该路径中上一个结点的下标,即倒序存储。而我们需要顺序的输出其路径,故在此采用栈的存储方式,栈底为终点,栈顶为起点,并依次pop()出来。代码如下:
void MapVisualOutPut(char* cStart,char* cDest,CITIES*pCity,FILE*pCitiesFile,ALGraph G,char cKind) {
FILE* fP = fopen(FILEVISUALOUTPUTPATH, "w+t");
fprintf(fP, "<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><style type ='text/css'>body, html{width: 100%%; height: 100%%;margin : 0; font-family:'微软雅黑';}#allmap{height:100%%;width:100%%;}#r-result{width:100%%;}</style><script type = 'text/javascript' src = 'http://api.map.baidu.com/api?v=2.0&ak=nSxiPohfziUaCuONe4ViUP2N'></script><title>Shortest path from %s to %s</title></head><body><div id = 'allmap'></div></div></body></html><script type = 'text/javascript'>var map = new BMap.Map('allmap'); var point = new BMap.Point(0,0); map.centerAndZoom(point,2); map.enableScrollWheelZoom(true); ", cStart, cDest);
int j = 0;
int nDest = SearchCitiesSerialNumber(cDest, pCity, pCitiesFile);
int nStart = SearchCitiesSerialNumber(cStart, pCity, pCitiesFile);
stack<int>qStack;
while (nPath[nDest]!=-1)
{
qStack.push(nDest);
nDest = nPath[nDest];
}
qStack.push(nDest);
qStack.push(nStart);
cout << "The shortest path from " << cStart << " to " << cDest << " is :";
cout << cStart << "--->";
while (qStack.size() != 1) {
int w1 = qStack.top();
qStack.pop();
int w2 = qStack.top();
ArcNode Arc;
GetArc(G, w1, w2, Arc);
fprintf(fP, "var marker%d = new BMap.Marker(new BMap.Point(%.4f, %.4f));map.addOverlay(marker%d);\n", j, G.vertices[w1].City.dLongitude, G.vertices[w1].City.dLatitude, j);
fprintf(fP, "var infoWindow%d = new BMap.InfoWindow(\"<p style = 'font-size:14px;'>country: %s<br/>city : %s</p>\");marker%d.addEventListener(\"click\",function(){this.openInfoWindow(infoWindow%d);});var marker%d = new BMap.Marker(new BMap.Point(%.4f, %.4f));map.addOverlay(marker%d);\n", j, G.vertices[w1].City.cNation, G.vertices[w1].City.cCity, j, j, j + 1, G.vertices[w2].City.dLongitude, G.vertices[w2].City.dLatitude, j + 1);
fprintf(fP, "var infoWindow%d = new BMap.InfoWindow(\"<p style ='font-size:14px;'>country: %s<br/>city : %s</p>\");marker%d.addEventListener(\"click\",function(){this.openInfoWindow(infoWindow%d);});var contentString%.2d = '%s, %s --> %s, %s (%s - %.2f hours - $%f - \"%s\")';var path%d = new BMap.Polyline([new BMap.Point(%.4f, %.4f),new BMap.Point(%.4f, %.4f)], {strokeColor:'#18a45b',strokeWeight:8, strokeOpacity:0.8});map.addOverlay(path%d);path%d.addEventListener(\"click\",function(){alert(contentString%.2d);});", j + 1, G.vertices[w2].City.cNation,G.vertices[w2].City.cCity, j + 1, j + 1, j + 1, G.vertices[w1].City.cCity, G.vertices[w1].City.cNation, G.vertices[w2].City.cCity, G.vertices[w2].City.cNation, Arc.Information.cTripMode, Arc.Information.dTime, Arc.Information.dCost, Arc.Information.InfoType, j + 1, G.vertices[w1].City.dLongitude, G.vertices[w1].City.dLatitude, G.vertices[w2].City.dLongitude, G.vertices[w2].City.dLatitude, j + 1, j + 1, j + 1);
j++;
}
cout << "END" << endl;
fprintf(fP, "</script>");
}
6.结果
程序运行结果:
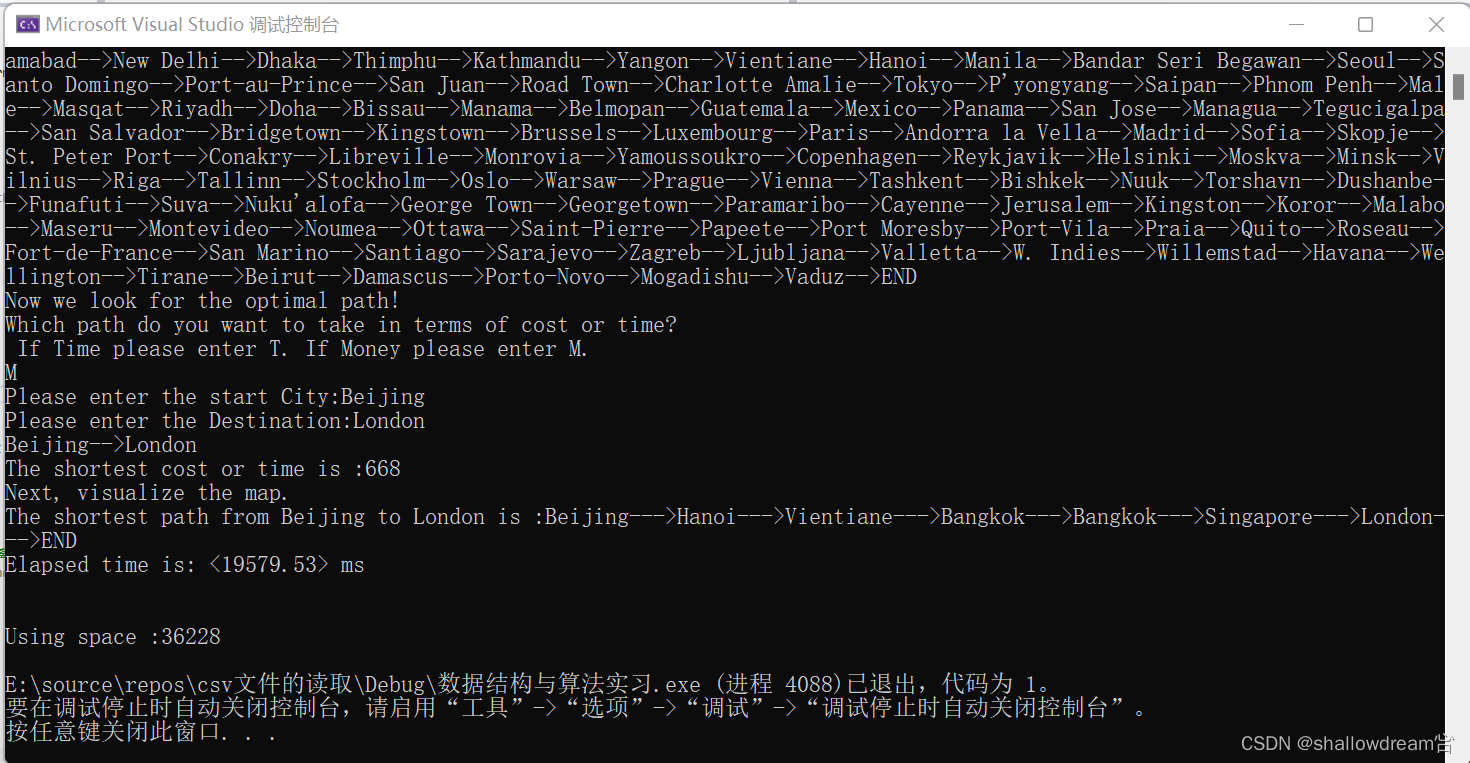
可视化输出结果:
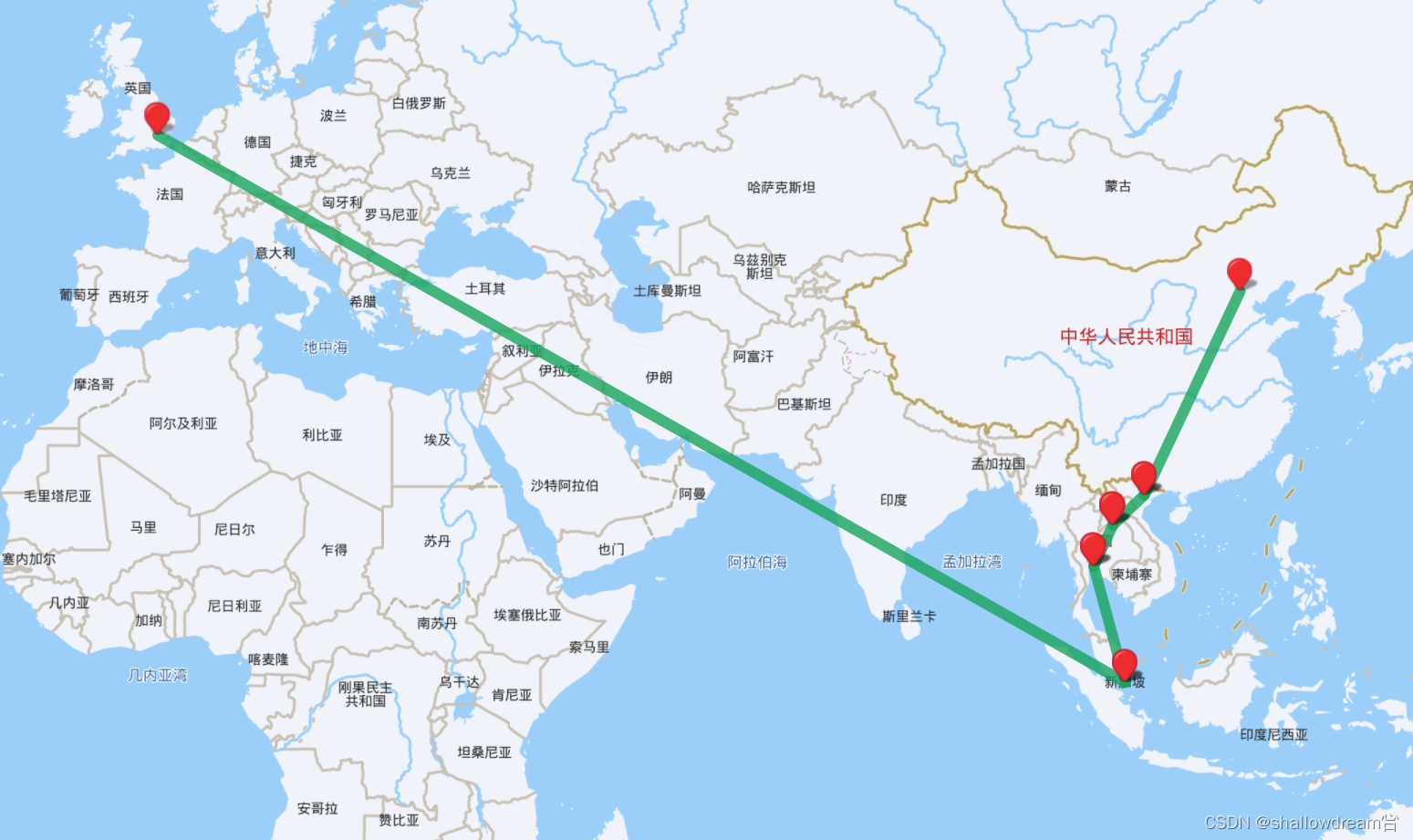
7.时间复杂度与空间复杂度分析:
1)时间复杂度
理论上,由时间复杂度的计算公式可得
𝑓(𝑛) =𝑛+𝑛+𝑛?3𝑛+𝑛?𝑛+𝑛+𝑛+𝑛?2𝑛?𝑛
=2𝑛3+4𝑛2+4𝑛
故时间复杂度为𝑇(𝑛)=𝑂(𝑛3)。
2)空间复杂度
空间复杂度:在main函数中创建了城市表pCity,网图Graph,辅助数组D,起点名数组nStart,终点名数组nEnd,路径数组 Path,以及其他函数中运行时的temp[1024]和 buf[1024]等。
int size = sizeof(pCity) + sizeof(Graph) + sizeof(nStart) + sizeof(nEnd) + sizeof(cStart) + sizeof(cDes) + sizeof(dShortPath) + sizeof(char) * 1024 * 2 + sizeof(char) * 1024 * 2;
cout << endl << endl << "Using space :" << size << endl;