目录
冒泡排序
void Bubble_Sort(int* const array, int array_size) {
for (int i = 1; i < array_size; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array_size - i; j++)
{
if (array[j] > array[j + 1])
{
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
九九乘法表
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <=i; j++) {
cout << j << "*" << i << "=" << i * j << "\t";
}
cout <<"\n" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
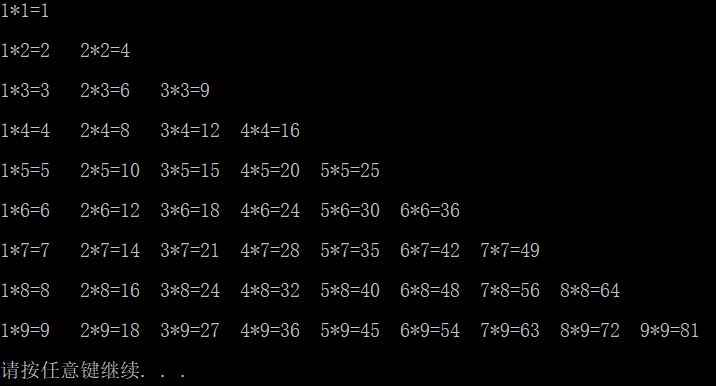
水仙花数
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
for (int i = 100; i < 1000; i++){
a = i / 100;//百位
b = i / 10 % 10;//十位
c=i % 10;//个位
if (pow(a, 3) + pow(b, 3) + pow(c, 3) == i) {
cout << "水仙花数: " << i << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
猜数字
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main() {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));//随机数种子
int num = rand() % 100 + 1;//生成1~100的一个随机数
int value;
while (num) {
cout << "输入一个数: ";
cin >> value;
if (value > num) {
cout << "猜大了" << endl;
}
else if(value < num){
cout << "猜小了" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "猜对了!" << endl;
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

时间戳
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "时间戳: " << (unsigned int)time(NULL) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

7的倍数,含有7就拍桌子
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
/*
!(i%7)//7的倍数
i/10==7//十位上有7
i%10==7//个位上有7
*/
if (!(i % 7) || i / 10 == 7 || i % 10 == 7) {
cout << "拍桌子(" << i << ")" << endl;
}
else {
cout << i << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
goto
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "1.XXXXXX" << endl;
cout << "2.XXXXXX" << endl;
goto FLAG;
cout << "3.XXXXXX" << endl;
cout << "4.XXXXXX" << endl;
FLAG:
cout << "5.XXXXXX" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

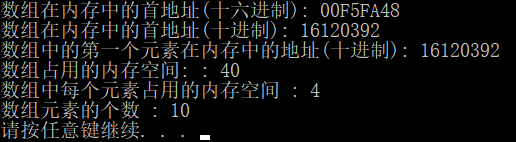
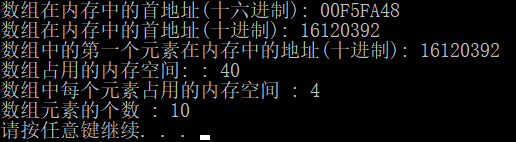
数组名
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
cout << "数组在内存中的首地址(十六进制): " << arr << endl;
cout << "数组在内存中的首地址(十进制): " << (int)arr << endl;
cout << "数组中的第一个元素在内存中的地址(十进制): " << (int)&arr[0] << endl;
cout << "数组占用的内存空间: : " << sizeof(arr) << endl;
cout << "数组中每个元素占用的内存空间 : " << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "数组元素的个数 : " << sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
最大值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = { 300,350,200,400,250 }, max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); i++) {
max = arr[i] > max ? arr[i] : max;
}
cout << "数组中最大值: " << max << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
数组逆序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = { 1,3,2,5,4,6,2}, temp = 0;
int num = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) - 1;//数组最后一个元素索引
for (int i = 0; i <= num/2; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[num - i];
arr[num - i] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= num; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

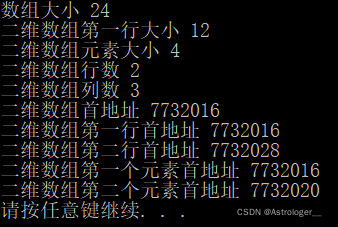
二维数组的数组名
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[][3] = {
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
cout << "数组大小 " << sizeof(arr) << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一行大小 " << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组元素大小 " << sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组行数 " << sizeof(arr)/ sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组列数 " << sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组首地址 " << (int)arr << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一行首地址 " << (int)arr[0] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第二行首地址 " << (int)arr[1] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一个元素首地址 " << (int)&arr[0][0] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第二个元素首地址 " << (int)&arr[0][1] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
成绩求和
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[][3] = {
{100,100,100},
{90,50,100},
{60,70,80}
};
string name[3] = { "张三","李四","王五" };
int raw = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int col = sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]);
for (int i = 0; i < raw; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
sum += arr[i][j];
}
cout << name[i] << "的总成绩: " << sum << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

两数相加函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int add(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
int main() {
cout << add(1, 3) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

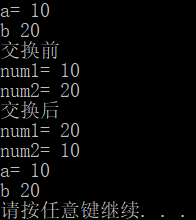
值传递,形参发生任何改变,都不会影响实参
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int num1, int num2) {
cout << "交换前" << endl;
cout << "num1= " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2= " << num2 << endl;
int temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
cout << "交换后" << endl;
cout << "num1= " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2= " << num2 << endl;
}
int main() {
int a = 10, b = 20;
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "b " << b << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "b " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数的定义
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//在main()之前定义
int max(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 > num2 ? num1 : num2;
}
int main() {
cout << max(10, 20) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

函数的声明和定义
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//在main()之前声明
int max(int num1, int num2);
int main() {
cout << max(10, 20) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//在main()之后定义
int max(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 > num2 ? num1 : num2;
}

函数的分文件编写
- 创建.h的头文件
- 创建.cpp的源文件
- 在头文件中写函数声明
- 在源文件中写函数的定义
//swap.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int a, int b);
//swap.cpp
#include "swap.h"
void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "b= " << b << endl;
}
//source.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "swap.h"
int main() {
swap(10, 20);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

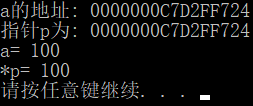
指针的定义和使用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 10;
//1.定义指针
int* p = &a;
cout << "a的地址: " << &a << endl;
cout << "指针p为: " << p << endl;
//2.使用指针
*p = 100;
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "*p= " << *p << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
指针所占内存空间
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
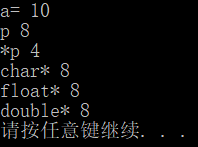
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
cout << "a= " << *p << endl;
cout << "p " << sizeof(p) << endl;//指针所占内存空间
cout << "*p " << sizeof(*p) << endl;//数据所占内存空间
cout << "char* " << sizeof(char*) << endl;
cout << "float* " << sizeof(float*) << endl;
cout << "double* " << sizeof(double*) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
空指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* p = NULL;//空指针
system("pause");
return 0;
}
野指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//野指针
//int* p = (int*)0x1100;//错误
system("pause");
return 0;
}
const 修饰指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//const修饰的值不能改
int a = 10, b = 20;
//1.常量指针
const int* p1 = &a;
p1 = &b;//正确
//2.指针常量
int* const p2 = &b;
*p2 = a;
//3.const 修饰指针和常量
const int* const p3 = &a;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
指针和数组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
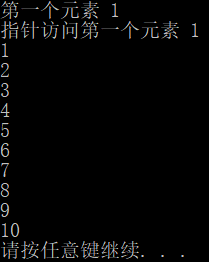
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int* p = arr;
cout << "第一个元素 " << arr[0] << endl;
cout << "指针访问第一个元素 " << *p << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); i++, p++) {
cout << *p << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
值传递和地址传递
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//值传递
void swap01(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
//地址传递
void swap02(int* p1, int* p2) {
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
int main() {
int a = 10, b = 20;
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "b= " << b << endl;
cout << "值传递" << endl;
swap01(a, b);
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "b= " << b << endl;
cout << "地址传递" << endl;
swap02(&a, &b);
cout << "a= " << a << endl;
cout << "b= " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

指针配合数组和函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubleSort(int* arr, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubleSort(arr, len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << "\t";
}
cout <<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体定义和使用
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
Student s1;
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 18;
s1.score = 60;
Student s2 = { "李四",19,70 };
cout << "姓名: " << s2.name
<< " 年龄: " << s2.age
<< " 成绩: " << s2.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体数组
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
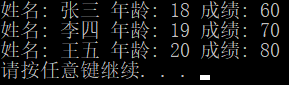
Student stuArray[3] = {
{"张三",18,60},
{"李四",19,70},
{"王五",20,80}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << "姓名: " << stuArray[i].name
<< " 年龄: " << stuArray[i].age
<< " 成绩: " << stuArray[i].score << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结构体指针
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
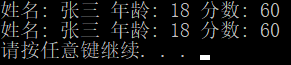
Student s1 = {"张三",18,60};
cout << "姓名: " << s1.name
<< " 年龄: " << s1.age
<< " 分数: " << s1.score << endl;
Student* p = &s1;
cout << "姓名: " << p->name
<< " 年龄: " << p->age
<< " 分数: " << p->score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结构体嵌套结构体
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
struct Teacher {
int id;
string name;
int age;
Student stuArray[2];
};
int main() {
Teacher t;
t.name = "老王";
t.id = 001;
t.age = 50;
t.stuArray[0].name = "张三";
t.stuArray[0].age = 18;
t.stuArray[0].score = 60;
t.stuArray[1].name = "李四";
t.stuArray[1].age = 19;
t.stuArray[1].score = 70;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结构体做函数参数
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
void print1(Student stu) {
cout << "值传递打印 " << " 姓名: " << stu.name
<< " 年龄: " << stu.age
<< " 分数: " << stu.score << endl;
};
void print2(Student* p) {
p->name = "李四";
cout << "地址传递打印 " << " 姓名: " << p->name
<< " 年龄: " << p->age
<< " 分数: " << p->score << endl;
};
int main() {
Student s = { "张三",18,60 };
cout << "main函数中打印 " << " 姓名: " << s.name
<< " 年龄: " << s.age
<< " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
print1(s);
print2(&s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体中const的使用场景
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
void print1(const Student* p) {
cout << "地址传递打印 " << " 姓名: " << p->name
<< " 年龄: " << p->age
<< " 分数: " << p->score << endl;
};
int main() {
Student s = { "张三",18,60 };
cout << "main函数中打印 " << " 姓名: " << s.name
<< " 年龄: " << s.age
<< " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
print1(&s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体案例1
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string sName;
int score;
};
struct Teacher
{
string tName;
Student sArray[5];
};
void allocatespace(Teacher tArray[], int len) {
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tArray[i].tName = "teacher_";
tArray[i].tName += nameSeed[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName = "student_";
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName += nameSeed[j];
int random = 60 + rand() % 41;
tArray[i].sArray[j].score = random;
}
}
};
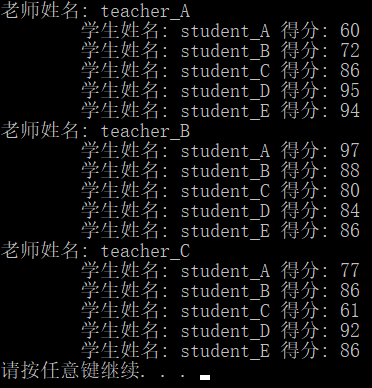
void printinfo( Teacher tArray[],int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "老师姓名: " << tArray[i].tName << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cout << "\t学生姓名: " << tArray[i].sArray[j].sName
<< " 得分: " << tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl;
}
}
};
int main() {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
Teacher tArray[3];
int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(tArray[0]);
allocatespace(tArray, len);
printinfo(tArray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结构体案例2
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Hero {
string name;
int age;
string sex;
};
void bubbleSorrt(Hero HeroArray[], int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) {
if (HeroArray[j].age > HeroArray[j + 1].age) {
Hero temp = HeroArray[j];
HeroArray[j] = HeroArray[j + 1];
HeroArray[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
void printinfo(Hero HeroArray[], int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << HeroArray[i].name << "\t"
<< HeroArray[i].age << "\t"
<< HeroArray[i].sex << endl;
}
};
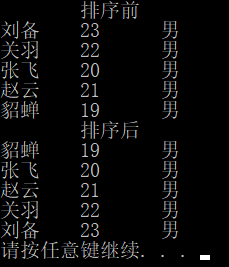
int main() {
Hero HeroArray[5] = {
{"刘备",23,"男"},
{"关羽",22,"男"},
{"张飞",20,"男"},
{"赵云",21,"男"},
{"貂蝉",19,"男"}
};
int len = sizeof(HeroArray) / sizeof(HeroArray[0]);
cout << "\t排序前" << endl;
printinfo(HeroArray, len);
bubbleSorrt(HeroArray, len);
cout << "\t排序后" << endl;
printinfo(HeroArray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
MPI并行——梯形积分
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
#include "mpi.h"
using namespace std;
double f(double x) {
return x*x*x;
}
double trap(double a, double b, int n) {
double h = (b - a) / n;
double sum = (f(a) + f(b)) / 2;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
sum += f(a + i * h);
}
return sum * h;
}
int main(void) {
int n = 9000;
double a = -2, b = 2;
int rank, comm_sz;
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(NULL, NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_sz);
int local_n = n / comm_sz;
double local_width = (b - a) / comm_sz;
double local_a = a + rank * local_width;
double local_b = local_a + local_width;
double local_sum = trap(local_a, local_b, local_n);
double cacha_sum;
MPI_Reduce(&local_sum, &cacha_sum, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if (rank == 0) {
cout << "With n = " << n << " trapeziods, our estimate" << endl;
cout << "of the integral from " << a << " to " << b << " = " << cacha_sum << endl;
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
With n = 9000 trapeziods, our estimate
of the integral from -2 to 2 = -8.88178e-16