上次文章我们实现了单向链表,链接如下 : 单向链表的实现与讲解
而这篇文章博主就对双向链表如何实现以及实现原理进行讲解;
双向链表和单向链表本质上区别不大,双向链表就比单向链表每个节点多了一个先驱prev,以实现链表能够逆向链接:

双向链表需要有一个头结点引用head 以及一个尾结点引用last
而有力单向链表的知识基础,双向链表实现以及理解上就会容易很多,讲解如下 :
快速跳转:
1.节点类实现
class ListNode{
public int val; //数据域
public ListNode prev;//前驱域
public ListNode next;//后驱域
public ListNode(int val){ //一个参数的构造方法 实现对数据域的数据赋值
this.val=val; //this : 表示当前对象引用(注意不是当前对象)
}
}
2. 双向链表各个模块功能实现
2.1 头插法
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data); //实例化插入的节点
if (this.head == null) {//链表为空情况
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head; //node的next改为head
this.head.prev = node; //head的prev改为node
this.head = node; //此时新的head为node
}
}

2.2 尾插法
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);//实例化插入的节点
if (head == null) { //链表为空情况
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
this.last.next = node; //last尾结点的next改为node
node.prev = this.last; //node的前驱prev改为last
this.last = node; //此时last为node
}
}

2.3 查找关键字key是否在单链表当中
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head; //定义cur引用指向head
while (cur!=null){ //遍历链表
if (cur.val==key){
return true; //找到返回TRUE
}
cur=cur.next; //没找到继续找下一个节点
}
return false; //遍历完成没有返回true 则没有找到 返回false
}
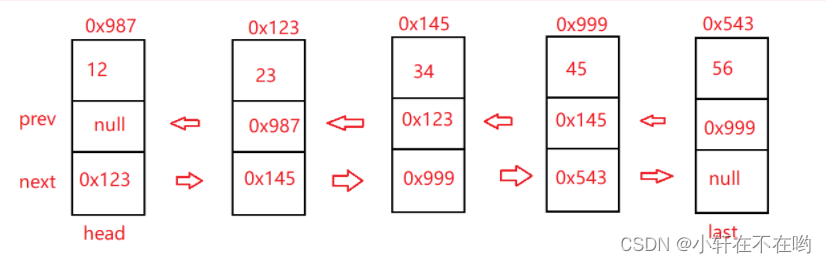
2.4 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
单向链表删除节点操作要先找到需要删除的那个节点的前一个节点,在进行删除操作;而双向链表不需要找前一个节点,找到要删除的节点它本身就可以进行操作
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head; //cur引用来遍历
while(cur!=null){ //遍历
if (cur.val==key){
if (cur==head){ //要删除的节点是头节点情况
head=head.next; //head直接引用向下一个节点
if(head!=null){
head.prev=null; //下一个节点的prev改为null
}else{
last=null; //因为last是成员变量 不手动制空会一直浪费着内存
}
}else if(cur==last){ //删除节点是尾结点情况
cur.prev.next=cur.next; //尾结点的前一个节点的next改为此时尾结点的next 也就是null
last=last.prev; //last引用向前一个节点 实现删除
}else{ //节点既不是头结点也不是尾结点的情况
cur.prev.next=cur.next; //前一个节点的next直接指向后一个节点
cur.next.prev=cur.prev; //后一个节点的prev直接指向前一个节点 实现删除
}
return; //只删除一个 删除执行的话返回
}else{
cur=cur.next; //没有找到的话 继续查找下一个节点
}
}
}
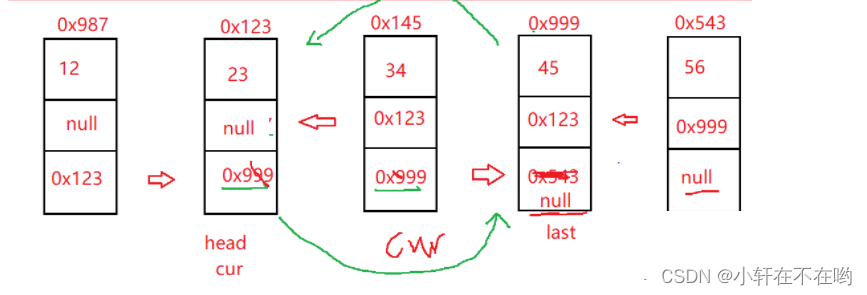
2.5 删除所有值为key的节点
步骤与删除一次key相同 只是在删除操作后不return 继续进行遍历删除
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
if (cur.val==key){
if (cur==head){
head=head.next;
if(head!=null){
head.prev=null;
}else{
last=null;
}
}else if(cur==last){
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
last=last.prev;
}else{
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
cur.next.prev=cur.prev;
}
// return; 删除一次是直接return 删除所有的话就不return 继续进行遍历删除
}else{
cur=cur.next;
}
}
}
2.6 得到单链表的长度
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
ListNode cur=this.head; //cur引用来遍历
int count=0; //计数器
while (cur!=null){ //遍历操作
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count; //返回长度
}
2.7 打印单链表
public void display(){
ListNode cur=this.head;//cur引用来遍历
while(cur!=null){//遍历
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
2.8任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
回顾上次的单向链表,我们要在index位置插入需要找到index位置前面一个节点,而这里的双向链表 我们要在index插入 就只需要找到index位置的节点进行操作
首先我们要完成一个查找index位置节点的方法
public ListNode searchIndex(int index){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while (index!=0){
cur=cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur; //找到index位置的节点进行返回
}
进行插入操作 :
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data); //实例化需要插入的节点
if (index<0 || index>size()){ //判断index是否合法
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if (index==0){ //头插法
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index==size()){// 尾插法
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur=searchIndex(index); //找到index位置节点定义为cur
// 进行插入操作 :插入操作需要改变**4个**引用域的值 实现插入
node.next=cur.prev.next;
cur.prev.next=node;
node.prev=cur.prev;
cur.prev=node;
}

需要改变的4个引用域就是蓝色圈起来的4个引用域 具体改变代码 :
node.next=cur.prev.next;
cur.prev.next=node;
node.prev=cur.prev;
cur.prev=node;
照着进行画图就能很容易理解 ~
2.9 清空链表
public void clear(){
//不采用直接把head last制空的暴力情况方法
//而是采取逐一情况prev last的操作
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.prev=null;
cur.next=null;
cur=curNext;
}
//不要忘记把head last 引用也制空
this.head=null;
this.last=null;
}

清空成功 !
3. 整体 MyLinkedList 代码展示
class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public class MyLinkedList {
ListNode head;
ListNode last;
// 2、无头双向链表实现
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
this.last.next = node;
node.prev = this.last;
this.last = node;
}
}
public ListNode searchIndex(int index){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while (index!=0){
cur=cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
if (index<0 || index>size()){
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if (index==0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index==size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur=searchIndex(index);
node.next=cur.prev.next;
cur.prev.next=node;
node.prev=cur.prev;
cur.prev=node;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while (cur!=null){
if (cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
if (cur.val==key){
if (cur==head){
head=head.next;
if(head!=null){
head.prev=null;
}else{
last=null;
}
}else if(cur==last){
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
last=last.prev;
}else{
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
cur.next.prev=cur.prev;
}
return;
}else{
cur=cur.next;
}
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
if (cur.val==key){
if (cur==head){
head=head.next;
if(head!=null){
head.prev=null;
}else{
last=null;
}
}else if(cur==last){
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
last=last.prev;
}else{
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
cur.next.prev=cur.prev;
}
// return;
}else{
cur=cur.next;
}
}
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
ListNode cur=this.head;
int count=0;
while (cur!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public void display(){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear(){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.prev=null;
cur.next=null;
cur=curNext;
}
this.head=null;
this.last=null;
}
}
4. 部分测试 test 代码展示 :
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList=new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addFirst(1);
myLinkedList.addFirst(2);
myLinkedList.addFirst(3);
// System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
myLinkedList.display();
// System.out.println(myLinkedList.contains(2));
// myLinkedList.remove(3);
// myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println("-------------------");
myLinkedList.clear();
myLinkedList.display();
}
}

5. 总结
讲解到这里 双向链表的实现就已经完成了
对于链表的学习我们一定要多画图理解 多思考 多写代码 才能真正学好链表
如果觉得博主的文章对自己有所帮助 欢迎大家多多点赞收藏 ~