目录
简要解析
?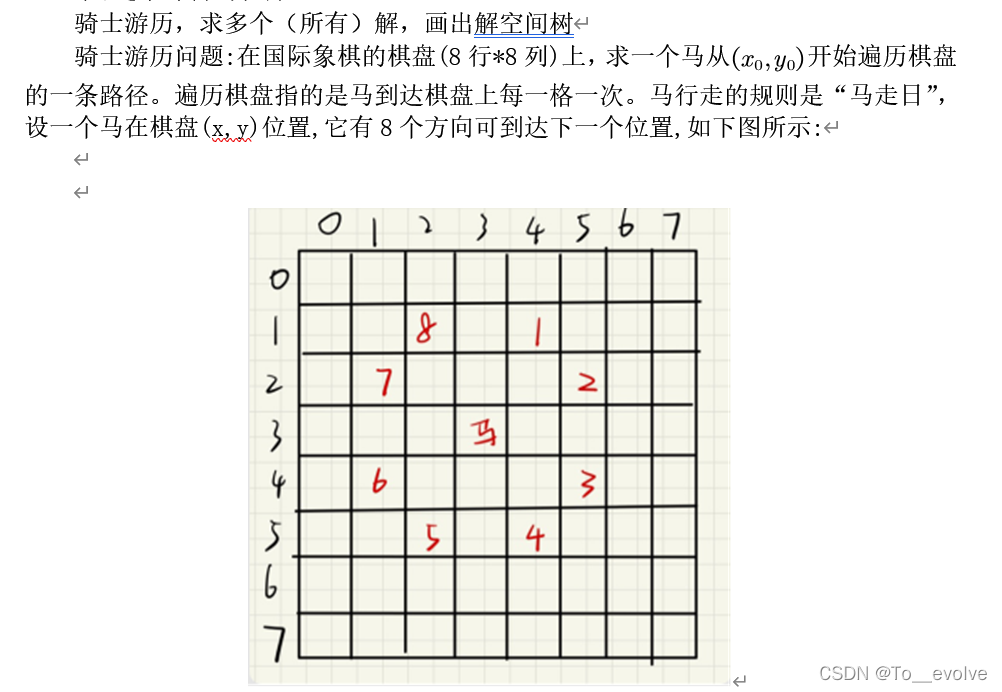
?
?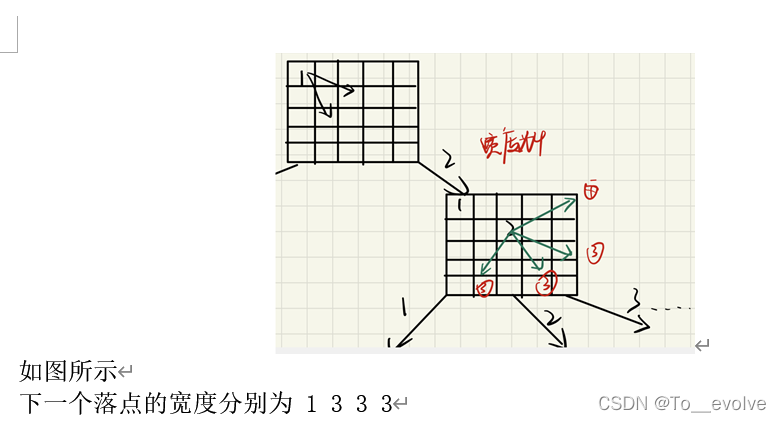
?
?
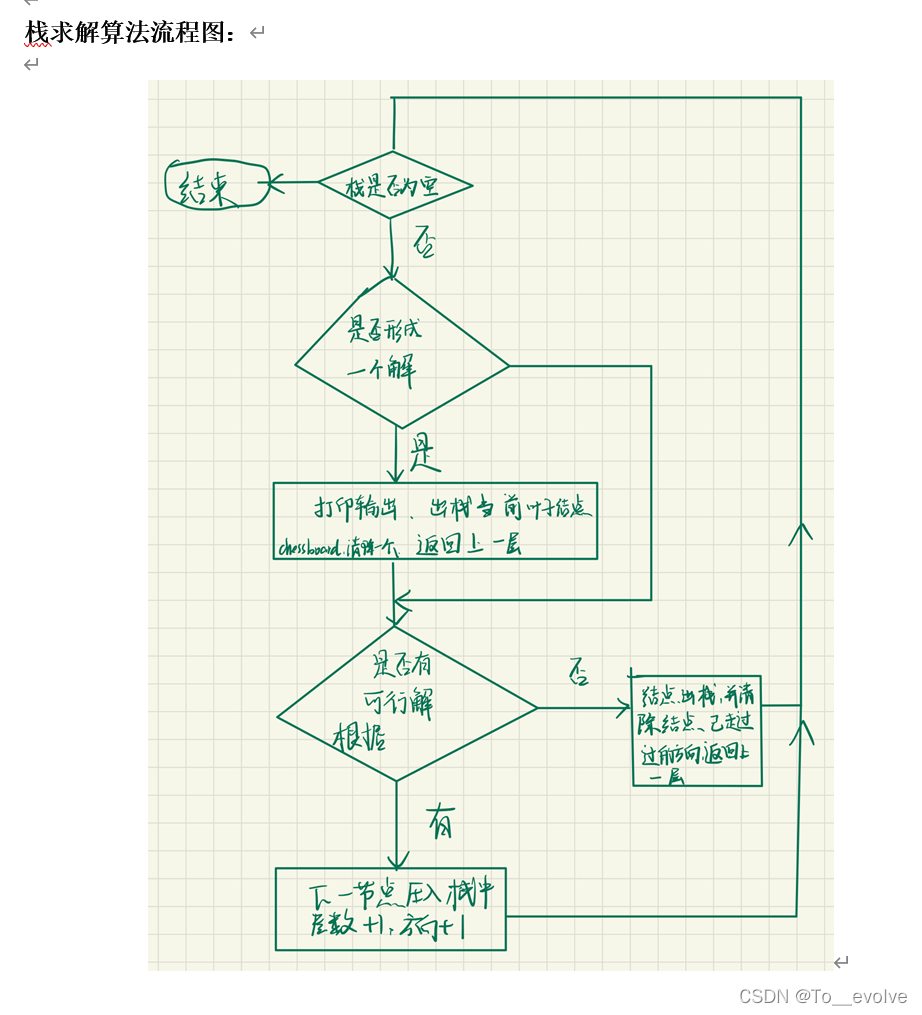
回溯法
回溯法都叫backTrack
一解(预见算法、栈实现回溯)
/**
? ? * x[] 走过的方向
? ? * dirList 第i层的可选方向
? ? * p 点坐标
? ? * i 层数
? ? * chessboard[][] 记录走法
? ? * 需要入栈的变量 : dirList p
? ? * 技术难题: dirList的入栈出栈 与使用
? ? * 时间复杂度O(n^2*n)=O(n^3) <--> 空间复杂度O(n*n)
? ? */
public void backTrack(Point p) //非递归方式的 栈 深度优先 回溯
? { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //栈如何转化多个分叉的递归
? ? ? ?int[]x=new int[n*n+1];
? ? ? ?pathlen=1;
? ? ? ?int i=1;
? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=1;
? ? ? ?LinkedStack<Point> stack=new LinkedStack<>();
? ? ? ?stack.push(p);
? ? ? ?SeqList<Integer> dirList;
? ? ? ?while (p!=null || !stack.isEmpty()) ?//当前p在i+1层
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?if(i==n*n)
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?count++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("第"+count+"个解");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stack.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?printMat();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=0;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?i--;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?break;
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?dirList=select(p);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?//对于预见算法select 当到达第24层时,p的下一节点只有一个,而且宽度为0
? ? ? ? ? ?if(x[i]<dirList.size() ) //找到可行解
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?p=restrict(p,dirList.get(x[i]));
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?x[i]++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?i++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?pathlen=i;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=i;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stack.push(p);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?else ?//没有下一个可行点,回溯
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[stack.peek().x][stack.peek().y] = 0;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stack.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?p=stack.peek();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?x[i]=0;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?i--;
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }多解(预见算法、栈实现回溯)
一个解就是找到一个解就退出循环,结束程序
/**
? ? * x[] 走过的方向
? ? * dirList 第i层的可选方向
? ? * p 点坐标
? ? * i 层数
? ? * chessboard[][] 记录走法
? ? * 需要入栈的变量 : dirList p
? ? * 技术难题: dirList的入栈出栈 与使用
? ? * 时间复杂度O(n^2*n)=O(n^3) <--> 空间复杂度O(n*n)
? ? */
public void backTrack(Point p) //非递归方式的 栈 深度优先 回溯
? { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //栈如何转化多个分叉的递归
? ? ? ?int[]x=new int[n*n+1];
? ? ? ?pathlen=1;
? ? ? ?int i=1;
? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=1;
? ? ? ?LinkedStack<Point> stack=new LinkedStack<>();
? ? ? ?stack.push(p);
? ? ? ?SeqList<Integer> dirList;
? ? ? ?while (p!=null || !stack.isEmpty()) ?//当前p在i+1层
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?if(i==n*n)
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?count++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("第"+count+"个解");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stack.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?printMat();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=0;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?i--;
// ? ? ? ? ? ? ? break;
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?dirList=select(p);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?//对于预见算法select 当到达第24层时,p的下一节点只有一个,而且宽度为0
? ? ? ? ? ?if(x[i]<dirList.size() ) //找到可行解
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?p=restrict(p,dirList.get(x[i]));
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?x[i]++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?i++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?pathlen=i;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=i;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stack.push(p);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?else ?//没有下一个可行点,回溯
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[stack.peek().x][stack.peek().y] = 0;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?stack.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?p=stack.peek();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?x[i]=0;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?i--;
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }全解(回溯,暴力递归)
protected void backTrack(int i,Point p)
{
? ?if(i<=this.n*this.n)
? {
? ? ? ?this.pathlen=i;
? ? ? ?chessboard[p.x][p.y]=i;
? ? ? ?if(i==this.n*this.n)
? ? ? ? ? ?return;
?
? ? ? ?for(int j=1;j<=8;j++)
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?Point next=restrict(p,j); //八个方向 每个方向都递归
? ? ? ? ? ?if(next!=null) ?//有下一个位置,则前进到下一个位置
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?backTrack(i+1,next);
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(i+1==pathlen) ?//下一步走完 就没有后路了,所以路径终止在p0到p(i+1)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(show)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?path++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print("第"+path+"条路径");
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(i+1==this.n*this.n)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?count++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print("第"+count+"个解");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print("时刻:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)/1000+"s");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?list.add(new ChessBoard(chessboard));
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?// ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? this.print(); //输出一条路径/一个解
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?printMat();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?chessboard[next.x][next.y]=0; ?//next走完后,退回到前一个递归函数的状态,走下一个next方向
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? }
}运行结果图
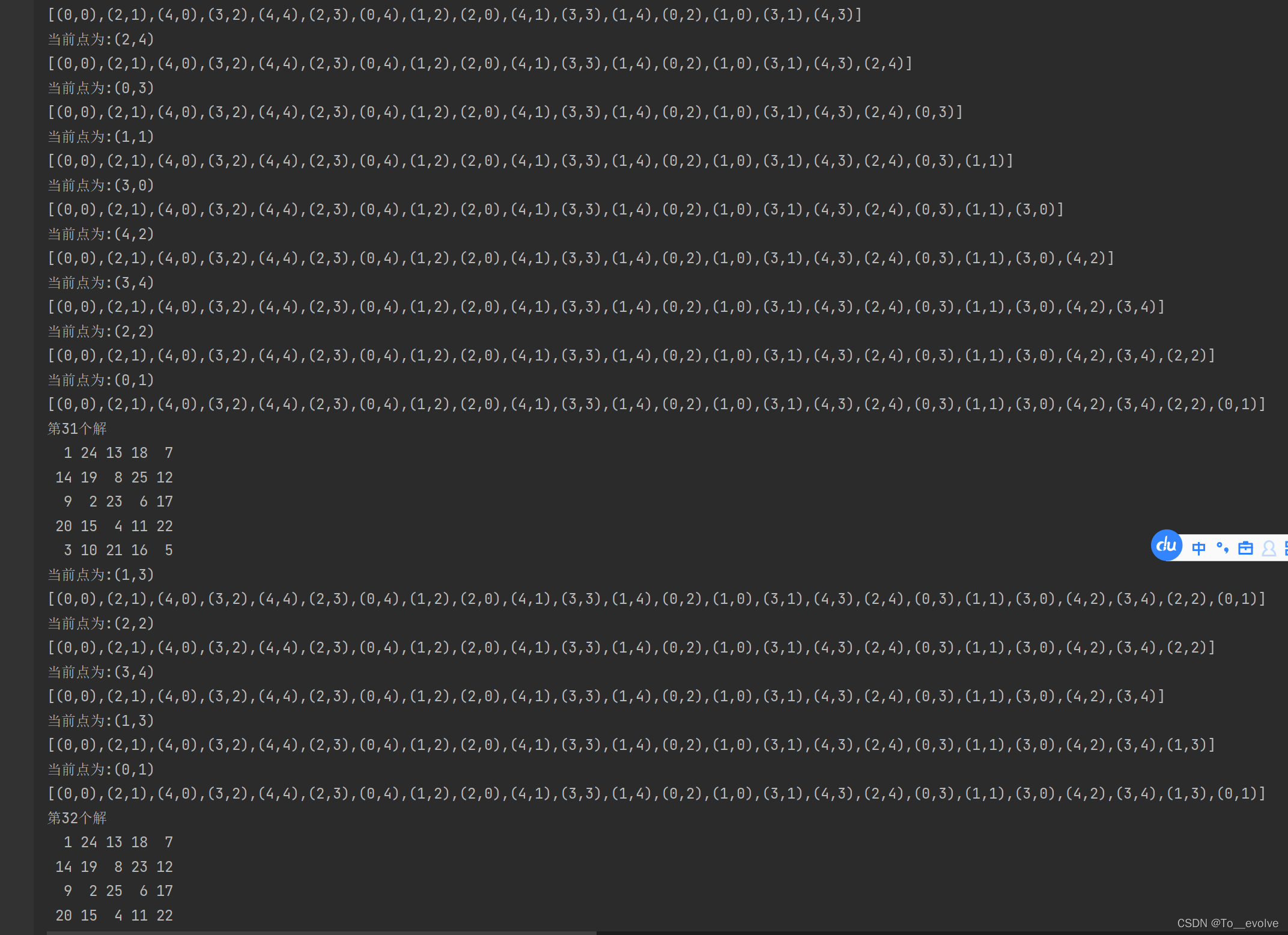
?
其他代码
变量
protected final int n; ?//棋盘规格为 n*n
protected int chessboard[][];
protected boolean show;
protected int pathlen,path,count;构造函数
public Knight_Stack(int n, int x, int y, boolean show)
{
? ?if(n>=3 && n<=50)
? ? ? ?this.n = n;
? ?else
? ? ? ?throw new IllegalArgumentException("n="+n);
? ?chessboard=new int[n][n]; //初始值为0
? ?System.out.println("n="+n+",point="+new Point(x,y));
? ?this.show=show;
? ?pathlen=0;
? ?path=0;
? ?count=0;
// backTrack(1,new Point(x,y)) ; //递归
? ?backTrack(new Point(x,y)); ?//栈
? ?System.out.println("共有"+count+"个解");
}判断该点的direction方向是否可走
? ?protected Point restrict(Point point,int direction)
? {
? ? ? ?int x=point.x,y=point.y;
? ? ? ?switch(direction)
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?case 1:x-=2 ;y++; break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 2:x--; ?y+=2;break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 3:x++; ?y+=2;break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 4:x+=2; y+=1;break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 5:x+=2; y--; break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 6:x+=1; y-=2;break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 7:x-=1; y-=2;break;
? ? ? ? ? ?case 8:x-=2; y-=1;break;
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?if(x>=0 && x<this.n && y>=0 && y<this.n && this.chessboard[x][y]==0)
? ? ? ? ? ?return new Point(x,y); ? ? ?//0表示还没有经过,没有走过
? ? ? ?return null;
? }预见算法
protected SeqList<Integer> select(Point p) ?//返回大小为n的线性表,方向按照 路的“宽度”从小到大存放
? { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //求得下一步8个方向位置的路的“宽度”,并将元素从大到小拍放在线性表,,不如排序线性表。。
? ? ? ?if(show)
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println("当前点为:" + p);
// ? ? ? ? ? print();//打印当前路径
? ? ? ? ? ?printMat();
? ? ? }
// ? ? ? 计算宽度,以当前点为下一节点,计算自己可走的路数
? ? ? ?Point next;
? ? ? ?int minRoad=8;
? ? ? ?SeqList<Integer> list=new SeqList<>();
? ? ? ?for(int k=1;k<=8;k++) ? //选择宽度最小的方向,并且将宽度最小的方向
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?int avl = 0;
? ? ? ? ? ?next=restrict(p,k);
? ? ? ? ? ?if(next!=null && chessboard[next.x][next.y]==0) ?//下一步,不仅要有,还得时未走过的
? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (restrict(next, i) != null)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?avl++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(avl<minRoad)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?minRoad=avl;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?list.clear();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(avl==minRoad)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?list.insert(k);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return list;
? }打印路径
? ?protected void print() ?//输出路径 从点(x,y)开始
? {
? ? ? ?String str="[";
? ? ? ?for(int k=1;k<=n*n;k++)
? ? ? ? ? ?for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(chessboard[i][j]==k) ?//得到顺序路径上的一点p(i,j)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?str+=new Point(i,j)+",";
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ?if(str.length()>1)
? ? ? ? ? ?str=str.substring(0,str.length()-1);
? ? ? ?System.out.println(str+"]");
? }打印棋盘
private void printMat()
? {
? ? ? ?for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.printf("%5d",chessboard[i][j]);
? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println();
? ? ? }
? }多解的全部代码
package chapter_10_courseDesign;
import chapter_1_1_SeqLIst.SeqList;
import chapter_3_1_Stack_Queue.LinkedStack;
public class Knight //二维数组chessBoard存储n*n棋盘的一个解,使用预见算法 回溯算法
{
protected final int n; //棋盘规格为 n*n
protected int chessboard[][];
protected boolean show;
protected int pathlen,path,count;
public Knight(int n, int x, int y, boolean show)
{
if(n>=3 && n<=12)
this.n = n;
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException("n="+n);
chessboard=new int[n][n]; //初始值为0
System.out.println("n="+n+",point="+new Point(x,y));
this.show=show;
pathlen=1;
path=0;
count=0;
// backTrack(1,new Point(x,y));
backTrack(new Point(x,y));
System.out.println("共有"+count+"个解");
}
/**
* x[] 走过的方向
* dirList 第i层的可选方向
* p 点坐标
* i 层数
* chessboard[][] 记录走法
* 需要入栈的变量 : dirList p
* 技术难题: dirList的入栈出栈 与使用
* 时间复杂度O(n^2*n)=O(n^3) <--> 空间复杂度O(n*n)
*/
public void backTrack(Point p) //非递归方式的 栈 深度优先 回溯
{ //栈如何转化多个分叉的递归
int[]x=new int[n*n+1];
pathlen=1;
int i=1;
chessboard[p.x][p.y]=1;
LinkedStack<Point> stack=new LinkedStack<>();
stack.push(p);
SeqList<Integer> dirList;
while (p!=null || !stack.isEmpty()) //当前p在i+1层
{
if(i==n*n)
{
count++;
System.out.println("第"+count+"个解");
stack.pop();
printMat();
chessboard[p.x][p.y]=0;
i--;
// break;
}
dirList=select(p);
//对于预见算法select 当到达第24层时,p的下一节点只有一个,而且宽度为0
if(x[i]<dirList.size() ) //找到可行解
{
p=restrict(p,dirList.get(x[i]));
x[i]++;
i++;
pathlen=i;
chessboard[p.x][p.y]=i;
stack.push(p);
// dirStack.push(dirList);
}
else //没有下一个可行点,回溯
{
chessboard[stack.peek().x][stack.peek().y] = 0;
stack.pop();
// dirStack.pop();
p=stack.peek();
x[i]=0;
i--;
}
}
}
protected void backTrack(int i,Point p)
{
if(i<=this.n*this.n)
{
this.pathlen=i;
chessboard[p.x][p.y]=i;
if(i==this.n*this.n) //到达叶子节点,直接返回,回溯
return;
SeqList<Integer> direList=this.select(p); //预见算法给出的方向选择
for(int j=0;j<direList.size();j++)
{
Point next=restrict(p,direList.get(j));
if(next!=null) //有下一个位置,则前进到下一个位置
{
backTrack(i+1,next);
if(i+1==pathlen) //下一步走完 就没有后路了,所以路径终止在p0到p(i+1)
{
if(show)
{
path++;
System.out.print("第"+path+"条路径");
}
if(i+1==this.n*this.n)
{
count++;
System.out.print("第"+count+"个解");
}
System.out.println();
printMat();
}
chessboard[next.x][next.y]=0; //next点走完后,退回到前一个递归函数的状态,走下一个next方向
}
}
}
}
protected void print() //输出路径 从点(x,y)开始
{
String str="[";
for(int k=1;k<=n*n;k++)
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(chessboard[i][j]==k) //得到顺序路径上的一点p(i,j)
str+=new Point(i,j)+",";
}
if(str.length()>1)
str=str.substring(0,str.length()-1);
System.out.println(str+"]");
}
private void printMat()
{
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
System.out.printf("%3d",chessboard[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
}
protected SeqList<Integer> select(Point p) //返回大小为n的线性表,方向按照 路的“宽度”从小到大存放
{ //求得下一步8个方向位置的路的“宽度”,并将元素从大到小拍放在线性表,,不如排序线性表。。
if(show)
{
System.out.println("当前点为:" + p);
print();//打印当前路径
// printMat();
}
// 计算宽度,以当前点为下一节点,计算自己可走的路数
Point next;
int minRoad=8;
SeqList<Integer> list=new SeqList<>();
for(int k=1;k<=8;k++) //选择宽度最小的方向,并且将宽度最小的方向
{
int avl = 0;
next=restrict(p,k);
if(next!=null && chessboard[next.x][next.y]==0) //下一步,不仅要有,还得时未走过的
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
if (restrict(next, i) != null)
avl++;
if(avl<minRoad)
{
minRoad=avl;
list.clear();
}
if(avl==minRoad)
list.insert(k);
}
}
return list;
}
protected Point restrict(Point point,int direction)
{
int x=point.x,y=point.y;
switch(direction)
{
case 1:x-=2 ;y++; break;
case 2:x--; y+=2;break;
case 3:x++; y+=2;break;
case 4:x+=2; y+=1;break;
case 5:x+=2; y--; break;
case 6:x+=1; y-=2;break;
case 7:x-=1; y-=2;break;
case 8:x-=2; y-=1;break;
}
if(x>=0 && x<this.n && y>=0 && y<this.n && this.chessboard[x][y]==0)
return new Point(x,y); //0表示还没有经过,没有走过
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
Knight knight=new Knight(5,0,0,true);
System.out.println("用时"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms");
}
}
