搜索二叉树的定义是:在一个二叉树上,左节点一定比父节点小,右节点一定比父节点大,其他定义跟二叉树相同。
代码实现:
public class node {
int data;
public node left, right=null;
public node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public node(int data, node left, node right) {
this.data = data;
this.right = right;
this.left = left;
}
//二叉搜索树
public static void insert(node root, node node) {
if (root.data >= node.data) {
if (root.right != null) {
insert(root.right, node);
}else{
root.right=node;
}
} else {
if (root.left != null) {
insert(root.left,node);
}else {
root.left=node;
}
}
}
//前序遍历
public static void before(node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println("data:" + root.data);
before(root.left);
before(root.right);
}
//中序遍历
public static void mid(node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
mid(root.left);
System.out.println("data:" + root.data);
mid(root.right);
}
//后序遍历
public static void after(node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
after(root.left);
after(root.right);
System.out.println("data:" + root.data);
}
public static boolean search(int target, node root) {
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.data > target) {
search(target, root.left);
} else if (root.data < target) {
search(target, root.right);
} else {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}node.java中:data 节点存放的数据,left,right 左右子节点
before() after() mid()为三种前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历。关键方法 insert() search()
insert():参数:root node root为你的根节点,node为你要插入的节点。递归调用insert()当递归到某个节点的右节点为空时表示可以插入数据
流程:
这里有六个节点作为示例:圆中为数据,简单的一个节点。选定3为根节点,随机插入0 2 1 4 5 6?
?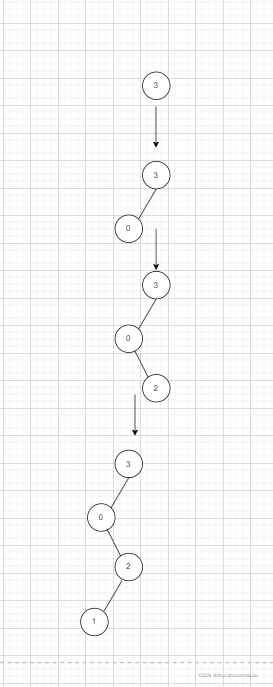
第一步,根节点3,第二步分别插入021 比三大的数跟这个类似,不做展示了。
插入0的时候没有问题,放在3的左边,插入2的时候,递归,2<3,2>0先看当前节点(也就是3)的右边是否有数据,为什么不看当前节点左子节点的数据,因为,当前节点的左子节点一定比当前节点大,所以只找当前节点右边的数据。当右边节点为空的时候,才会插入数据,这样2就插入完成了,现在轮到1了,对于1,跟上面类似..
但是这样会造成一个问题:这样的查找效率很低,对于这样特定的数据,所以要使用平衡二叉树中的旋转,重新选定节点来平衡二叉树。关于二叉树的文章,过几天发布。
主函数:
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
node root = new node(0);
node root1 = new node(2);
node root2 = new node(1);
node root3 = new node(3);
node root4 = new node(4);
node root5 = new node(5);
node root6 = new node(6);
node.insert(root3,root);
node.insert(root3,root2);
node.insert(root3,root1);
node.insert(root3,root4);
node.insert(root3,root5);
node.insert(root3,root6);
node.mid(root3);
boolean i= node.search(10,root3);
System.out.println(i);
}
}
如有错误,请指出,谢谢!!