二叉树
简述

递归序(递归访问)
- 递归:访问次序
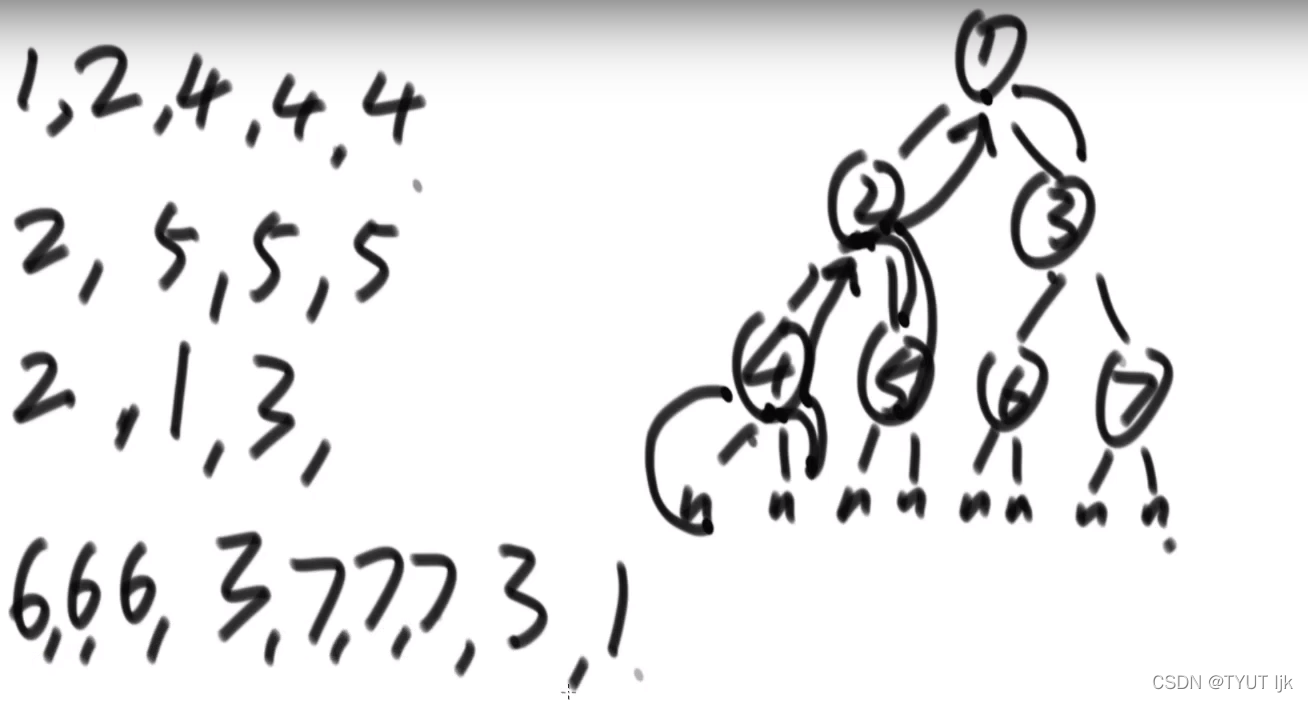
递归序:1,2,4,4,4,2,5,5,5,2,1,3,6,6,6,3,7,7,7,3,1
先序:第一次在递归序出现就打印,第二,三次访问时无操作:1,2,4,5,3,6,7
中序:第二次在递归序出现就打印,第一,三次访问时无操作:4,2,5,1,6,3,7
后序:第三次在递归序出现就打印,第一,二次访问时无操作:4,5,2,6,7,3,1
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head == null){
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.println(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void posOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head == null){
return;
}
posOrderRecur(head.left);
posOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.println(head.value + " ");
}
非递归访问
- 非递归:通过手写栈实现
1 先序:
(1)从栈中弹出一个结点
(2)打印(处理)该结点
(3)先右后左(如果有)压入栈中(保证出栈是左,右)
(4)重复,直至栈为空
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
Node p = stack.pop();
System.out.println(p.value);
if (p.right != null){
//先压入右子树
stack.push(p.right);
}
if (p.left != null){
stack.push(p.left);
}
}
}
}
2 中序:
(1)每颗子树的左边界进栈
(2)依次弹出的过程中打印(处理),弹出结点的右子树(及其左边界)进栈
(3)重复1,2
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = head;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || p != null){
if (p != null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}else {
p = stack.pop();
System.out.println(p.value + " ");
p = p.right;
}
}
}
}
3 后序:需要一个收集栈
(1)从栈中弹出一个结点
(2)将该结点放入收集栈(父节点在收集栈底)
(3)先左后右(如果有)压入栈中(保证收集栈里是右,左)
(4)重复,直至栈为空
(5)打印(处理)收集栈(出栈是左,右,父)
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> temp = new Stack<>(); //收集栈
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
Node p = stack.pop();
temp.push(p); //压入收集栈
if (p.left != null){
//先压入左子树
stack.push(p.left);
}
if (p.right != null){
stack.push(p.right);
}
}
while (!temp.isEmpty()){
Node p = temp.pop();
System.out.println(p.value + " ");
}
}
}
直观打印树
public static class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int date){
//构造函数
this.value = date;
}
}
public static void printTree(Node head){
System.out.println("Binary Tree");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 12);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len){
//head 头结点
//height 目前深度
//to 表示关系,H:头结点;↖:表示父节点在其左上;↙:表示父节点在其左下
//len 树显示长度的控制,可自行调整
if (head == null){
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "↙", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "↖" , len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num){
String space = " ";
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(4);
head.left.right = new Node(5);
head.right.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(7);
head.left.right.right = new Node(8);
head.right.right.left = new Node(9);
printTree(head);
}
理想图:
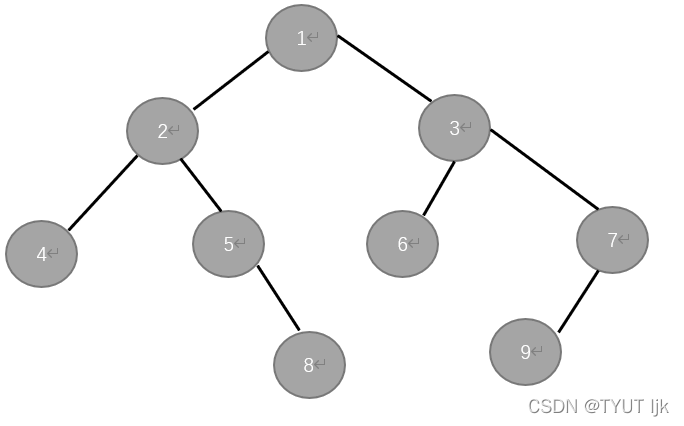
效果图:H:头结点;↖:表示父节点在其左上;↙:表示父节点在其左下

题目一:求树的最大宽度(广度优先)
层次遍历
public static void levelOrder(Node head){
if (head == null){
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
Node p = head;
queue.add(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
p = queue.poll();
if (p.left != null){
queue.add(p.left);
}
if (p.right != null){
queue.add(p.right);
}
}
}
- 笔试代码:
(1)思路:三个值,当前结点所在层,每层中的结点个数,树中结点最多的层
(2)实现方法:结合层次遍历,使用HashMap使得每个结点与对应的层绑定。出队时,将对应层数的结点加一,最后找到结点最多的层即可
public static int levelMax(Node head){
if (head == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
int level = 1; //层数
int levelNum = 0; //该层的结点数
int nodeMax = 0; //最多结点个数
HashMap<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Node p = head;
map.put(p, 1);
queue.add(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
p = queue.poll();
if (map.get(p) == level){
//当前结点层与要记录层相同
levelNum++;
}else {
//当前结点层与要记录层不相同,进入下一层,更新数据
nodeMax = Math.max(nodeMax, levelNum); //最大值更新
level++; //层数更新
levelNum = 1; //重置对应层的结点数
}
if (p.left != null){
map.put(p.left, level + 1);
queue.add(p.left);
}
if (p.right != null){
map.put(p.right, level + 1);
queue.add(p.right);
}
}
return nodeMax;
}
- 面试思路:
(1)思路:四个值,当前层的结束结点,当前层下一次的结束结点,每层中的结点个数,树中结点最多的层
(2)实现方式:结合层次遍历,第一层,该层的结束结点就是head,到了第二层将在第一层记录的下一层结束结点作为当前层的结束结点,在出,入对的同时更新下一次的结束结点,同时记录每层中的结点个数。
public static int levelMax(Node head){
if (head == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
Node levelEnd = head; //本层结束结点
Node levelNextEnd = null; //下一次结束结点
int levelNum = 0; //该层的结点数
int nodeMax = 0; //最多结点个数
Node p = head;
queue.add(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
p = queue.poll();
if (p.left != null){
//时刻更新levelNextEnd
levelNextEnd = p.left;
queue.add(p.left);
levelNum++;
}
if (p.right != null){
levelNextEnd =p.right;
queue.add(p.right);
levelNum++;
}
if (p == levelEnd){
//遍历到该层最后一个结点,数据更新
levelEnd = levelNextEnd;
nodeMax = Math.max(levelNum, nodeMax);
levelNum = 0;
levelNextEnd = null;
}
}
return nodeMax;
}
题目二:二叉树相关概念判断
1. 如何判断是否为搜索二叉树(排序二叉树)
思路:中序遍历二叉树得到的序列,若为升序序列则为搜索二叉树
递归中序:
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head == null){
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.println(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
代码修改:
public static int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean checkBST(Node head){
if (head == null){
return true;
}
if (!checkBST(head.left)){
//递归左子树
return false;
}
if (head.value <= preValue){
//右边 <= 左边,不满足BST
return false;
}else {
preValue = head.value;
}
return checkBST(head.right);
}
非递归中序:
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head){
if (head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = head;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || p != null){
if (p != null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}else {
p = stack.pop();
System.out.println(p.value + " ");
p = p.right;
}
}
}
}
代码修改:
public static boolean checkBST(Node head){
if (head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = head;
int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || p != null){
if (p != null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}else {
p = stack.pop();
if (p.value <= preValue){
return false;
}else {
preValue = p.value;
}
p = p.right;
}
}
}
return true;
}
总结:两种均为动态检查,也可先将二叉树的序列存入list类的集合中,在判断序列是否有序
2. 如何判断是否为完全二叉树
思路:广度优先(层次遍历),判断1:只要有结点是有右孩子,而无左孩子就返回false;判断2:从第一个子树不完整的结点开始,其后结点都要为叶子结点
public static boolean isCBT(Node head){
if (head == null){
return true;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
boolean flag = false; //表示是否遇到了子树不完整的结点
Node p = head;
queue.add(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
p = queue.poll();
if ((p.left == null && p.right != null) || flag && (p.left != null && p.right != null)){
//不为满二叉树的条件
return false;
}
if (p.left != null){
queue.add(p.left);
}
if (p.right != null){
queue.add(p.right);
}
if (p.left == null || p.right == null){
//子树不完整
flag = true;
}
}
return true;
}
3. 如何判断是否为满二叉树
思路:统计二叉树的深度L,节点数为N,若N = 2 ^ L - 1,则为满二叉树
方法:递归调用,求左子树的L,N;求右子树的L,N;求该树的L,N
public static boolean isFull(Node head){
ReturnType returnType = process(head);
//1 << x, 2的x次方
return returnType.num == (1 << returnType.height - 1);
}
public static class ReturnType{
//自定义类型
public int height; //树的高度
public int num; //节点数
public ReturnType(int height, int num){
//构造函数
this.height = height;
this.num = num;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node head){
if (head == null){
return new ReturnType(0, 0);
}
ReturnType leftTree = process(head.left); //递归调用
ReturnType rightTree= process(head.right);
int height = Math.max(leftTree.height, rightTree.height) + 1; //高度
int num = leftTree.num + rightTree.num + 1; //节点数
return new ReturnType(height, num);
}
4. 如何判断是否为平衡二叉树
思路:平衡二叉树条件:(1)左子树平衡,左高度;(2)右子树平衡,右高度;(3)|左高度 - 右高度| <= 1
结合递归实现
public static boolean isBalancedTree(Node head){
return process(head).isBalanced;
}
public static class ReturnType{
//自定义类型
public boolean isBalanced; //树是否平衡
public int height; //树高
public ReturnType(boolean isBalanced,int height){
//构造函数
this.isBalanced = isBalanced;
this.height = height;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node head){
if (head == null){
//空树平衡,高度0
return new ReturnType(true, 0);
}
ReturnType leftTree = process(head.left); //递归调用
ReturnType rightTree= process(head.right);
int height = Math.max(leftTree.height, rightTree.height) + 1;
boolean isBalanced = leftTree.isBalanced && rightTree.isBalanced
&& Math.abs(leftTree.height - rightTree.height) < 2;
return new ReturnType(isBalanced, height);
}
5. 二叉树递归套路(树型DP,动态规划)
思路:在判断二叉树是什么树时?分解为左子树是否满足,右子树是否满足,左右子树合并后是否满足(树型DP)
- 二叉树递归套路:判断是否为搜索二叉树
(1)左树搜索,左的max,min;(2)右树搜索,右的min,max;(3)左max < head.value < 右min
public static boolean isBSTree(Node head){
return process(head).isBST;
}
public static class ReturnType{
//自定义类型
public boolean isBST; //树是否为搜索树
public int min; //树的最小值
public int max; //树的最大值
public ReturnType(boolean isBST,int min, int max){
//构造函数
this.isBST = isBST;
this.min = min;
this.max = max;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node head){
if (head == null){
//空树的min,max不好设置,直接设置为null
return null;
}
ReturnType leftTree = process(head.left); //递归调用
ReturnType rightTree= process(head.right);
int min = head.value; //min,max的设置
int max = head.value;
if (leftTree != null){
min = Math.min(min, leftTree.min);
max = Math.max(max, leftTree.max);
}
if (rightTree != null){
min = Math.min(min, rightTree.min);
max = Math.max(max, rightTree.max);
}
boolean isBST = true; //isBST设置
if (leftTree != null && (leftTree.isBST || leftTree.max > head.value)){
//左不为空的条件下:左子树不是搜索二叉树或左的max > head,value
//不满足搜索二叉树
isBST = false;
}
if (rightTree != null && (rightTree.isBST || rightTree.min < head.value)){
isBST = false;
}
return new ReturnType(isBST, min, max);
}
- 在判断满二叉树,平衡二叉树时都是此方法
题目三:俩节点最低公共祖先
- 笔试思路:
(1)使用HashMap建立,每个节点与其父节点的关系
(2)使用HashSet存储,node1所有的祖先节点
(3)依次找node2的祖先节点,并在node1的HashSet中寻找是否有相同的,当遇到第一个相同的便是最低公共祖先节点
public static Node lowCommonAncestor(Node head, Node node1, Node node2){
HashMap<Node, Node> fatherMap = new HashMap<Node,Node>();
fatherMap.put(head, head); //头节点的父节点为自己
process(head, fatherMap);
HashSet<Node> setNode1 = new HashSet<Node>(); //建立node1的祖先节点集
Node p = node1;
while (p != fatherMap.get(head)){
//从当前节node1点从下往上遍历头节点
setNode1.add(p);
p = fatherMap.get(p);
}
p = node2;
while (p != fatherMap.get(head)){
//从当前节node2点从下往上遍历头节点
if (setNode1.contains(p)){
//有相同就是最低公共祖先节点
return p;
}
p = fatherMap.get(p);
}
return null;
}
public static void process(Node head, HashMap<Node, Node> fatherMap){
//节点与父节点关系的建立
if (head == null){
return;
}
fatherMap.put(head.left, head);
fatherMap.put(head.right, head);
process(head.left, fatherMap);
process(head.right, fatherMap);
}
- 面试思路:
情况分析:
(1)node1是node2的祖先节点,或node2是node1的祖先节点
(2)node1与node2不互为祖先节点,需要向上遍历才能找到
方法:遍历树节点,碰到node1,node2返回对应节点,其余的节点碰到都只是返回空
情况一:
情况二:
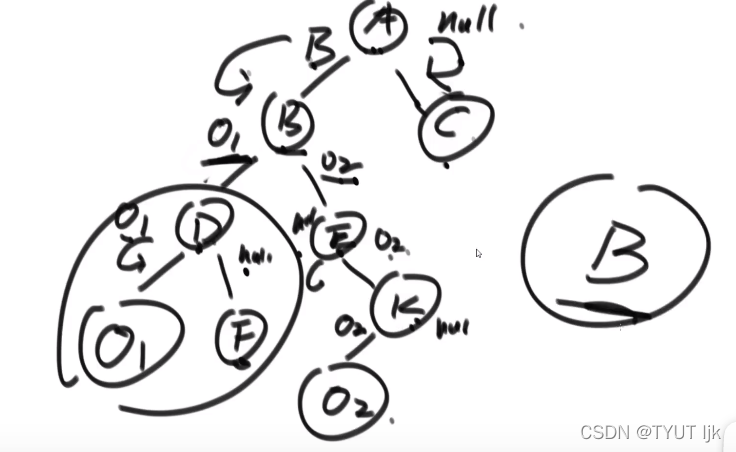
public static Node lowCommonAncestor(Node head, Node node1, Node node2){
if (head == null || head == node1 || head == node2){
//node1,node2时返回对应值
return head;
}
Node left = lowCommonAncestor(head.left, node1, node2);
Node right = lowCommonAncestor(head.right, node1, node2);
if (left != null && right != null){
//情况二,两个节点互不为公共祖先
//则同时左右返回为node1,node2的就是最低公共祖先
return head;
}
//碰到node1,node2的其中一个时返回不空的
return left != null ? left : right;
}
题目四:树的后继节点查找(含父亲节点)

后继节点:在中序遍历的序列中,node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点
情况分析:
(1)node有右子树,则后继节点就是右子树最左边的节点
(2)node无右子树,则后继结点就是看node是那个结点左子树最右边的结点(判断当前节点是否是其祖先节点的左子树)
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node){
if (node == null){
return node;
}
if (node.right != null){
//当前节点存在右子树
return getLeftNode(node);
}
else {
//无右子树,通过父节点查找
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && parent.left != node){
//该节点是否为父节点的左子树
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getLeftNode(Node node){
if (node == null){
return node;
}
while (node.left != null){
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
题目五:二叉树的序列化和反序列化

思路:使用 “" 表示相隔节点之间的表示方式;使用 "#” 表示空结点
先序序列:序列化
public static String serialByPre(Node head){
if (head == null){
return "#_";
}
String str = head.value + "_";
str += serialByPre(head.left);
str += serialByPre(head.right);
return str;
}
反序列化
public static Node reconByPreString(String preStr){
//将字符串分割,存入队列
String[] values = preStr.split("_");
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++){
queue.add(values[i]);
}
return reconPreOrder(queue);
}
public static Node reconPreOrder(Queue<String> queue){
//通过队列,还原树
String value = queue.poll();
if (value.equals("#")){
return null;
}
Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value));
head.left = reconPreOrder(queue);
head.right = reconPreOrder(queue);
return head;
}
题目六:折纸问题

问题分析:
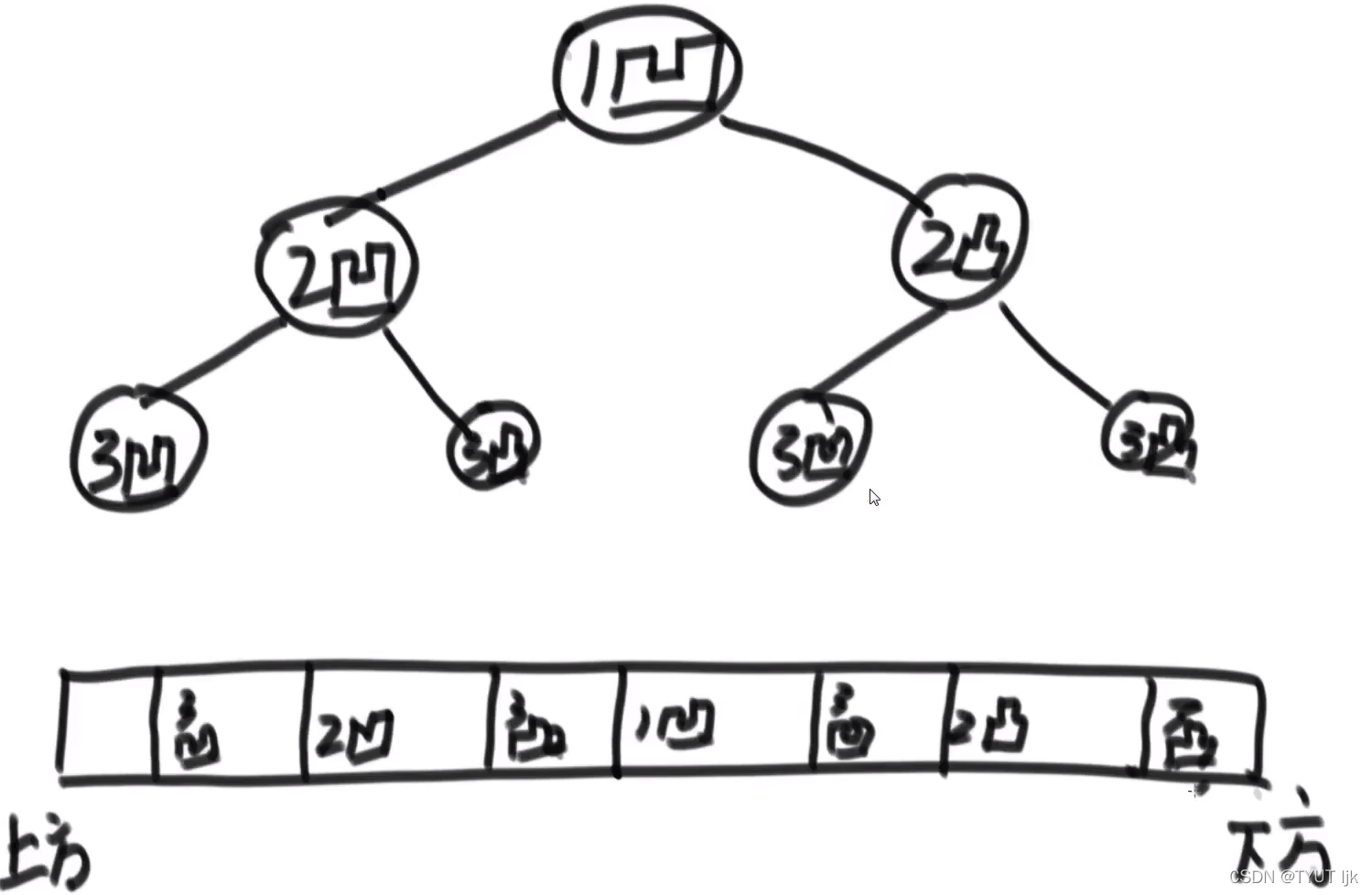
思路:找到折纸的规律,使用树的方式来表示。父节点与左子树都是凹,右子树都是凸
方法:给定N,确定树的高度,模拟树的中序遍历便可以得到折痕方向
public static void printAllFolds(int N){
printProcess(1, N, true);
}
public static void printProcess(int height, int N, Boolean down){
//模拟树的中序遍历
//height当前高度,N为树高
//down = true -> 凹,down = false ->凸
if (height > N){
return;
}
printProcess(height + 1, N, true);
System.out.println(down ? "凹" : "凸");
printProcess(height + 1, N, false);
}