/*呜呜呜我要逼自己打代码,不能再偷懒了呜呜呜*/
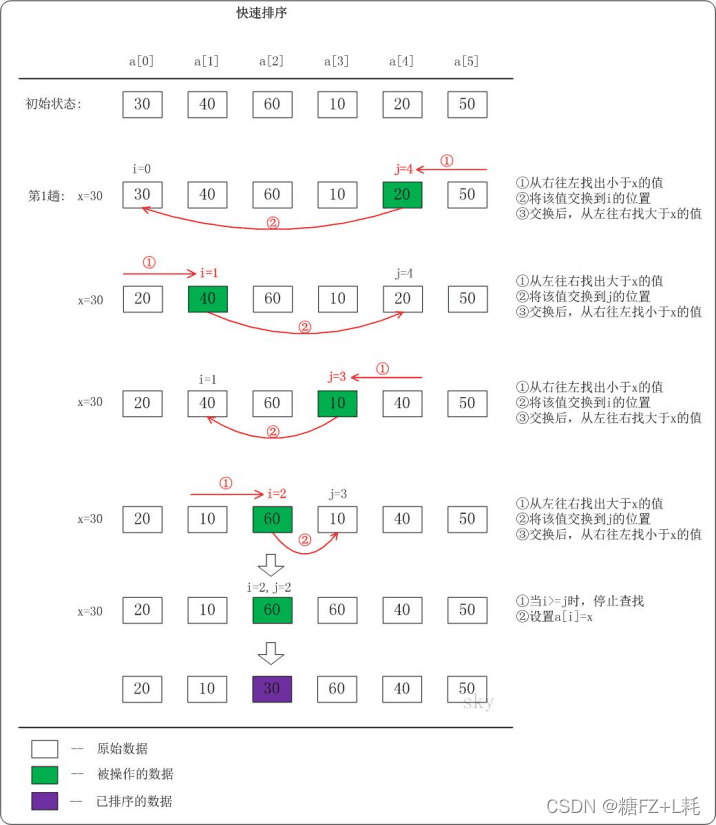
快速排序
快速排序时间复杂度
快速排序的时间复杂度在最坏情况下是O(N2),平均的时间复杂度是O(N*lgN)。
这句话很好理解:假设被排序的数列中有N个数。遍历一次的时间复杂度是O(N),需要遍历多少次呢?至少lg(N+1)次,最多N次。
(01) 为什么最少是lg(N+1)次?快速排序是采用的分治法进行遍历的,我们将它看作一棵二叉树,它需要遍历的次数就是二叉树的深度,而根据完全二叉树的定义,它的深度至少是lg(N+1)。因此,快速排序的遍历次数最少是lg(N+1)次。
(02) 为什么最多是N次?这个应该非常简单,还是将快速排序看作一棵二叉树,它的深度最大是N。因此,快读排序的遍历次数最多是N次。
coding:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int q[N], n;
void Swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void Quick_sort(int left,int right)
{
if (left >=right) return;
// why subtract(减) one here?because subtract one is aim to start //
//at the zero of the array index(数组索引)//(加一,又减一取二分一平均值的时候抵消)
int i = left - 1, j = right + 1, val = q[left + right >> 1];
while (i < j)
{
do i++; while (q[i] < val);//star at the left and comparing
do j--; while (q[j] > val);//star at the right and comparing
if (i < j)
{
Swap(q[i], q[j]);
}
Quick_sort(left, j);//Swap the values on the left
Quick_sort(j + 1, right);//Swap the values on the right
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n ;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin>> q[i];
Quick_sort(0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << q[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}模板题: 【模板】快速排序 - 洛谷
归并排序
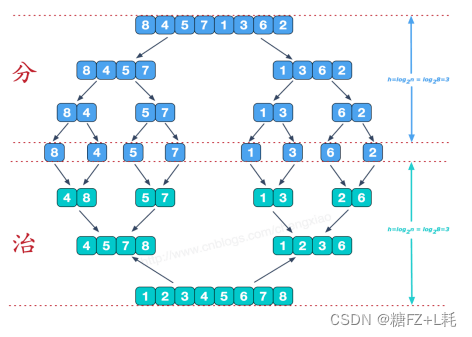
coding:
// Merge_sort学习.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int q[N], n;
int temp[N];
void Merge_Sort(int l,int r)
{
if (l >= r) return ;
int mid = l + r >> 1;//divide by two
Merge_Sort(l, mid), Merge_Sort(mid + 1, r);//sort left andthen right
int i = l, j = mid + 1, k = l;
//Divided into three cases
while (i <= mid && j <= r)
{
if (q[i] < q[j]) temp[k++] = q[i++];
else temp[k++] = q[j++];
}//if left and the right both suit ,to do it
while (i <= mid) temp[k++] = q[i++];//only left suits,so execuit the left
while (j <= r) temp[k++] = q[j++];//only right suits,so execuit the right
//拷贝打印
memcpy(q + l, temp + l, sizeof(int) * (r - l + 1));
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> q[i];
Merge_Sort(0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout<<q[i]<<' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}