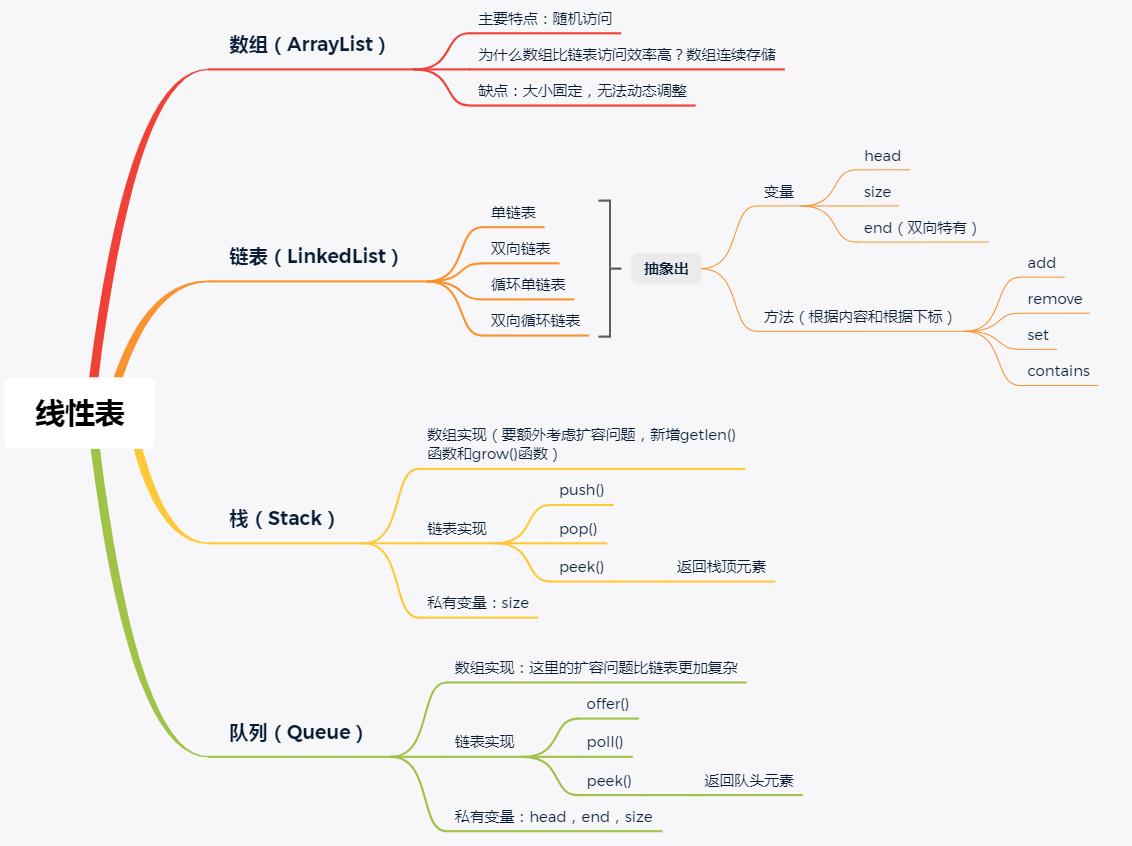
1, 数组
Q1: 数组我们都很熟悉,那你理解的数组是什么样的呢?它的最主要特点是什么呢?
数组在内存空间上是连续存储 -> 随机访问
某一个下标位置 = 数组的起始位置 + 下标 * 单个数组单元大小
Q2: 为什么数组的索引是一般都是从0开始的呢? 历史遗留问题
"易语言" -> 数组下标从1开始
如果从1开始:
某一个下标位置 = 数组的起始位置 + (下标-1) * 单个数组单元大小
Q3: 为什么数组的效率比链表高?
第一层:
数组在内存空间上是连续存储
链表是非连续存储, 访问要一步一步next向后查找
第二层:
频繁的数据在缓存中置换, 比较消耗硬件开销
2, 链表
2.1链表的分类
链表是由结点构成的
// 单链表
除了尾结点以外每个结点都有一个后继结点
// 循环单链表
在单链表的基础上, 让尾结点的下一个指向头结点
// 双向链表
是在单链表的基础上, 让每一个结点都有前后指向(除了头尾结点)
// 双向循环链表
是在双向链表的基础上, 让头的前一个指向尾结点, 尾的后一个指向头结点
// 注意:
// 对于单链表和双链表而言
// 双向链表更浪费内存空间
// 双向链表根据下标查找性能是优于单链表的
2.2数组和链表的对比
数组和链表的插入,删除,随机访问操作的时间复杂度刚好相反。
① 数组使用的是连续的内存空间,可以利用CPU的高速缓存预读数据。链表的内存空间不是连续的,不能有效预读数据。当然如果数组过大,系统没有足够的连续内存空间,会抛出OOM
(out of memory error)申请程序内存较大,虚拟机无法满足我们。
② 数组的缺点是大小固定,没法动态的调整大小。如果要存储一些对象,如果数组太大,浪费内存空间;如果数组太小,我们需要重新申请一个更大数组,并将数据拷贝过去,耗时。
③如果业务对内存的使用非常苛刻,数组更适合。因为结点有指针域,更消耗内存。而且对链表的频繁插入和删除,会导致结点对象的频繁创建和销毁,有可能会导致频繁的GC活动。
3, 线性表的实现
线性表根据定义 --> 有下标/位序的概念 --> 可以提供根据下标的操作(根据下标的增删改查)
二叉搜索树: 添加, 删除,查找, 修改
举例:实现单链表和双链表:
单链表:
/**
* 第一个角度: 使用者, 实现的线性表是一个数据容器,
* 第二个角度: 数据结构表现: 实现的线性表有下标操作
* 第三个角度: 底层结构: 链表 (先用单链表)
*/
public class MyLinkedList {
private Node head; // MyLinkedList底层持有的单链表的头结点
private int size; // 用来保存我们这个线性表(外在表现), 存储了多少数据
/**
* 链表的添加
* @param str : 要添加的元素
* @return: 添加是否成功
*/
public boolean add(String str) {
// 判断链表在添加之前是否为空
if (isEmpty()){
// 如果原链表为空, 新添加的元素作为头结点存在
head = new Node(str, null);
size++;
return true;
}
// 走到这, 意味着链表不空 --> 可以把这个新添加的元素, 放在链表尾部
Node mid = head;
while (mid.next != null){
mid = mid.next;
}
mid.next = new Node(str, null);
size++;
return true;
}
/**
* 根据内容在链表上删除元素
* @param str: 要删除的元素
* @return: 删除是否成功
*/
public boolean remove(String str) {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("list is empty");
if (str == null){
// 删除的是否是头结点
if (str == head.value){
// 删除的是头结点
head = head.next;
size--;
return true;
}
// 删除的是普通结点: 先找到这个要删除的结点, 再删除
Node mid = head;
// 如果mid之后不是null(后面还有元素可以遍历查找), 并且后面这个结点的value也不是要查找的值 --> 向后遍历
while (mid.next != null && str != mid.next.value ){
mid = mid.next;
}
// 上述循环有两周跳出条件
// 1, 没找到(遍历完了都没找到)
if (mid.next == null)return false;
// 2, 找到了 --> 删除mid.next
mid.next = mid.next.next;
size--;
}else {
// 删除的是否是头结点
if (str.equals(head.value)){
// 删除的是头结点
head = head.next;
size--;
return true;
}
// 删除的是普通结点: 先找到这个要删除的结点, 再删除
Node mid = head;
// 如果mid之后不是null(后面还有元素可以遍历查找), 并且后面这个结点的value也不是要查找的值 --> 向后遍历
while (mid.next != null && !str.equals(mid.next.value)){
mid = mid.next;
}
// 上述循环有两周跳出条件
// 1, 没找到(遍历完了都没找到)
if (mid.next == null)return false;
// 2, 找到了 --> 删除mid.next
mid.next = mid.next.next;
size--;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 查找某个元素是否存在
* @param str: 要查找的元素
* @return: 某个元素是否存在
*/
public boolean contains(String str) {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("list is empty");
Node mid = head;// 定义一个遍历结点
//遍历结点不是null, 遍历结点的值不是要查找值 --> 向后遍历
while (mid != null && !str.equals(mid.value)){
mid = mid.next;
}
// 遍历结点变成null --> 没有存储这个元素
if (mid == null)return false;
// 如果mid!=null , 一定找到了
return true;
}
/**
* 根据内容修改
* @param oldValue : 要修改的值
* @param newValue : 修改后的值
* @return: 修改是否成功
*/
public boolean set(String oldValue, String newValue) {
// 判断链表是否为空
if (isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("list is empty");
Node mid = head;// 定义一个遍历结点
//遍历结点不是null, 遍历结点的值不是要查找值 --> 向后遍历
while (mid != null && !oldValue.equals(mid.value)){
mid = mid.next;
}
// 遍历结点变成null --> 没有存储这个元素
if (mid == null)return false;
// 走到这意味着找到了
mid.value = newValue;
return true;
}
/**
* 根据下标的添加方法
* @param index : 要添加的位置
* @param str : 要添加的内容
* @return : 添加是否成功
*/
public boolean add(int index, String str) {
if(index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is Illegal ");
// 要添加的位置是否是头位置
if (index == 0){
head = new Node(str, head);
size++;
return true;
}
// 根据下标查找位置, 添加
Node mid = head; // 遍历结点指向引用
int tag = 1; // 遍历的下标标记
// tag != index:意味着还没有遍历到, 想添加的位置 --> 接着向后遍历
while (tag != index){
tag++;
mid = mid.next;
}
// 经过上述 遍历: mid就是要添加位置之前的一个元素
mid.next = new Node(str, mid.next);
size++;
return true;
}
/**
* 根据下标删除内容
* @param index: 要删除的下标位置
* @return: 被删除的元素
*/
public String remove(int index) {
// 判断下标是否合法
if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is Illegal ");
// 删除的是头元素
if (index == 0){
String oldValue = head.value;
head = head.next;
size--;
return oldValue;
}
// 删除普通情况:
// 根据下标找到对应结点, 删除
// 根据下标查找位置
Node mid = head; // 遍历结点指向引用
int tag = 1; // 遍历的下标标记
// tag != index:意味着还没有遍历到, 想添加的位置 --> 接着向后遍历
while (tag != index){
tag++;
mid = mid.next;
}
// mid要查找下标的前一个位置
String oldValue = mid.next.value;
// 删除
mid.next = mid.next.next;
size--;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 根据下标查找下标位置存储的元素
* @param index : 要查找的下标位置
* @return : 这个位置的元素
*/
public String get(int index) {
// 判断下标是否合法
if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is Illegal ");
Node mid = head;
int tag = 0;
while (tag != index){
tag++;
mid = mid.next;
}
// mid 就是要查找的位置
return mid.value;
}
/**
* 根据下标修改
* @param index : 要修改的下标位置
* @param newValue : 新的值
* @return: 旧的被替换的值
*/
public String set(int index, String newValue) {
// 判断下标是否合法
if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is Illegal ");
Node mid = head;
int tag = 0;
while (tag != index){
tag++;
mid = mid.next;
}
// mid 就是要查找的下标位置
String oldValue = mid.value;
mid.value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
// 如下两个方法, 是一般作为一个数据容器都应该具有的方法
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
/**
* 单链表的结点
*/
class Node{
String value;
Node next;
public Node(String value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
双向链表的实现:
/**
* 用双向链表实现一个线性表
*
* 使用者: 数据容器
* 数据结构: 线性表 --> 普通增删改查, 根据下标的增删改查
* 底层结构: 双向链表
*/
public class MyDBLinkedList<T> {
private Node head;// 双向链表的头结点
private Node end; // 双向链表的尾结点
private int size; // 存储的元素个数
public boolean add(T value){
// 判断双向链表是否为空
if (isEmpty()){
// 新元素, 既是头结点, 又是尾结点
head = new Node(null, value, null);
end = head;
size++;
return true;
}
// 如果链表不空, 这个新元素添加到尾部
end.next = new Node(end, value, null);
end = end.next;
size++;
return true;
}
public boolean remove(T value){
// 判断链表是否为空
if (isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("list is empty");
// 如果链表不空, 判断删除的是否是头结点
if (value.equals(head.value)){
// 删除的是头结点
// 判断一下是不是这个链表中只剩这一个元素了
if (size == 1){
head = null;
end = null;
size = 0;
return true;
} else {
// 链表中删除头结点, 还剩多个元素 -> 头结点后移
head = head.next;
head.pre = null;
size--;
return true;
}
}
// 判断删除的是不是尾元素
if (value.equals(end.value)){
// 尾元素前移
end = end.pre;
end.next = null;
size--;
return true;
}
// 处理删除普通的中间结点
Node mid = head;
// 查找mid之后是否还有元素, 并且不是要找的
while (mid.next != null && !value.equals(mid.next.value)){
mid = mid.next;
}
// 有可能没有存储这个元素
if (mid.next == null) return false;
// 走到这: 意味着找到了, mid.next
Node removeNode = mid.next;
removeNode.next.pre = removeNode.pre;
removeNode.pre.next = removeNode.next;
size--;
return true;
}
public boolean add(int index, T value){
if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("size =" + size + "; index = " + index);
// 判断添加位置是否是头位置
if (index == 0){
// 判断是否链表中没有任何元素
if (isEmpty()){
// 添加的元素既是头又是尾
head = new Node(null, value, null);
end = head;
size++;
return true;
}else {
// 链表中原本就存在元素
Node newNode = new Node(null, value, head);
head.pre = newNode;
head = newNode;
size++;
return true;
}
}
// 判断添加的是不是尾位置
if (index == size){
return add(value);
}
Node mid = head;
// 添加的位置是中间位置
if (index < size/2){// 偏头的位置
// 从头向后遍历
int tag = 1;
while (tag != index){
tag++;
mid = mid.next;
}
// mid 是添加位置的前一个位置
}else {// 偏尾的位置
// 从尾向前遍历
mid = end;
int tag = size;
while (tag != index){
tag--;
mid = mid.pre;
}
// mid 是添加位置的前一个位置
}
// 把元素添加到mid之后
Node newNode = new Node(mid, value, mid.next);
mid.next = newNode;
newNode.next.pre = newNode;
size++;
return true;
}
public T remove(int index){
// 下标范围检查
if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("size =" + size + "; index = " + index);
// 删除的是头结点
if (index == 0){
T value = head.value;
// 判断链表是不是仅剩一个元素
if (size == 1){
head = null;
end = null;
}else {
head = head.next;
head.pre = null;
}
size--;
return value;
}
// 删除的是尾结点
if (index == size-1){
T value = end.value;
end = end.pre;
end.next = null;
size--;
return value;
}
// 删除的中间结点 --> 先找到要删除的结点, 再删除
Node mid = head;
// 添加的位置是中间位置
if (index < size/2){// 偏头的位置
// 从头向后遍历
int tag = 1;
while (tag != index){
tag++;
mid = mid.next;
}
}else {// 偏尾的位置
// 从尾向前遍历
mid = end;
int tag = size;
while (tag != index){
tag--;
mid = mid.pre;
}
}
// mid 是查找位置的前一个位置
Node removeNode = mid.next;
removeNode.next.pre = removeNode.pre;
removeNode.pre.next = removeNode.next;
size--;
return removeNode.value;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
class Node{
T value;// 值域
Node pre;// 前指针域
Node next;// 后指针域
public Node(Node pre, T value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
// 服务器
// 1, 服务器是一个物理电脑
// 2, 有的时候指的是一个运行在物理服务器的一段程序
4, 栈的实现
先用链表: push, pop, peek
/**
* 使用单链表实现一个栈
* push:入栈
* pop:出栈
* peek:查看栈顶元素
*/
public class MyLinkedStack <T> {
private Node top; // 底层链表/栈的栈顶
private int size;
// 入栈操作
public boolean push(T value){
top = new Node(value, top);
size++;
return true;
}
// 出栈操作
public T pop(){
// 判断栈是否为空
if (isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
T value = top.value;
top = top.next;
size--;
return value;
}
// 查看栈顶元素
public T peek(){
// 判断栈是否为空
if (isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
return top.value;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
class Node{
T value;
Node next;
public Node(T value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
用数组实现栈:
? 数组面临扩容问题
? 数组面临初始化的问题
/**
* 用数组实现一个栈
*
* 使用者: 只是个数据容器, 提供添加和删除方法
* 数据结构: 栈, 数据的出入顺序是有限定的
* 底层结构: 数组
*/
public class MyArrayStack <T> {
private final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10;
private final int MAX_CAPACITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private Object[] objs; // 用数组实现一个栈的, 底层数组,数组的长度就是栈的容量,但不是存储元素的数量
private int size ; // 数组中存储的元素数量
/**
* MyArrayStack的无参构造函数,创建一个大小为10的object栈
*/
public MyArrayStack(){
this.objs = new Object[INIT_CAPACITY];
// this.objs = new Object[10];
}
/**
* MyArrayStack的有参构造函数,创建一个大小为initCapacity的object栈
* @param initCapacity:栈能存放的数据多少
*/
public MyArrayStack(int initCapacity){
if (initCapacity < 1 || initCapacity > MAX_CAPACITY) throw new IllegalArgumentException("parame is Illegal");
this.objs = new Object[initCapacity];
}
// 性能
// 1, 功能实现没有
// 2, 代码可读性
// 3, 性能问题
// 解耦
public boolean push(T value){
// 判断数组是否满了, 如果满了, 需要扩容
if (size == objs.length){
// 需要扩容
int newLen = getLen(); // 获取新的数组长度
grow(newLen); // 根据新的长度扩容数组
}
// 走到这, 意味着数组是有空位置的 --> 存储
objs[size] = value;
size++; //这两步是一体的,可以写成objs[size++] = value;
return true;
}
// 根据旧长度, 获取一个新长度
//特殊情况:1. 新长度不在合理区间内 2. 旧长度和新长度相等(原本的长度已经是最大值了)
private int getLen() {
// 旧长度
int oldLen = objs.length;
// 新长度
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
if (newLen > MAX_CAPACITY || newLen < 0){
newLen = MAX_CAPACITY;
}
if (oldLen == newLen){// 如果这个条件满足, 意味着, 原本的长度已经是最大值了
throw new RuntimeException(" stack can not add");
}
return newLen;
}
// 扩容: 把旧数组的数据转移到新数组
private void grow(int newLen) {
// 创建一个新数组
Object[] newObjs = new Object[newLen];
// 把旧数组的数据转移到新数组
for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {
newObjs[i] = objs[i];
}
objs = newObjs;
}
// 出栈方法
public T pop(){
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
T oldValue = (T)objs[size - 1];
// objs[size - 1] = null;
size--;
return oldValue;
}
// 查看栈顶元素
public T peek(){
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
return (T)objs[size - 1];
}
//栈作为数据容器应该具有的两种方法
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
5, 队列实现
先用链表: 单链表
/**
* 使用单链表模拟一个队列
* @param <T>
// offer: 入归列
// poll: 出队列
// peek: 查看队头元素
*/
public class MyLinkedQueue <T> {
private Node head;// 队列的头结点
private Node end; // 队列的尾结点
private int size;// 队列中存储的元素个数
public boolean offer(T value){
// 判断原链表是否为空
if (isEmpty()){
// 新添加的元素, 既是头结点, 又是尾结点
head = new Node(value, null);
end = head;
size++;
return true;
}
// 如果原链表不空, 新添加的结点在尾部
end.next = new Node(value, null);
end = end.next;
size++;
return true;
}
public T poll(){
// 判断没有元素
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("queue is empty");
// 如果仅剩一个元素
if (size == 1){
T value = head.value;
head = null;
end = null;
size--;
return value;
}
// 如果链表有多个元素, 出头
T value = head.value;
head = head.next;
size--;
return value;
}
public T peek(){
// 判断没有元素
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("queue is empty");
return head.value;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
private int size(){
return size;
}
class Node {
T value; //值域
Node next; // 下一个结点指向
public Node(T value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
用下数组:
注意一点:用链表实现队列时,里面的扩容方法是不能将数据直接一一对应的转移到新数组,因为有end和head指针,这样会使得后边一部分的元素为空:
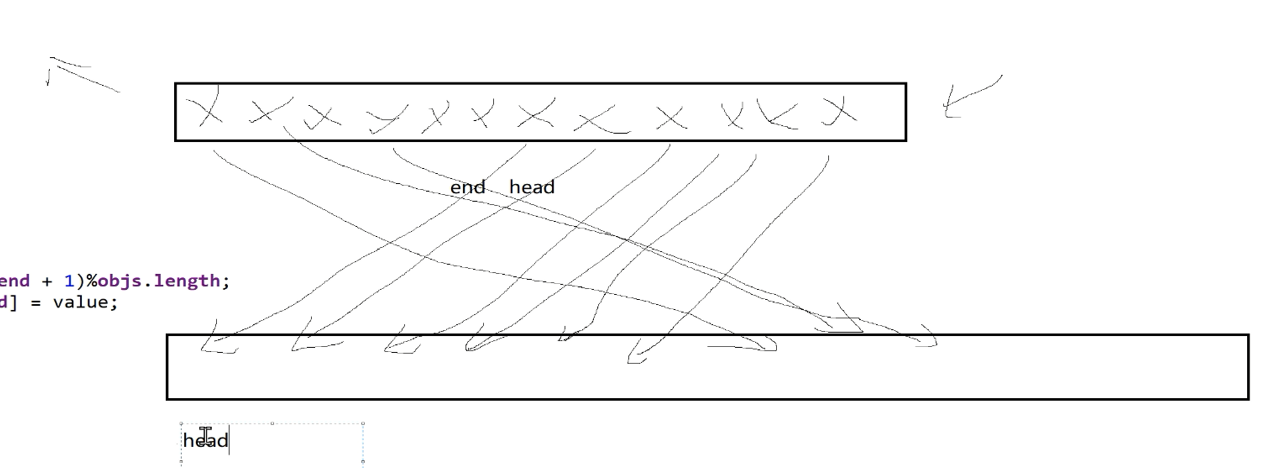
所以扩容的代码应该这样写:
private void grow(int newLen) {
// 创建一个新数组
Object[] newObjs = new Object[newLen];
// 把旧数组的数据转移到新数组
for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {
// newObjs[i] = objs[i];
int tag = (head + i) % objs.length;
newObjs[i] = objs[tag];
}
objs = newObjs;
head = 0;
end = size - 1;
}
总体的写法是这样的:
/**
* 使用循环数组实现队列
*/
public class MyArrayQueue <T> {
//队列的三种方法:
// offer:增添
// poll:删除
// peek:返回值是头指针指向的元素
private final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10;
private final int MAX_CAPACITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private Object[] objs; // 用数组实现一个队列, 底层数组
private int size ; // 数组中存储的元素数量
private int head; // 在数组中队头的下标标记
private int end; // 在数组中队尾的下标标记
// 默认的构造方法
public MyArrayQueue(){
this.objs = new Object[INIT_CAPACITY];
}
// 指定长度的构造方法
public MyArrayQueue(int initCapacity){
if (initCapacity < 1 || initCapacity > MAX_CAPACITY) throw new IllegalArgumentException("parame is Illegal");
this.objs = new Object[initCapacity];
}
//入队操作
//特殊情况:1. 容量太小:判断需要扩容
public boolean offer(T value){
if (size == objs.length){
int newLen = getLen();
grow(newLen);
}
// 走到这, 意味着数组有位置可以添加
// 单独处理如果第一次添加(头和尾在一个地方)
if (isEmpty()){
objs[head] = value;
end = head;
size++;
return true;
}
end = (end + 1)%objs.length;
objs[end] = value;
size++;
return true;
}
private void grow(int newLen) {
// 创建一个新数组
Object[] newObjs = new Object[newLen];
// 把旧数组的数据转移到新数组
for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {
// newObjs[i] = objs[i];
int tag = (head + i) % objs.length;
newObjs[i] = objs[tag];
}
objs = newObjs;
head = 0;
end = size - 1;
}
private int getLen() {
// 旧长度
int oldLen = objs.length;
// 新长度
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
if (newLen > MAX_CAPACITY || newLen < 0){
newLen = MAX_CAPACITY;
}
if (oldLen == newLen){// 如果这个条件满足, 意味着, 原本的长度已经是最大值了
throw new RuntimeException(" stack can not add");
}
return newLen;
}
public T poll(){
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("queue is empty");
// 单独处理一下仅剩一个元素的情况
if (size == 1){
T value = (T)objs[head];
head = 0;
end = 0;
size --;
return value;
}
T value = (T)objs[head];
head = (head + 1)% objs.length;
size--;
return value;
}
//看头部节点
public T peek(){
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("queue is empty");
return (T)objs[head];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
}